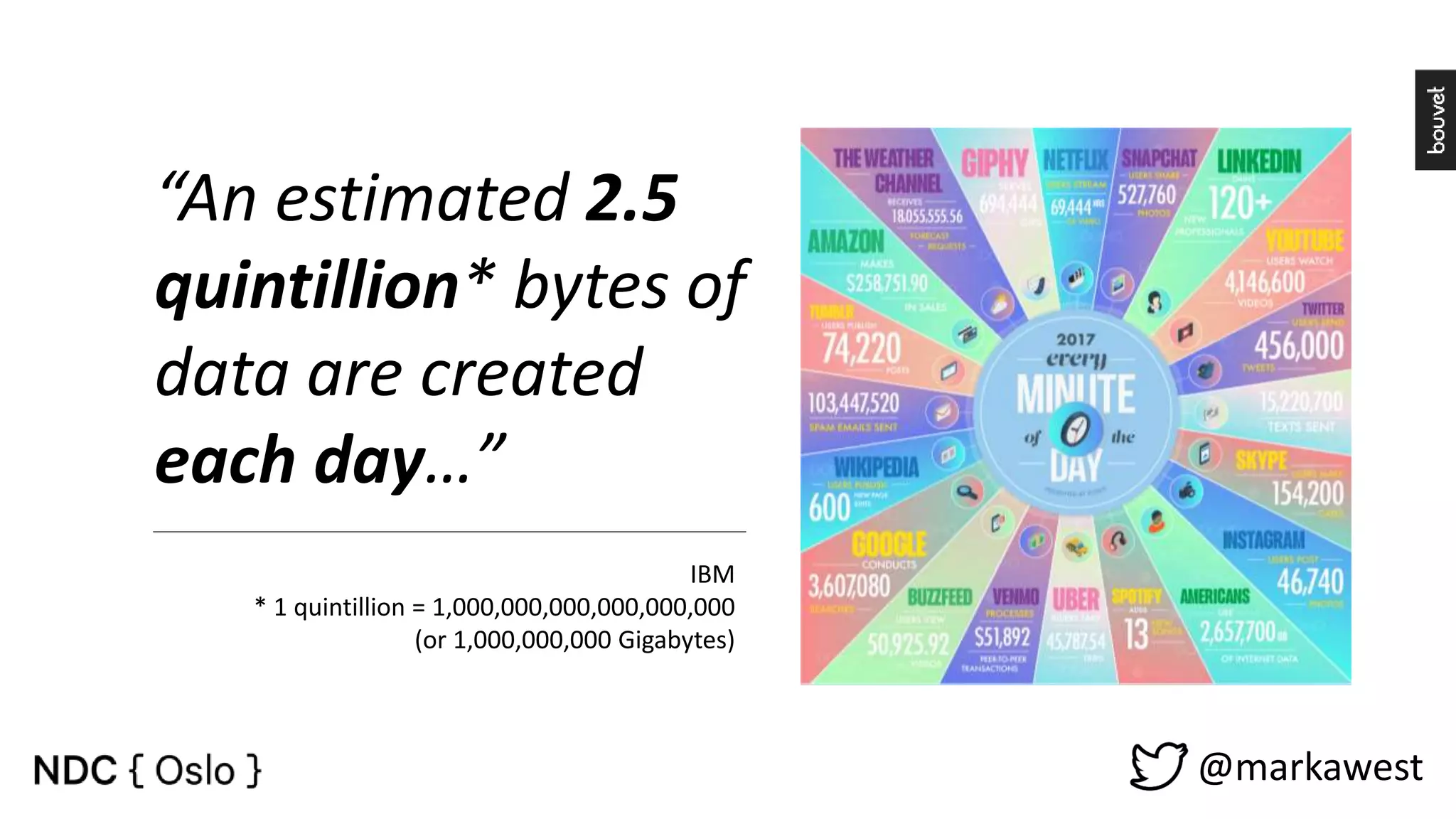
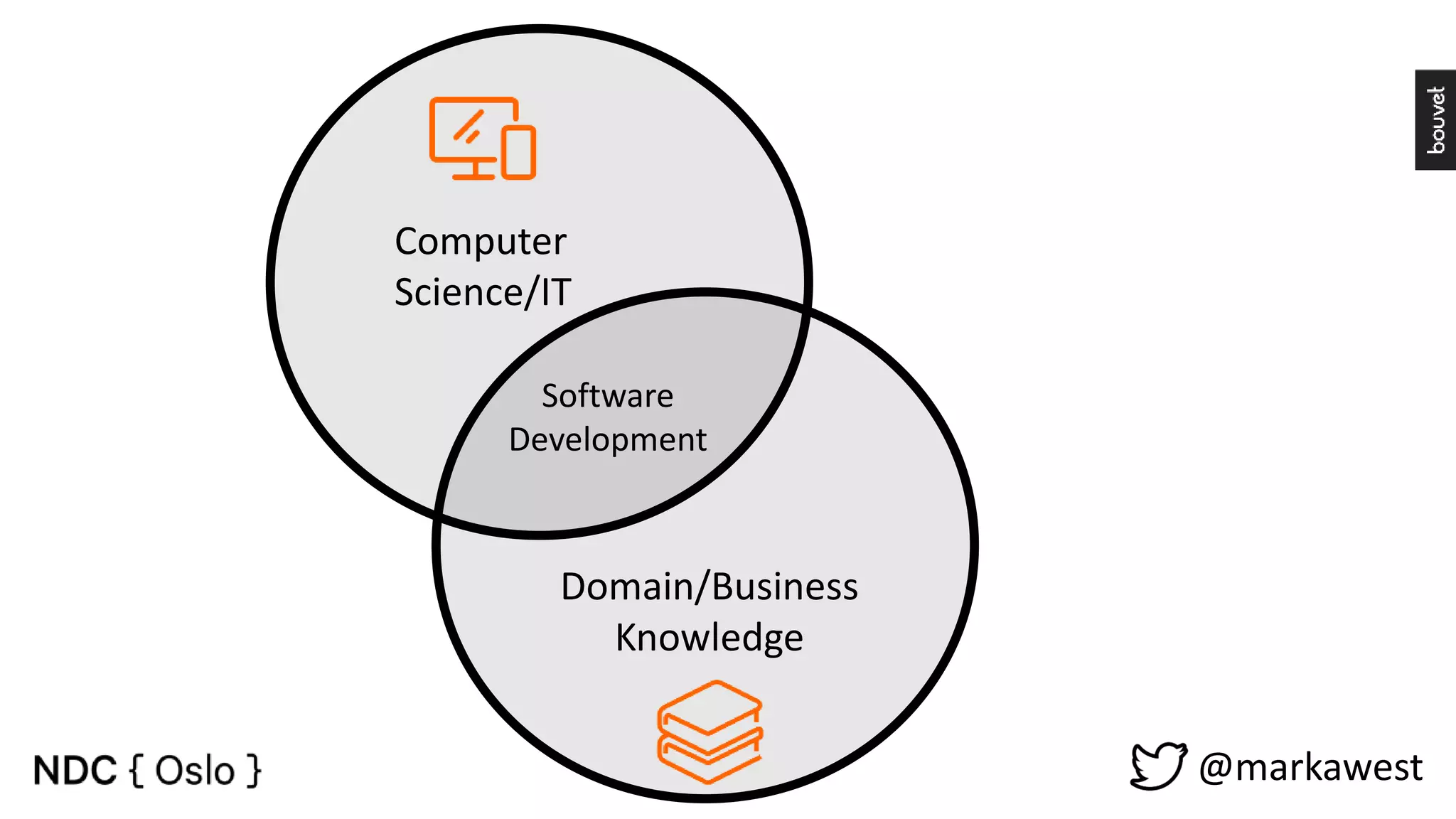
