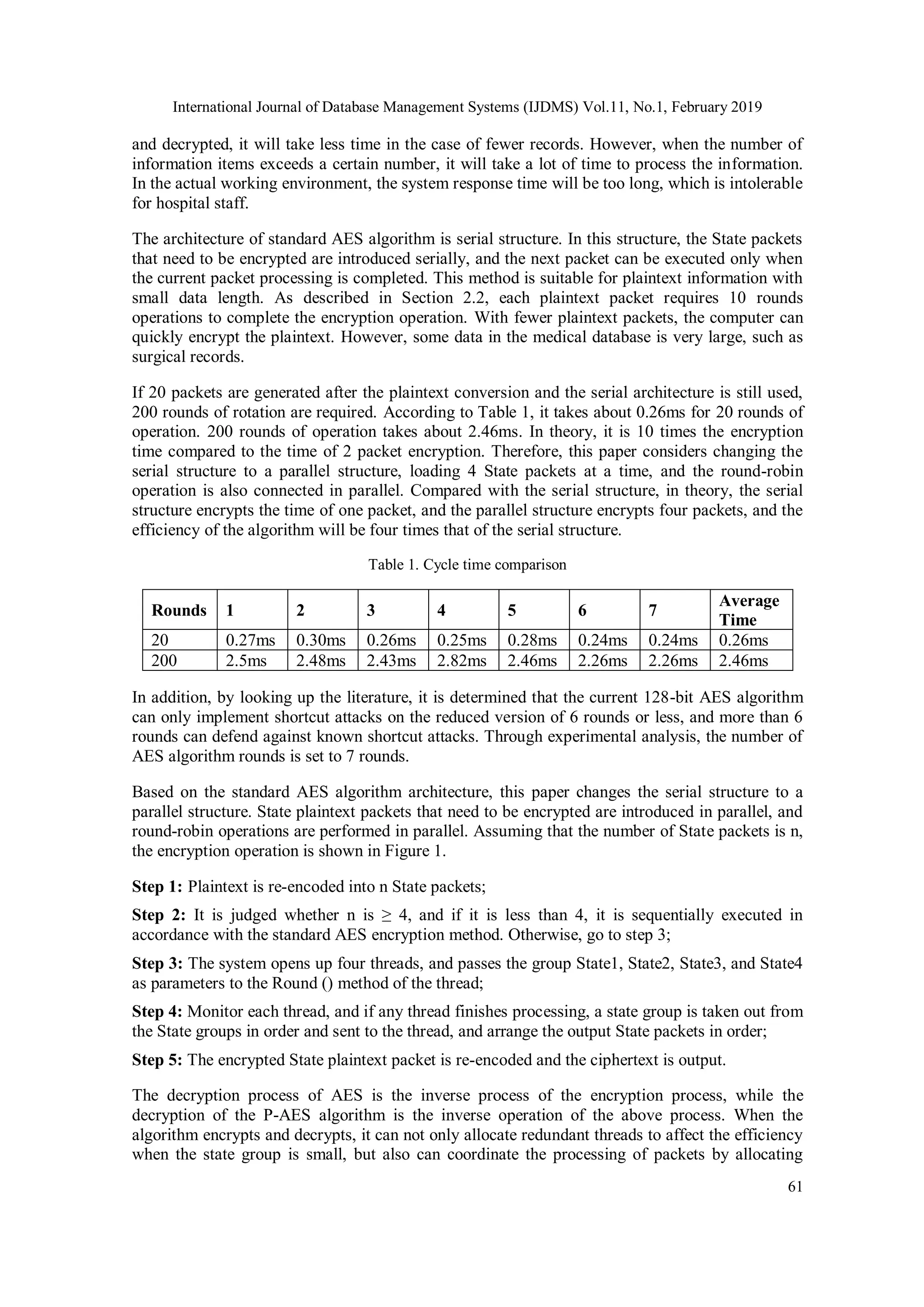
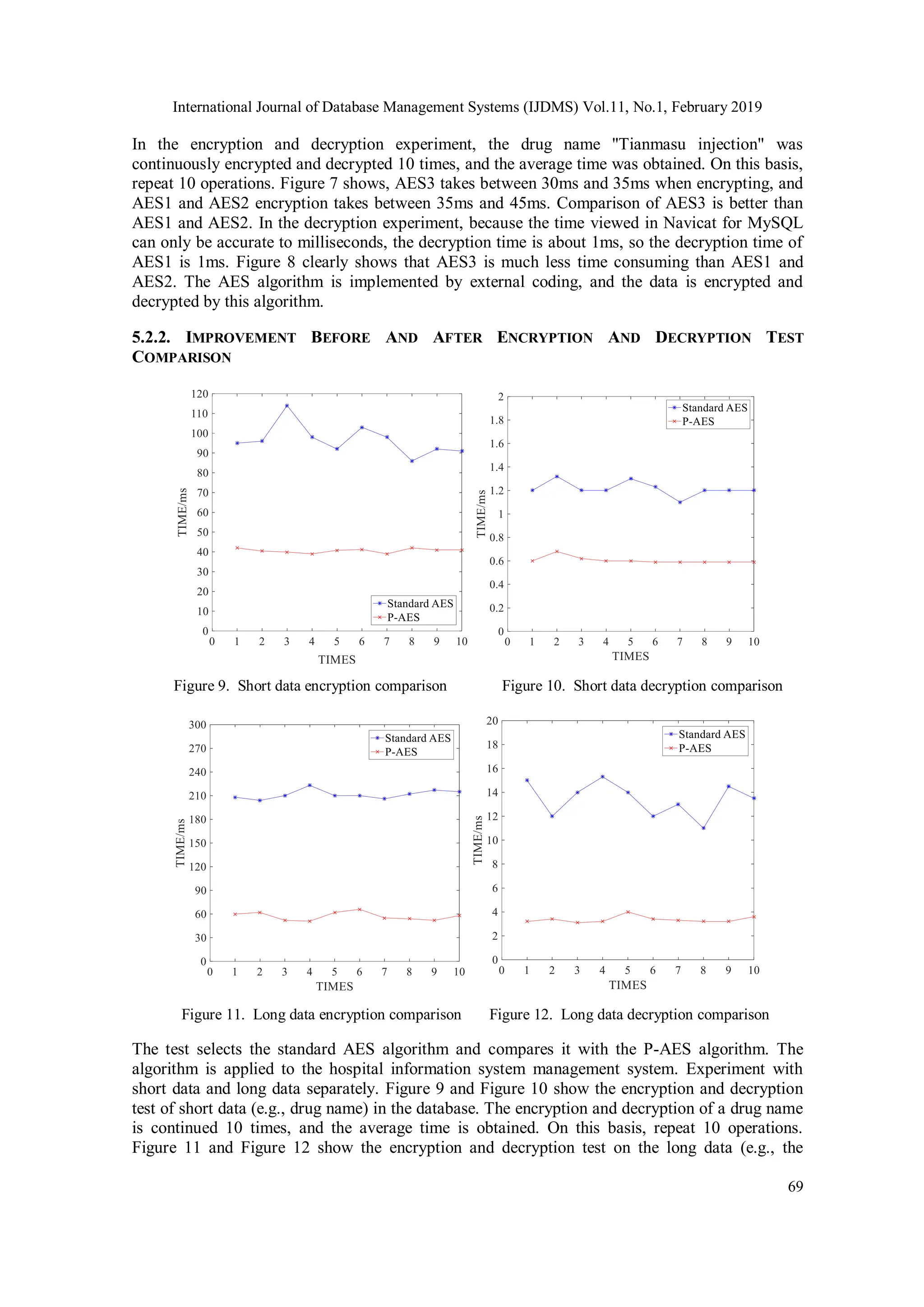
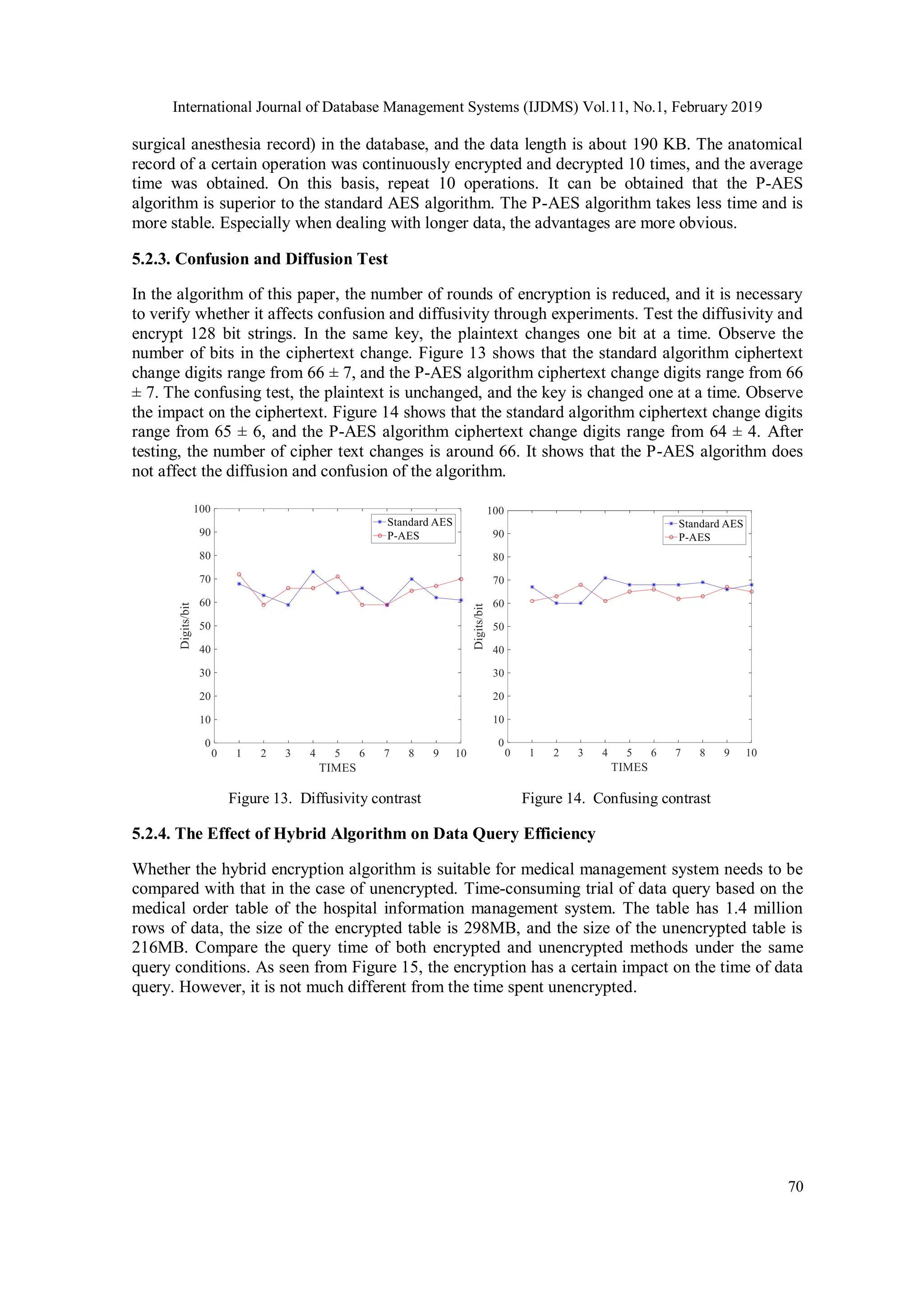
Cloud database are derivatives of Cloud computing. At present, most medical institutions store data in cloud database. Although the cloud database improves the efficiency of use, it also poses a huge impact and challenge to the secure storage of data. The article proposes a hybrid algorithm to solve the data security problem in the hospital cloud database. First, the AES algorithm is improved. The improved algorithm is called P-AES algorithm. The P-AES algorithm is then combined with the RSA algorithm, called a hybrid algorithm. The experimental results show that the hybrid encryption algorithm has the advantages of fast encryption and decryption speed, high security, good processing ability for longer data, and can solve the data security problem in cloud database to a certain extent. The algorithm has been successfully applied to hospital information management system.
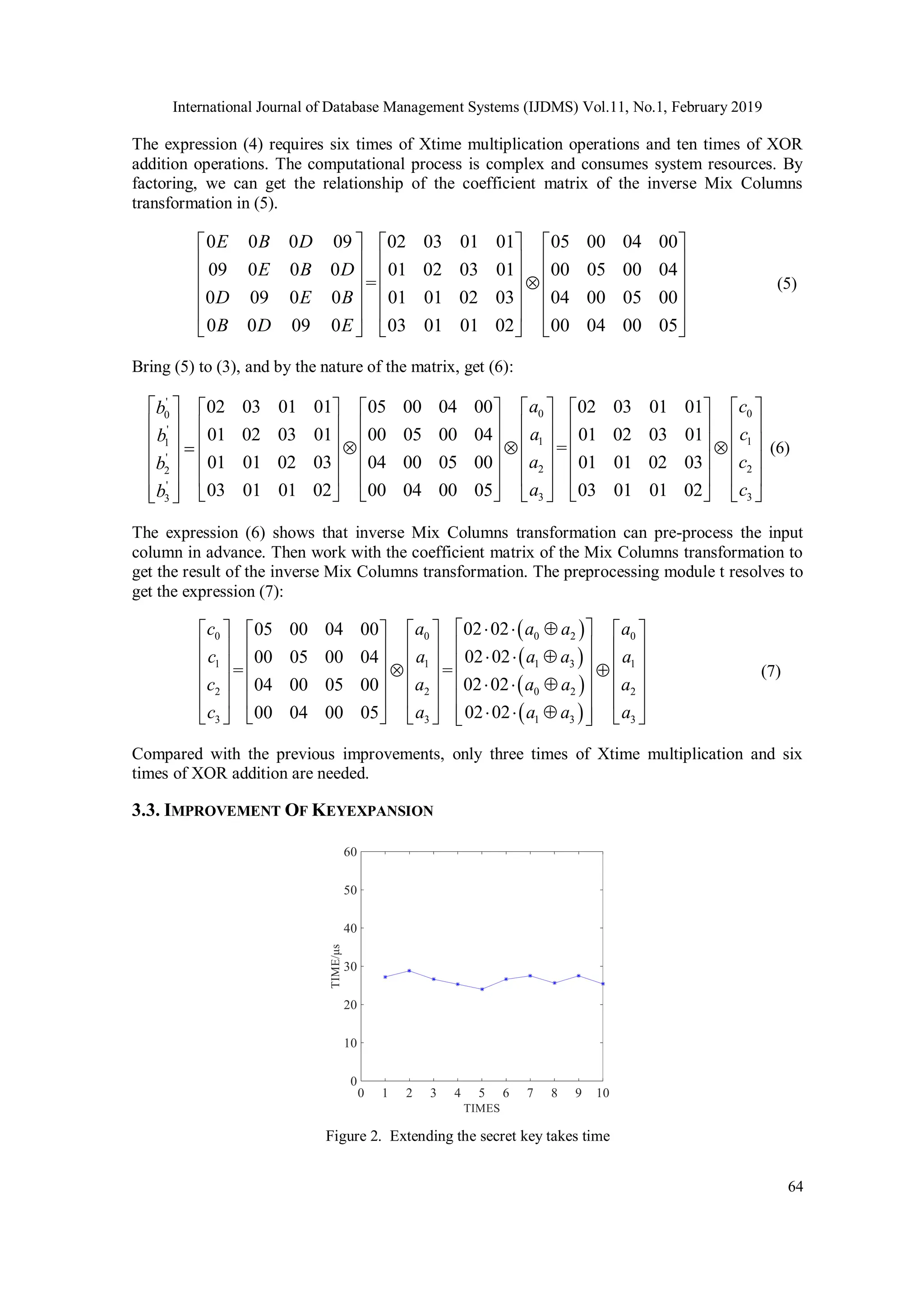
![International Journal of Database Management Systems (IJDMS ) Vol.11, No.1, February 2019 DOI : 10.5121/ijdms.2019.11104 57 HYBRID ENCRYPTION ALGORITHMS FOR MEDICAL DATA STORAGE SECURITY IN CLOUD DATABASE Fenghua Zhang1 ,Yaming Chen2 ,Weiming Meng3 and Qingtao Wu4 1 Computer Technology, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luo Yang, China 2,3 Computer Science and Technology, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luo Yang, China 4 Professor, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luo Yang, China ABSTRACT Cloud database are derivatives of Cloud computing. At present, most medical institutions store data in cloud database. Although the cloud database improves the efficiency of use, it also poses a huge impact and challenge to the secure storage of data. The article proposes a hybrid algorithm to solve the data security problem in the hospital cloud database. First, the AES algorithm is improved. The improved algorithm is called P-AES algorithm. The P-AES algorithm is then combined with the RSA algorithm, called a hybrid algorithm. The experimental results show that the hybrid encryption algorithm has the advantages of fast encryption and decryption speed, high security, good processing ability for longer data, and can solve the data security problem in cloud database to a certain extent. The algorithm has been successfully applied to hospital information management system. KEYWORDS Hospital System, AES, RSA, Hybrid Encryption 1. INTRODUCTION Hospital information construction is an important measure to improve the level of medical services. Nowadays, most hospitals have a set of perfect medical information management system. The system is divided into several