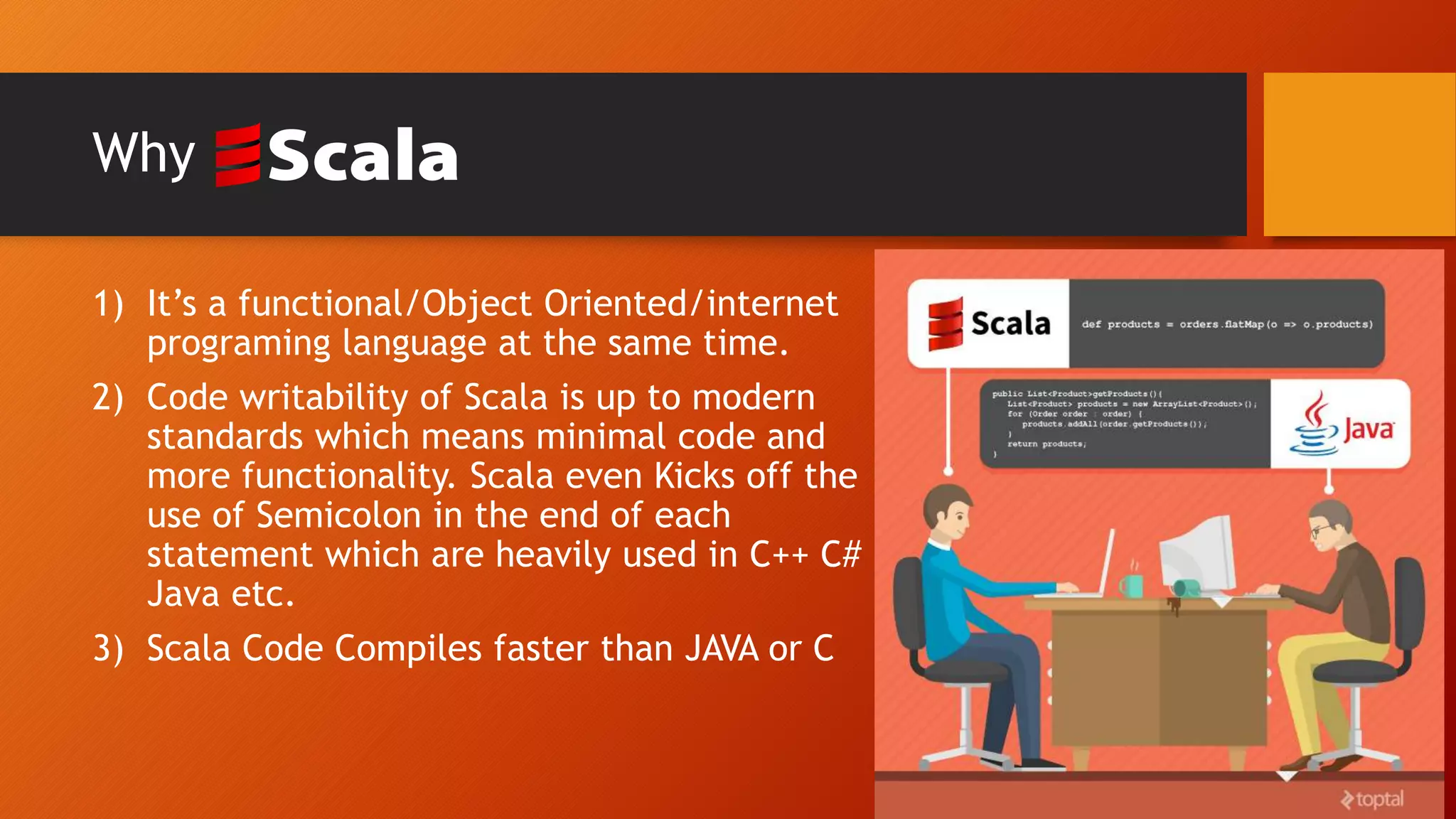
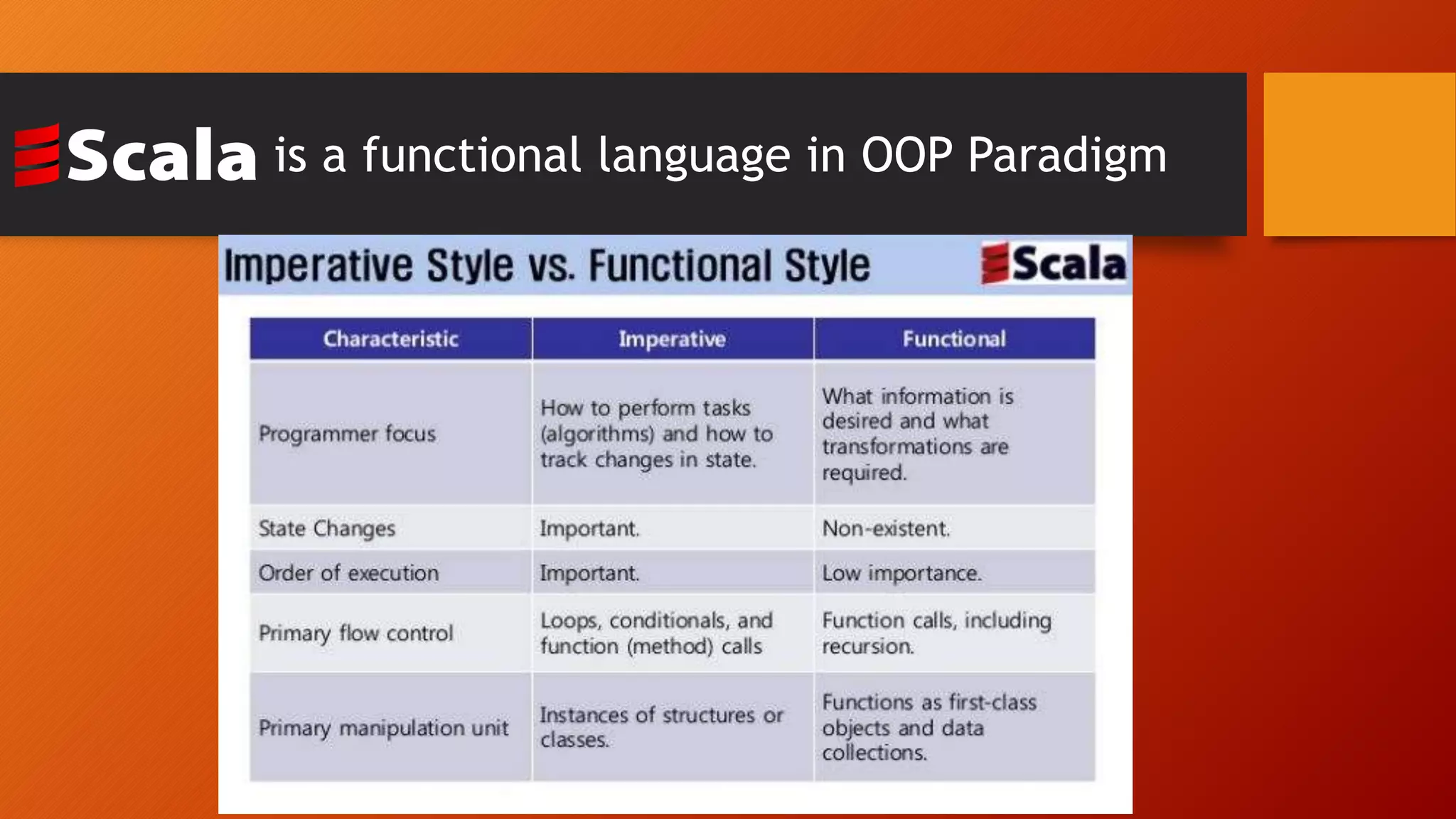
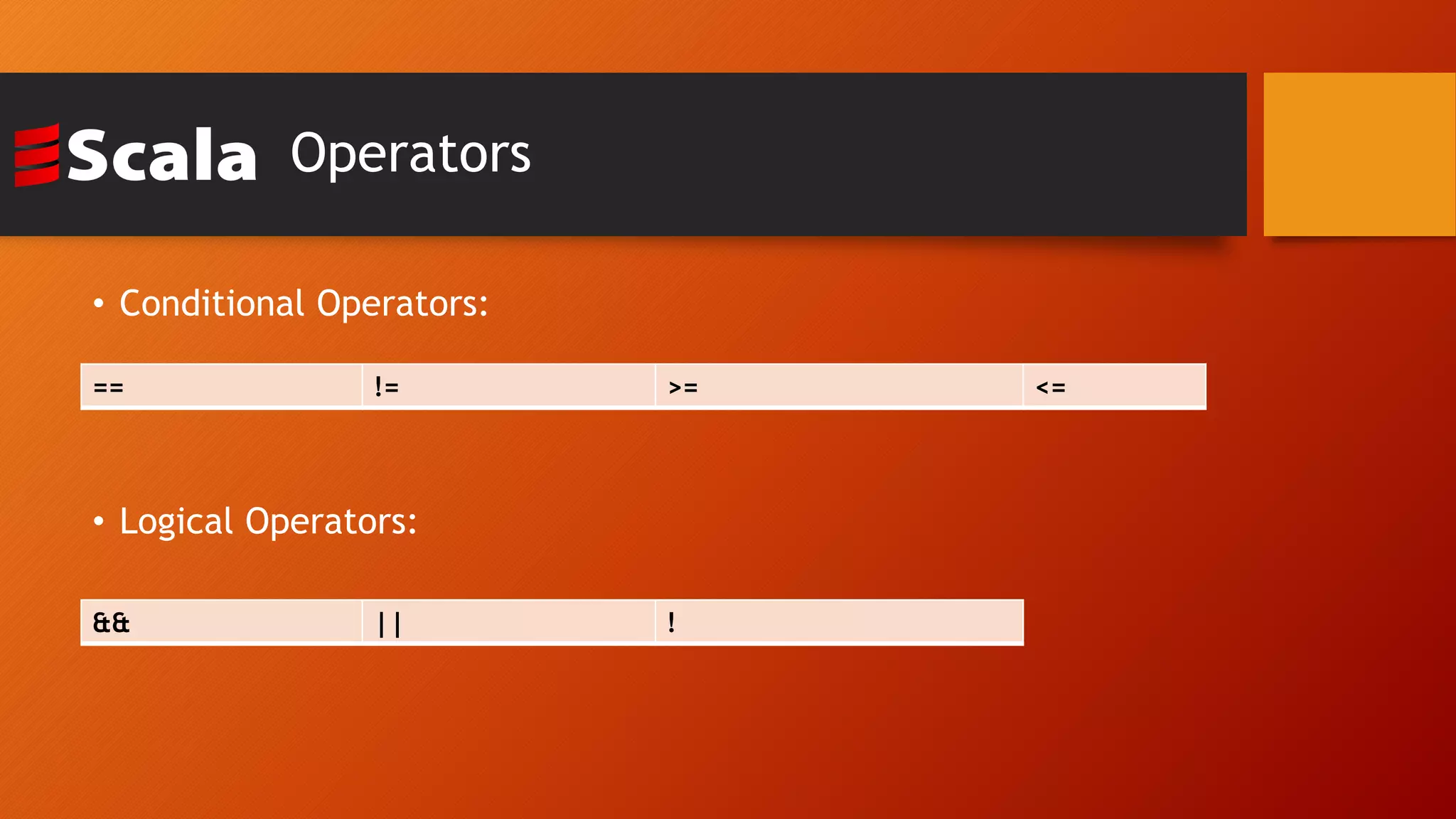
This document provides an introduction to the Scala programming language. It discusses that Scala was created by Martin Odersky in 2003 as a hybrid functional and object-oriented language that runs on the Java Virtual Machine. Some key points made include that Scala code compiles to Java bytecode, allows importing of Java libraries, and supports features like functions as first-class objects. The document also provides examples of Hello World programs in Scala and Java for comparison, and demonstrates basic Scala concepts like variables, conditionals, loops, and lists.






![Hello World! • object Sacala { • def main(args: Array[String]) { • println (“Hello World”) • } Declaration of the Object and then Object name which will be our source code/file name Definition of the function main() and some arguments to be passed to it’s object Printing something as simple as one command and passing variables/constants/strings Note: There is no colon ; needed to end of the statement.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalapresentation-170916201226/75/Introduction-to-Scala-language-9-2048.jpg)
![Hello World in Java public class HelloJava { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Hello World!"); } } Hello World in Scala object HelloScala { def main(args: Array[String]){ println("Hello World!") } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalapresentation-170916201226/75/Introduction-to-Scala-language-10-2048.jpg)





![Arrays • Array in Scala is same as Java and C++ in functionality although the syntax is a little changed. Java Scala C++ int[] myIntArray = new int[3]; int[] myIntArray = {1,2,3}; var z:Array[String] = new Array[String](3) z(0) = “Emad"; z(1) = “Noyan"; z(2) = “Saif“ Or var z = Array(“Zubair", “Anwar", “Malik") int n[ 10 ] n={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,0}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalapresentation-170916201226/75/Introduction-to-Scala-language-17-2048.jpg)



