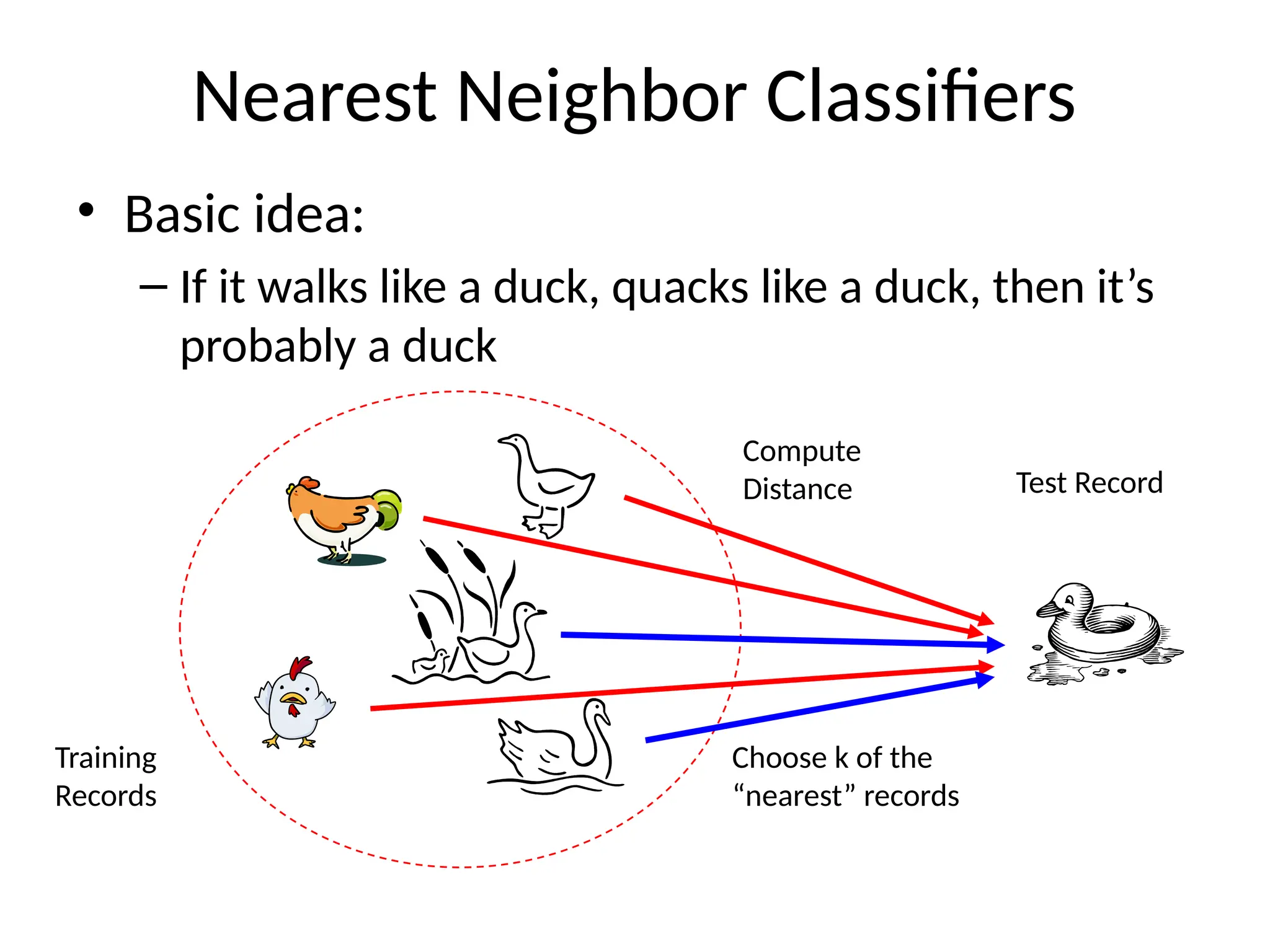
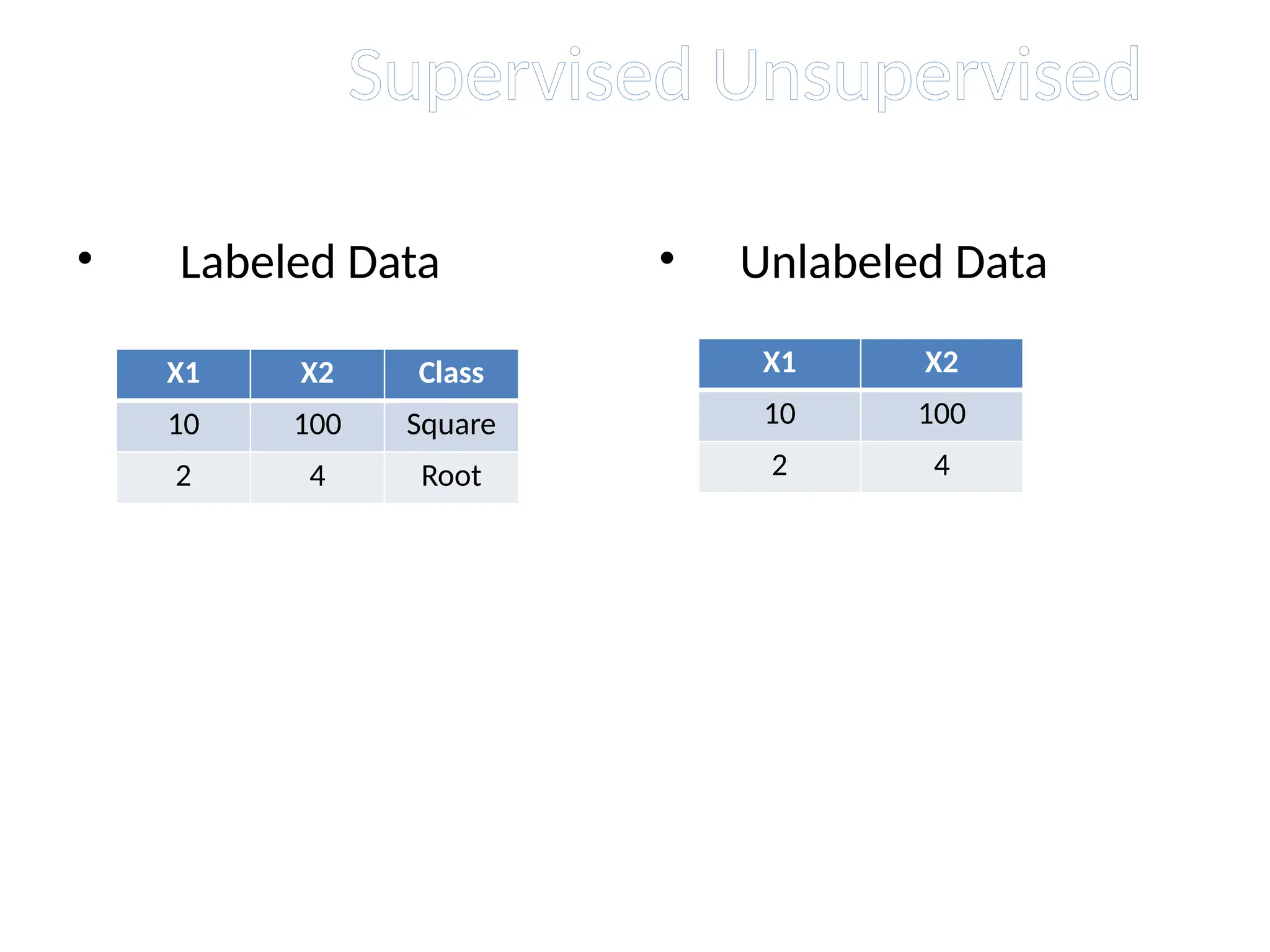
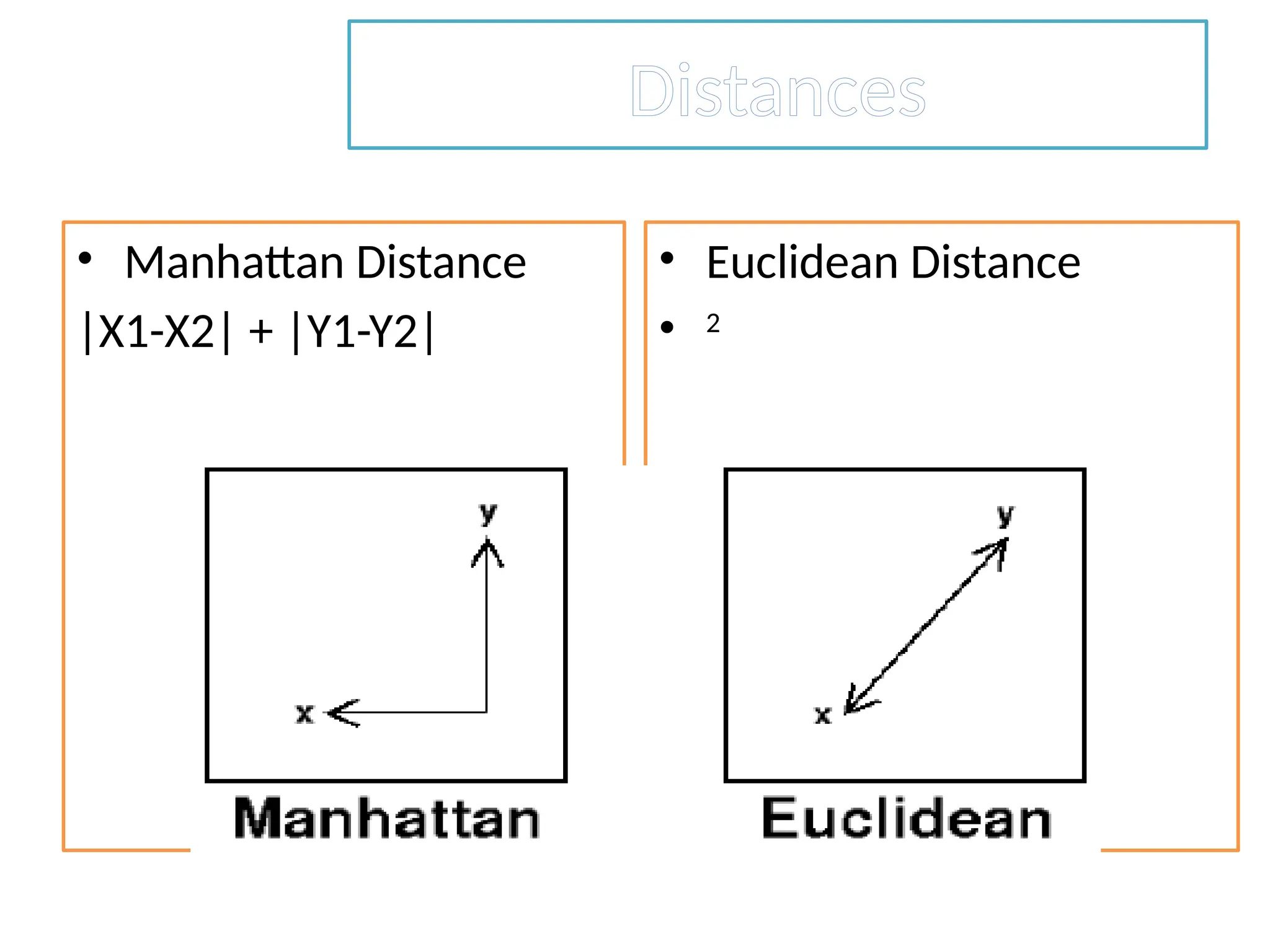
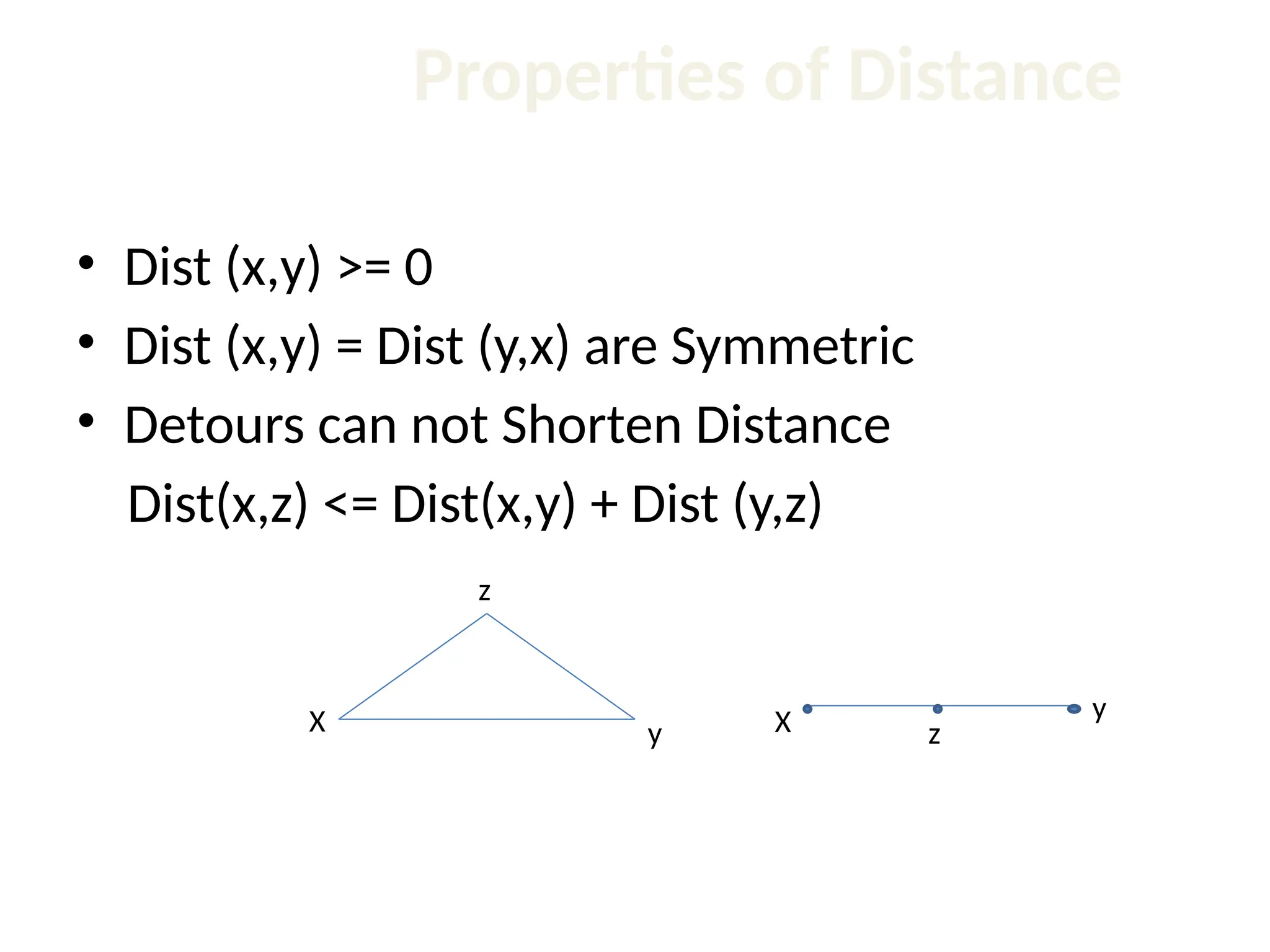