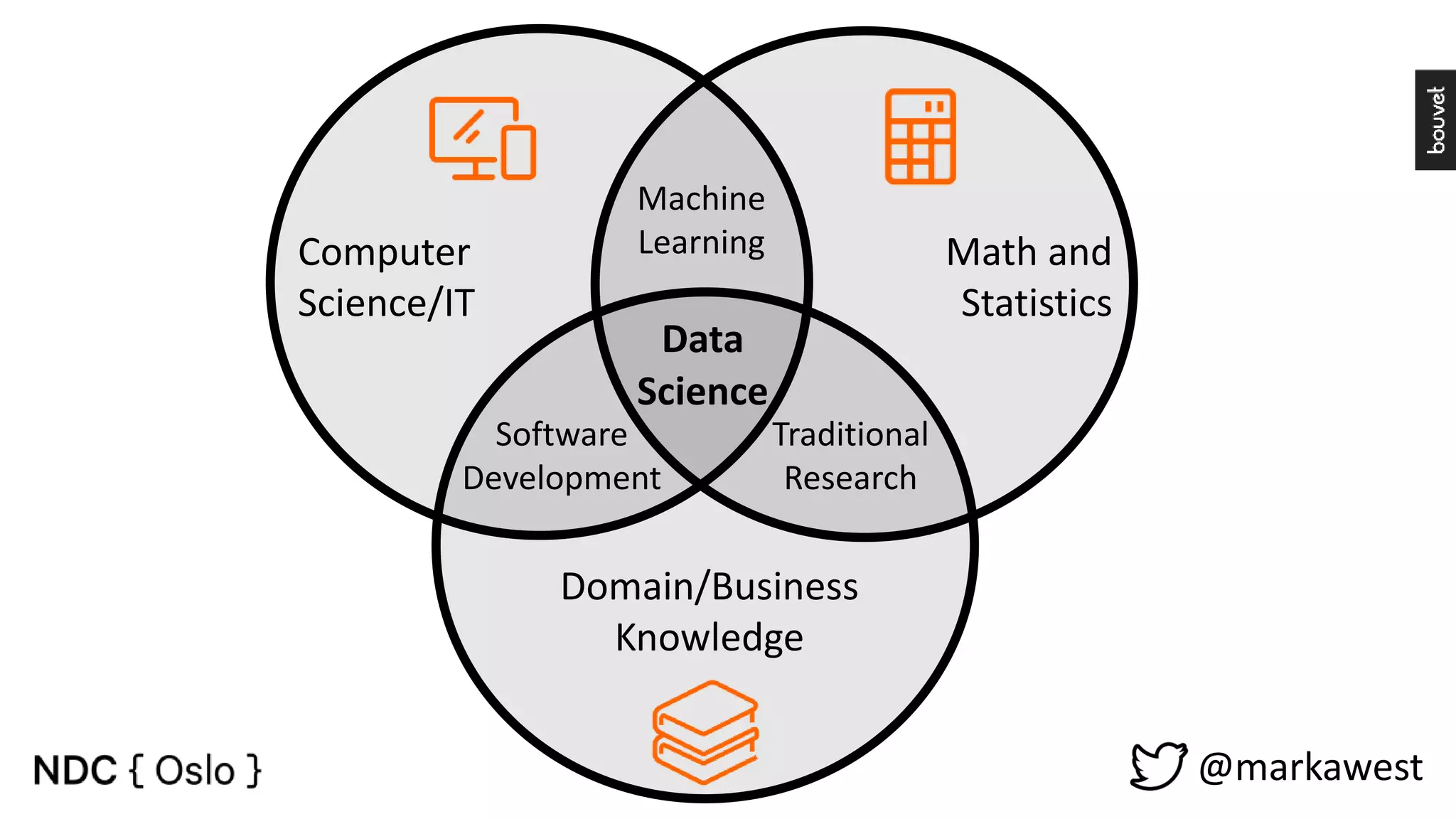
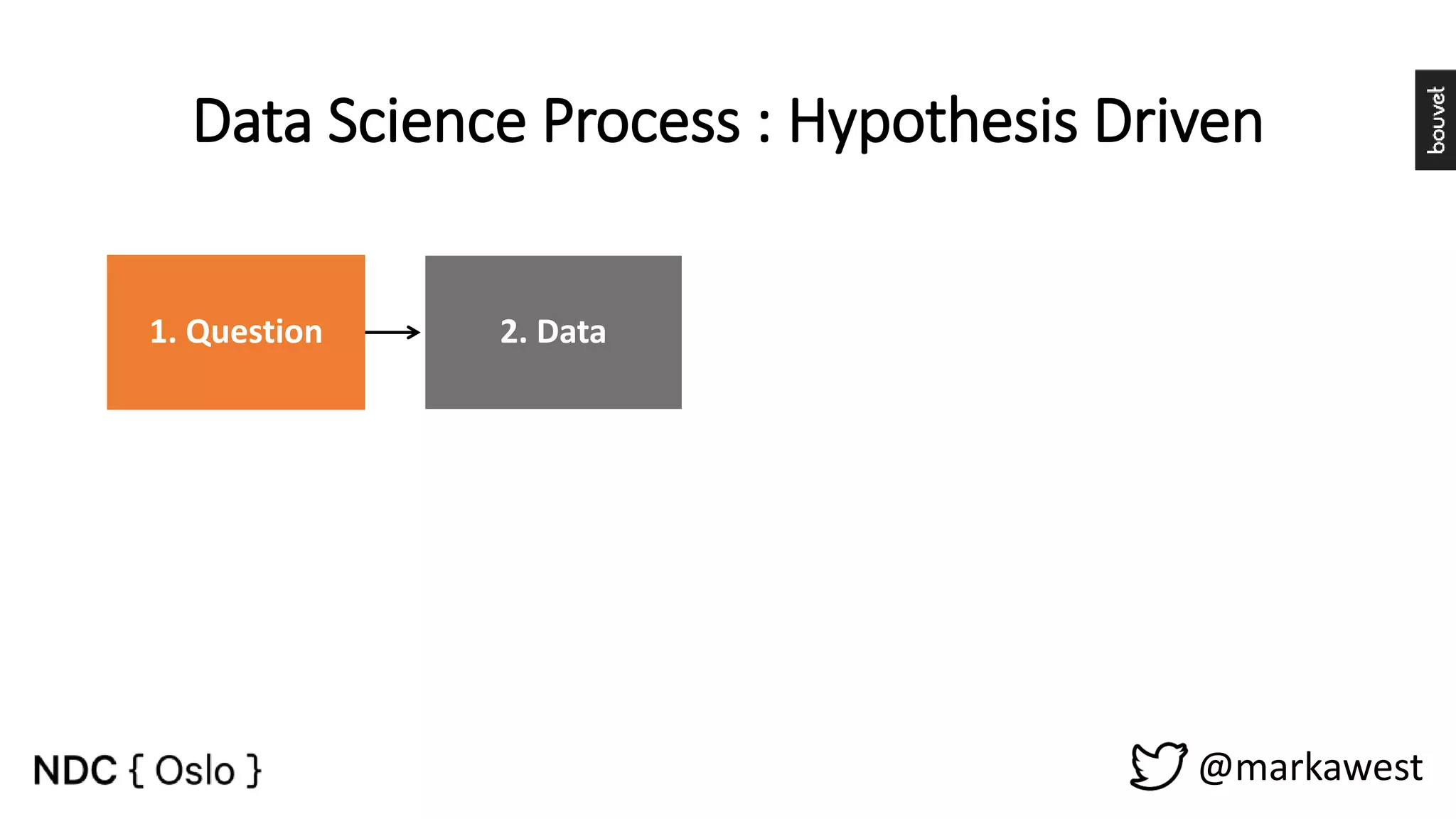
