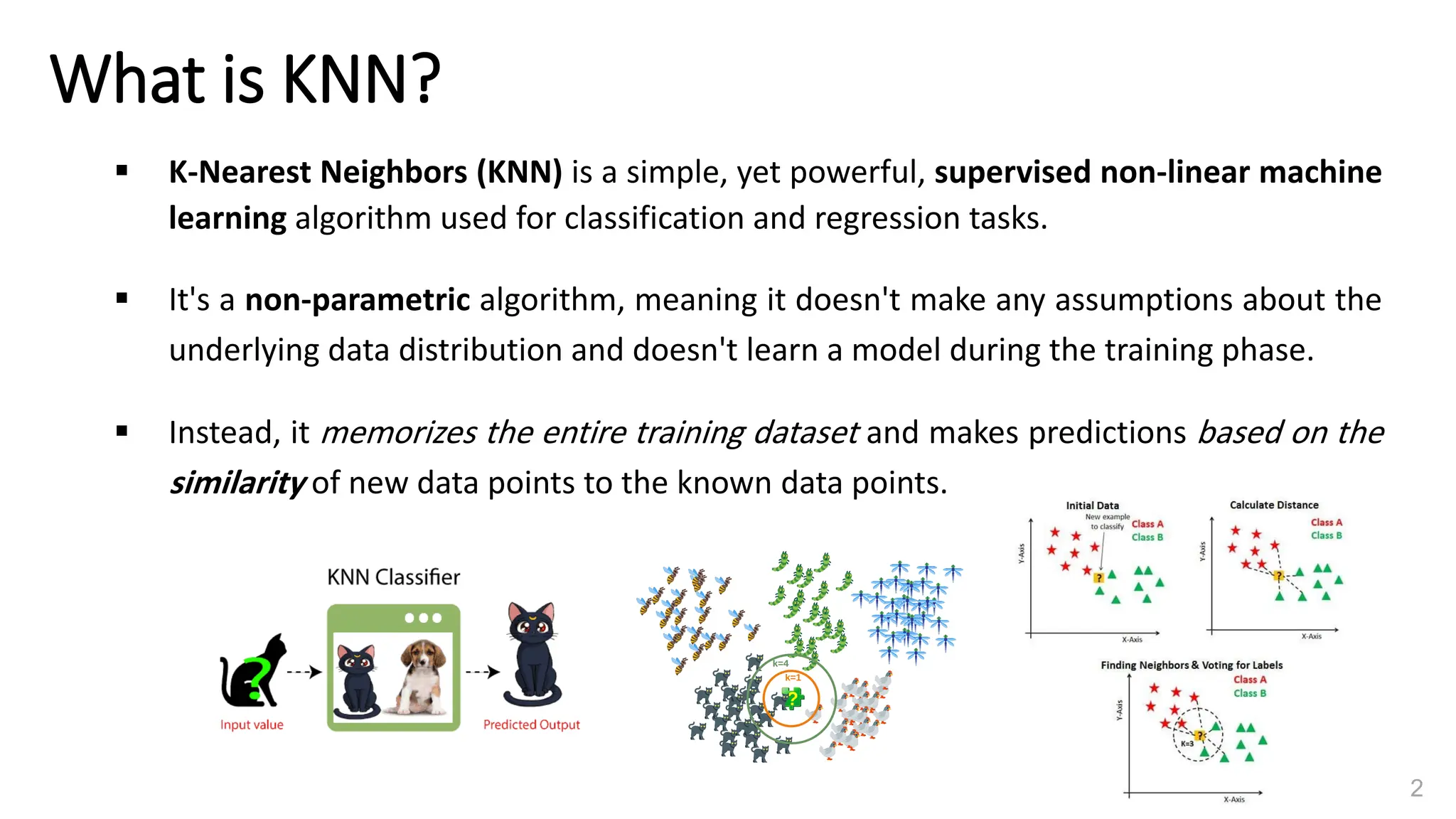
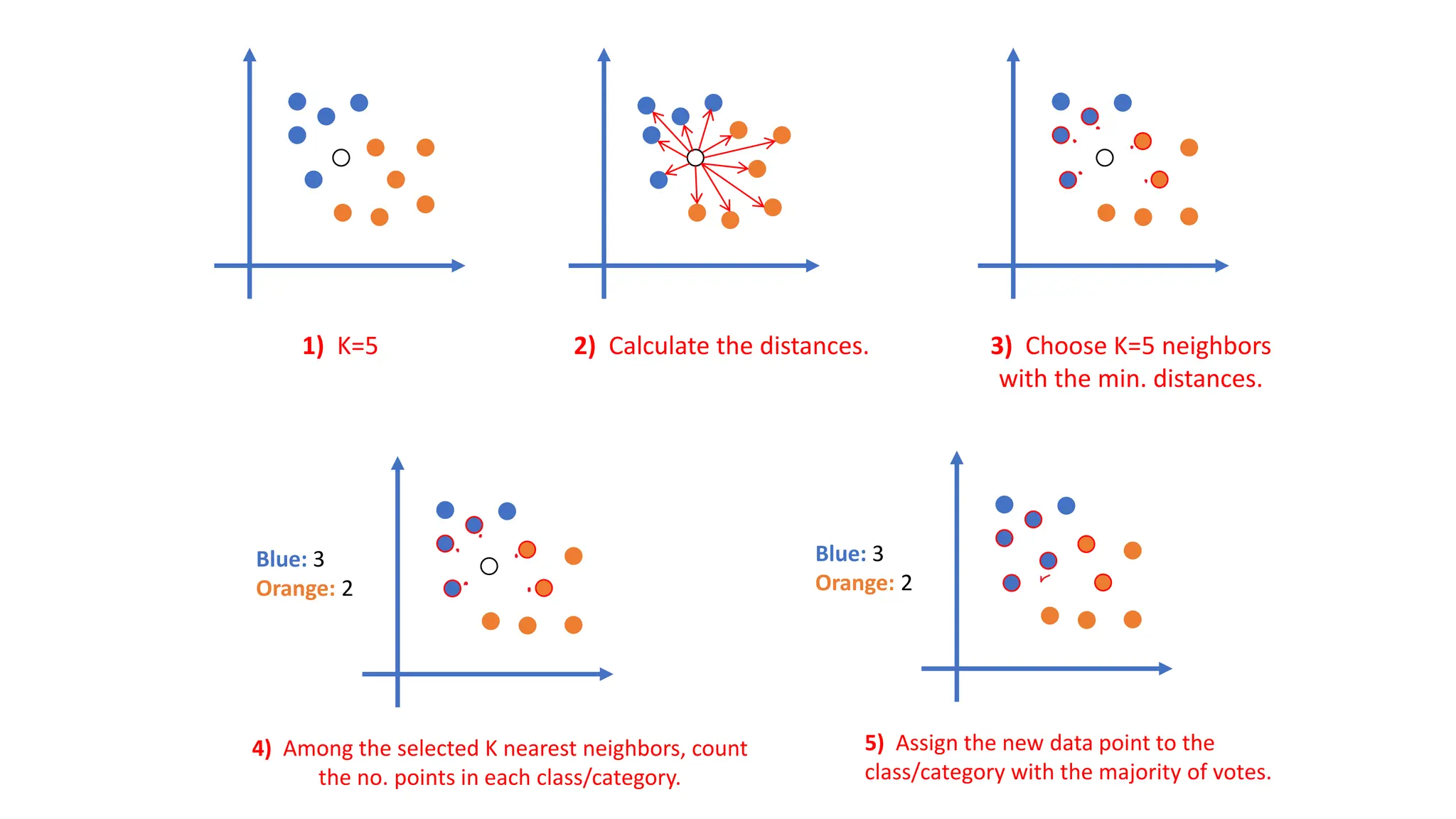
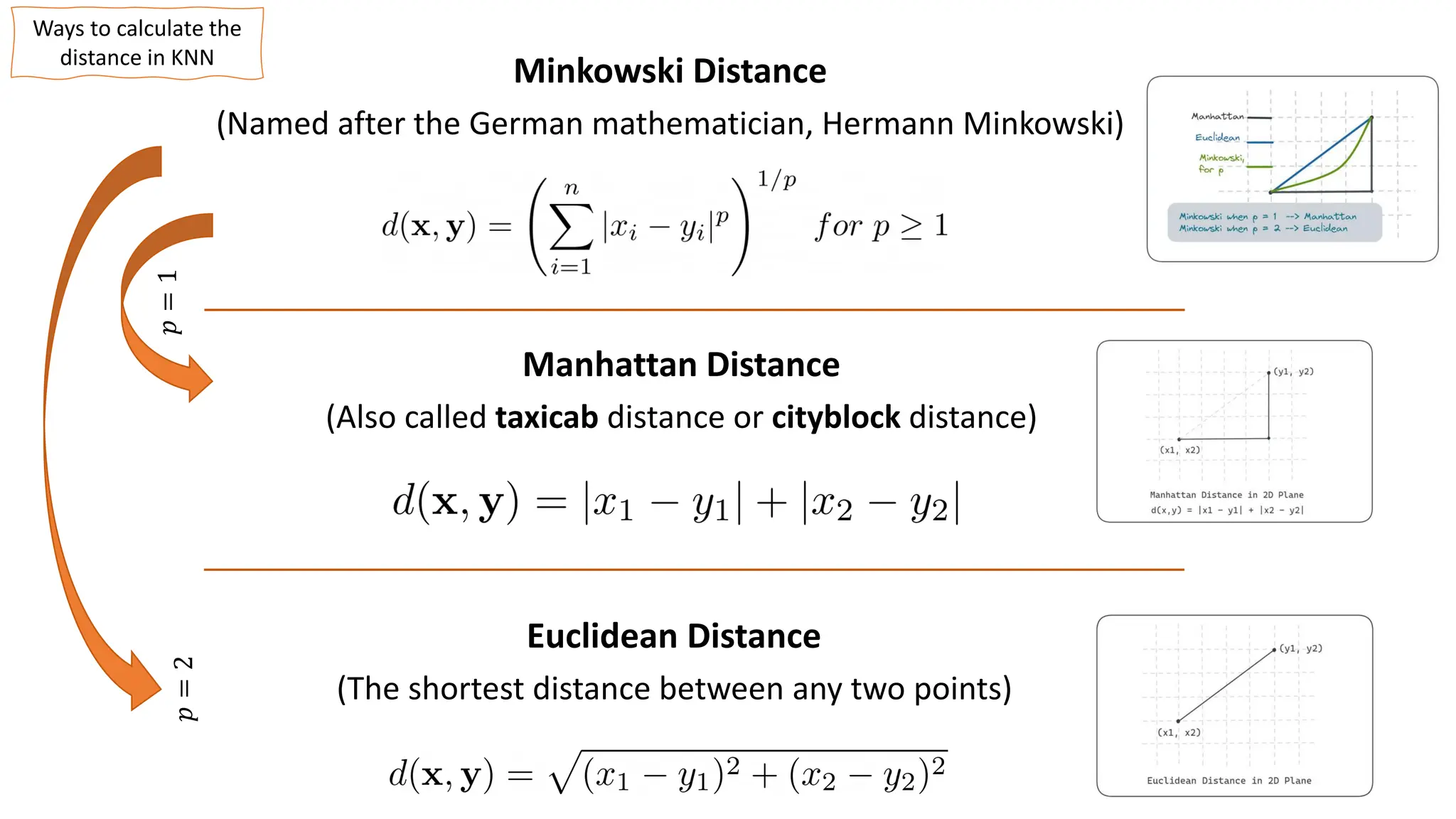