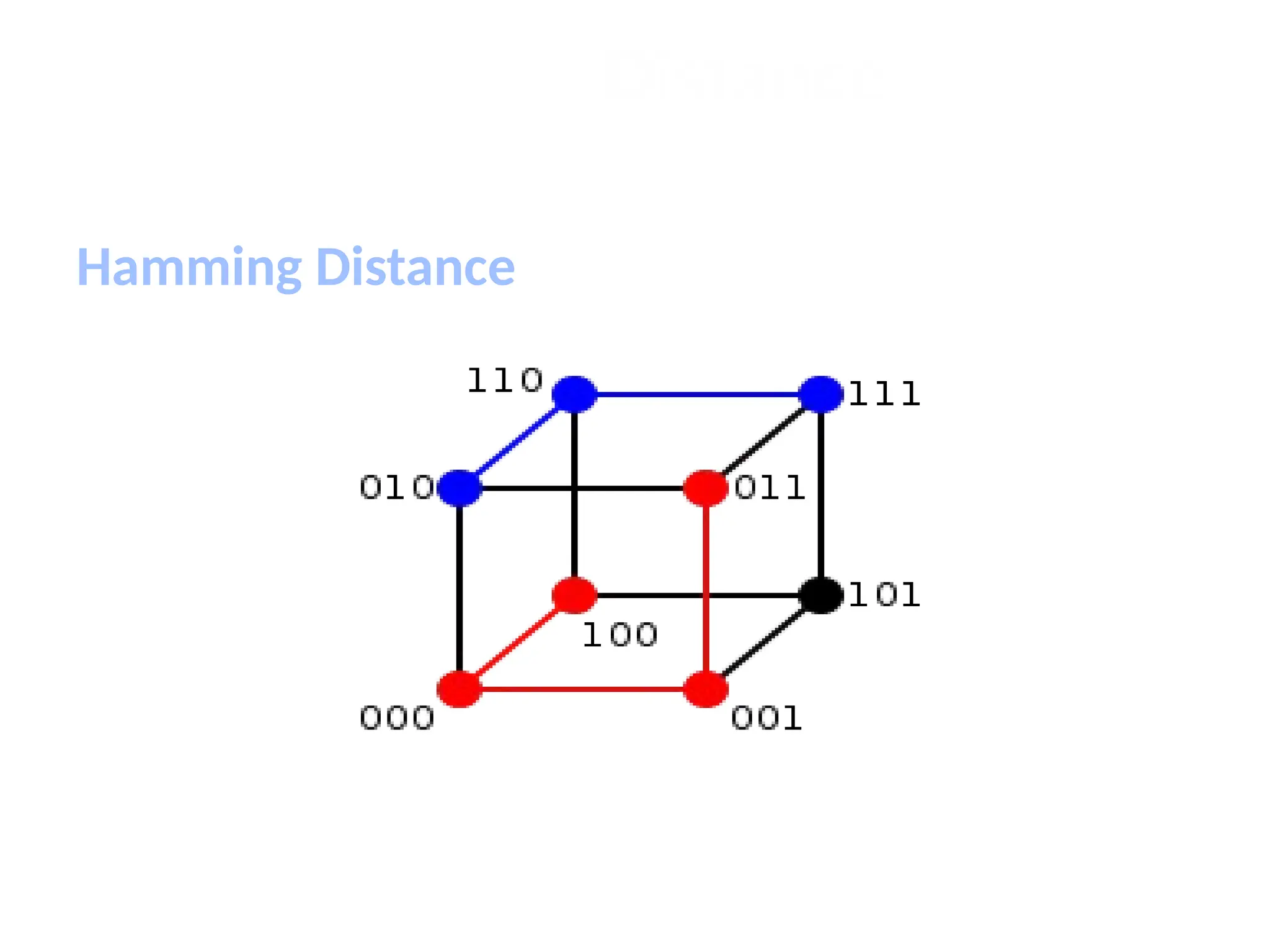
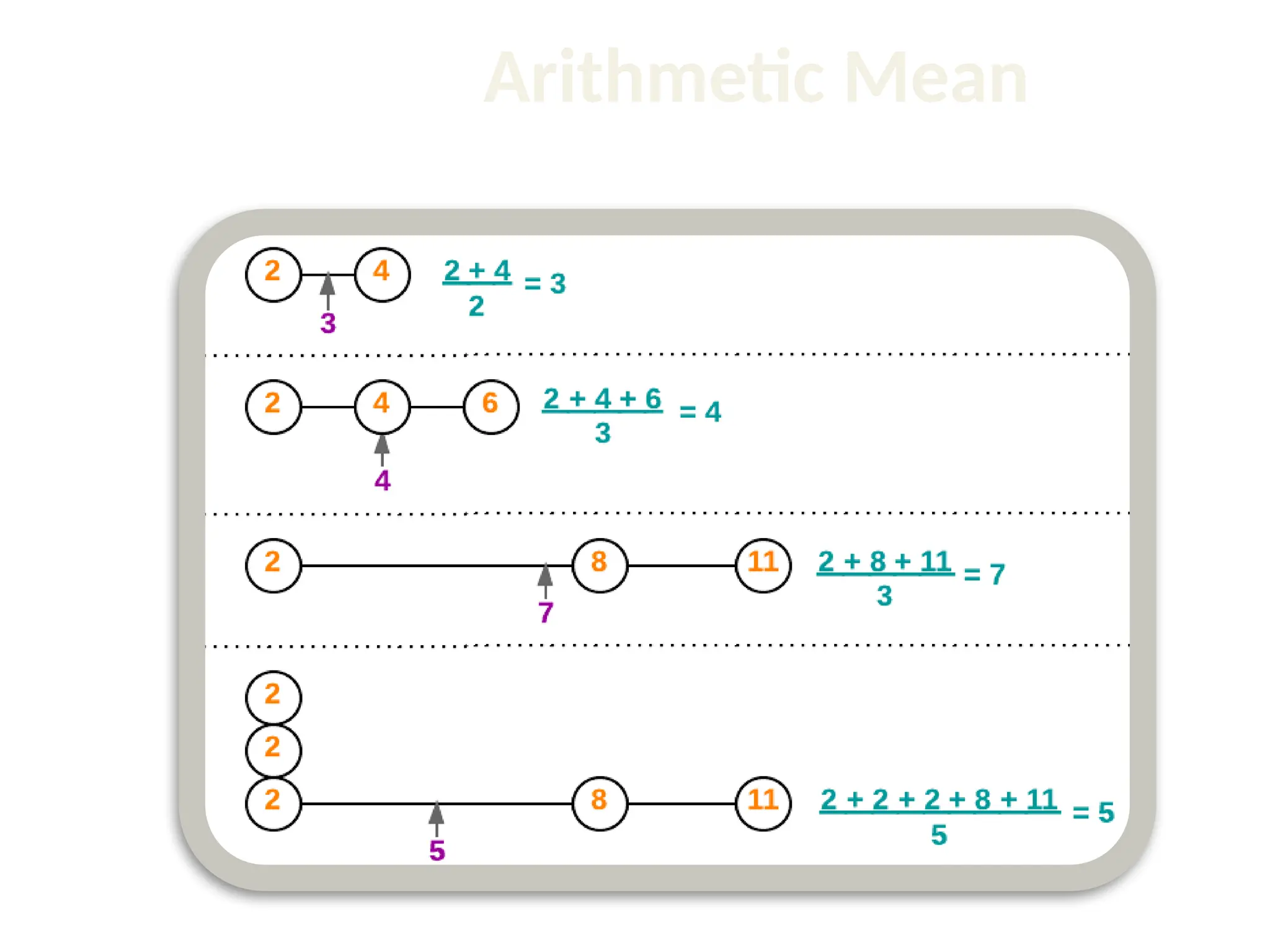
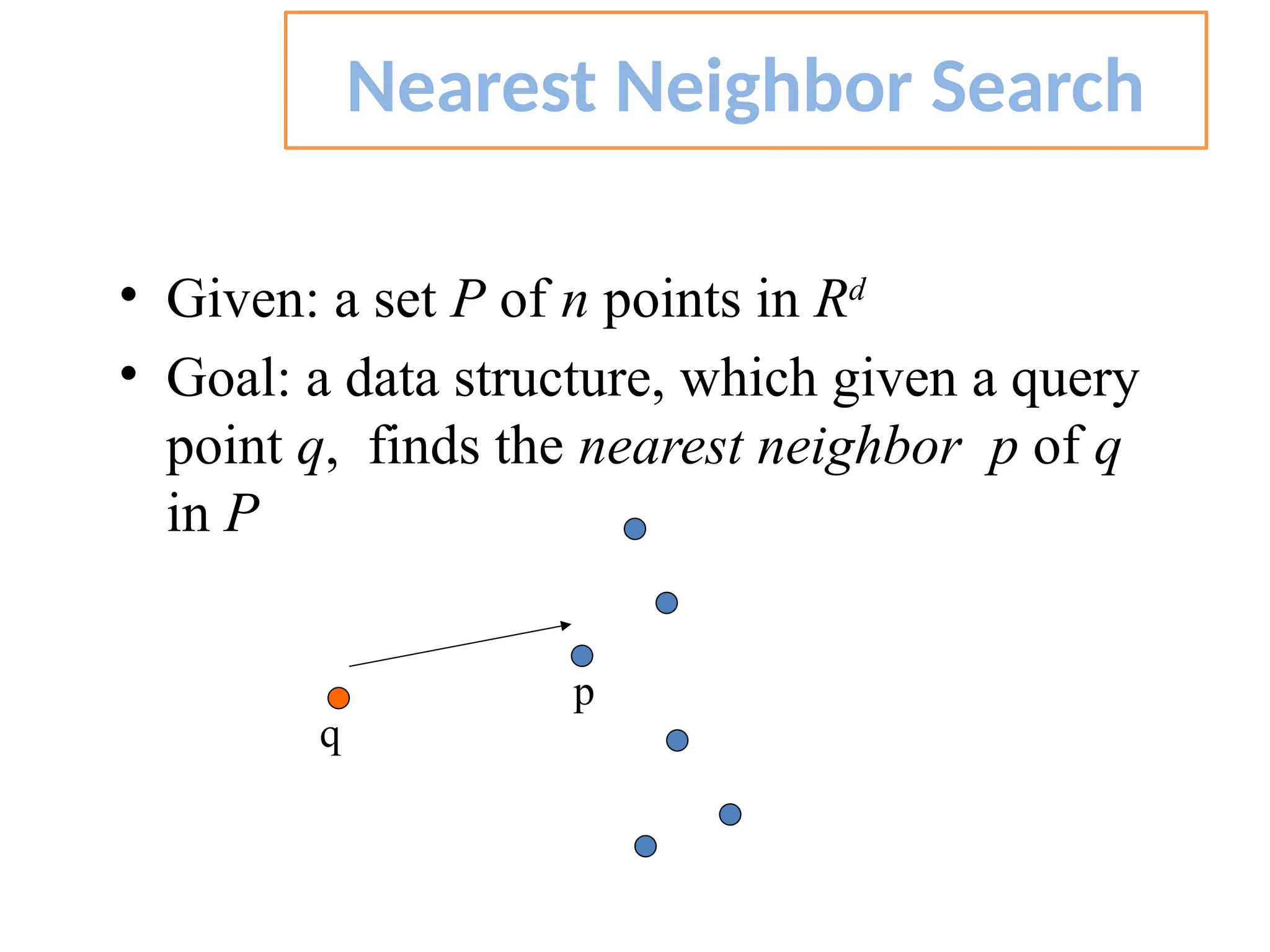
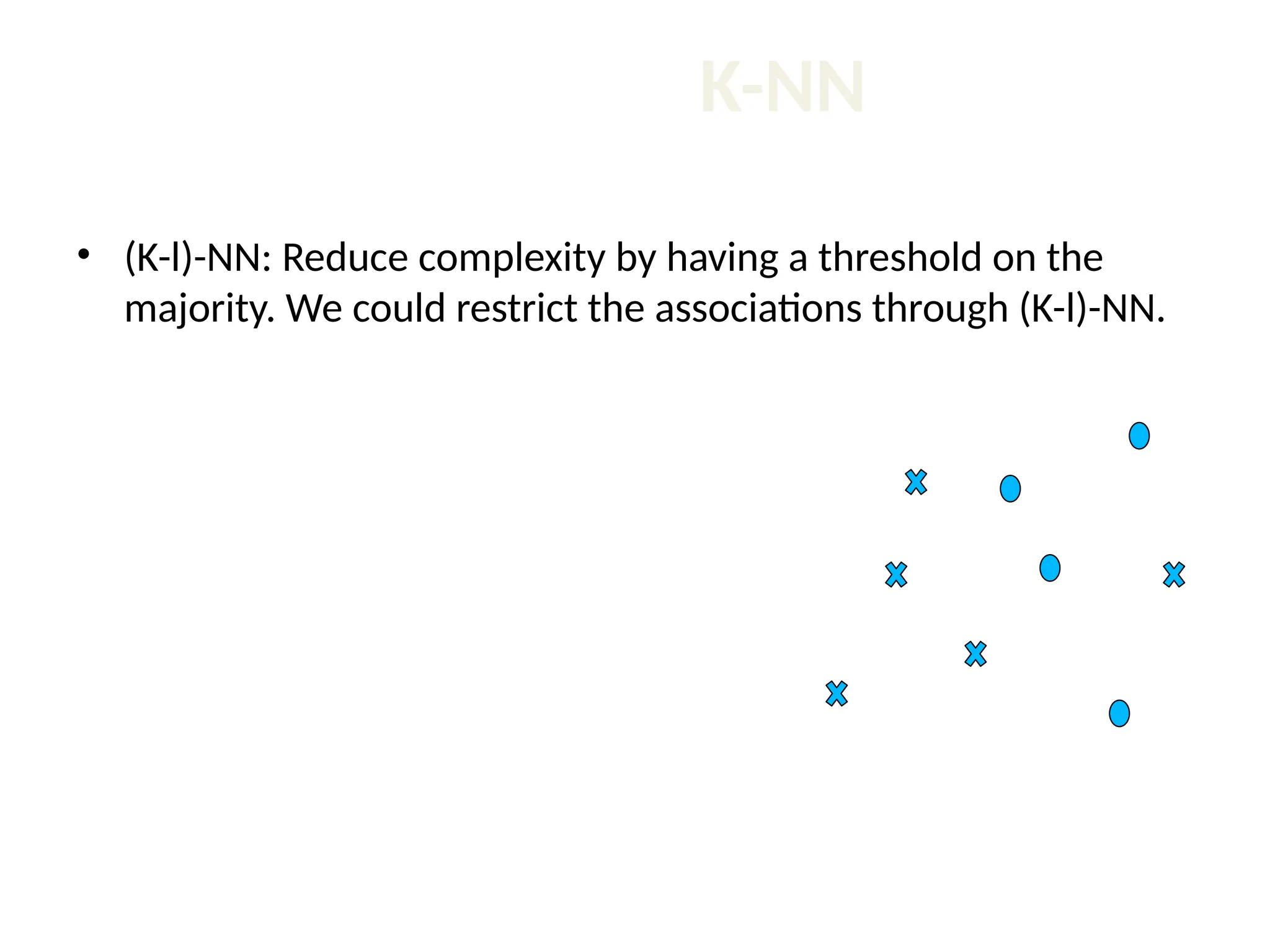
