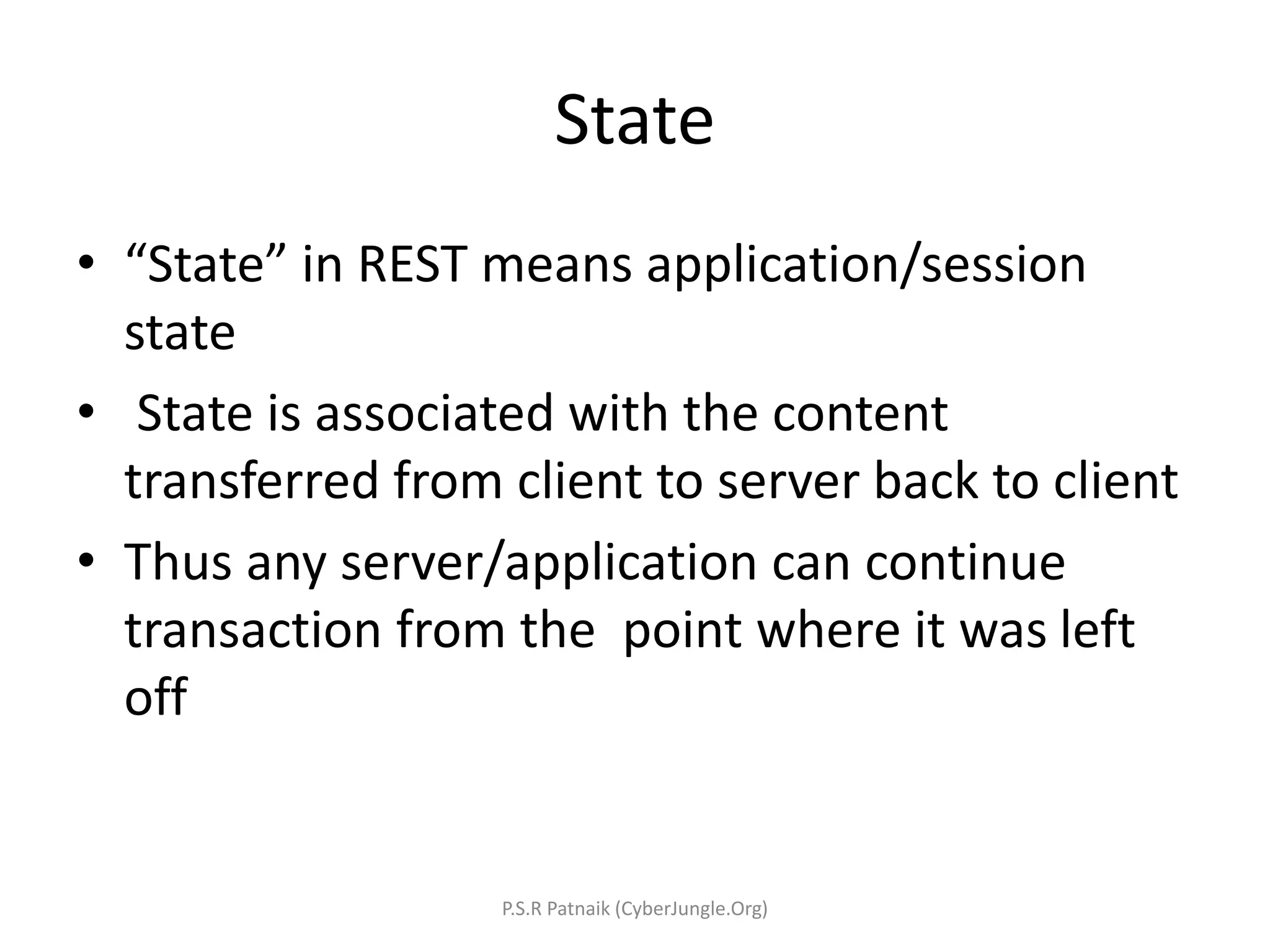
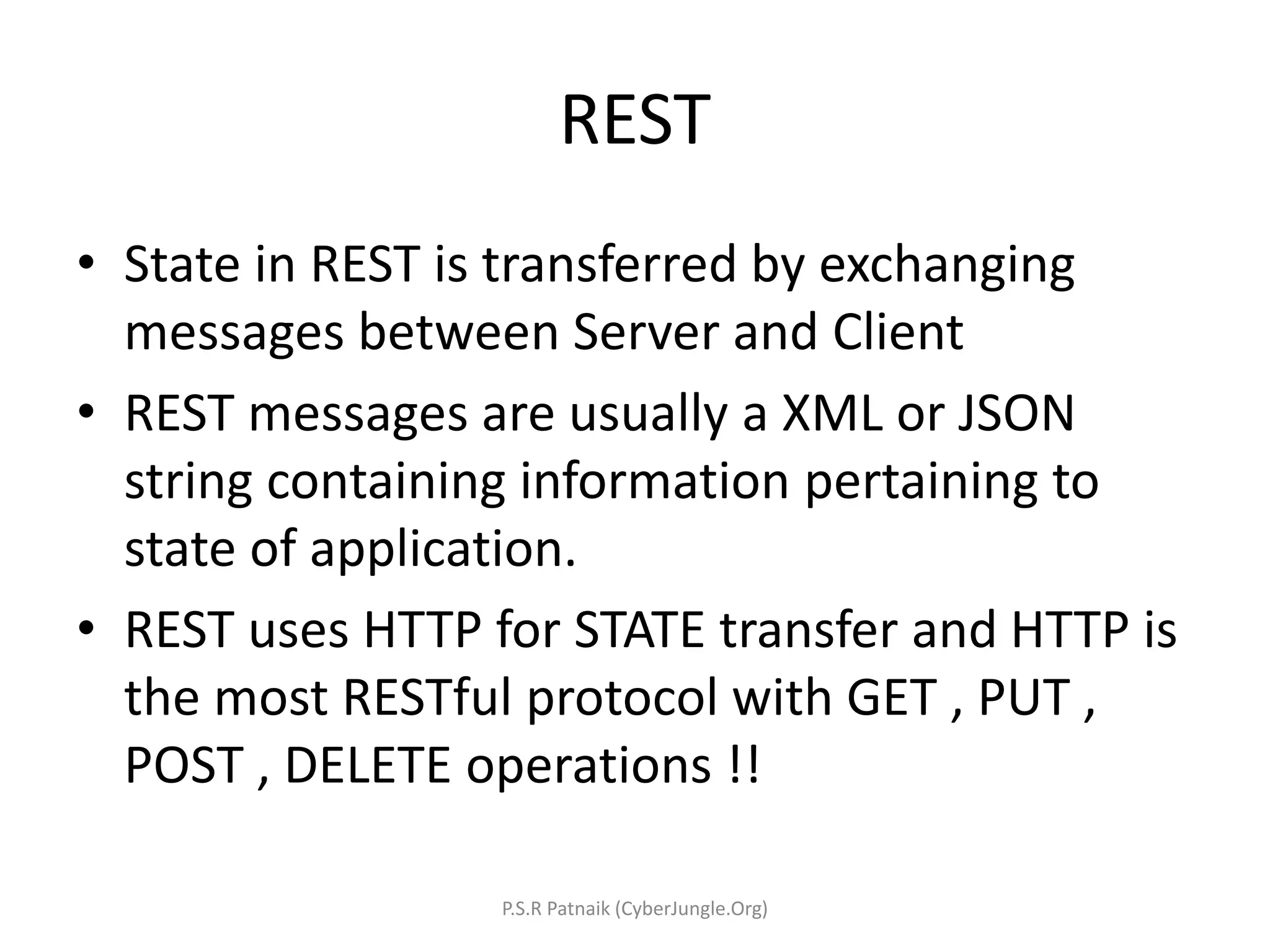
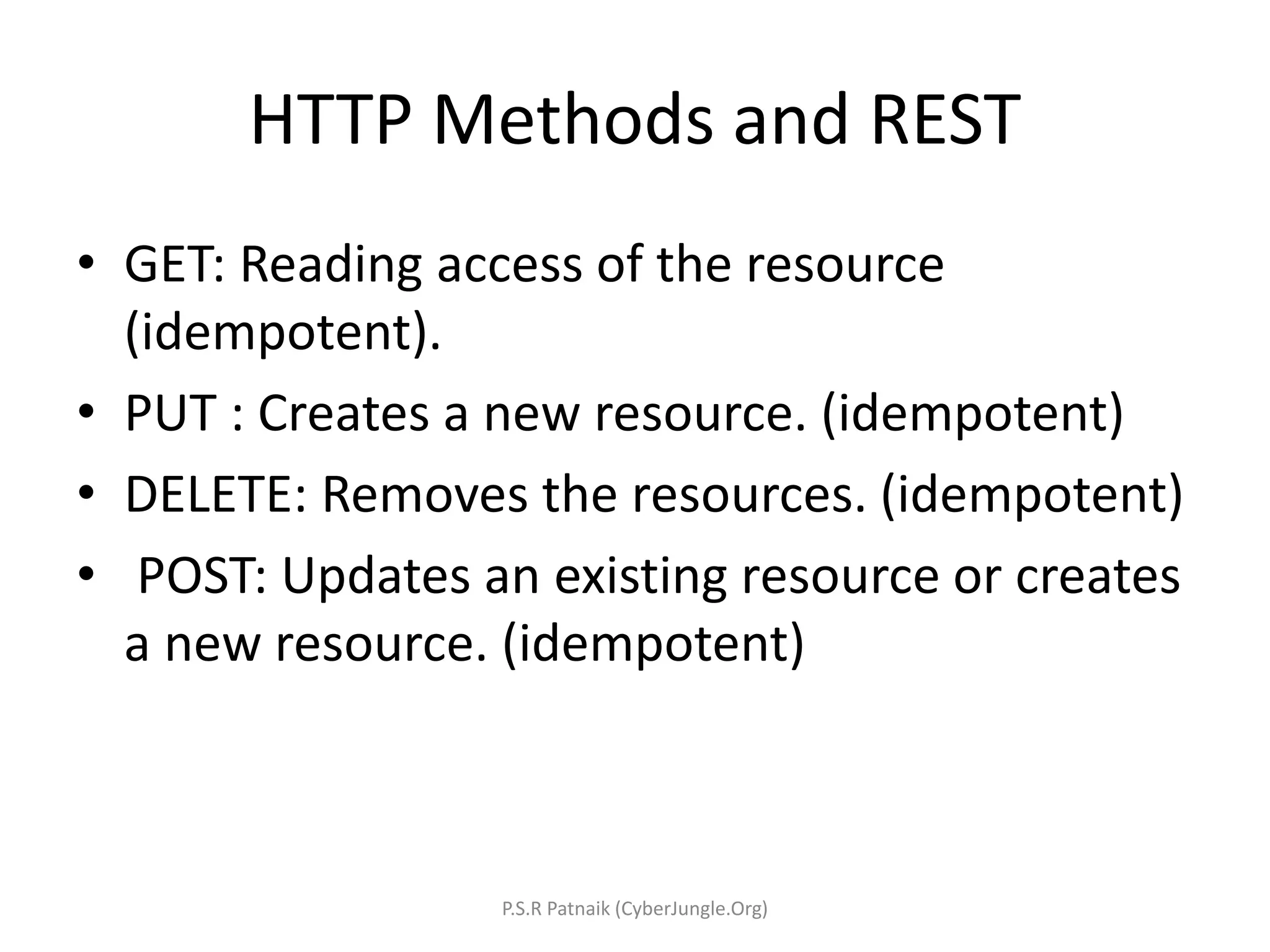
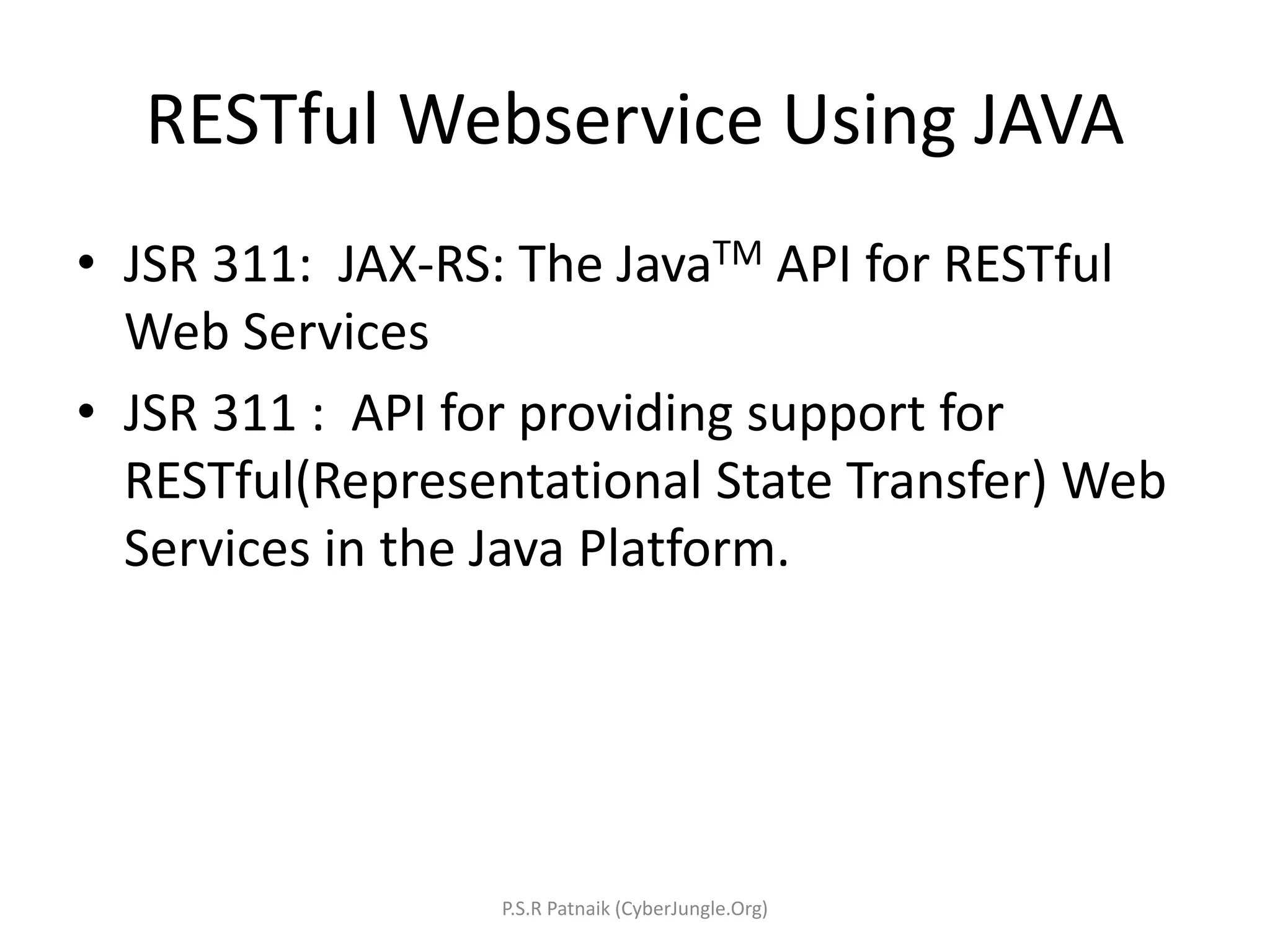
