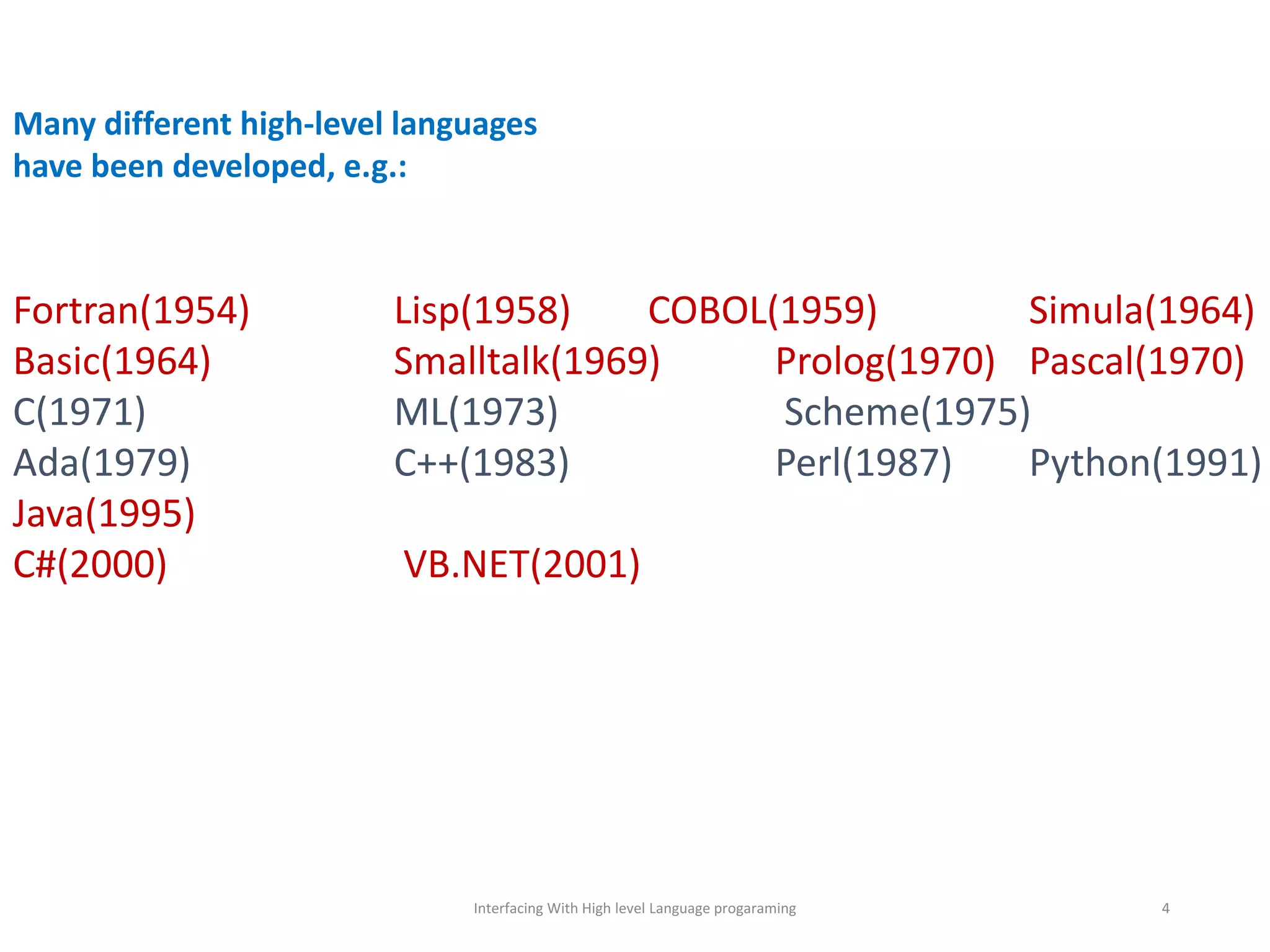
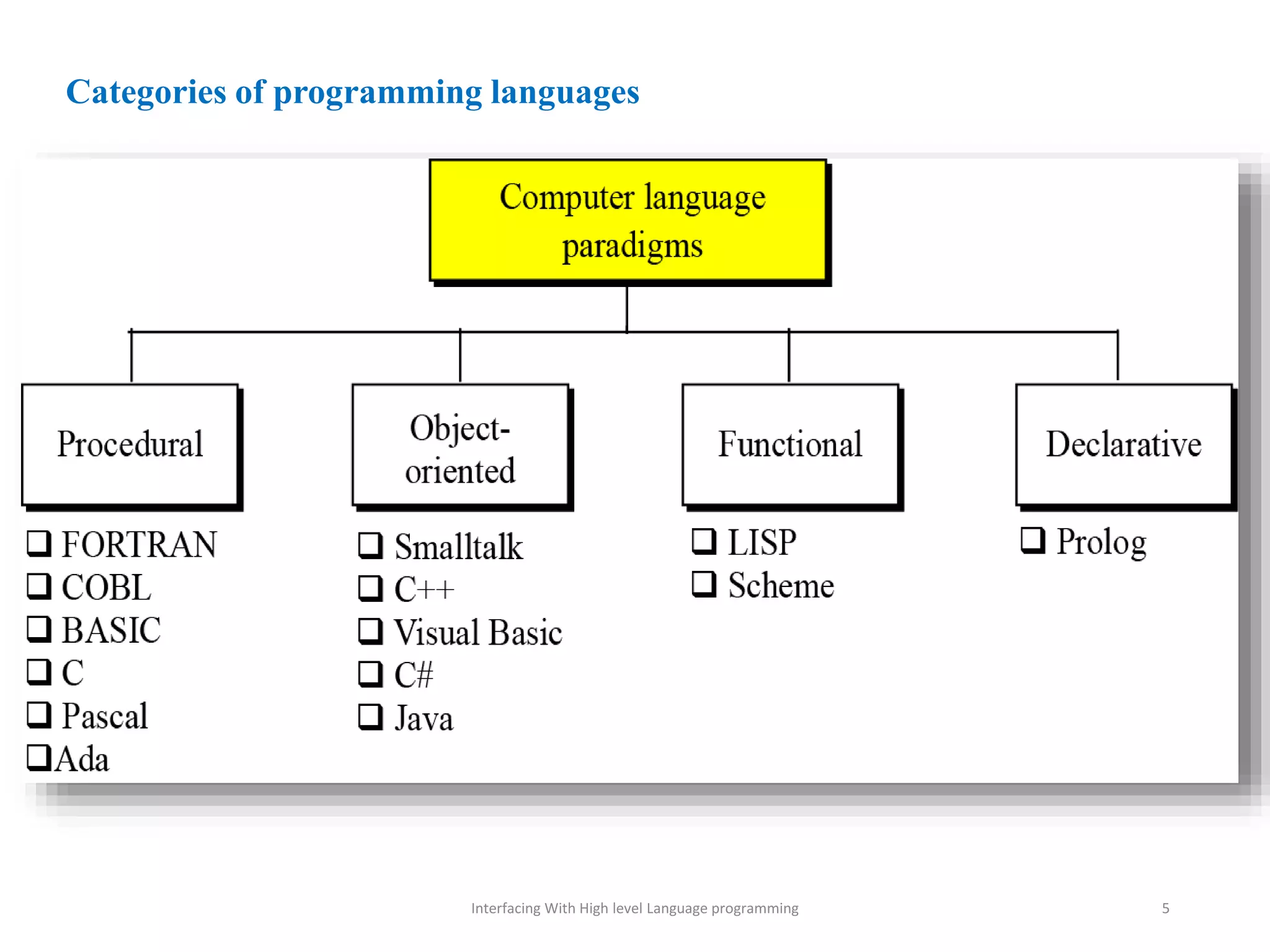
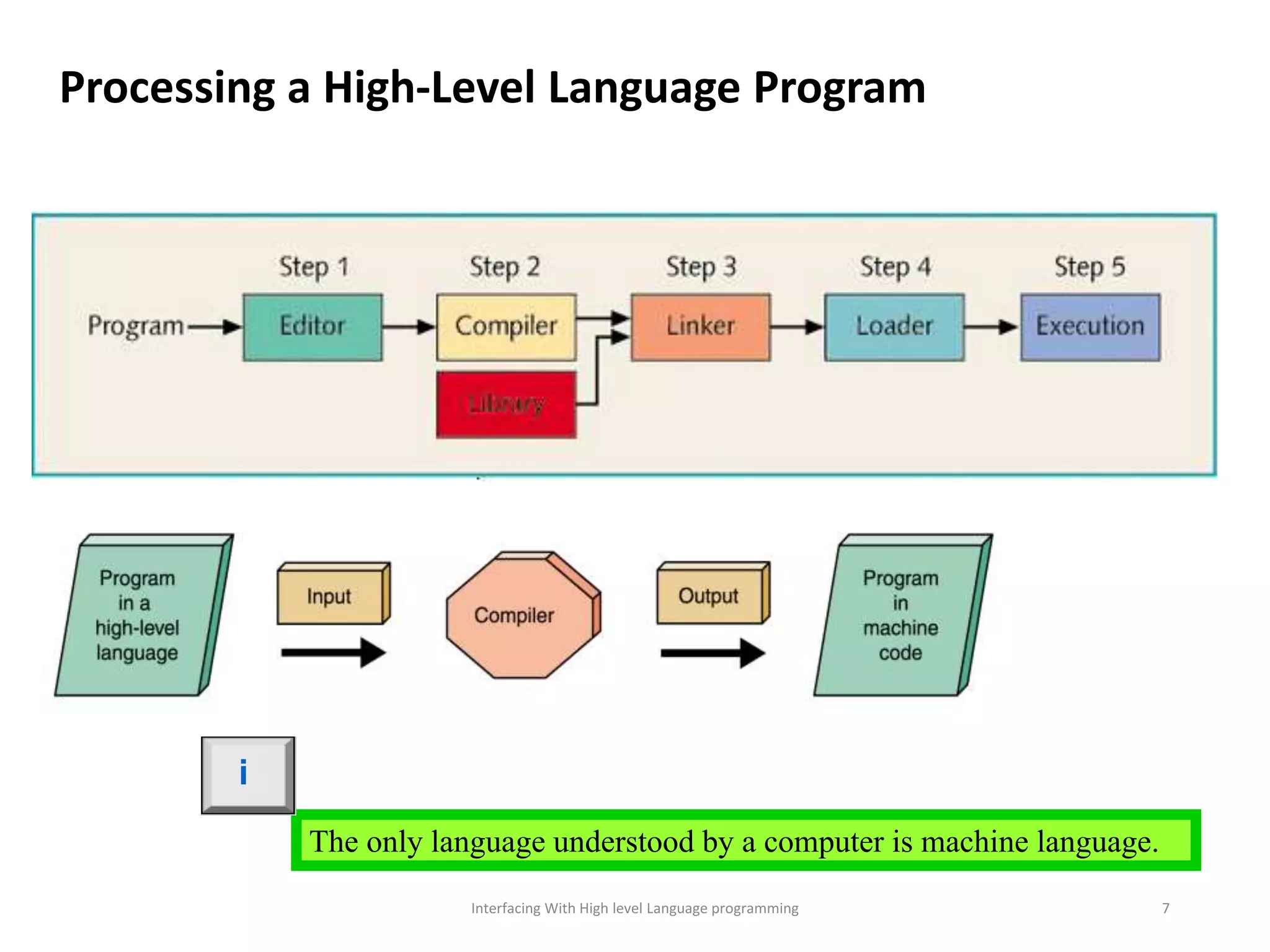