subsystems, such as His, Lis, Pace, etc. These systems work together to ensure the normal operation of hospitals. In addition, it also has a large number of mobile devices and sensors to provide a variety of data for the hospital information management system. Although these software and equipment improve the quality of hospital services, hospitals are also facing tremendous pressure of data storage. If the hospital continues to follow the traditional data storage mode, it will not only make the hospital construction cost more, but also can’t solve the problem of "information island" between hospitals, which does not meet the development requirements of hospital information construction. The application of cloud computing can solve the above problems. It provides users with low cost, high computing and massive storage of network application services [1]. Cloud database is a kind of database that deploys and virtualizes in cloud computing environment. It enhances the storage capacity of the database, eliminates the repeated configuration of personnel, hardware and software, and makes it easier to upgrade software and hardware. However, users lose absolute control over the storage of data, and the security of the system depends on the information security strategy of cloud system [2, 3]. As a result, data will be attacked by hackers, peeped by service providers, large-scale leaks and other issues. Especially the hospital database stores a large number of users' private information, such as medical record information, doctor's advice](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/11119ijdms04-250604114121-058b6a55/75/Hybrid-Encryption-Algorithms-for-Medical-Data-Storage-Security-in-Cloud-Database-1-2048.jpg)
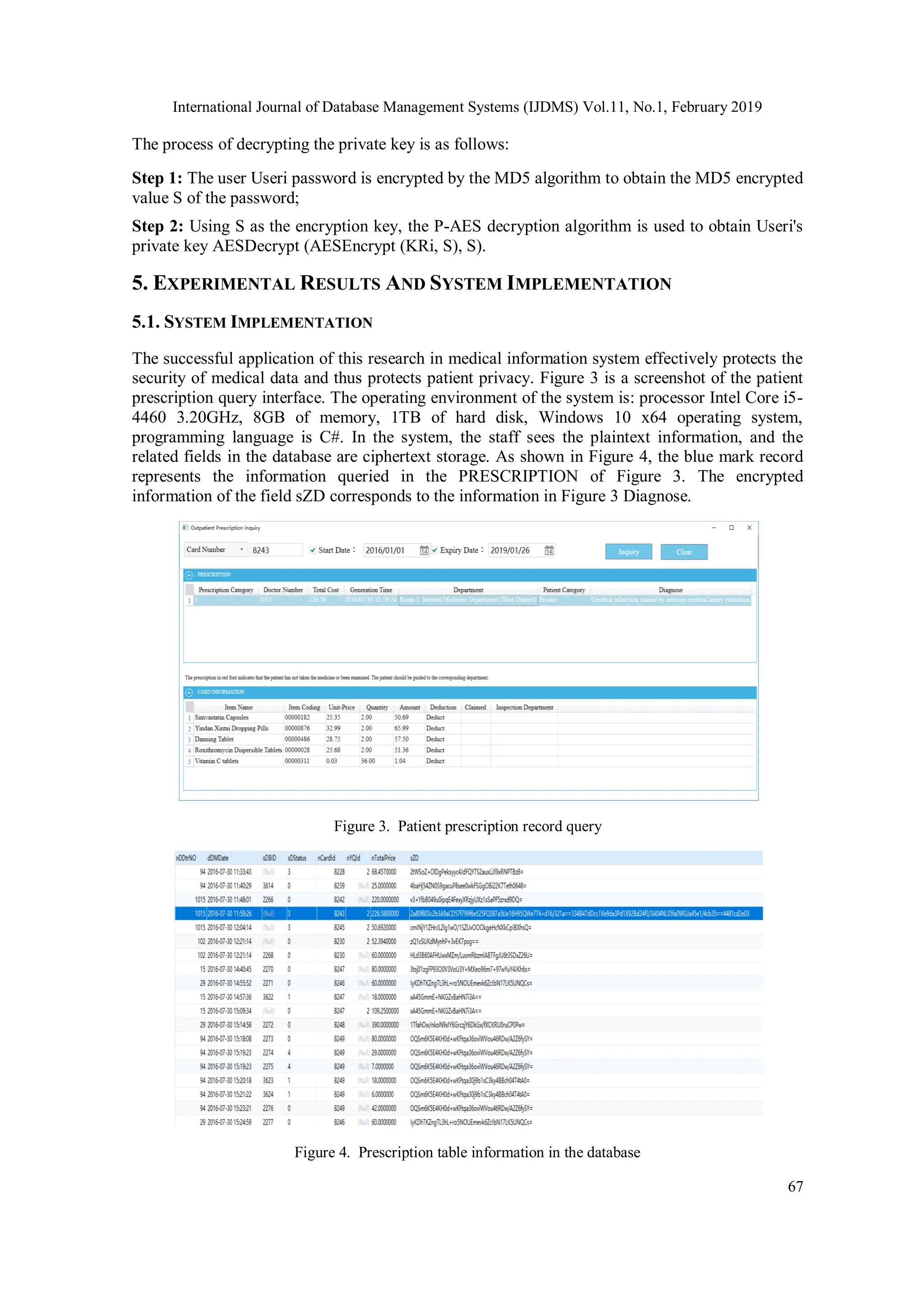
![International Journal of Database Management Systems (IJDMS) Vol.11, No.1, February 2019 58 information and prescription information and so on. Protecting data security in cloud databases has become an important issue in the field of information security [4]. 2. RELATED WORK 2.1. LITERATURE RESEARCH Encryption data can effectively solve the data security problem of cloud database. Even if the data is leaked, the criminals only get encrypted data. If they cannot be deciphered, the data will not be of any use to them. At present, the research work mainly focuses on the confidentiality of stored data, security audit and access control [5] and so on. According to the different types of secret keys, common data encryption algorithms can be divided into symmetric encryption algorithm and asymmetric encryption algorithm (public key encryption algorithm). Symmetric encryption algorithm uses the same secret key to encrypt and decrypt data. It has the characteristics of short