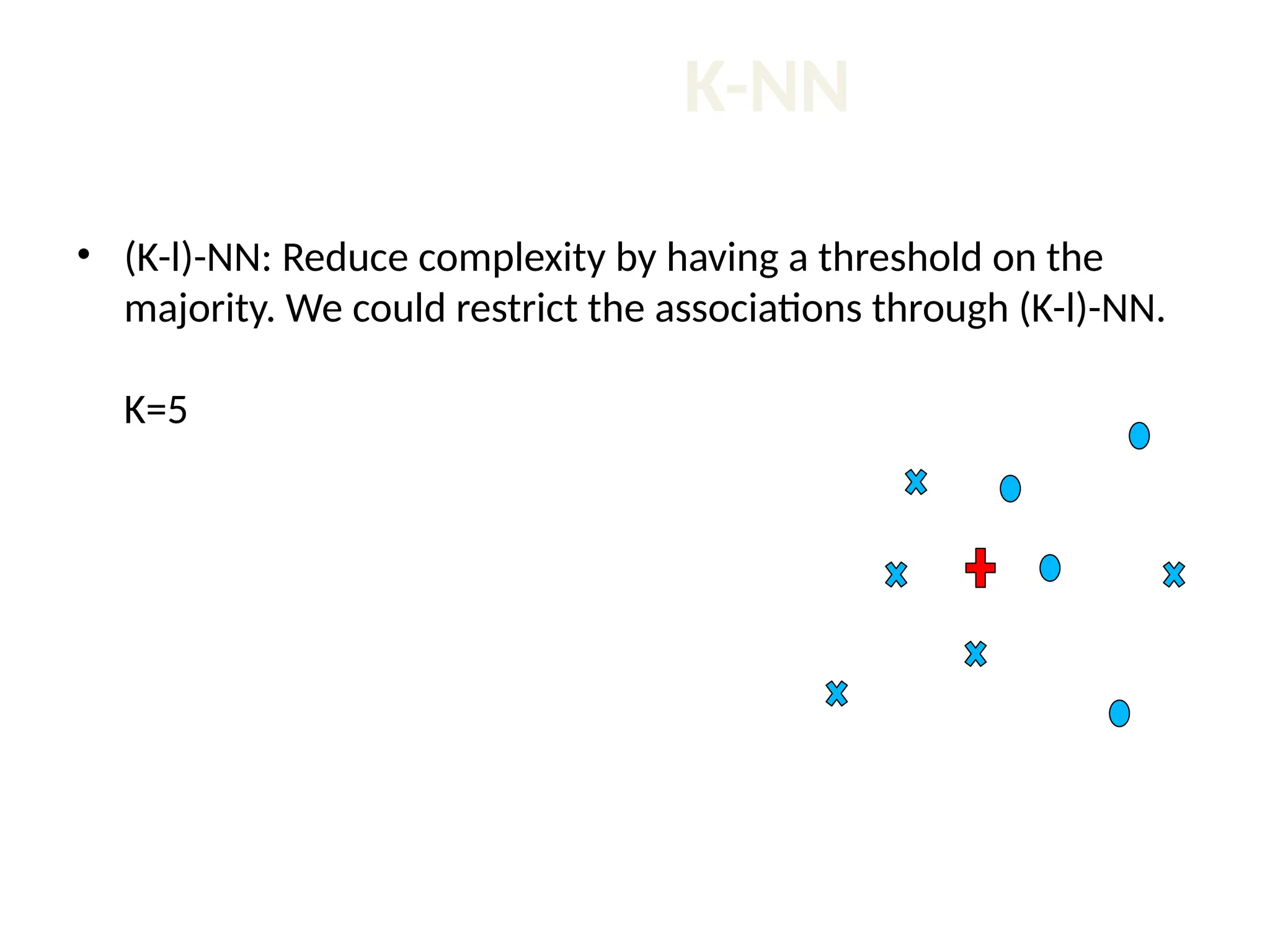
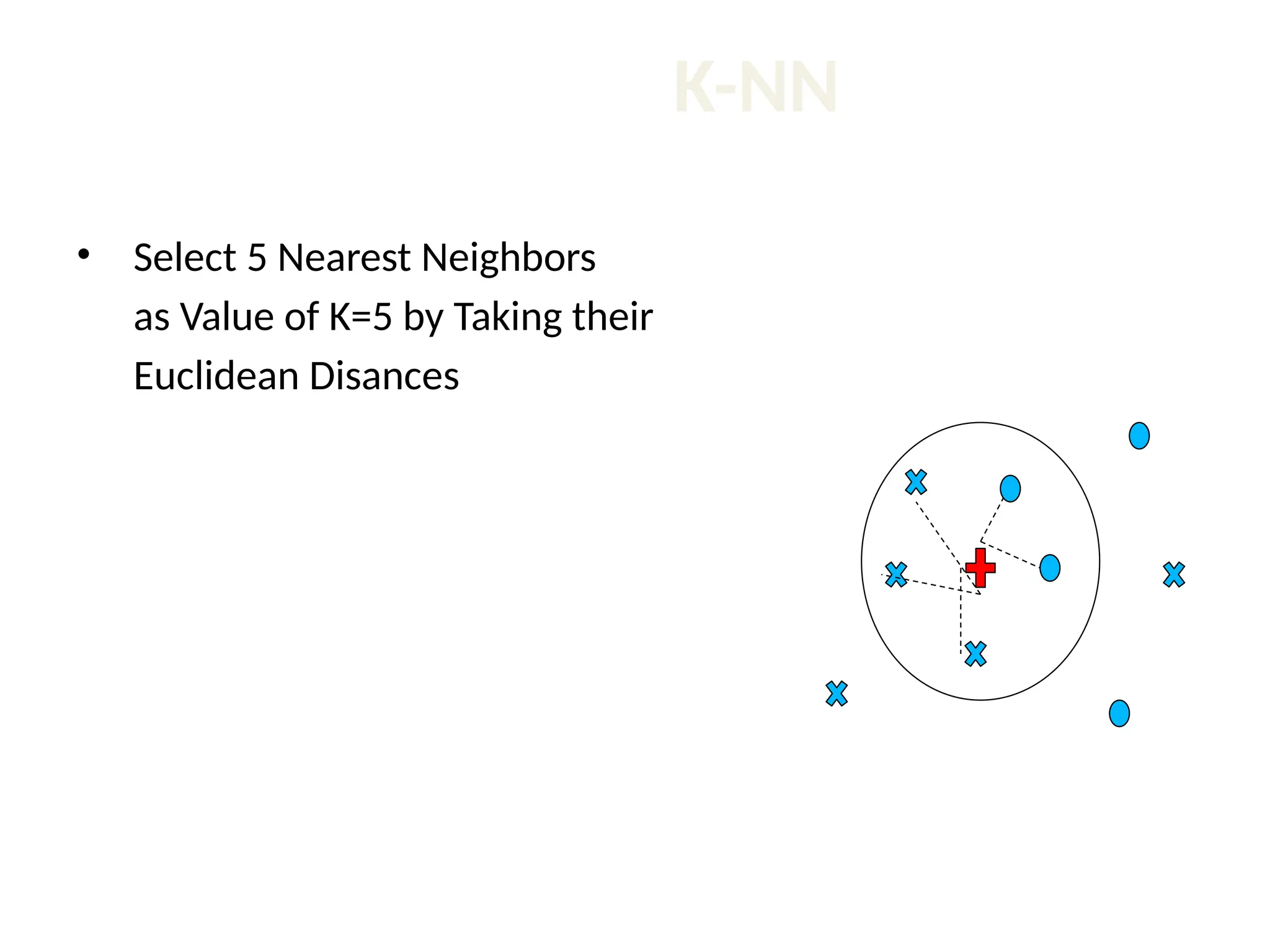
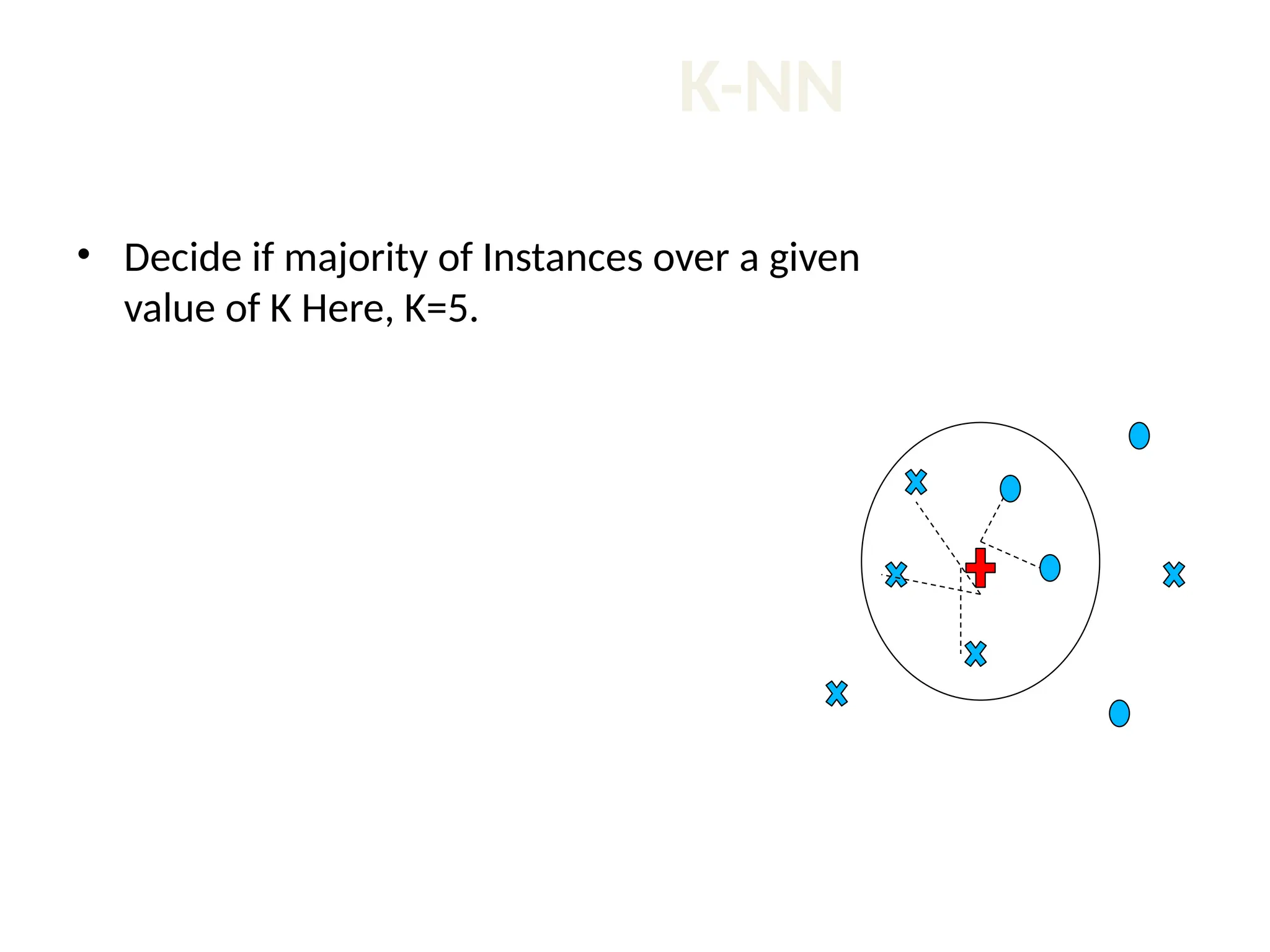
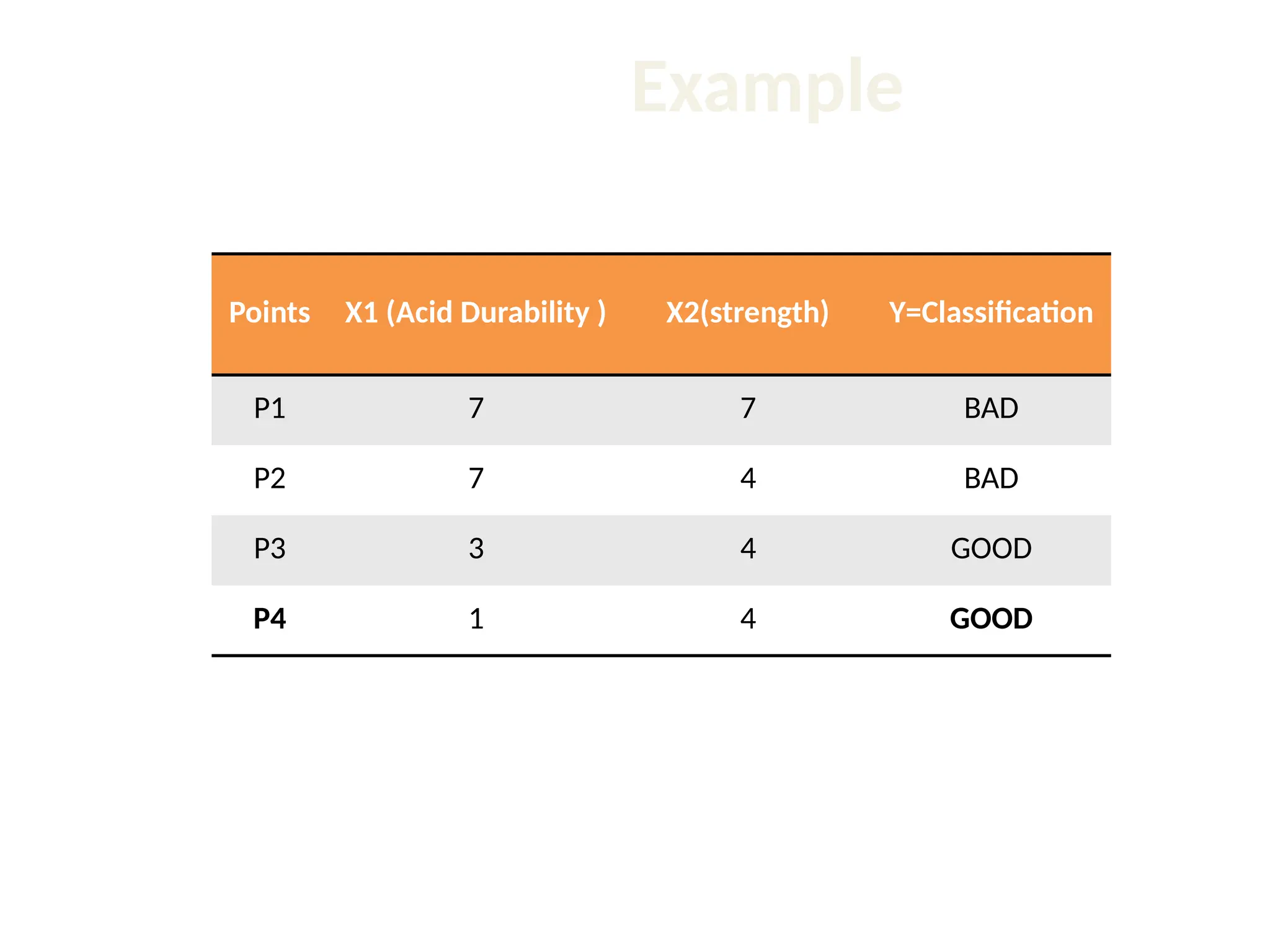