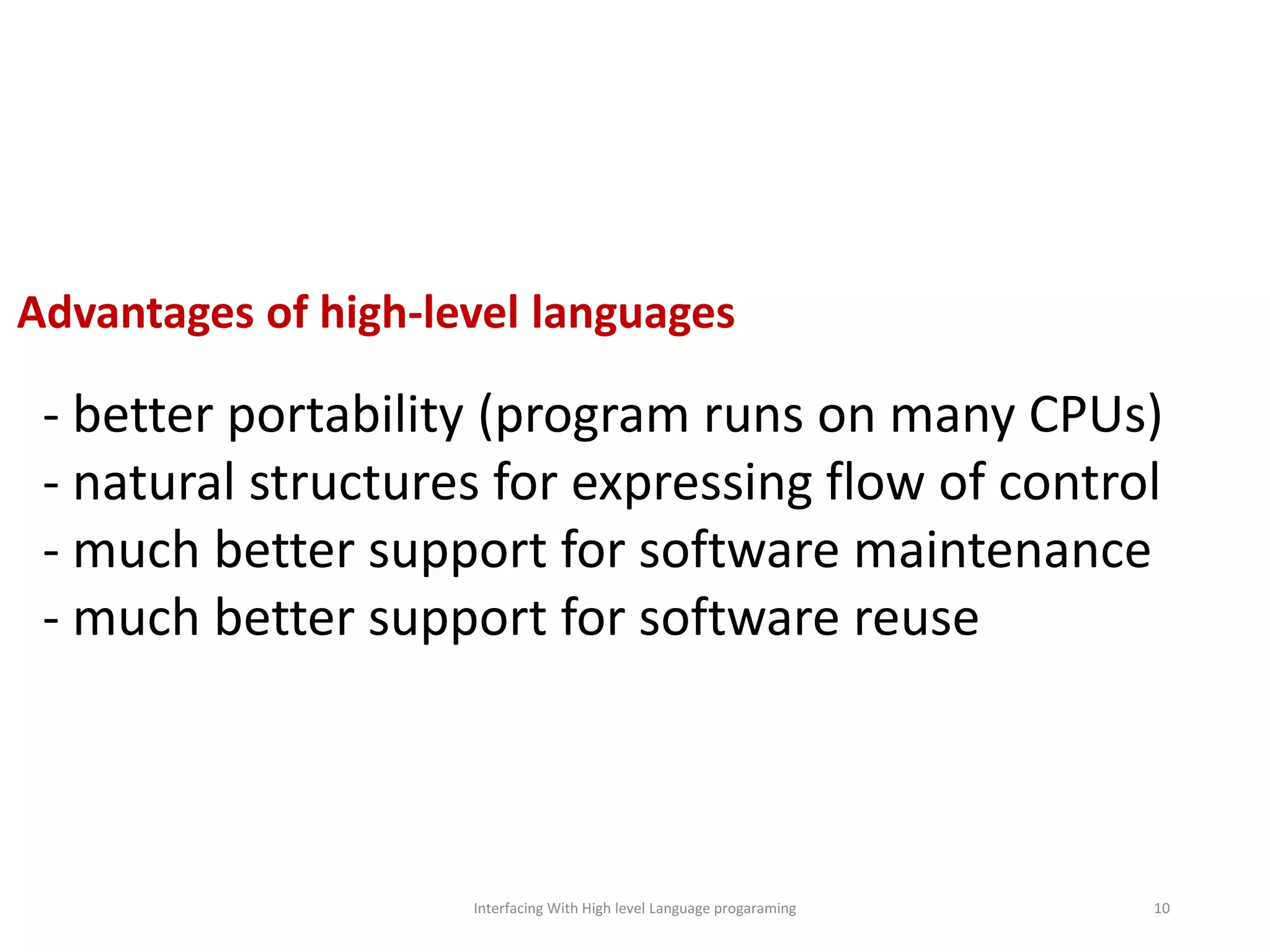
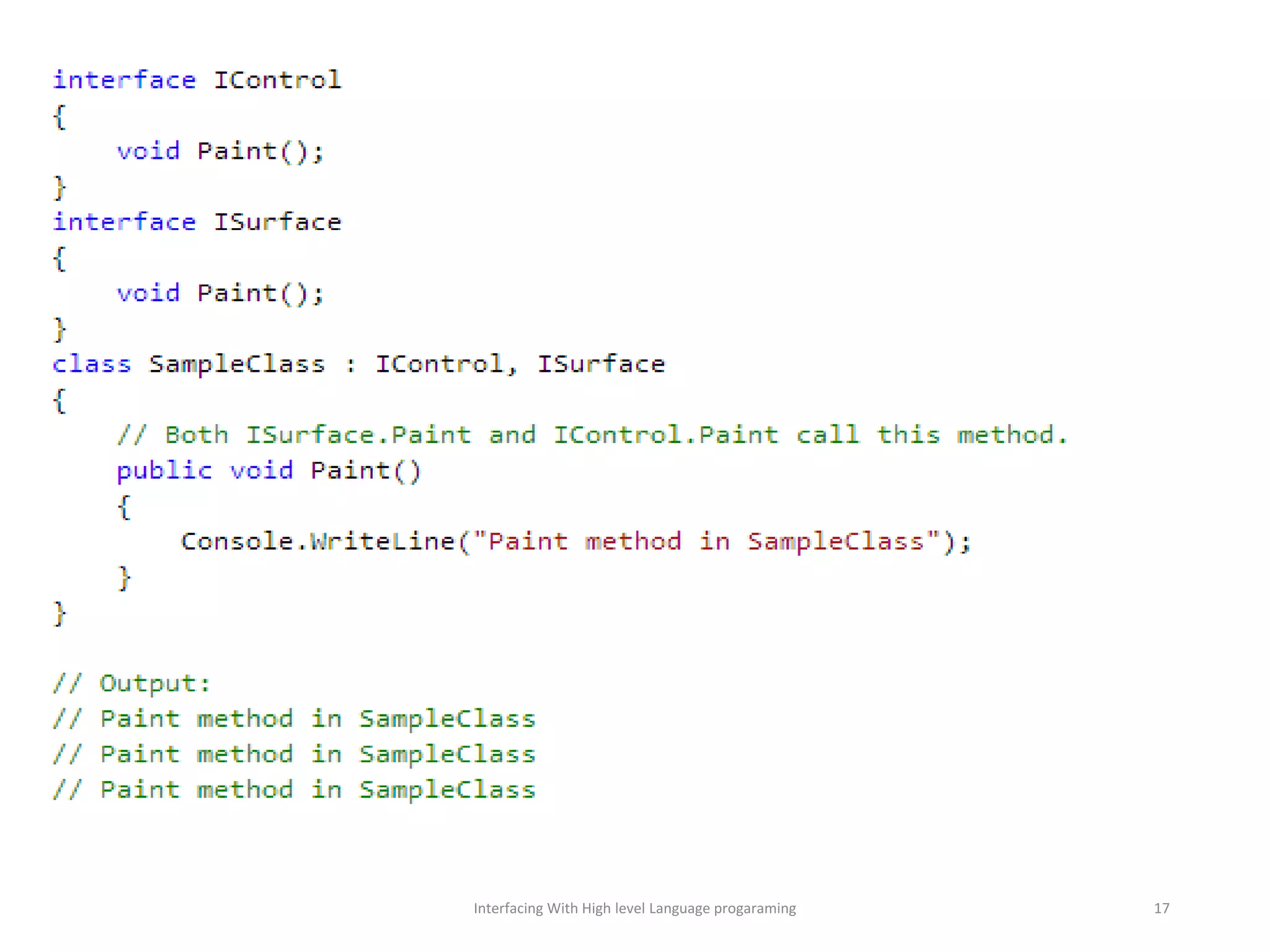