secret key length and fast encryption and decryption speed, but it is difficult to manage the secret key [6]. Asymmetric encryption algorithm uses public key encryption and private key decryption. The algorithm features high security, but encryption and decryption involves complex operations, so the speed is slow. Data Encryption Standard (DES) is a commonly used symmetric encryption algorithm. It is a block encryption algorithm. The standard DES algorithm encrypts data in groups of 64 bits, and the same algorithm is used for encryption and decryption. The key length is 64 bits, which is actually generated by 56 bits of secret key and additional 8 bits of parity check bits. The algorithm has high encryption and decryption efficiency, but the key length is too short and the security of the algorithm is relatively low [7]. In order to solve the problem of short length and low security of DES secret key. A triple DES (3DES) encryption method was proposed. This algorithm is equivalent to performing DES encryption algorithm three times for each data block, which is a distortion of DES algorithm. The 3DES algorithm is based on the DES algorithm. It is a packet encryption algorithm designed by combining packets. This method expands the key length from 56 bits to 112 bits, so the efficiency of encryption and decryption is very low. However, with the development of symmetric encryption technology, DES and 3DES are gradually replaced by the new encryption algorithm AES (Advanced Encryption Standard). As a new generation of data encryption standard, AES combines security, performance, efficiency, simplicity and flexibility. These features make AES the preferred choice in security- related applications [8]. In recent years, experts and scholars have done a lot of research on the efficiency and security of AES algorithm. Literature [9] provides a safer and more economical encryption mechanism, which randomizes the key of AES algorithm and hides the key data into the encrypted digital image by using the basic concepts of cryptography and digital watermarking. Then the pixels are repositioned to break the correlation between them. Literature [10] based on chaos theory, the AES algorithm S-box is replaced by another S-box. The new S- box has low correlation and shows significant performance improvement with increasing complexity. Document [11] proposes a method to provide different security services, such as authentication, authorization, and confidentiality. This method is used for different data security and privacy protection issues in cloud computing environments. The algorithm AES-128 is used to improve the security and confidentiality of data. In this method, data is encrypted using AES and then uploaded to the cloud. Literature [12] implements parallel execution of AES algorithm in the supercomputer that name is Shen Wei Tai Hu Light. Literature [13] uses biometric generation keys to improve the security of the AES algorithm. The 128 bit key generated by iris feature is combined with the 128 bit key randomly generated to form a 128 bit hybrid key. Although it improves the security of the algorithm, it increases the cost of application and is](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/11119ijdms04-250604114121-058b6a55/75/Hybrid-Encryption-Algorithms-for-Medical-Data-Storage-Security-in-Cloud-Database-2-2048.jpg)
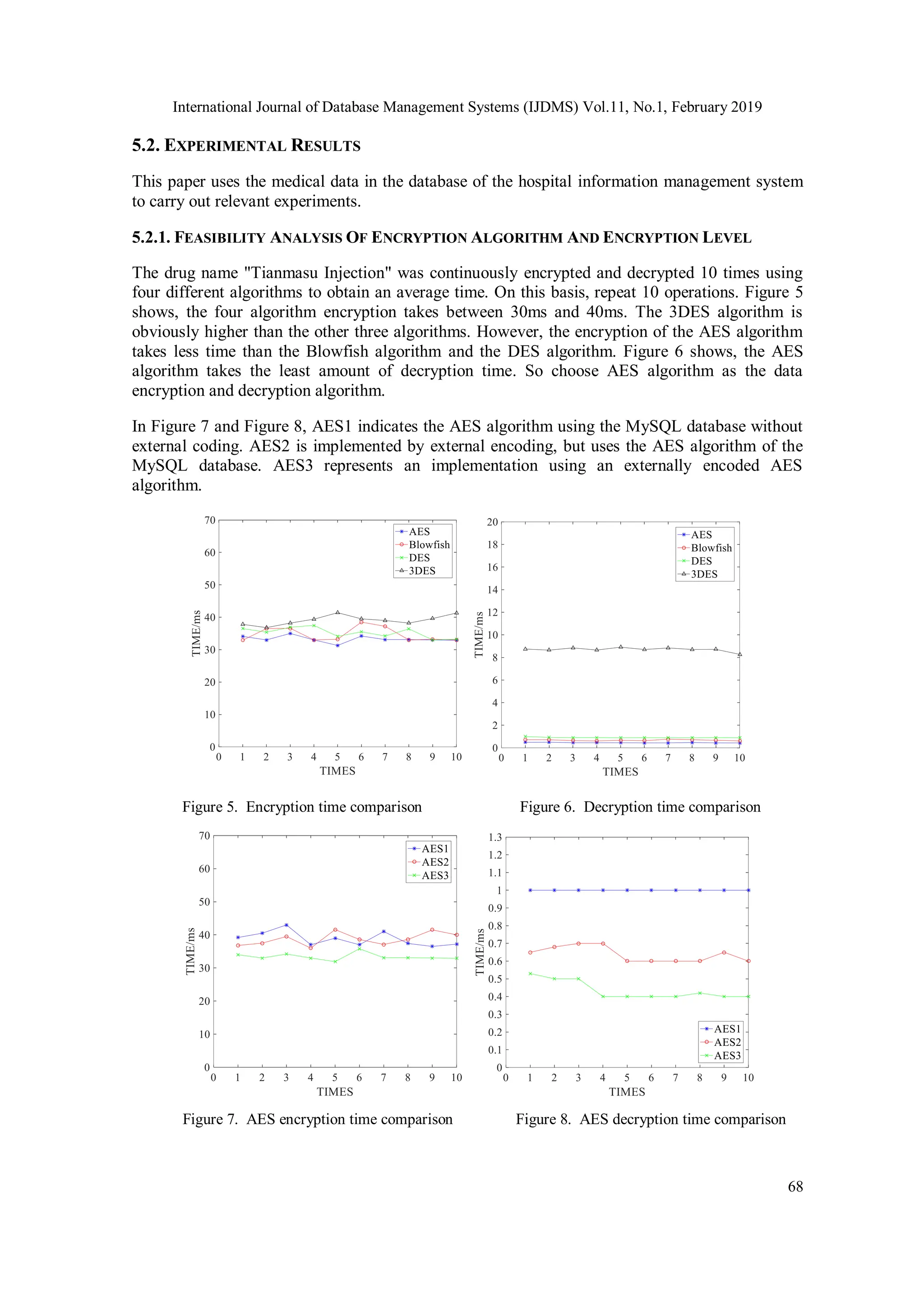
![International Journal of Database Management Systems (IJDMS) Vol.11, No.1, February 2019 59 difficult to popularize. Literature [14] implements AES-256 encryption and decryption algorithm on hardware. When encrypting, the round-key is generated in parallel to avoid encrypting period, which reduces the delay of each round of encrypting. Literature [15] implements the hardware implementation of AES algorithm on Xilinx Virtex-7 FPGA. The hardware design method is based entirely on pre-computed lookup tables (LUTs), which reduces the complexity of the architecture and provides high throughput and low latency. Literature [16] increases the number of rounds (Nr) of the encryption and decryption process of AES algorithm to 16. Although the system is more secure, the execution efficiency of the algorithm decreases with the increase of the number of rounds. However, none of these improvements involve the management of AES keys. In practical applications, the granularity of database encryption is different, and the number of secret keys produced is also different. Only by ensuring the secure storage of the data secret key can the encrypted data not be cracked. RSA, an asymmetric encryption algorithm, has high security and is widely used in user data encryption and digital signature [17]. However, the security of this algorithm depends on the decomposition of large numbers, which makes RSA's fastest operation speed much lower than DES algorithm and other symmetric encryption algorithms. Therefore, its low encryption and decryption efficiency is not suitable for encrypting large amounts of data. The combination of symmetric encryption algorithm and asymmetric encryption algorithm can make up for the shortcomings of each other. Using symmetric encryption algorithm to encrypt and decrypt information can improve the efficiency of encryption and decryption, and using asymmetric encryption algorithm to exchange secret keys. In this way, the secret key security of symmetric encryption algorithm can be guaranteed [18]. In the literature [19], a hybrid application of local file encryption system based on 3DES and