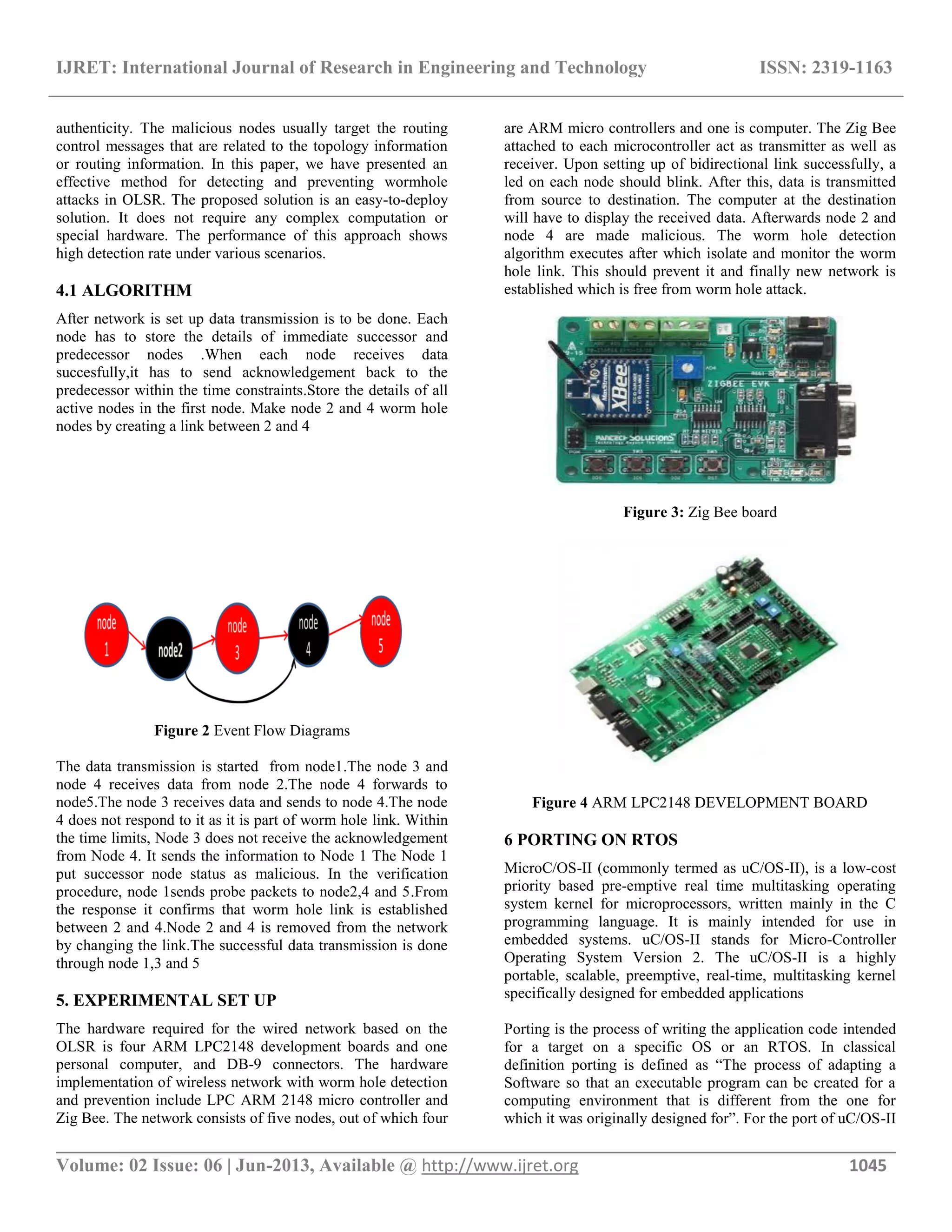
This paper presents a method for detecting and preventing wormhole attacks in ad hoc networks using real-time operating system (RTOS) environments. The proposed algorithm identifies suspicious links and employs a verification process to mitigate the risk of such attacks, enhancing the security and efficiency of wireless networks. The research outlines the characteristics of wormhole attacks and provides a detailed implementation strategy that utilizes the optimized link state routing protocol (OLSR).