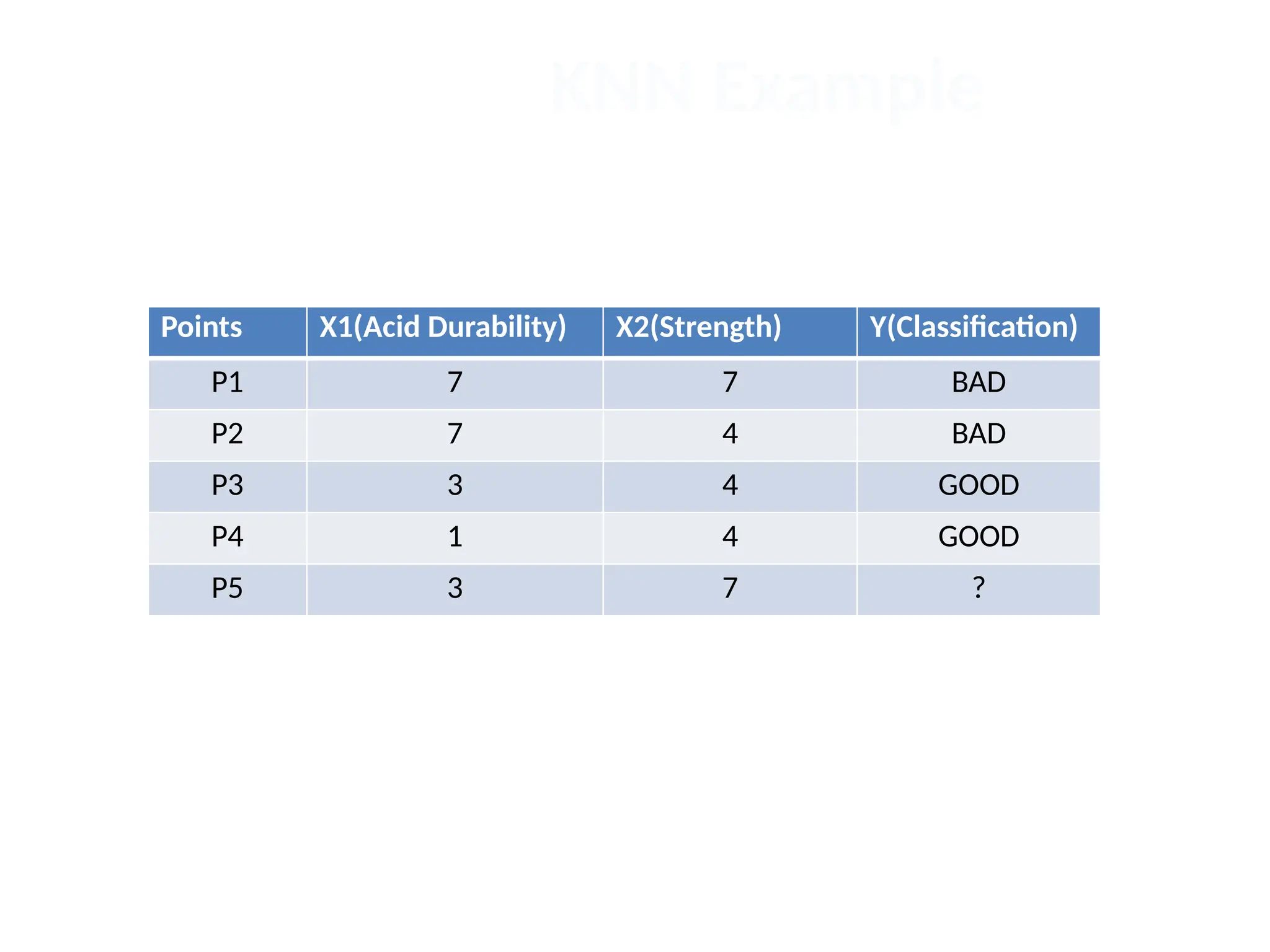
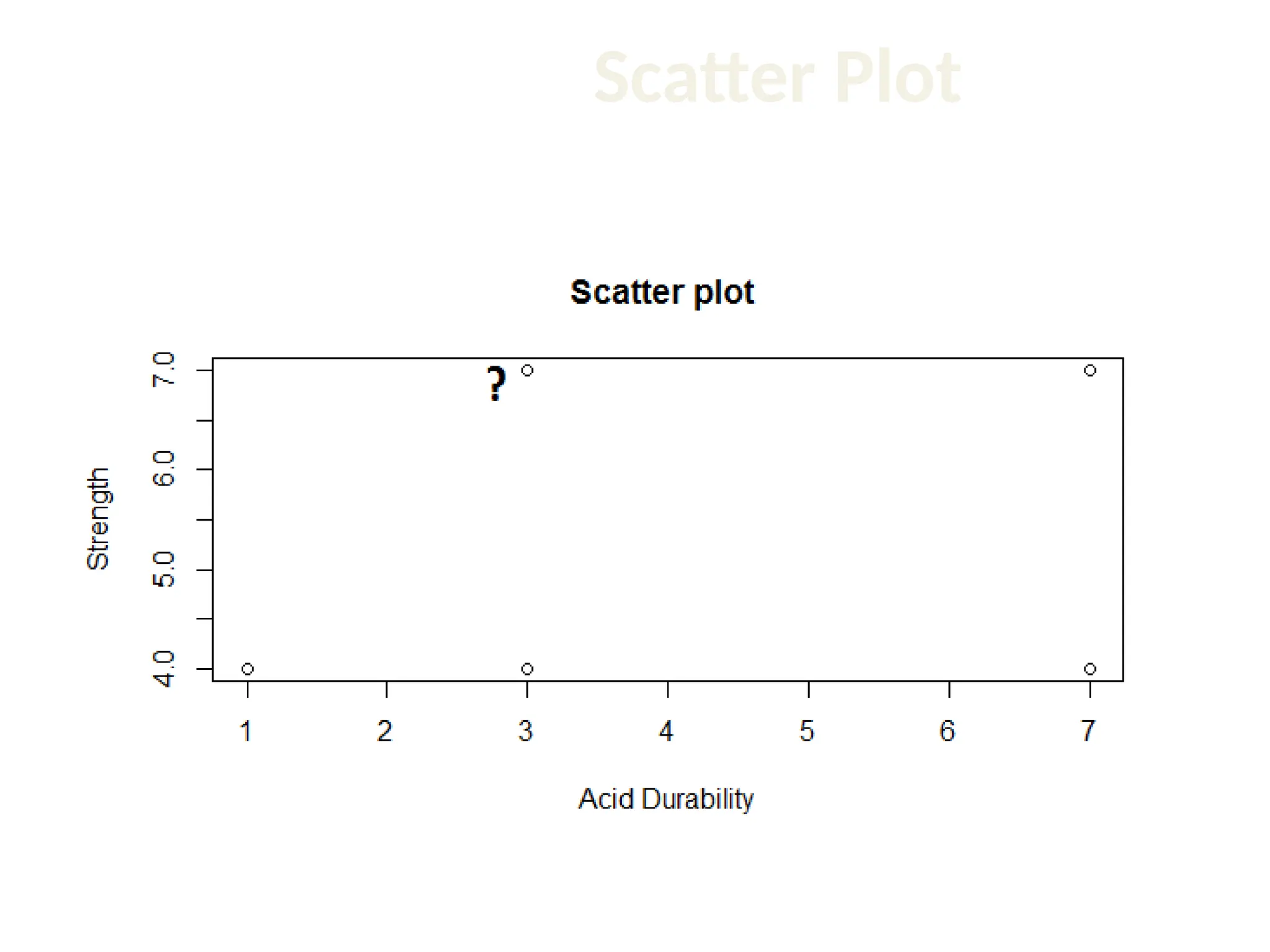
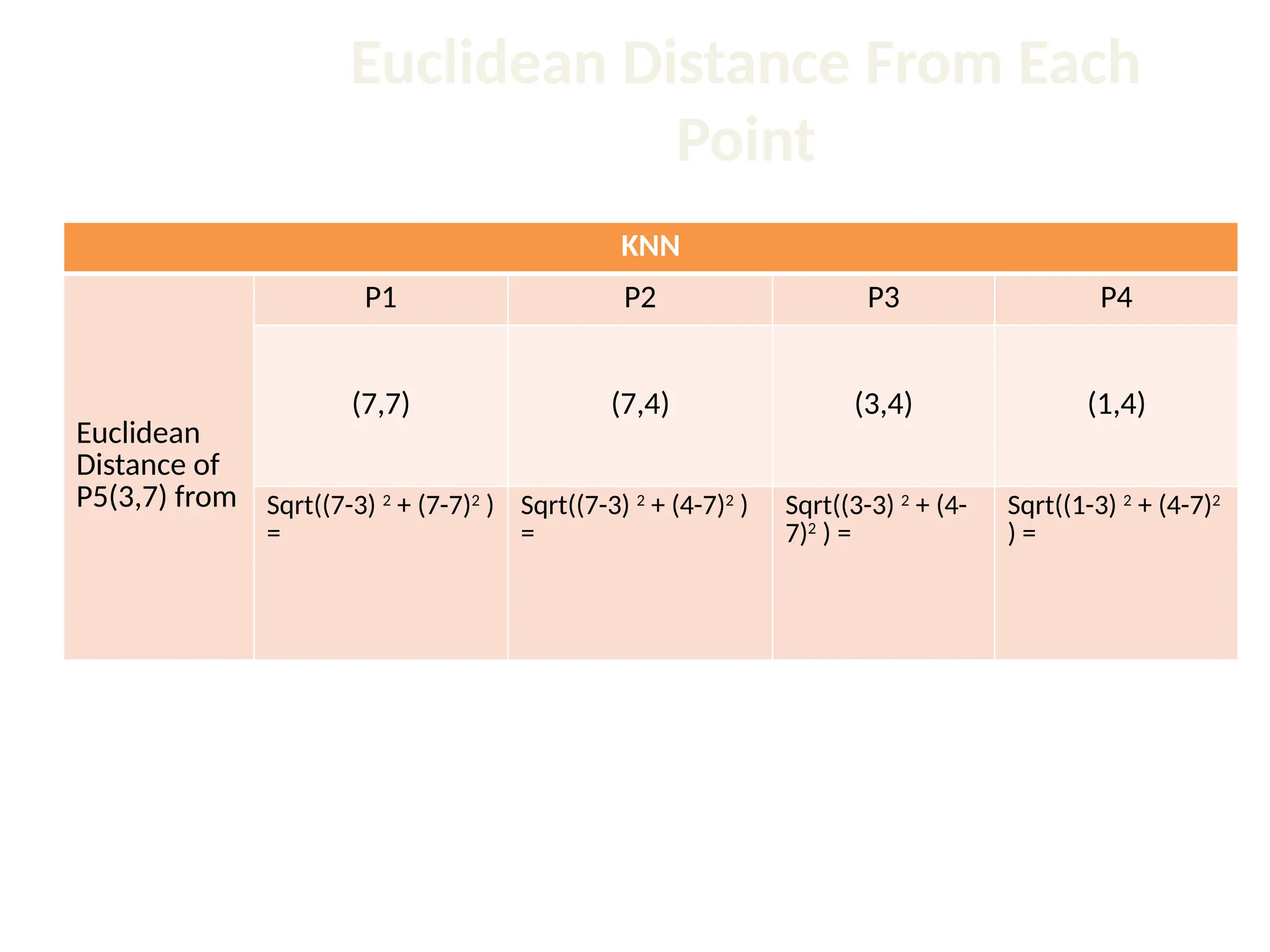
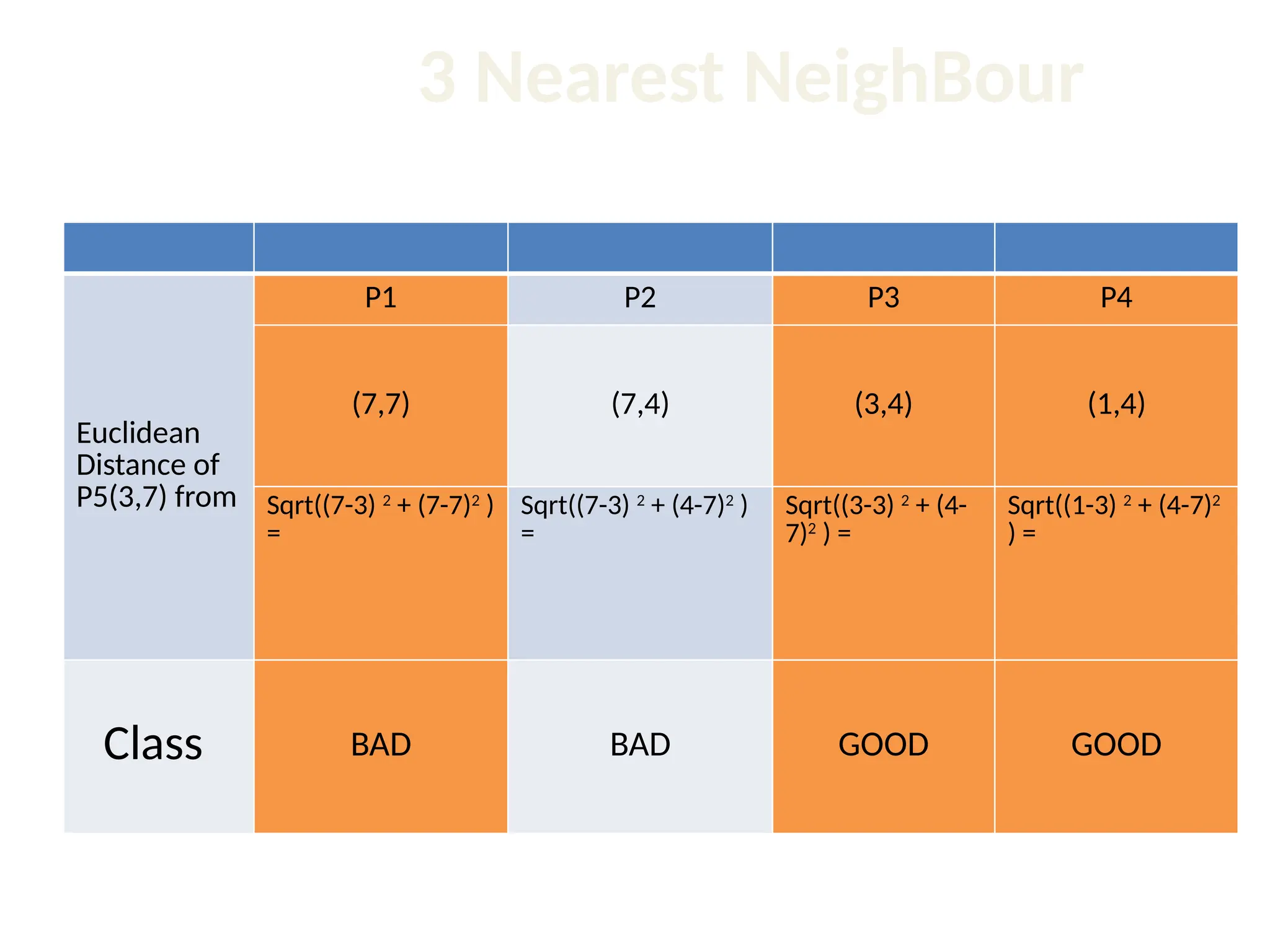