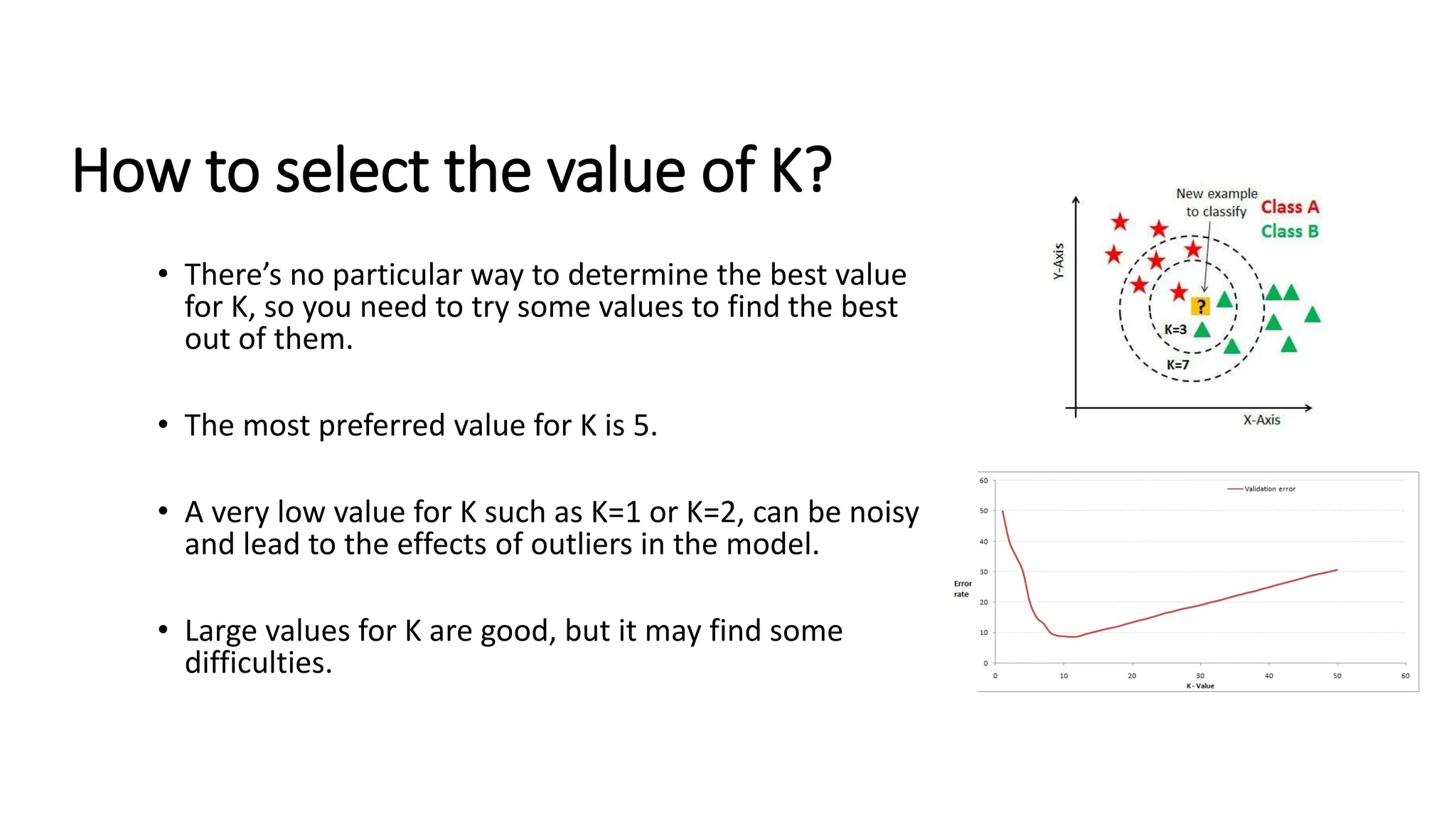
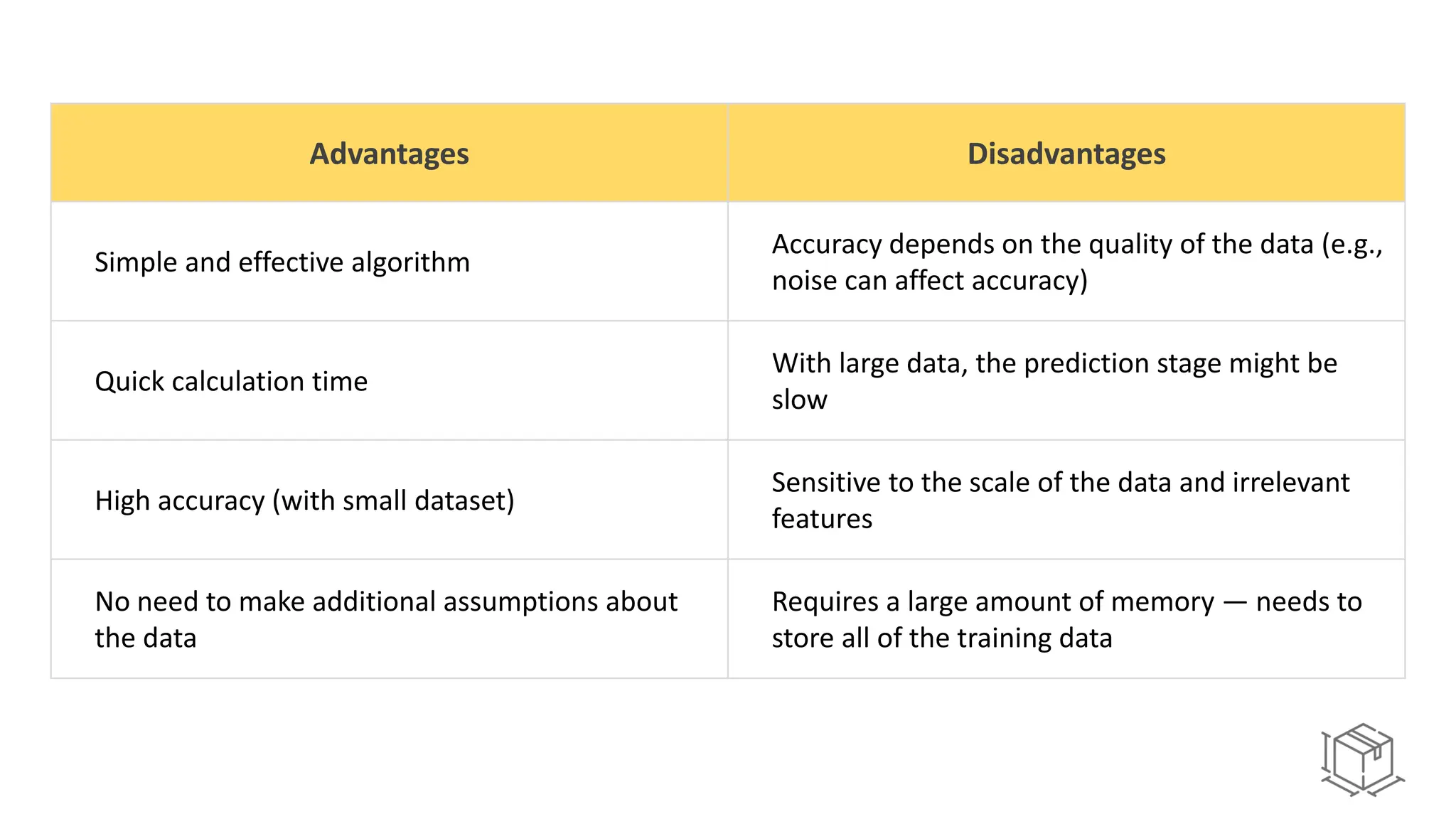