RSA algorithm is proposed, which provides better protection for personal privacy and important files. Although this method effectively solves the problem of symmetric secret key management, it is not suitable for encrypting and decrypting large quantities of data because of the low efficiency of the implementation of the 3DES algorithm. In the literature [20], a hybrid DES and SHA-1 encryption system based on VC++ environment is developed to ensure the concealment and integrity of data. On the one hand, the system uses triple DES and RSA algorithm to encrypt and hide data, on the other hand, SHA-1 algorithm is used to verify the integrity of data. In the literature [21], a new hybrid image encryption algorithm based on AES (CS-AES) is developed by using the RNG and S-Box generation algorithms designed. But this algorithm is still a disguised symmetric encryption algorithm based on AES. In the literature [22], combining the characteristics of symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption, a hybrid encryption system based on RSA and Blowfish algorithm is proposed and implemented on the device of FPGA. In the literature [23], a hybrid algorithm based on DES and RSA is proposed for text data. But this algorithm uses symmetric encryption algorithm DES, although the encryption efficiency is high, but the algorithm security is not high. Because medical information in the medical information system cloud database needs to be shared between untrusted entities, protecting patient privacy is one of the attributes that medical information systems must satisfy [24]. Aiming at the problem of data security in cloud database of medical information management system, a hybrid encryption algorithm based on AES and RSA is proposed by analyzing the characteristics of cloud database and medical data. This algorithm combines the characteristics of AES encryption algorithm (high encryption and decryption efficiency, high reliability, flexible secret key and grouping) and RSA algorithm (high security, easy implementation) to ensure the security of medical data in cloud database. The AES algorithm is improved to make it more suitable for medical information management system. The algorithm is successfully applied to the medical information management system, and the feasibility of the method is verified.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/11119ijdms04-250604114121-058b6a55/75/Hybrid-Encryption-Algorithms-for-Medical-Data-Storage-Security-in-Cloud-Database-3-2048.jpg)