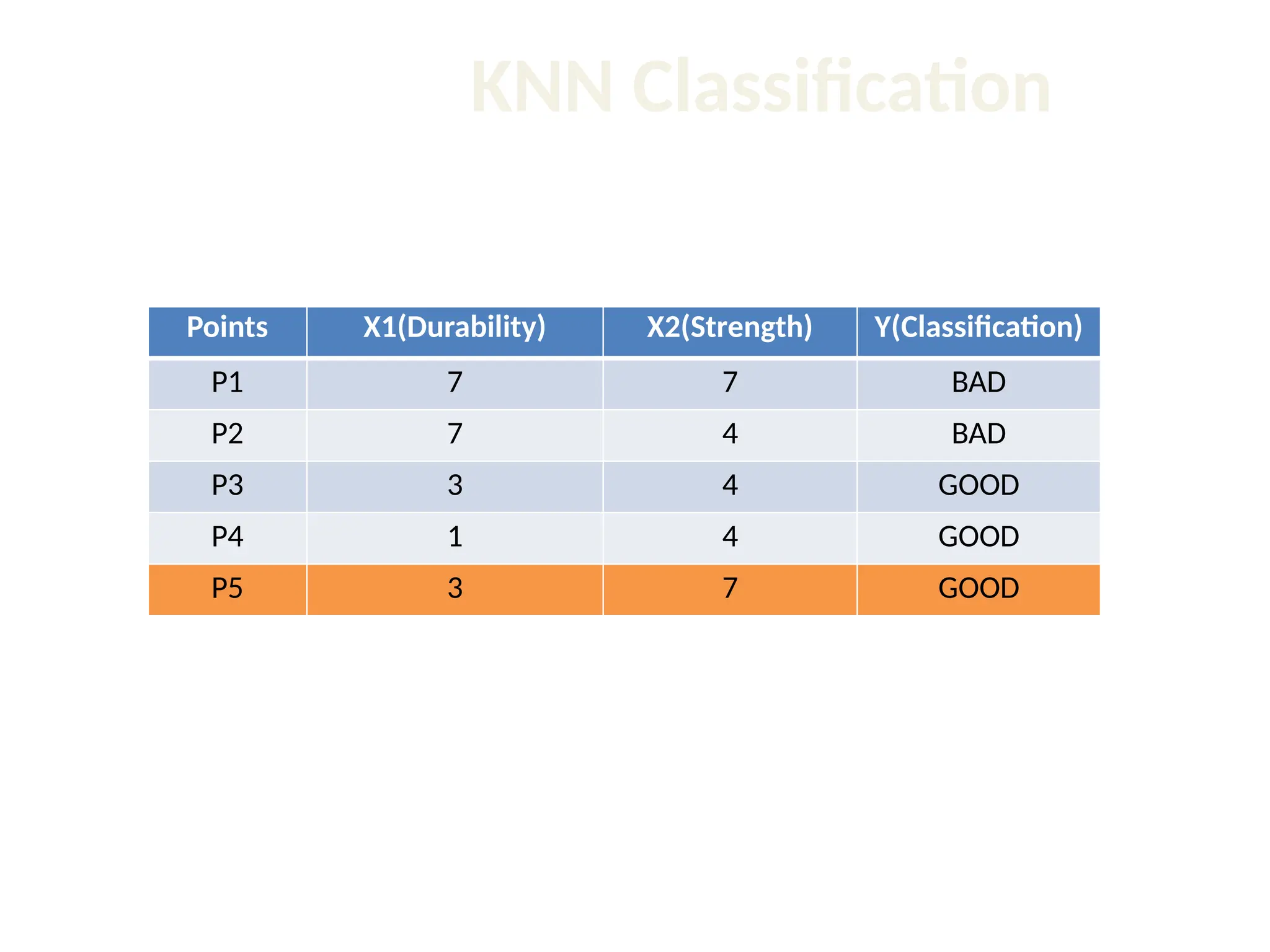
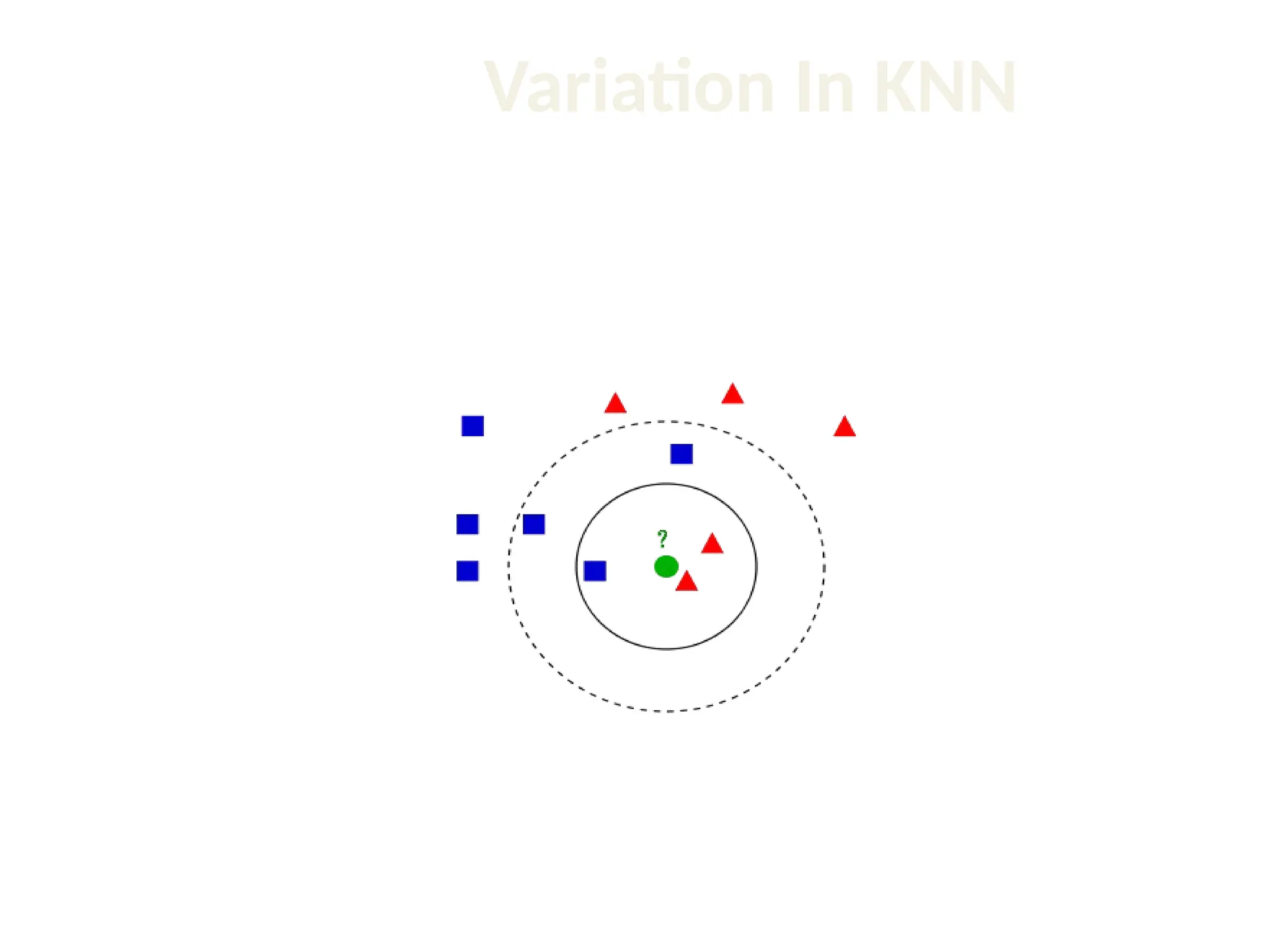
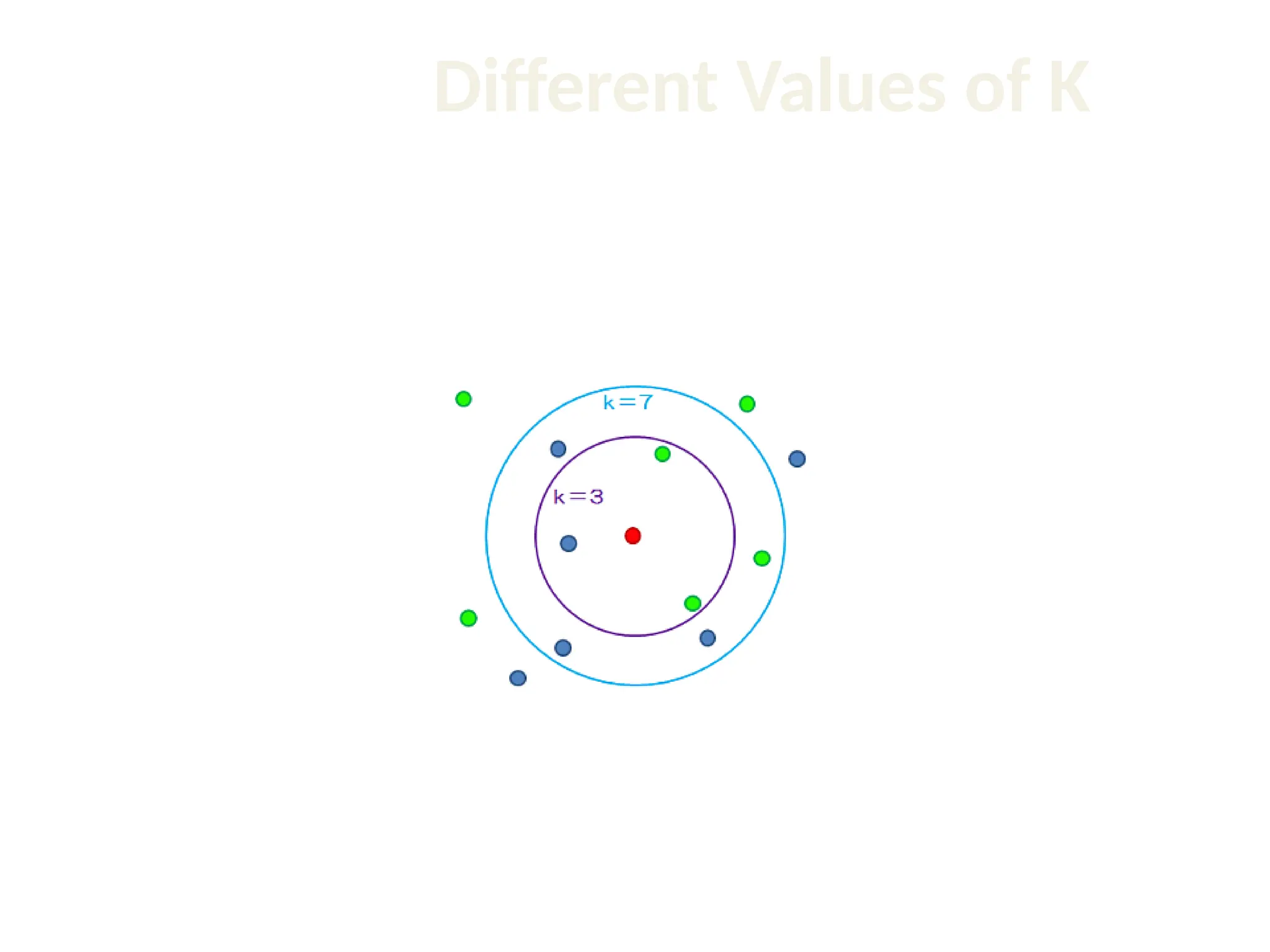
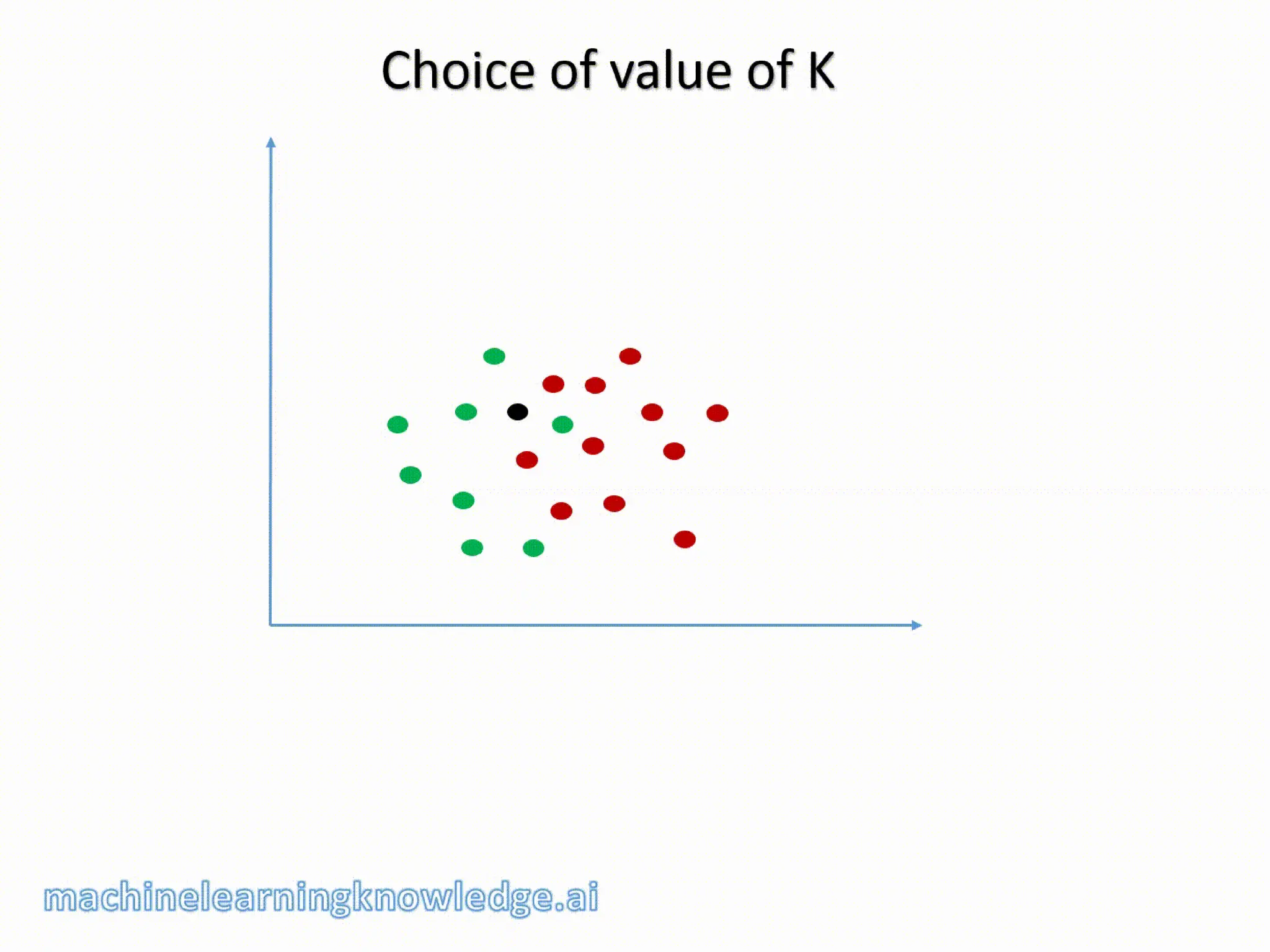