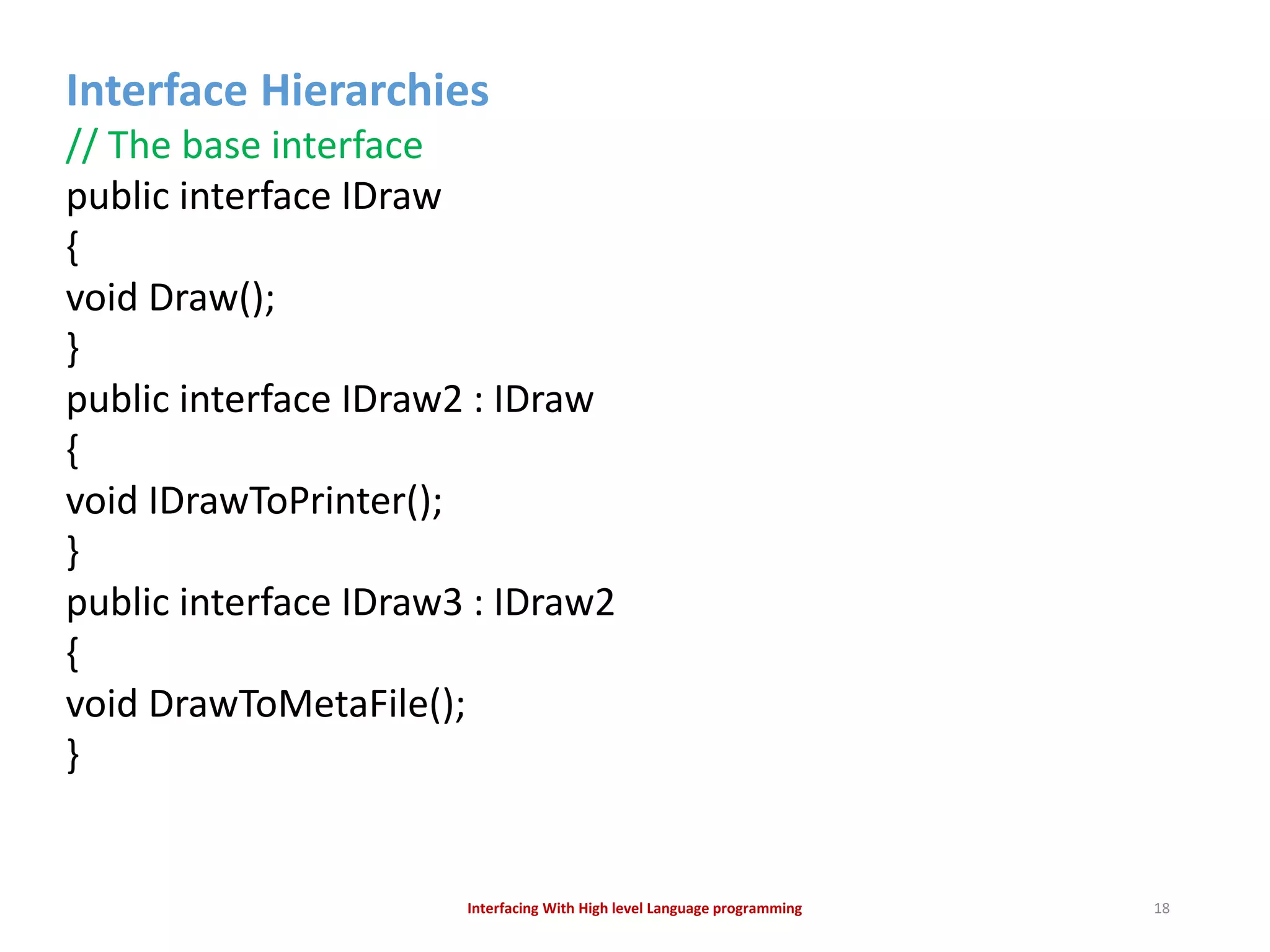
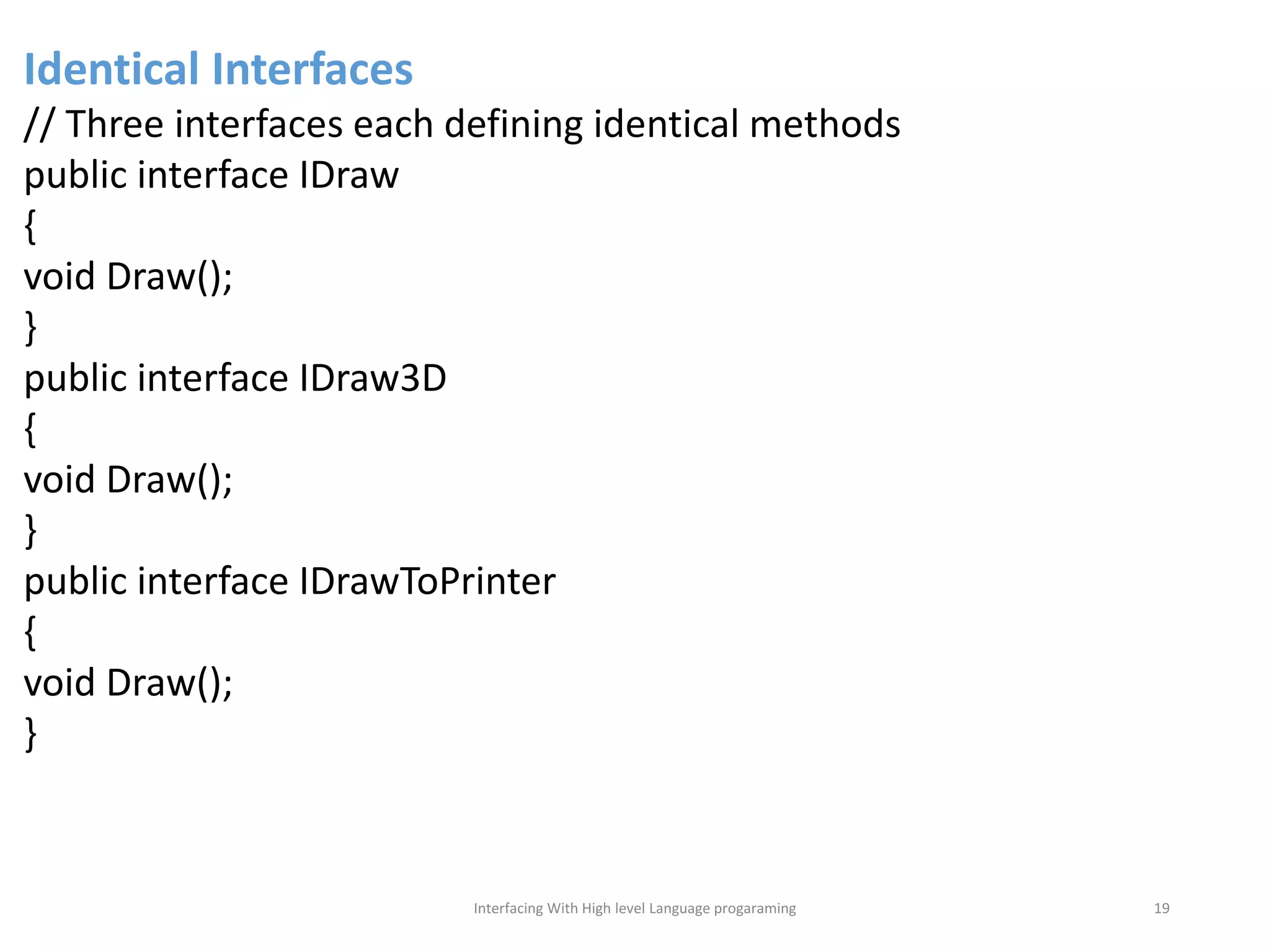
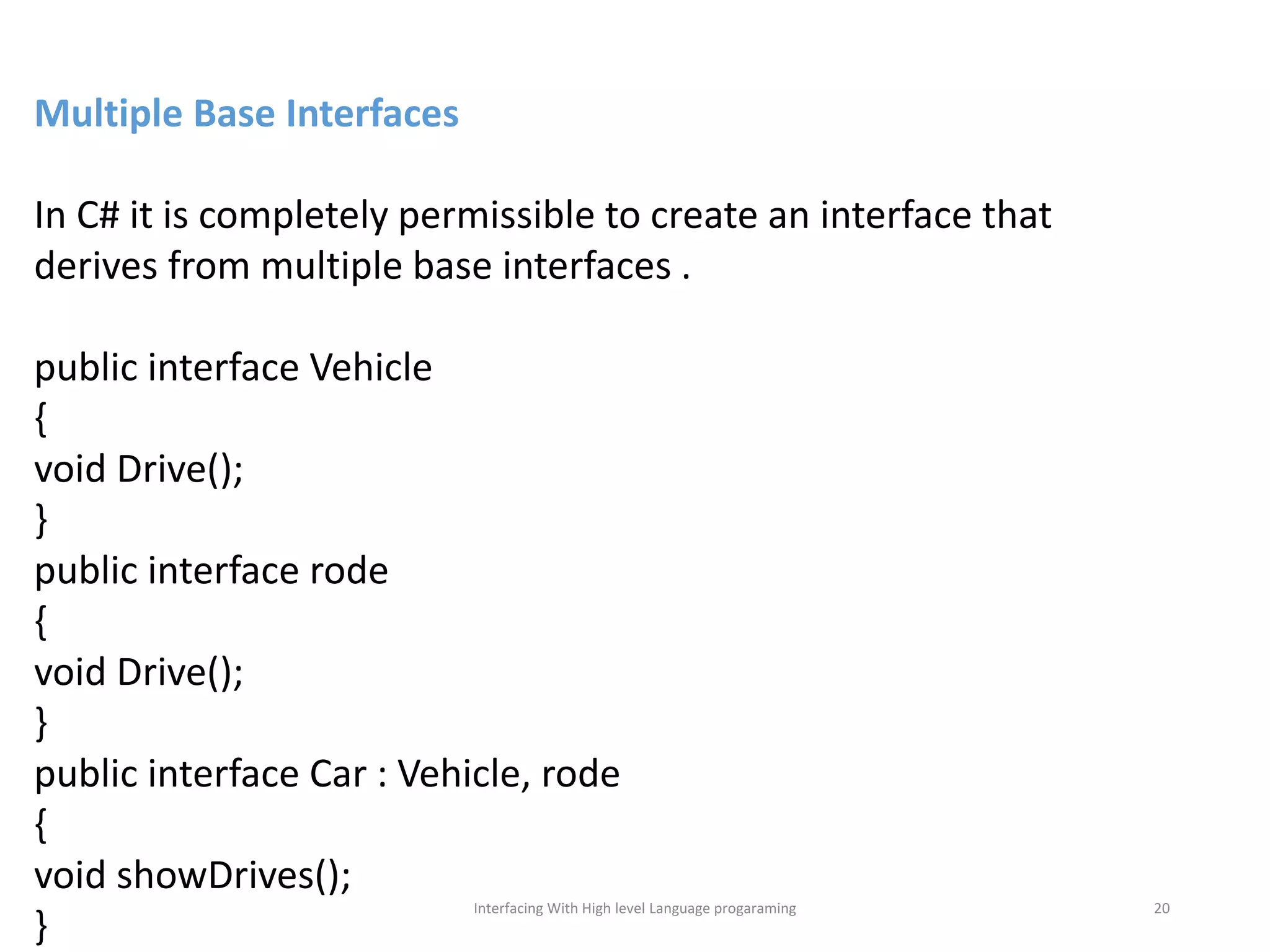