![International Journal of Database Management Systems (IJDMS) Vol.11, No.1, February 2019 62 multiple threads in the case of too many State packets, thereby improving the execution efficiency of the algorithm. Speed up the time of encryption and decryption. Plaintext Plaintext AddRoundKey AddRoundKey SubBytes SubBytes ShiftRows ShiftRows MixColumns MixColumns AddRounfKey AddRounfKey SubBytes SubBytes ShiftRows ShiftRows AddRounfKey AddRounfKey CipherKey CipherKey W[0,3] W[i,i+3] W[28,31] AddRoundKey AddRoundKey SubBytes SubBytes ShiftRows ShiftRows MixColumns MixColumns AddRounfKey AddRounfKey SubBytes SubBytes ShiftRows ShiftRows AddRounfKey AddRounfKey AddRoundKey AddRoundKey SubBytes SubBytes ShiftRows ShiftRows MixColumns MixColumns AddRounfKey AddRounfKey SubBytes SubBytes ShiftRows ShiftRows AddRounfKey AddRounfKey AddRoundKey AddRoundKey SubBytes SubBytes ShiftRows ShiftRows MixColumns MixColumns AddRounfKey AddRounfKey SubBytes SubBytes ShiftRows ShiftRows AddRounfKey AddRounfKey Ciphertext Ciphertext State 3 State 4 State n-2 State n-1 State 1 State 2 State n State 3 State 4 State n-2 State n-1 State 1 State 2 State n Open up four threads to divide plaintext groups into threads in sequence States processed by threads are arranged in order Nr-1 Roun ds Nr-1 Roun ds Seven Round Seven Round Figure 1. Improved encryption algorithm process 3.2. OPTIMIZATION OF MIXCOLUMNS AND INVMIXCOLUMNS MixColumns /InvMixColumns is a linear transformation of each column in the State. In the Mix Columns transformation, the column of State is interpreted as a polynomial in the Galois 8 2 GF , multiplication with a given polynomial under modular polynomial 4 1 x . If the column input of State is a x , the output is b x , we can get 4 • 1 b x a x c x mod x , where c x a reversible polynomial of the modular polynomial is 4 1 x . In the standard AES algorithm,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/11119ijdms04-250604114121-058b6a55/75/Hybrid-Encryption-Algorithms-for-Medical-Data-Storage-Security-in-Cloud-Database-6-2048.jpg)



![International Journal of Database Management Systems (IJDMS) Vol.11, No.1, February 2019 71 Figure 15. Comparison of average query time of projects with different data volumes 6. CONCLUSION The data in this paper is based on medical data from Yongcheng Chinese Medicine Hospital. This paper verifies that the AES algorithm and the database outer layer encryption method have higher encryption and decryption efficiency through relevant experiments. According to the characteristics of medical data, the P-AES algorithm is proposed. It has been proved by relevant experiments that it has higher encryption and decryption efficiency than the original algorithm and is more suitable for processing long data. Finally, based on this, combined with the RSA algorithm, a hybrid encryption algorithm is proposed and successfully applied in the medical information management system. Through query comparison, although data encryption will affect the efficiency of