![IJRET: International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology ISSN: 2319-1163 __________________________________________________________________________________________ Volume: 02 Issue: 06 | Jun-2013, Available @ http://www.ijret.org 1043 MALICIOUS ATTACK DETECTION AND PREVENTION IN AD HOC NETWORK BASED ON REAL TIME OPERATING SYSTEM ENVIRONMENT JITHESH PUTHENKOVILAKAM M-Tech Student, Electrical and Electronics Department, Amrita School of Engineering, Tamil Nadu, India, jithesh_kovil@rediffmail.com Abstract This paper deals with Real Time Operating System (RTOS) based secure wormhole detection and prevention in ad hoc networks. The wormhole attack can form a serious threat to wireless networks, especially against many ad hoc network routing protocols and location based wireless security systems. A wormhole is created in the ad hoc network by introducing two malicious nodes. These two nodes form a worm hole link and message is transmitted through this link. The next part of the work is to detect the wormhole link by defining worm hole detection and prevention algorithm. After detecting suspicious links, one node performs a verification procedure for each suspicious link. The detection procedure and verifying procedure of suspicious worm link are used for further prevention of wormhole attack in the ad hoc network. Index Terms: An algorithm to detect worm hole attack in a wireless network… -----------------------------------------------------------------------***----------------------------------------------------------------------- 1. INTRODUCTION An ad-hoc network is a decentralized wireless network in which each node can participate in routing by forwarding data to other nodes .A wireless network uses radio waves instead of cables to relay information to and from your computer. There is less need for technical support in setting up due to their simple nature .Even though the wireless networking provides many advantages, but it is also prone to many security threats which can potentially alter organization’s overall information security risk profile. The reason is that in many organizations the security information flows through the wireless network .The worm hole attack is one of the those security threats. The proposed algorithm for worm hole attack detection and prevention can provide better understanding to a designer in setting up wireless networks which have high productivity with fewer security risks. The ad-hoc network which is free from worm hole attack will have the capacity to avoid unauthorized intrusions to a wireless network. The wormhole attack is one of the severe malicious attacks, happening in the ad-hoc network .The two nodes in any end points in the network form a tunnel, known as worm hole tunnel. In this attack two existing nodes become malicious or two node can intrude into any point in the network and create worm hole link. These nodes are called worm hole nodes. In the wormhole attack, a worm hole node copies packets at one location in the network, tunnels them to another location through the another worm hole node. These packets can be retransmitted into the network or captured, depends on the intention of the attacker who establishes this attack. The wormhole attack is very powerful, and preventing the attack is very difficult because all the nodes between the worm hole link are shielded or got bypassed A strategic placement of this worm hole link can result in a significant breakdown in communication across a wireless network. In the optimized link state routing protocol (OLSR), if a wormhole attack is launched routing is easily disrupted because of the combined effect of two worm hole nodes. 2. RELATED WORKS In the paper by Farid Na¨ıt-Abdesselam[1] an efficient method is devised to detect and avoid wormhole attacks in the OLSR protocol. These methods first attempts to pinpoint links that may, potentially, be part of a wormhole tunnel. Then, a proper wormhole detection mechanism is applied to suspicious links by means of an exchange of encrypted probing packets between the two supposed neighbours (endpoints of the wormhole).The proposed solution exhibits several advantages, among which its non-reliance on any time synchronization or location information, and its high detection rate under various scenarios .In the paper by Shalini Jain, Dr.Satbir Jain[2] a novel trust-based scheme for identifying and isolating nodes that create a wormhole in the network without engaging any cryptographic means is presented. In the paper by Yih-Chun Hu [3] a general mechanism, called packet leashes, for detecting and thus defending against wormhole attacks, and implementing leashes is presented.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maliciousattackdetectionandpreventioninadhocnetworkbasedonrealtimeoperatingsystemenvironment-140804002245-phpapp01/75/Malicious-attack-detection-and-prevention-in-ad-hoc-network-based-on-real-time-operating-system-environment-1-2048.jpg)

![IJRET: International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology ISSN: 2319-1163 __________________________________________________________________________________________ Volume: 02 Issue: 06 | Jun-2013, Available @ http://www.ijret.org 1046 to any target embedded platform we first need the uC/OS-II kernel, which is CPU independent. For any port this kernel will be the same. Now the CPU specific code for the corresponding embedded platform used is needed. The third requirement is the BSP corresponding to the board carrying the microcontroller or microprocessor. The code written in c for worm hole detection and prevention is ported on uC/OS-II and built into ARMLPC 2148 development board. The priorities are set for various tasks required to set up the ad-hoc network, introduce worm hole attack, detect and prevent it. Figure 5 Code required for uC/OS-II Porting CONCLUSIONS The proposed algorithm used for implementing this project is developed keeping in mind the fact that it can provide better understanding to a designer in setting up wireless networks which have high productivity with fewer security risks. The wireless networking provides many advantages, but it is also coupled with new security threats which can potentially alter organization’s overall information security risk profile. Properly enhanced, this developed system will have the capacity to avoid unauthorized intrusions to a wireless network. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Author gratefully acknowledges the facilities available at the Amrita school of engineering, Coimbatore, sincerely thanks to my guide Dr.Madhu and Mr. Anu Kumar for helping me in theoretical and practical section. REFERENCES: [1]Issa Khalil, SaurabhBagchi & Ness B. Shroff, “LITEWORP: Detection and Isolation of the Wormhole Attack in Static MultihopWireless Networks”. The International Journal of Computer and Telecommunications Networking, Vol. 51, Issue 13, pp 3750- 3772, 2007 [2] Issah Khalil, “Mitigation of Control and data traffic attacks in wireless ad-hoc and sensor networks” IEEE Vol. 6, Issue 3, pp 344-362 [3]Sun Choi, Doo-young Kim, Do-hyeon Lee &Jae-il Jung “WAP: Wormhole Attack Prevention Algorithm in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks” IEEE International Conference on Sensor Networks,Ubiquitous, and Trustworthy Computing SUTC’08.pp 343- 348,2008 [4] Y.C. Hu, A. Perrig, and D.B. Johnson, “Wormhole Attacks in WirelessNetworks,” In IEEE JSAC, Vol. 24, No. 2, pp. 370-380,2006 BIOGRAPHIES Jithesh Puthenkovilakam is a student at at the Amrita University at Coimbatore and presently doing Master Of Technology in Embedded System. He received the BTech .Degree in Electrical and Electronics Engineering from the Kannur University .Post that he worked as a software Engineer .He was involved in avionics and automotive projects as a low level designer and programmer. In his thesis work at Amrita School of Engineering, he focused on security and performance in wireless ad hoc networks and malicious attacks. His research interests include systems and network security.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maliciousattackdetectionandpreventioninadhocnetworkbasedonrealtimeoperatingsystemenvironment-140804002245-phpapp01/75/Malicious-attack-detection-and-prevention-in-ad-hoc-network-based-on-real-time-operating-system-environment-4-2048.jpg)