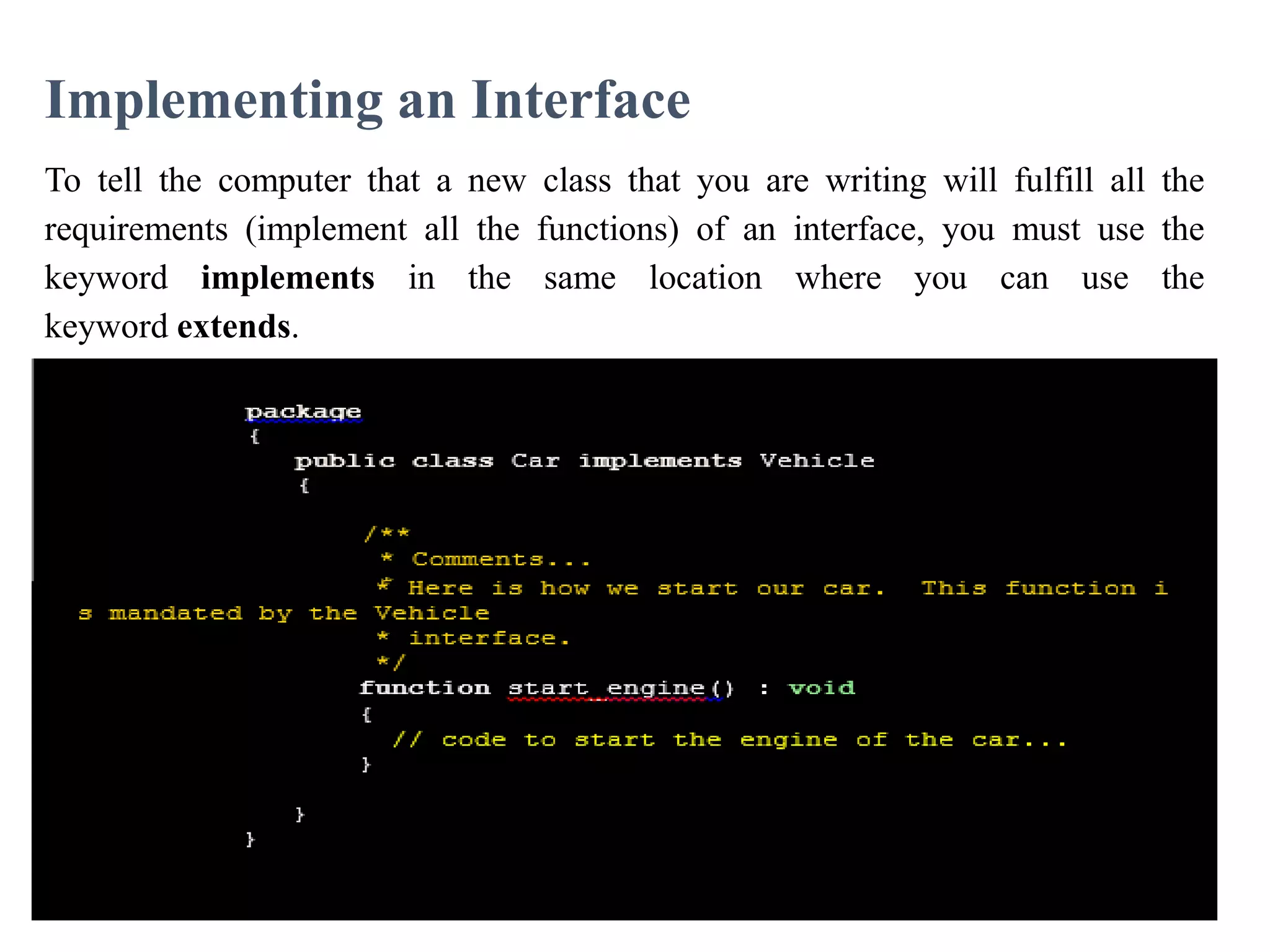
The document discusses interfacing with high-level programming languages, highlighting various programming languages, their advantages, and characteristics. It explains that high-level languages are more user-friendly, easier to learn and error-check, and can be run on different machine architectures. Additionally, it covers interface-based programming, including its implementation, use in object-oriented programming, and the concept of enforcing properties on classes through interfaces.