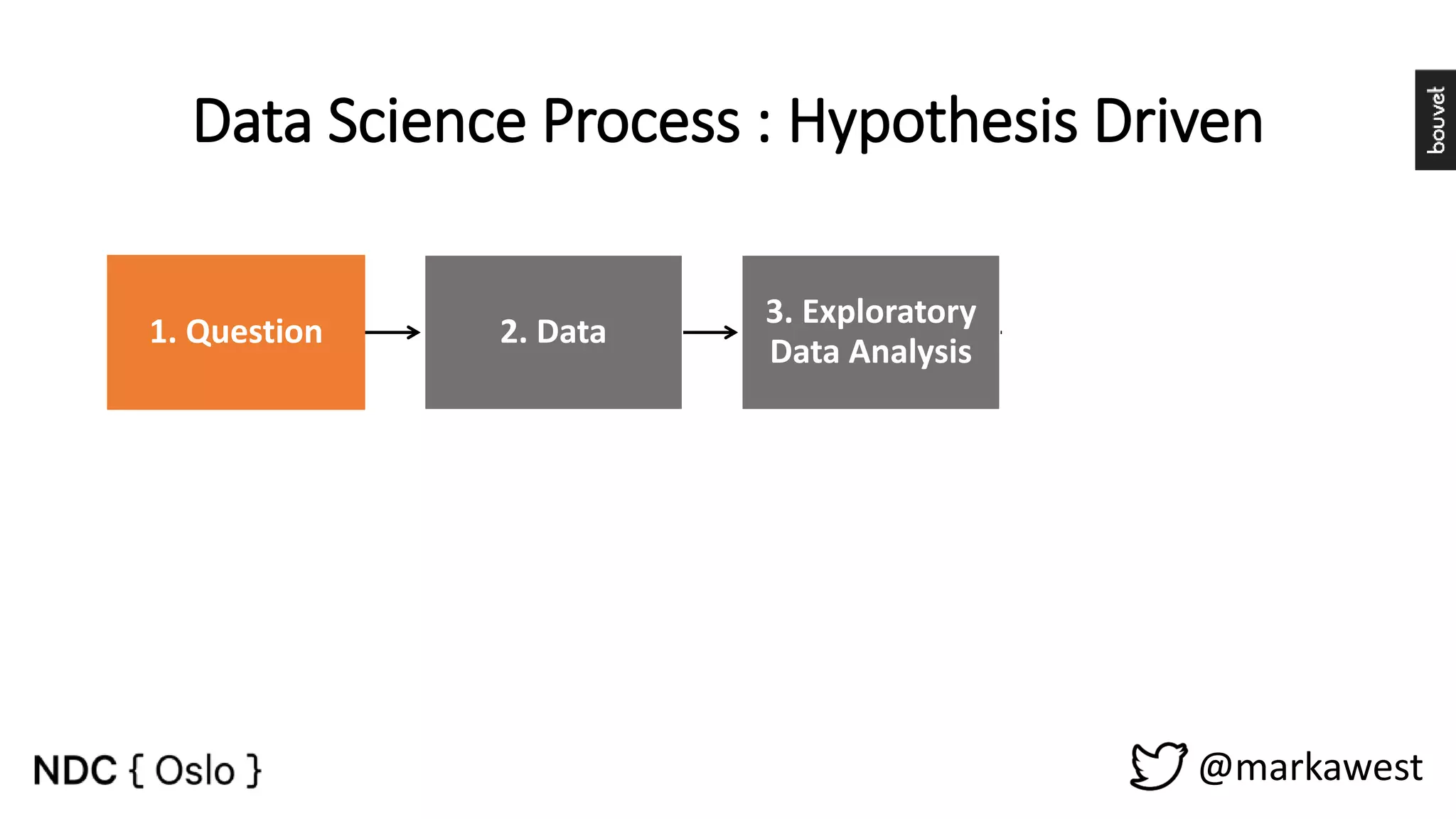
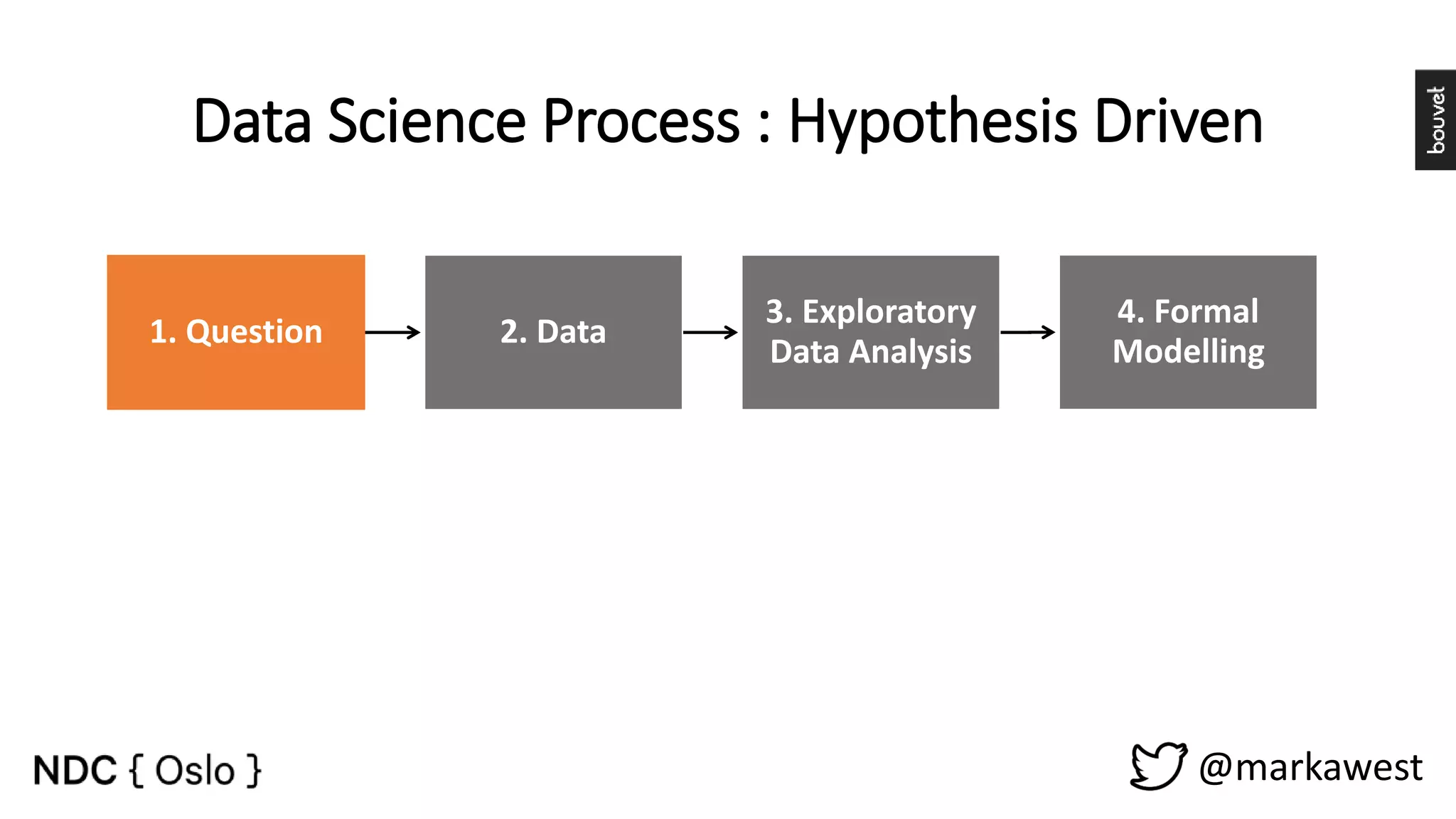