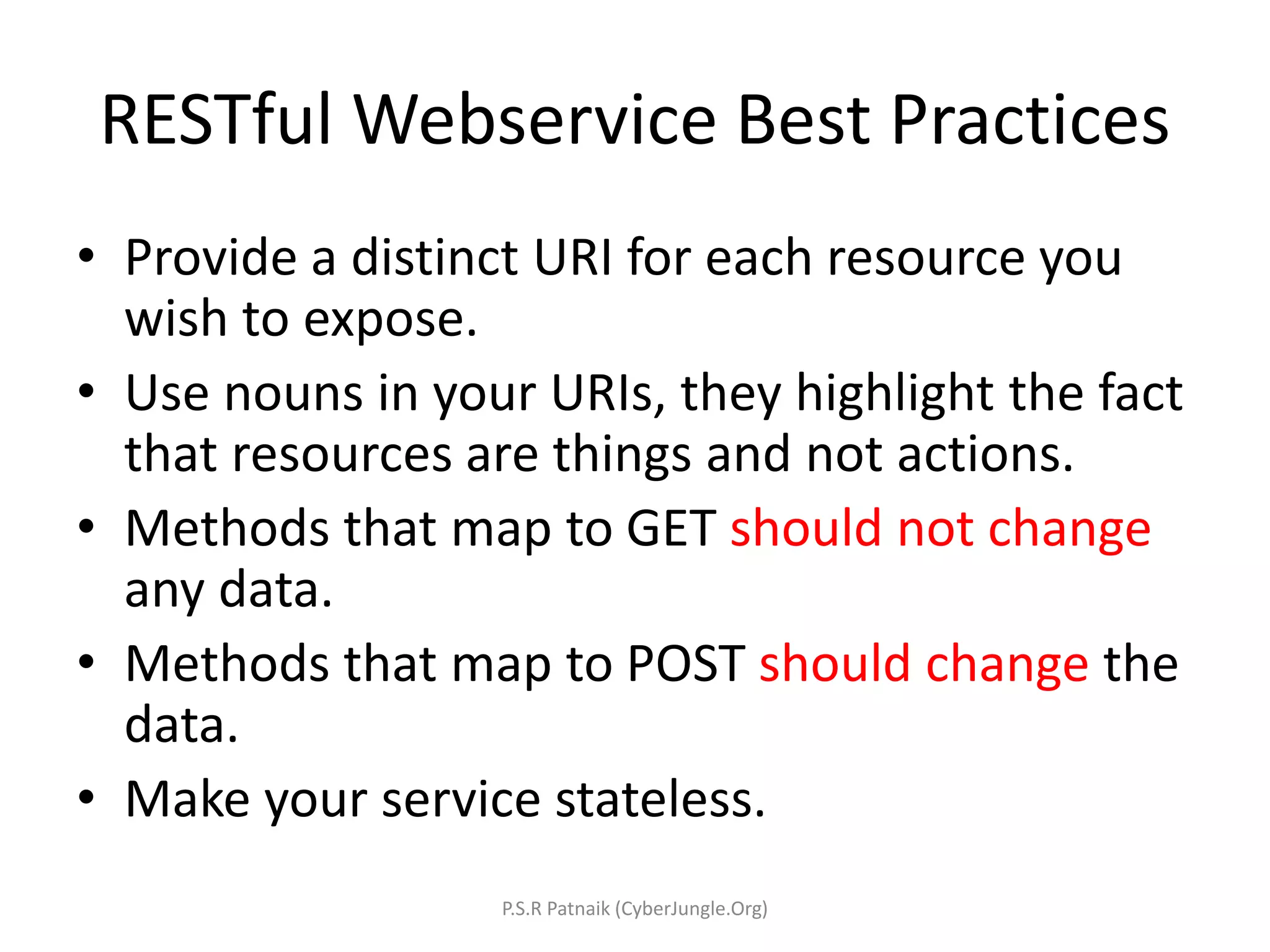
The document explains Representational State Transfer (REST) as an architectural style characterized by features such as client-server interaction, statelessness, caching, a uniform interface, and a layered system. It outlines the components of RESTful web services, including the use of HTTP methods, URIs for resources, and the importance of stateless communication. Additionally, it provides guidance on developing RESTful web services in Java using JAX-RS, best practices for designing them, and a simple example implementation using Jersey and Eclipse Kepler.