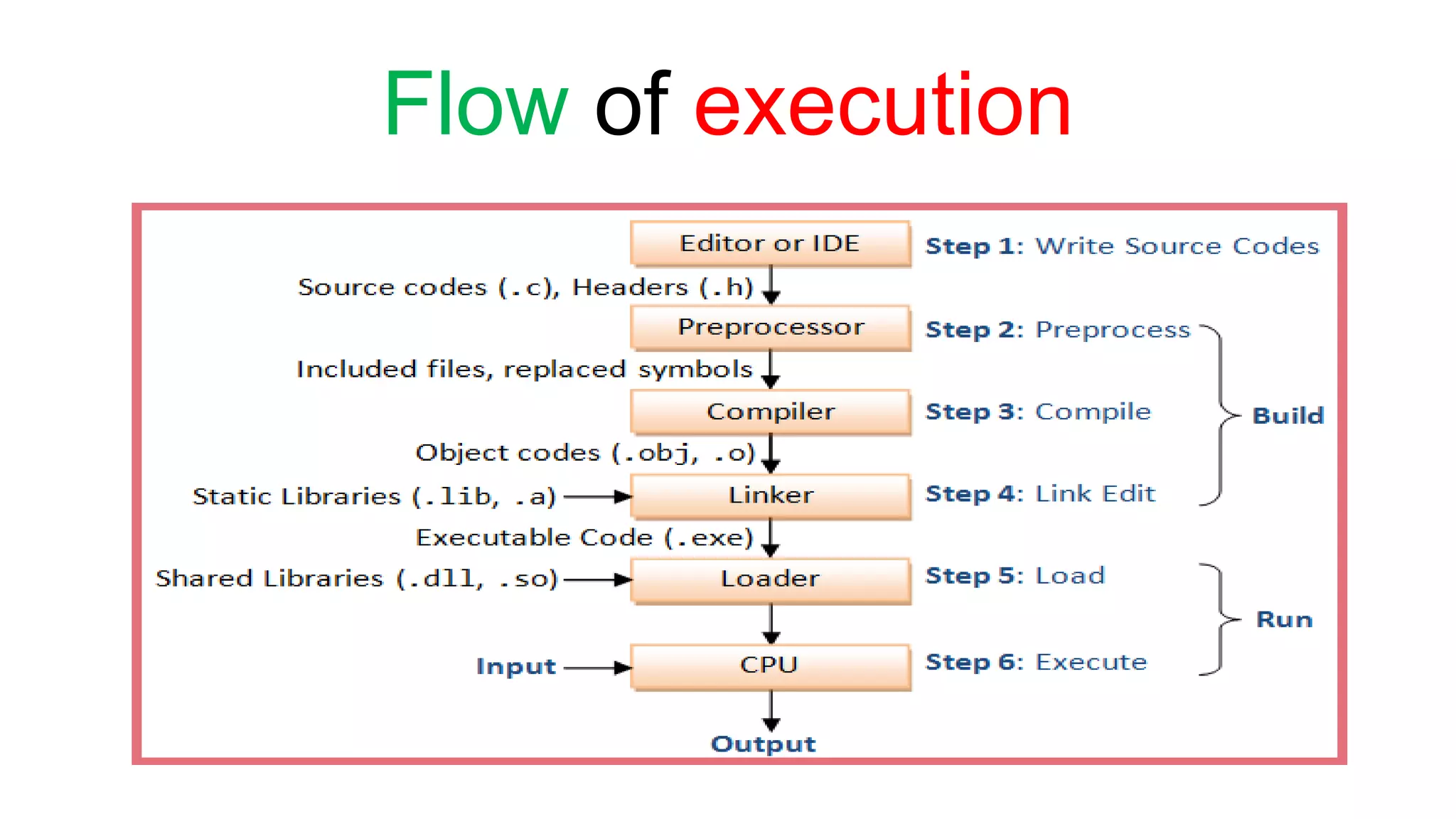
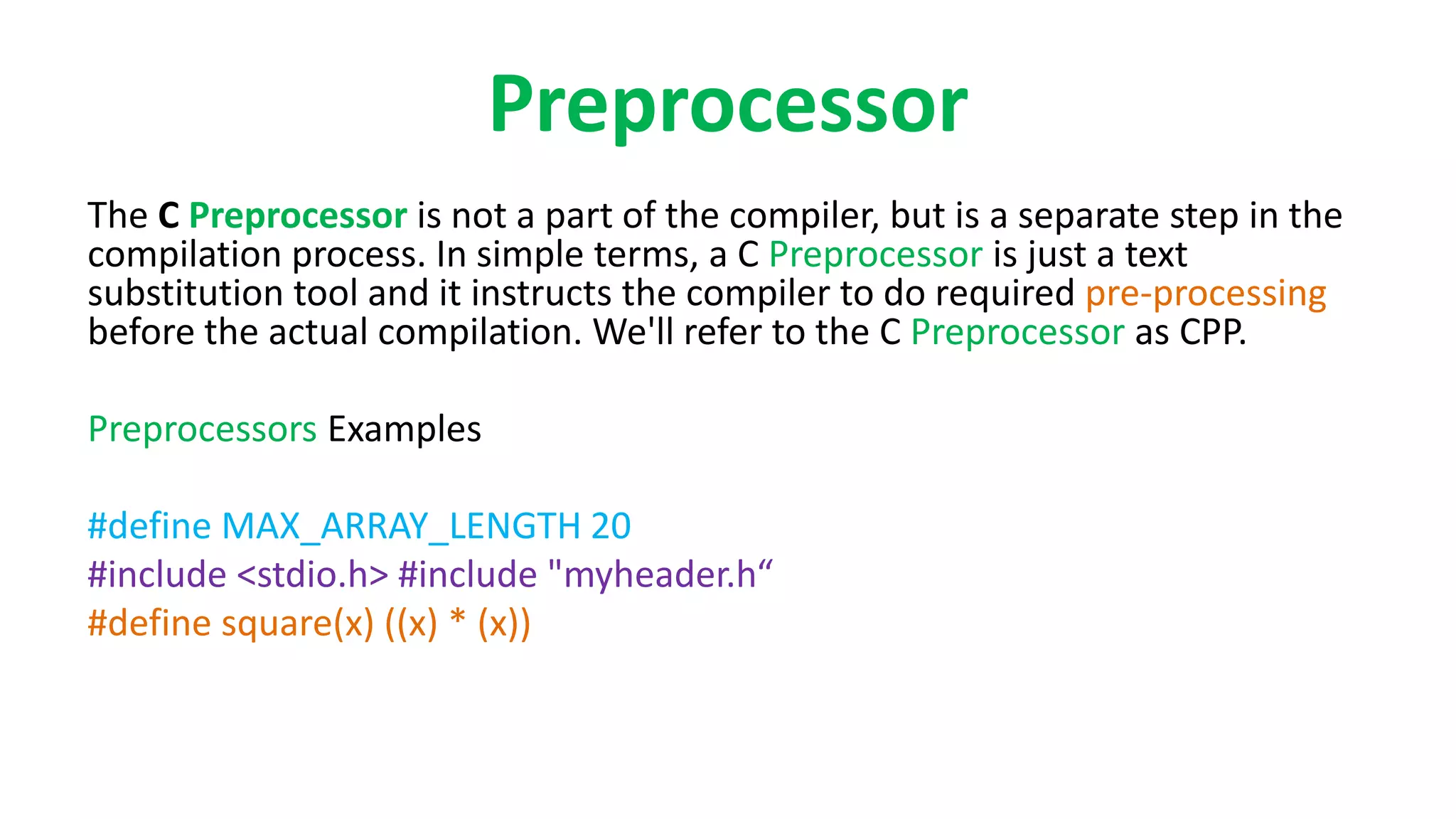
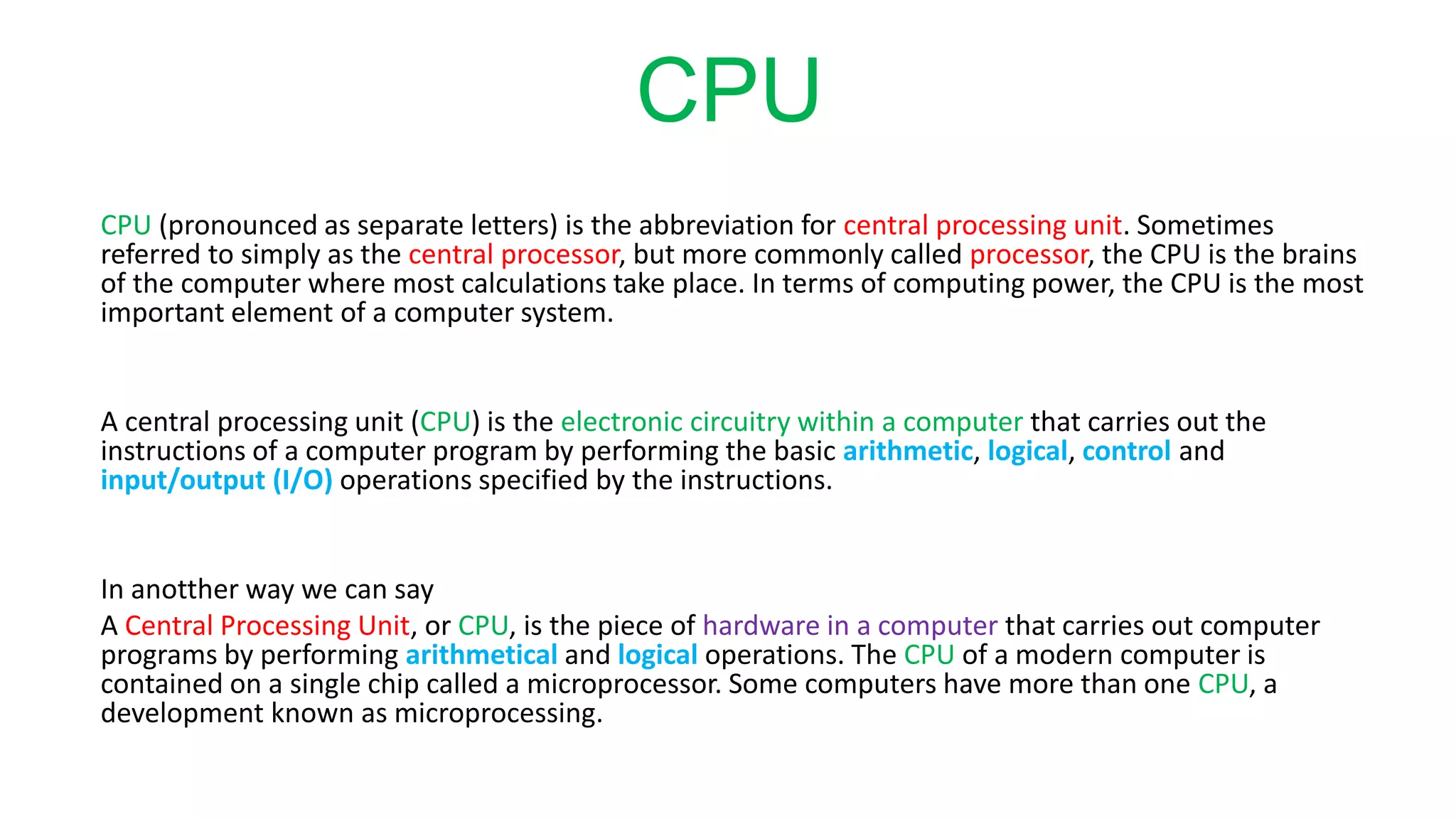
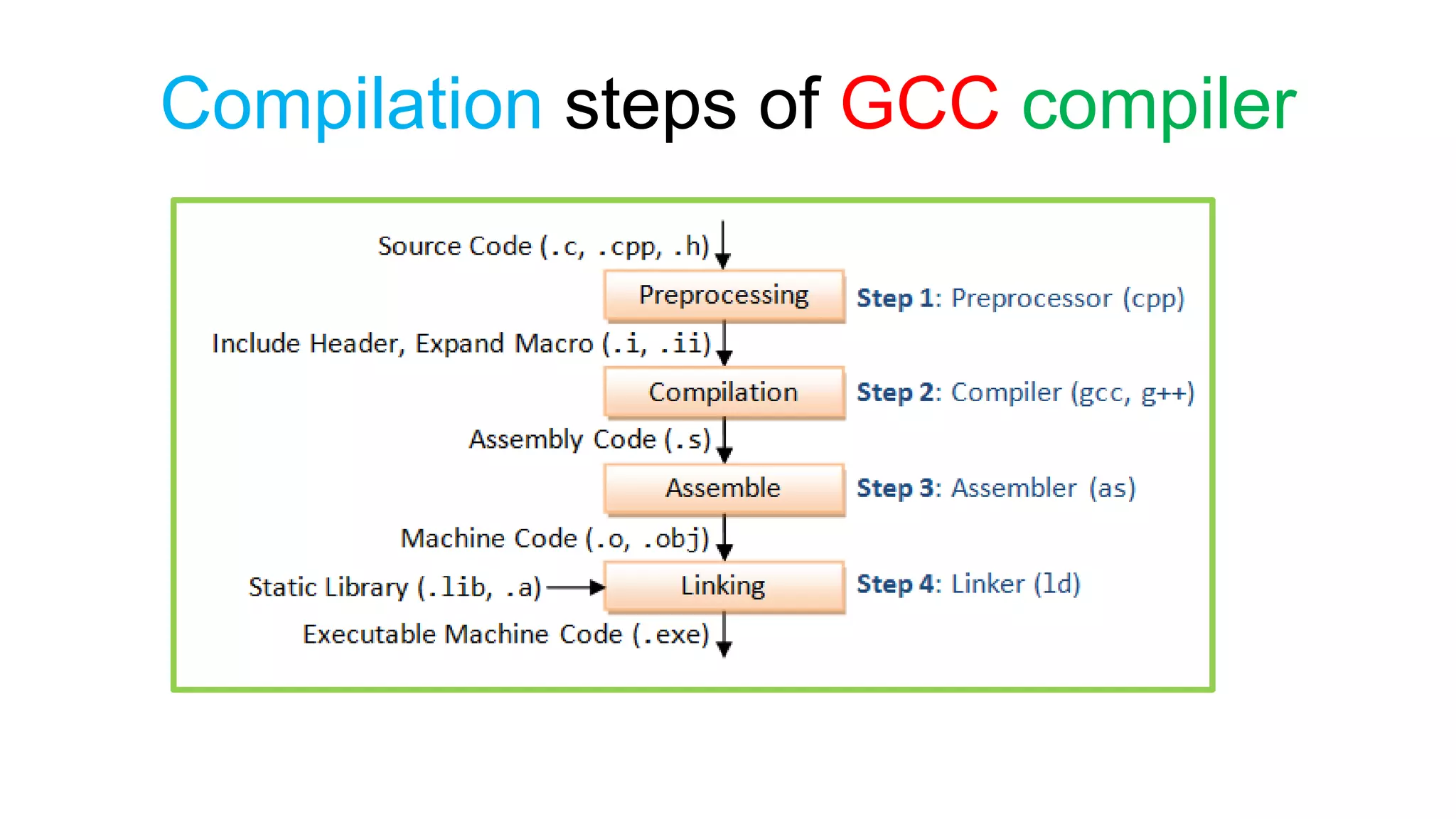
The document outlines the basic steps for C program execution: 1. Creating the program using an IDE or text editor, compiling the program using a compiler, and linking it with necessary library functions. 2. The preprocessor performs text substitution before compilation. The compiler translates source code to machine code. The linker combines object files and libraries. 3. The loader loads the machine code into memory for execution by the CPU, which performs arithmetic and logical operations to run the program.