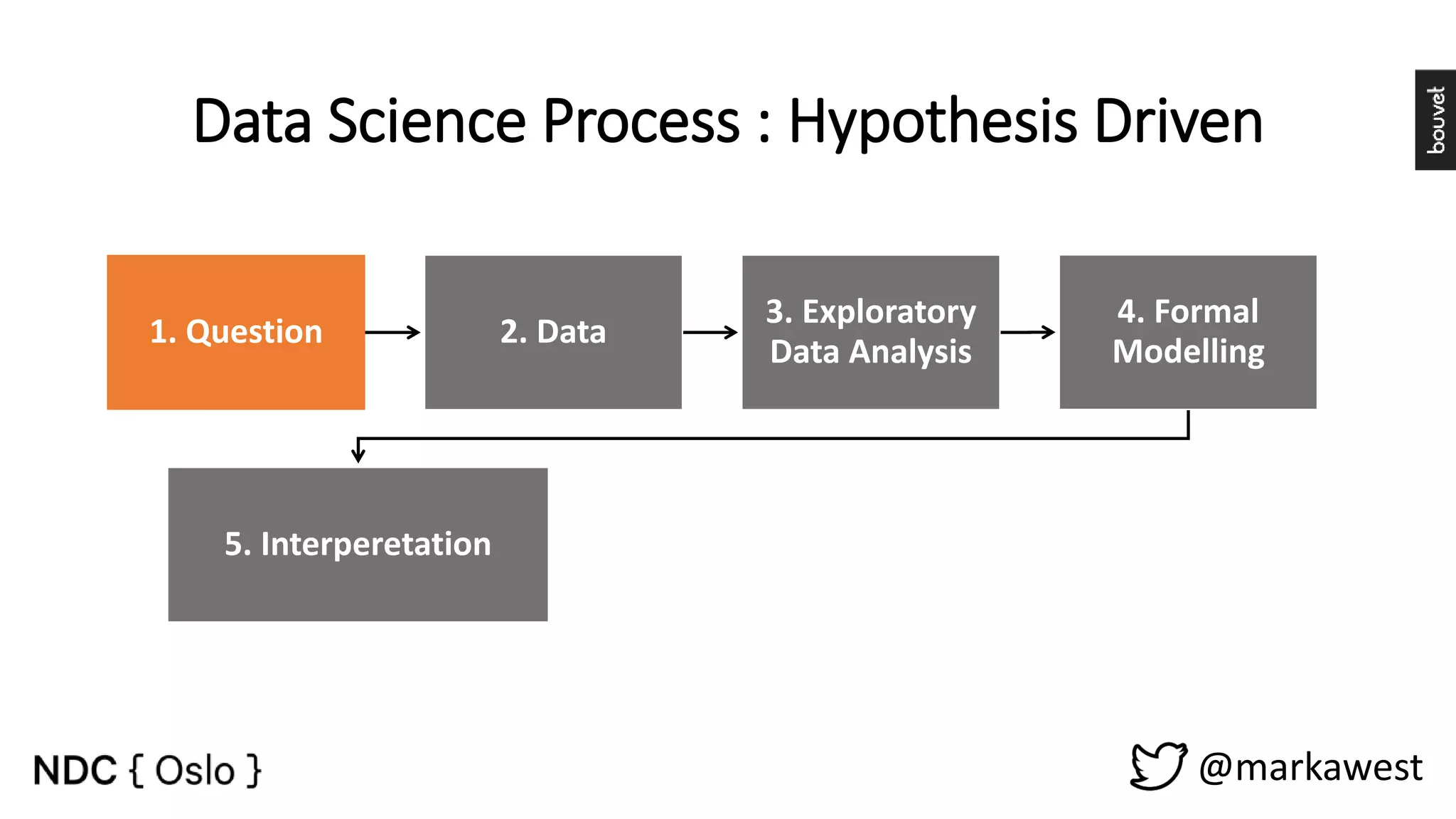
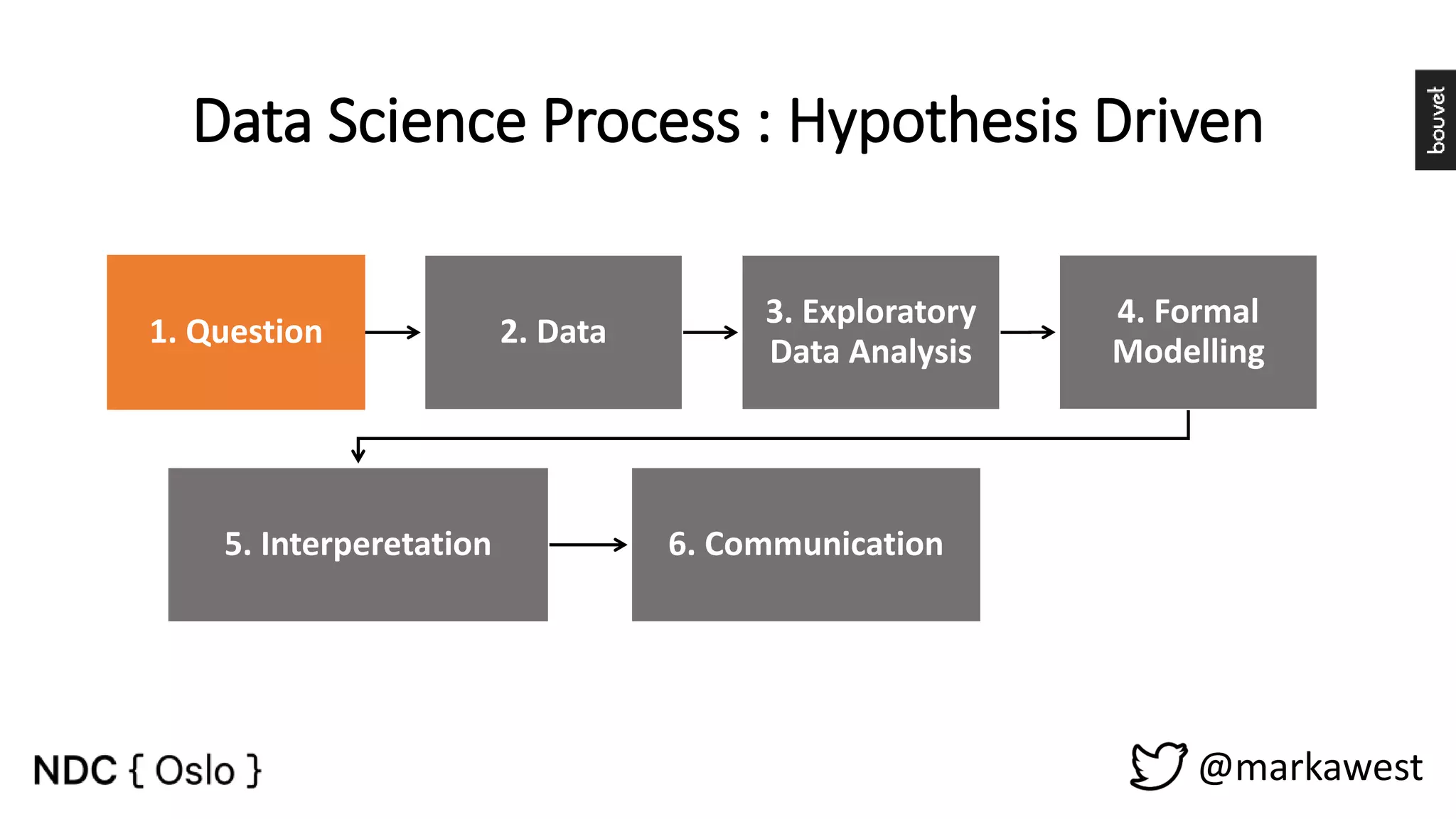