the query, it is within the user's acceptance. Therefore, the hybrid encryption algorithm can provide security protection for medical data stored in cloud database and protect patients' privacy. However, the P-AES algorithm also has certain limitations, and currently only text data can be encrypted. Cannot be used to encrypt data such as pictures and images. Moreover, the algorithm is based on AES-128 and can only encrypt data using a 128-bit key. There is still much room for improvement in the P-AES algorithm. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Thanks to the laboratory for providing the environment for my research practice. Thanks to my mentor and other members of the lab for their help in my paper research. Thanks to Yongcheng Central Hospital for supporting our work. It was because of their help that this article was successfully completed. REFERENCES [1] Wang Cong, Wang Qian & Ren Kui, (2011) “Ensuring data storage security in Cloud Computing”, IEEE International Conference on Parallel Distributed & Grid Computing. [2] Salma & T. J., (2013) “A flexible distributed storage integrity auditing mechanism in Cloud Computing”, IEEE International Conference on Information Communication & Embedded Systems. [3] S.Suganya, (2014) “Enhancing security for storage services in cloud computing”, IEEE Current Trends in Engineering and Technology, Vol. 3, No. 6, pp283-287. [4] Kaufman & L. M., (2009) “Data Security in the world of cloud computing”, IEEE Security & Privacy, Vol. 4, No. 7, pp61-64.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/11119ijdms04-250604114121-058b6a55/75/Hybrid-Encryption-Algorithms-for-Medical-Data-Storage-Security-in-Cloud-Database-15-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Database Management Systems (IJDMS) Vol.11, No.1, February 2019 72 [5] Takabi H, Joshi J. B. D. & Ahn G, (2010) “Security and privacy challenges in cloud computing Environment”, IEEE Security & Privacy, Vol. 6, No. 8, pp24-31. [6] Poh, G. S., Chin, J. J. & Yau, W. C., (2017) “Searchable symmetric encryption”, ACM Computing Surveys, Vol. 50, No. 3, pp1-37. [7] Qiu Weixing, Xiao Kezhi & Li Fang, (2011) “A kind of method of extension of the DES key," Computer Engineering, Vol. 5, No. 37, pp167-168. [8] T. Good & M. Benaissa, (2007) “Pipelined AES on FPGA with support for feedback modes (in a multi-channel environment)”, IET INFORMATION SECURITY, Vol. 1, No. 1, pp1-10. [9] Mondal, S. & Maitra, S., (2014) “Data security-modified aes algorithm and its applications”, ACM SIGARCH Computer Architecture News, Vol. 2, No. 42, pp1-8. [10] Elbadawy & A. M., (2010) “A new chaos Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) algorithm for data security”, IEEE International Conference on Signals & Electronic