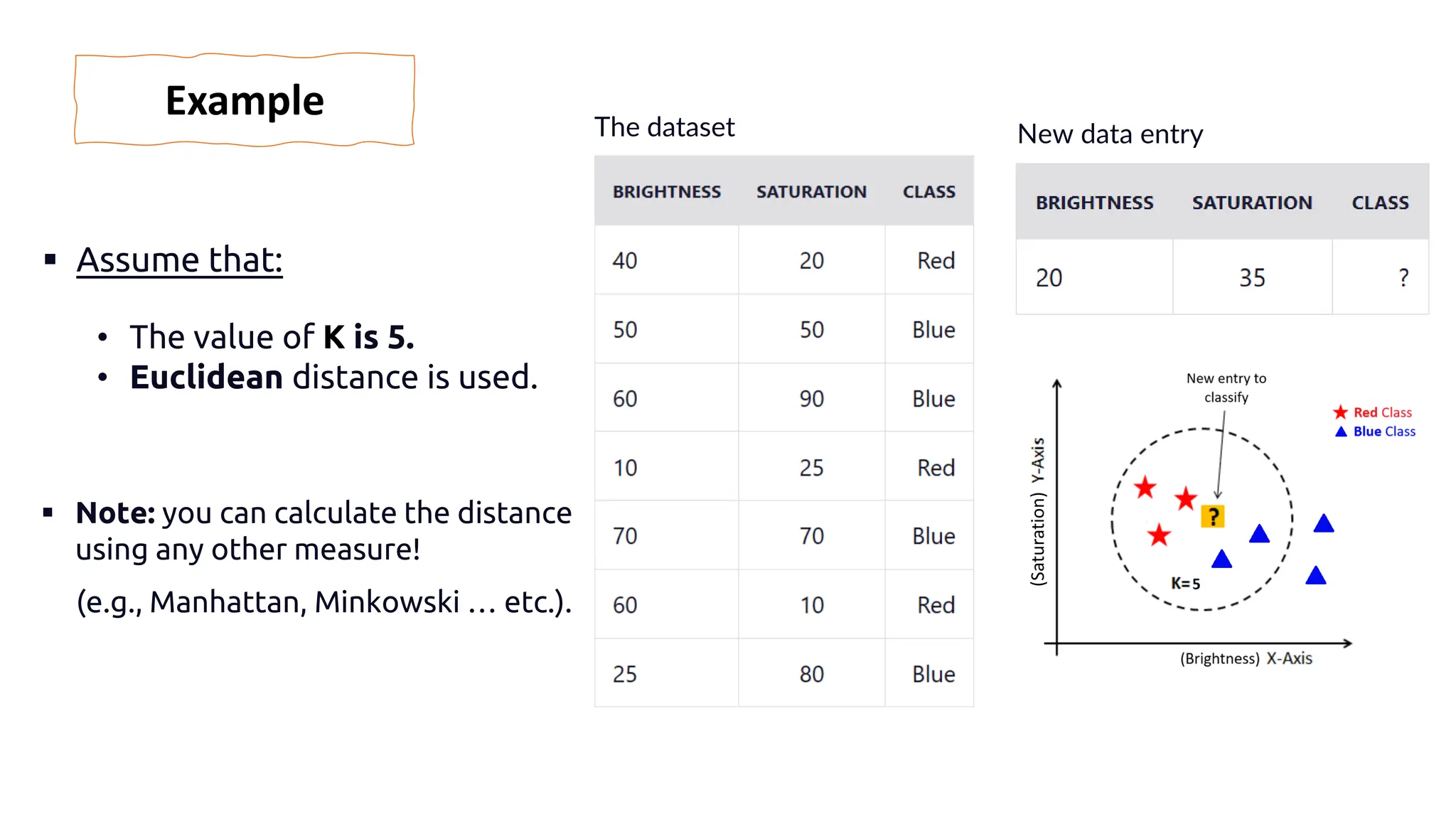
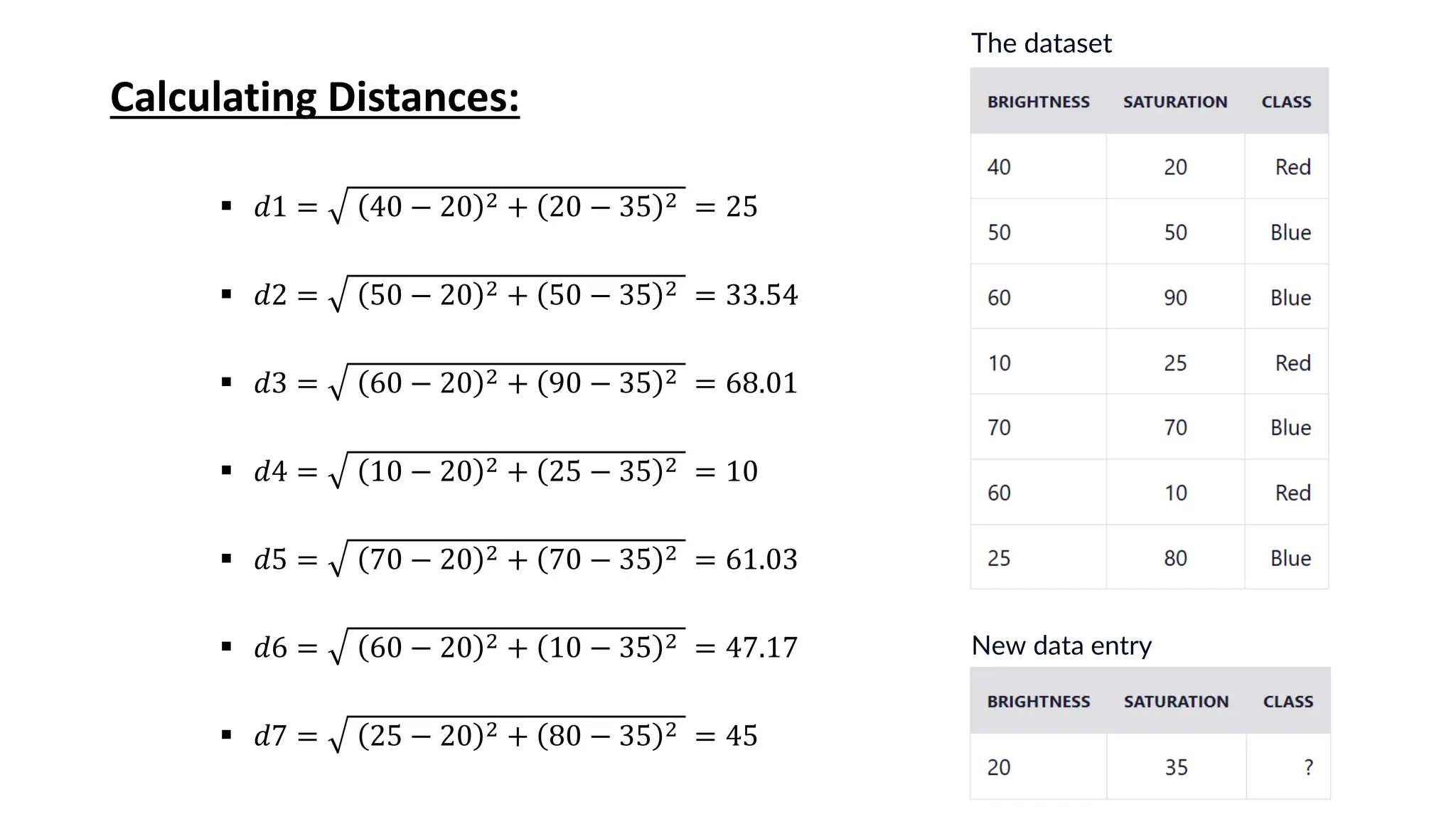
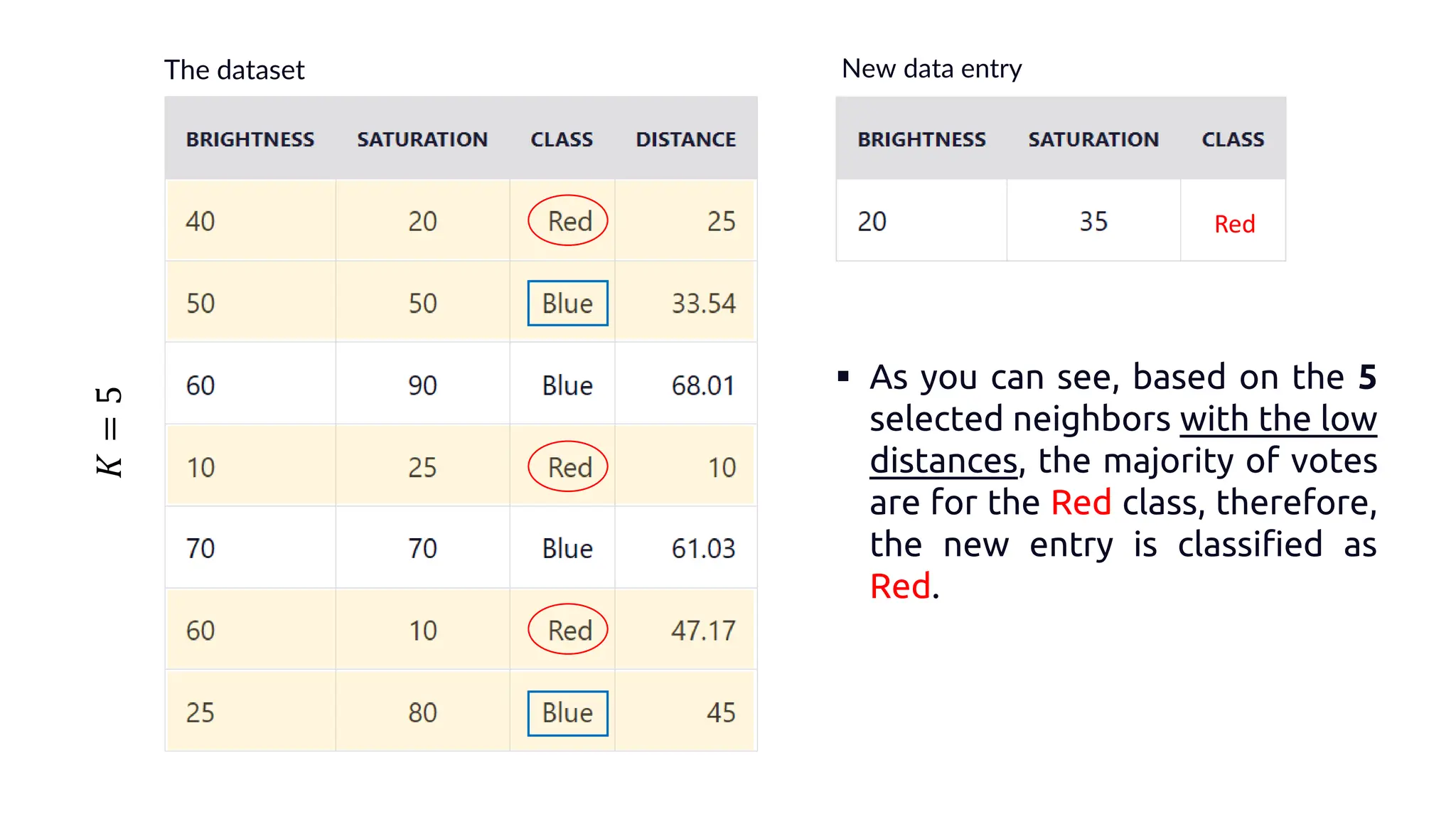