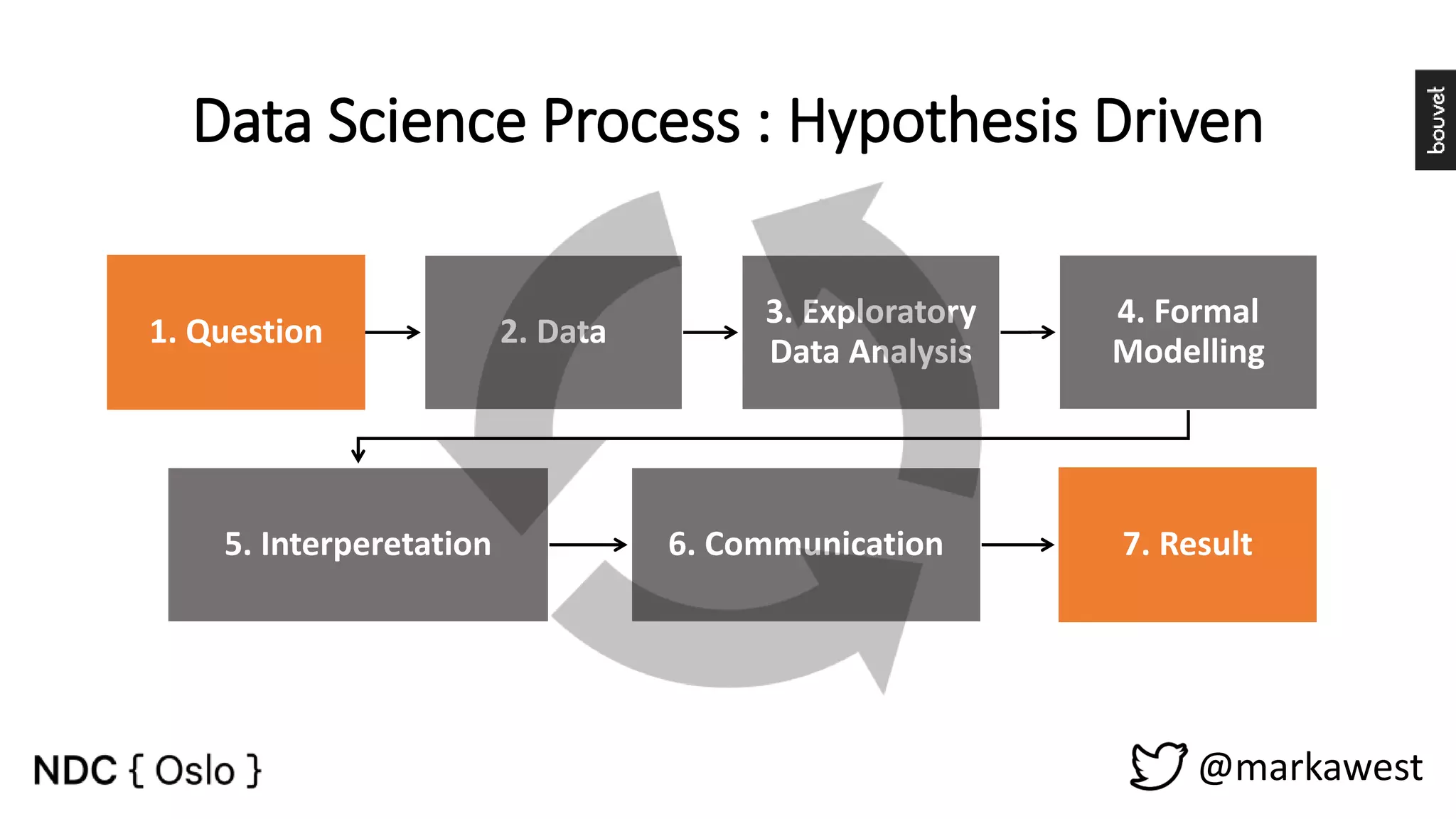
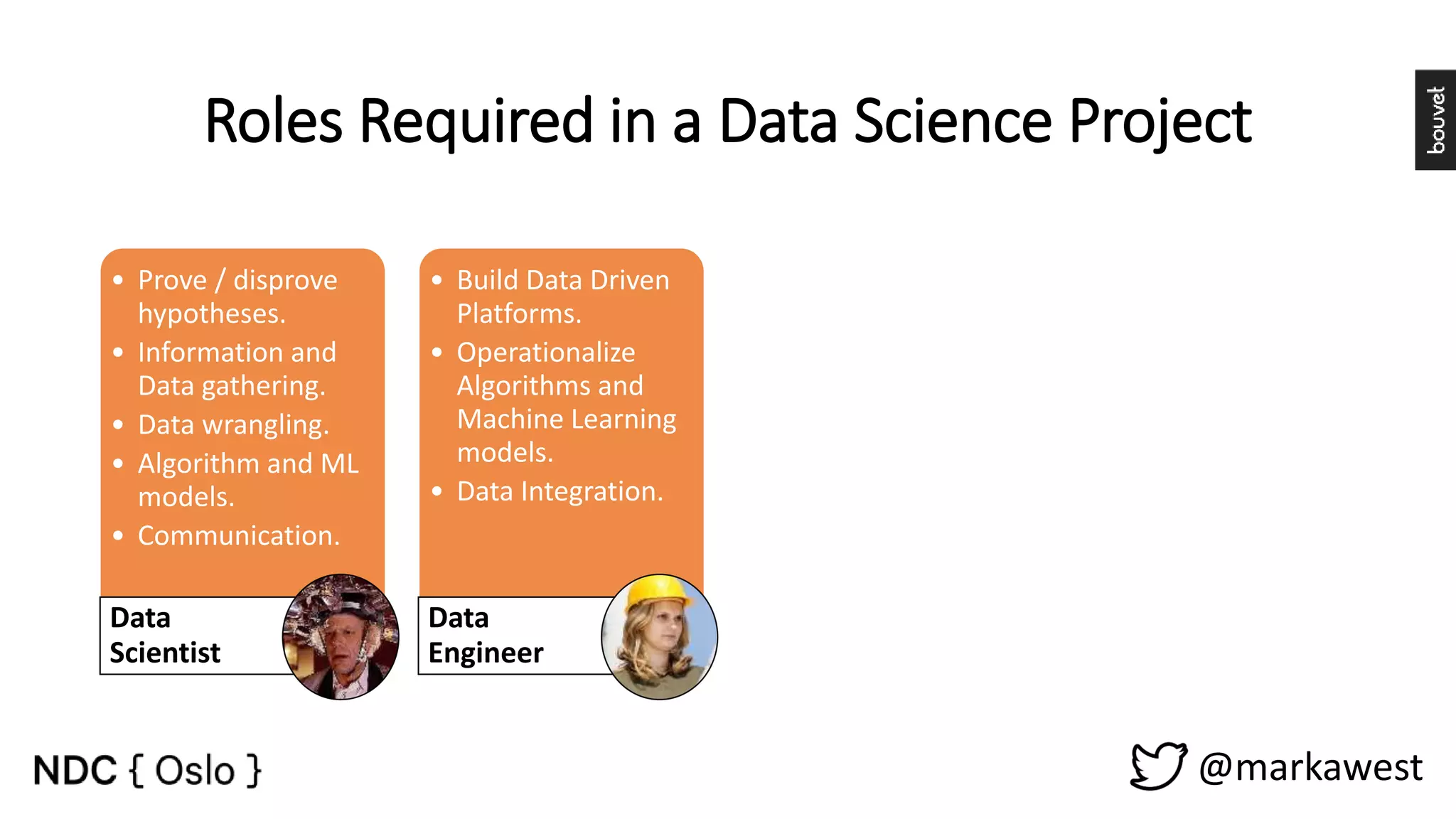