Systems, pp7-10. [11] Babitha M. P. & Babu K. R. R., (2017) “Secure cloud storage using AES encryption”, IEEE International Conference on Automatic Control & Dynamic Optimization Techniques. [12] Chen, Y, & Li K, (2017) “Implementation and Optimization of AES Algorithm on the Sunway TaihuLight”, IEEE International Conference on Parallel & Distributed Computing. Pp256-261. [13] Priya, S. S. S., & Karthigaikumar, P., (2015) “Generation of 128-Bit Blended Key for AES Algorithm”, CSI Emerging ICT for Bridging the Future , Vol. 2, No. 49, pp431-439. [14] Mohurle, M., & V. V. Panchbhai, (2017) “Review on realization of AES encryption and decryption with power and area optimization”, IEEE International Conference on Power Electronics, Vol. 2. [15] N. S. Sai Srinivas & Monhammed Akramuddin, (2016) “FPGA Based Hardware Implementation of AES Rijndael Algorithm for Encryption and Decryption”, IEEE International Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Optimization Techniques (ICEEOT-2016). [16] Puneet Kumar & Shashi B. Rana, (2016) “Development of modified aes algorithm for data security”, Optik - International Journal for Light and Electron Optics, Vol. 4, No. 127, pp2341-2345. [17] Rivest, R. L., Shamir, A., & Adleman, L., (1978) “A method for obtaining digital signatures and public-key cryptosystems”, Communications of the Acm, Vol. 2, No. 21, pp120-126. [18] Anane Nadjia & Anane Mohamed, (2015) “AES IP for hybrid cryptosystem RSA-AES”, IEEE International Multi-conference on Systems. No. 12. [19] HU Zhen, (2012) “Triple DES and RSA-based file encryption system”, Computer and Modernization, No. 9, pp101-105. [20] Jian Zhang & Xuling Jin, (2012) “Encryption System Design Based on DES and SHA-1”, IEEE International Symposium on Distributed Computing & Applications to Business, pp317-320. [21] Ünal Çavuşoğlu & Sezgin Kaçar, (2018) “A novel hybrid encryption algorithm based on chaos and S- AES algorithm”, Nonlinear Dynamics, Vol. 92, No. 4, pp1745-1759. [22] Viney Pal Bansal & Sandeep Singh, (2016) “A hybrid data encryption technique using RSA and Blowfish for cloud computing on FPGAs”, IEEE International Conference on Recent Advances in Engineering & Computational Sciences. [23] Smita Chourasia & Kedar Nath Singh, (2016) “An Efficient Hybrid Encryption Technique Based on DES and RSA for Textual Data”, Information Systems Design and Intelligent Applications, pp73-80. [24] Anand Sharma & Vibha Ojha, (2010) “Implementation Of Cryptography For Privacy Preserving Data Mining”, International Journal of Database Management Systems, Vol. 2, No. 3,pp57-65.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/11119ijdms04-250604114121-058b6a55/75/Hybrid-Encryption-Algorithms-for-Medical-Data-Storage-Security-in-Cloud-Database-16-2048.jpg)