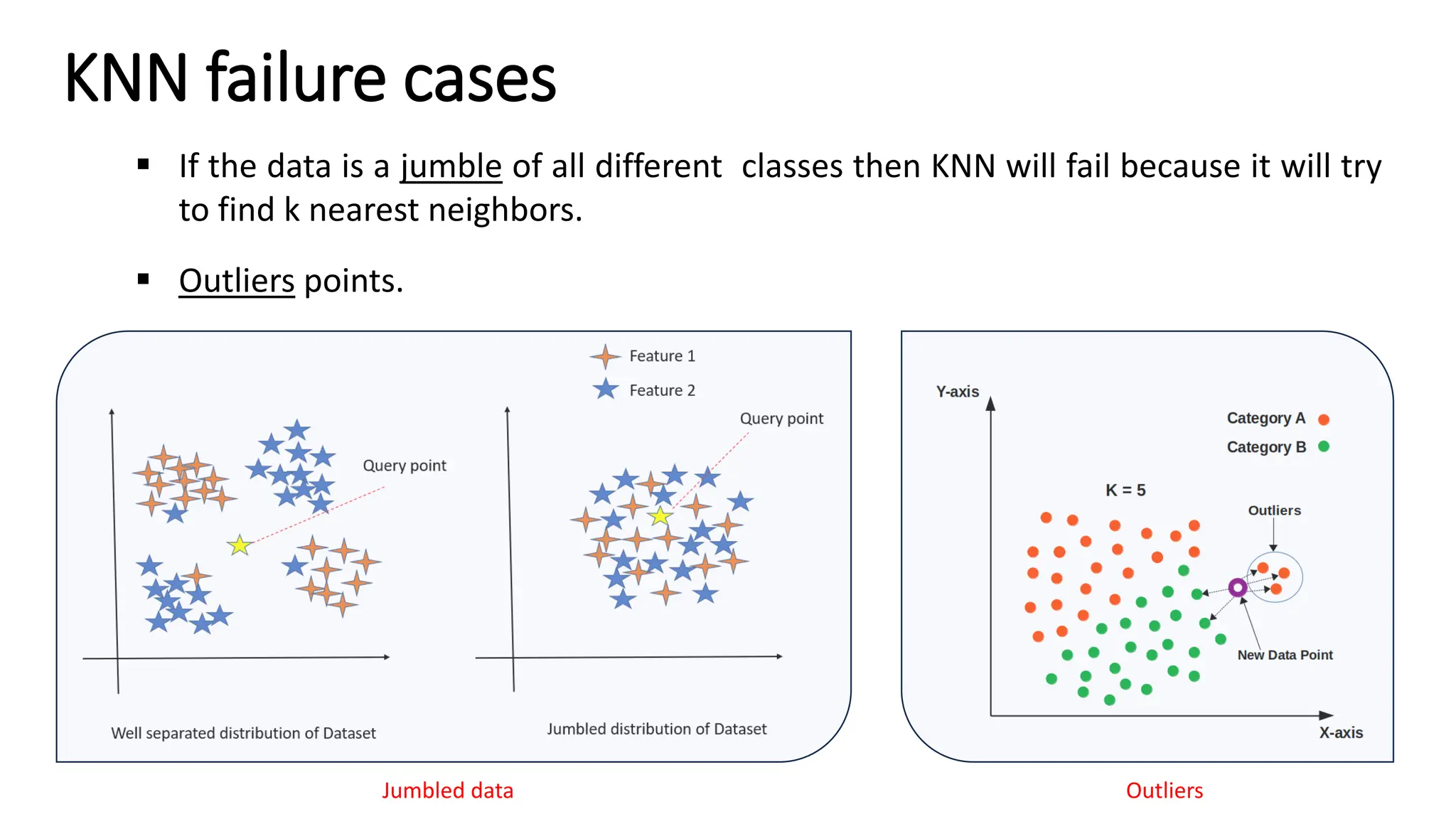
The document explains k-nearest neighbors (k-nn), a supervised machine learning algorithm used for classification and regression, detailing its workings and structure. Key steps in the k-nn process include selecting the number of neighbors (k), calculating distances, and classifying new data points based on the majority vote of the nearest neighbors. It also discusses advantages and disadvantages, such as simplicity, sensitivity to data quality, and memory requirements.