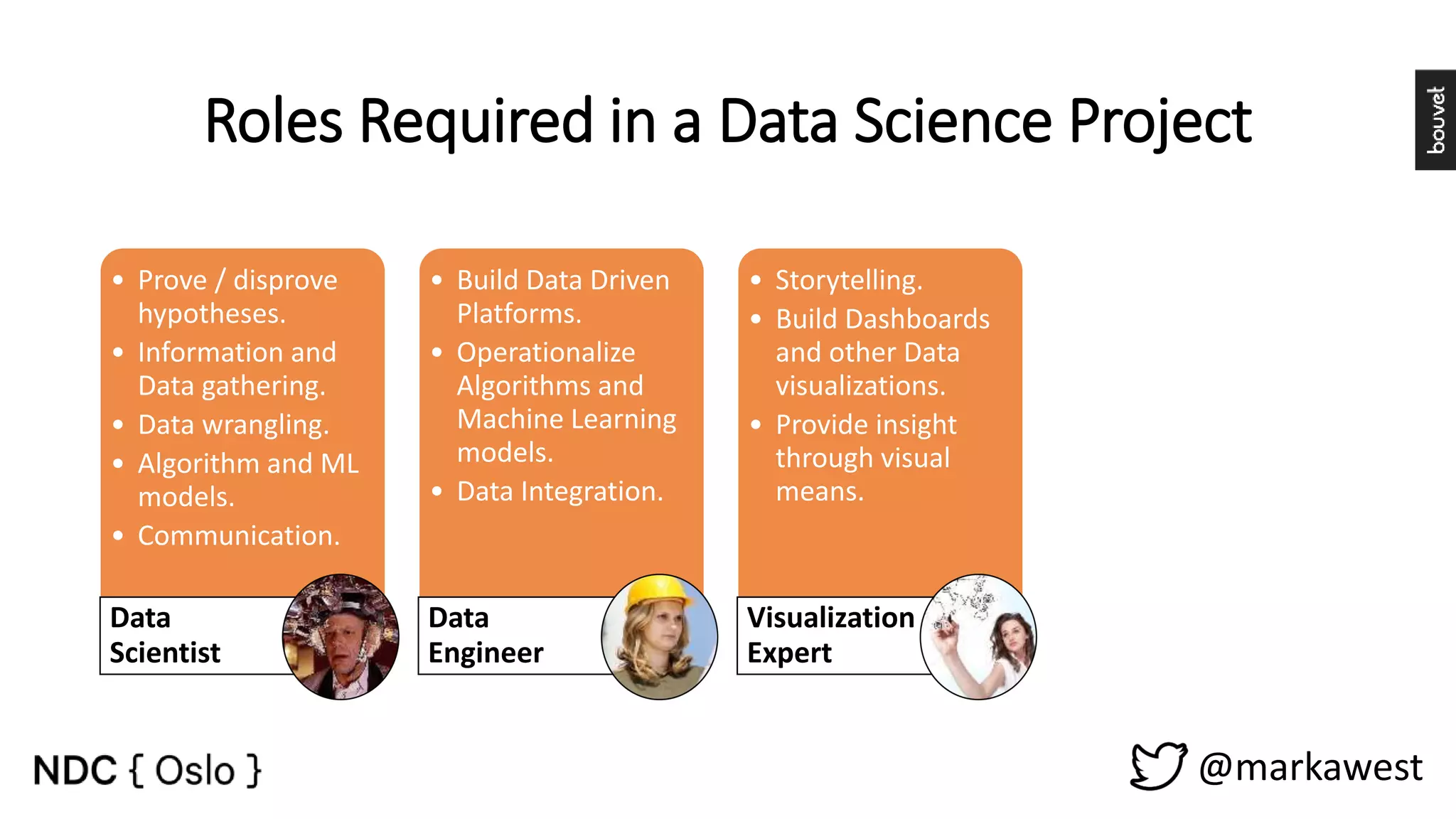
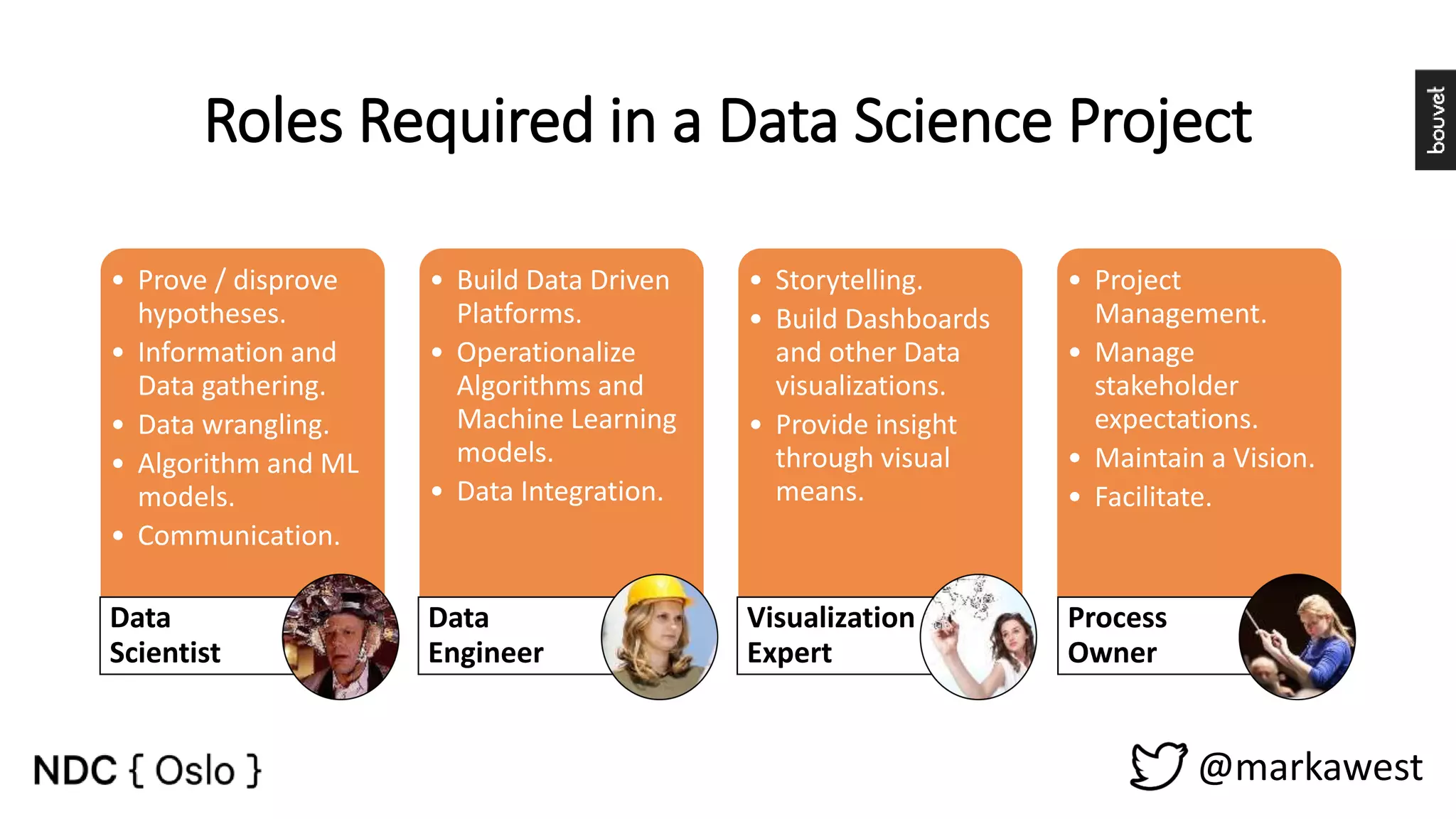