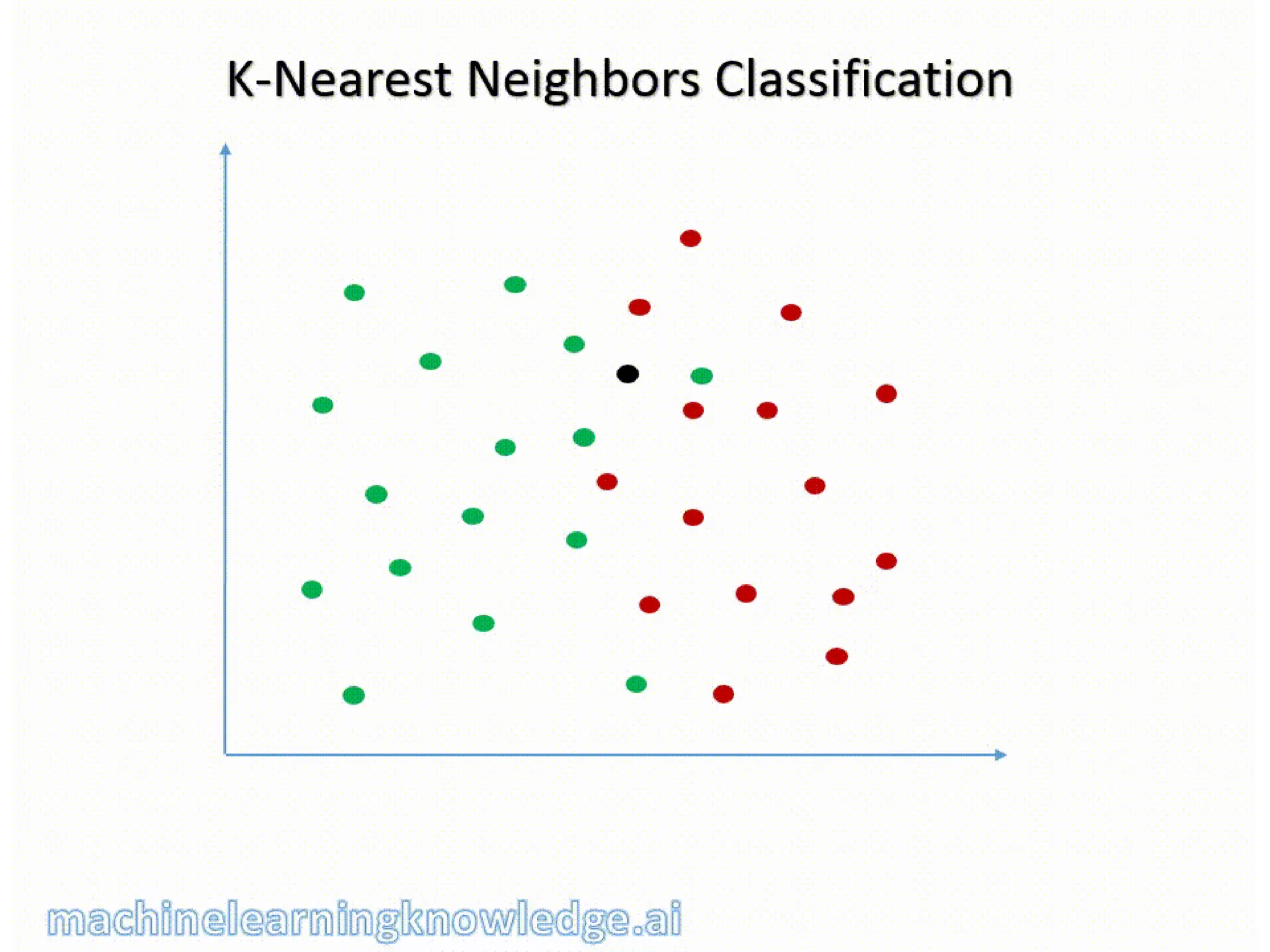
The document discusses the k-nearest neighbor (k-NN) classification algorithm, focusing on various distance measures to determine similarity between points. It covers supervised and unsupervised learning, explains different distance metrics like Euclidean and Manhattan distances, and illustrates the k-NN process through examples. Additionally, it highlights the impact of varying the number of neighbors (k) on classification outcomes.