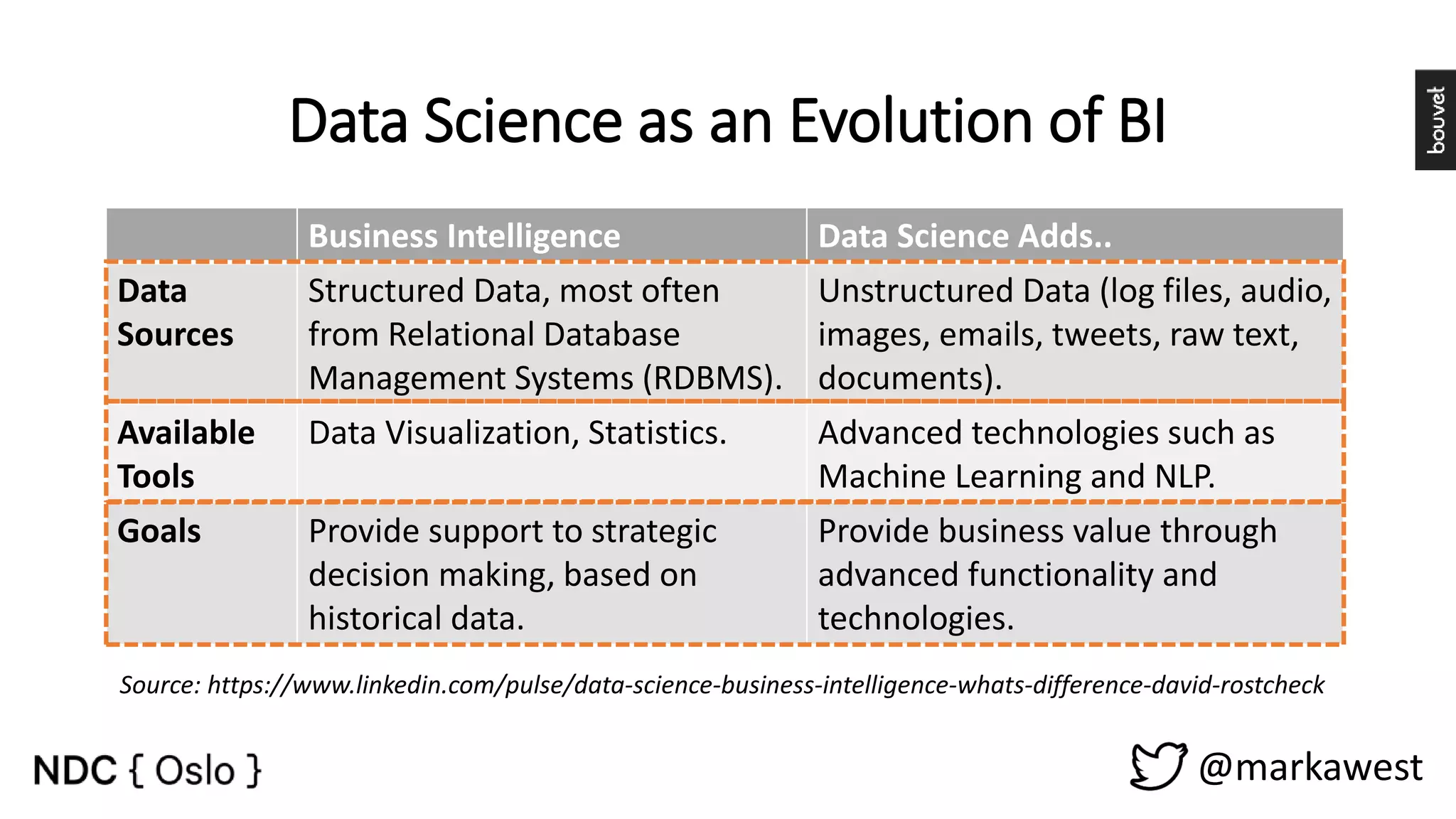
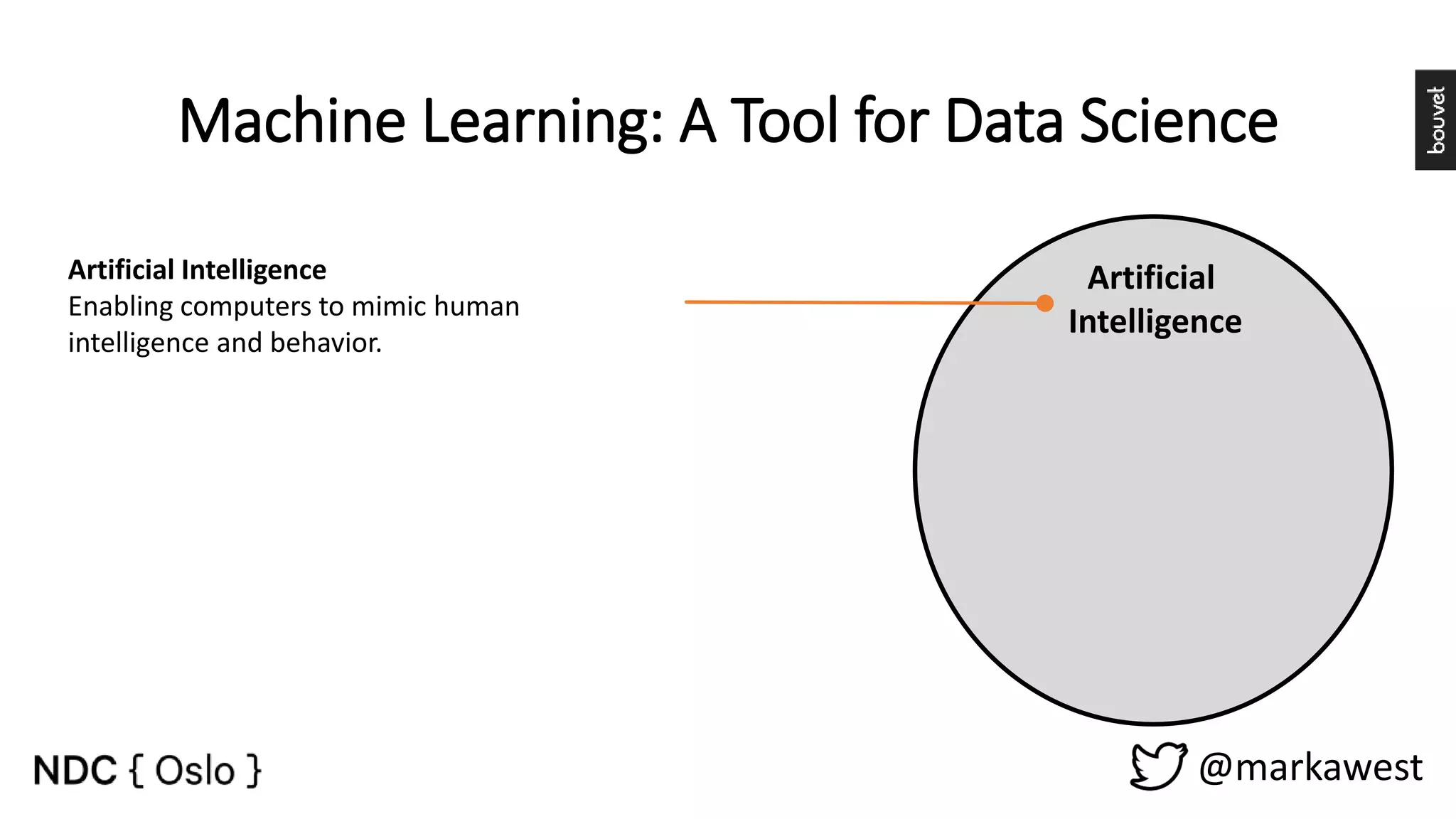
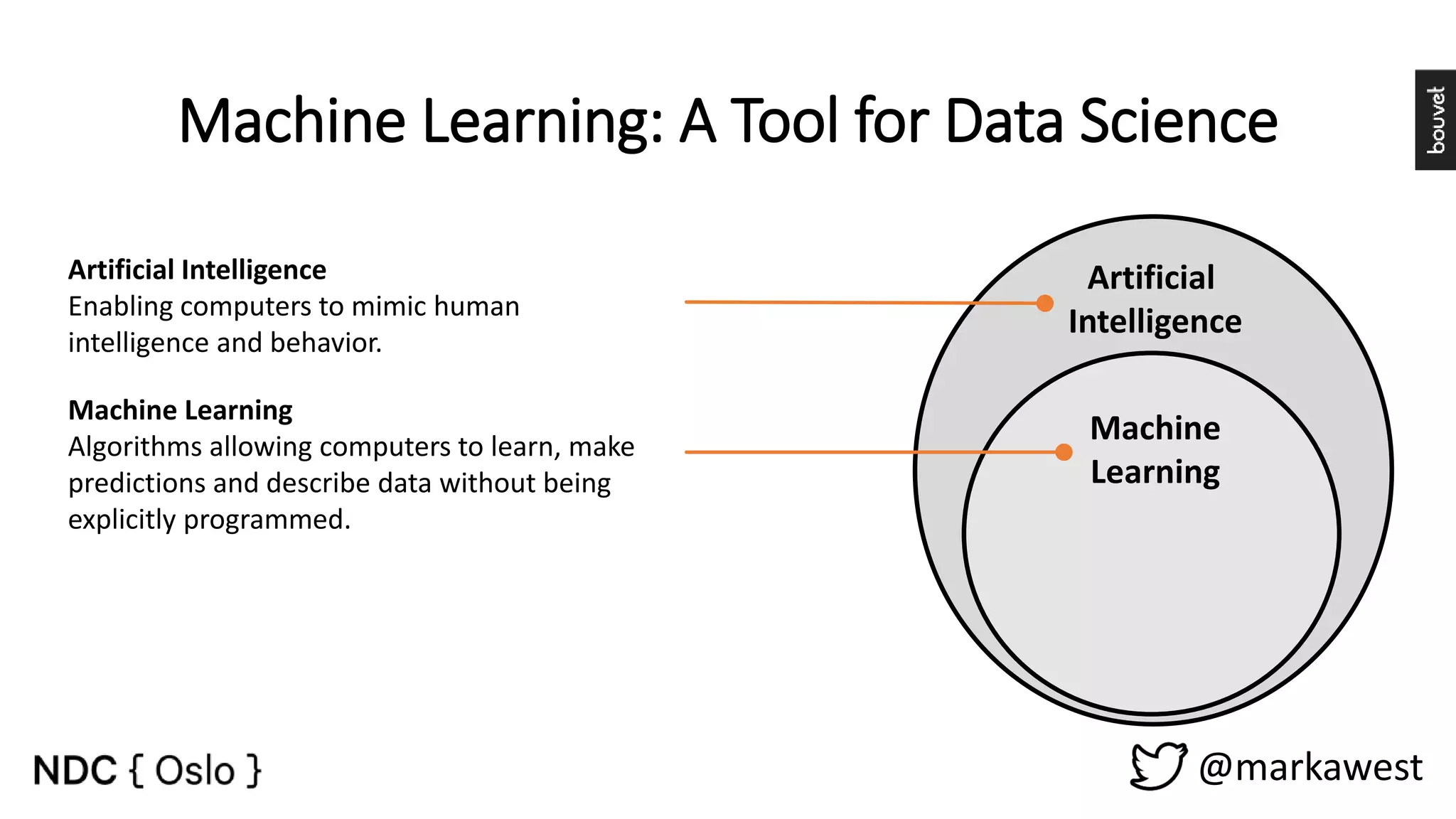
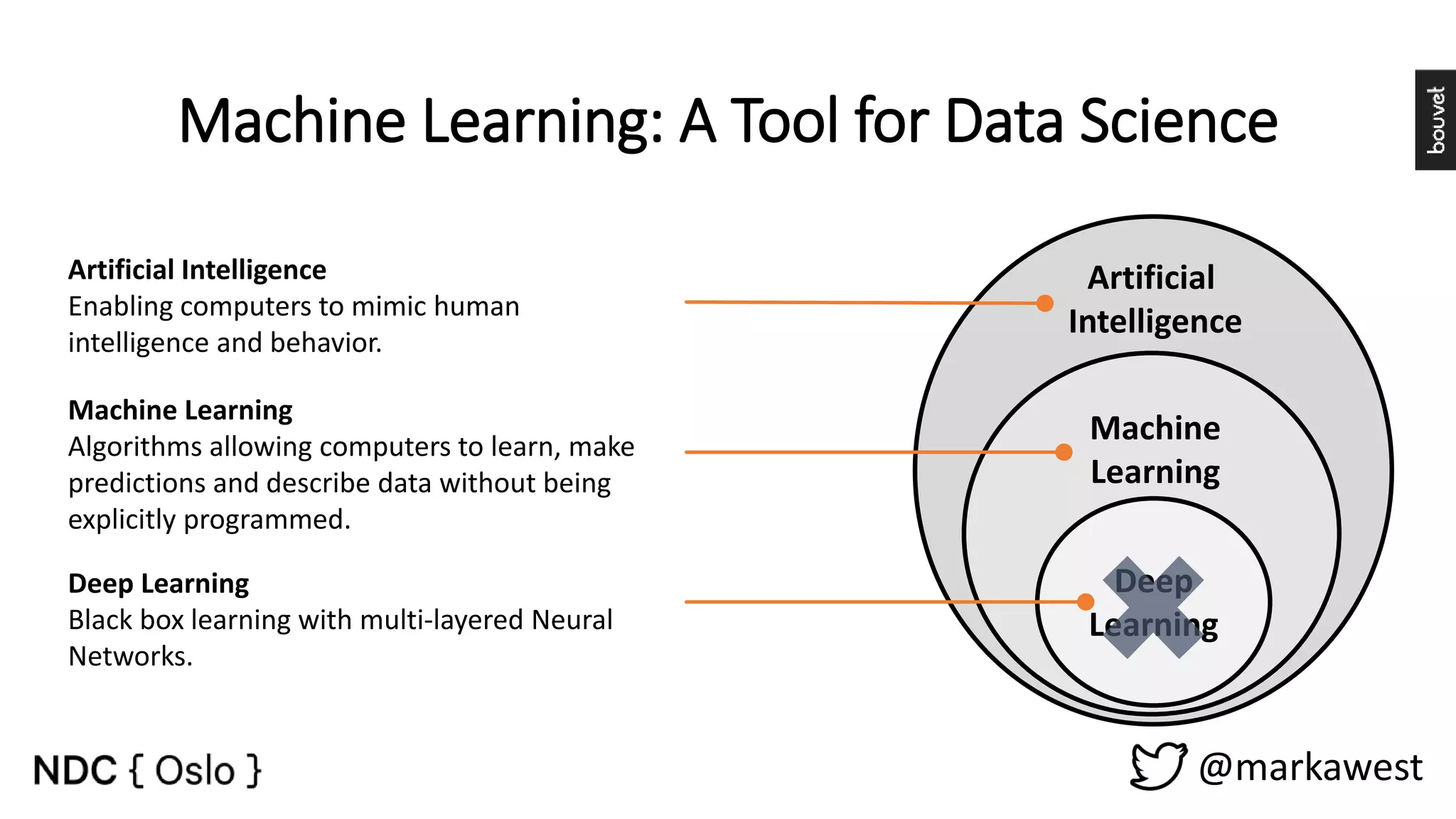
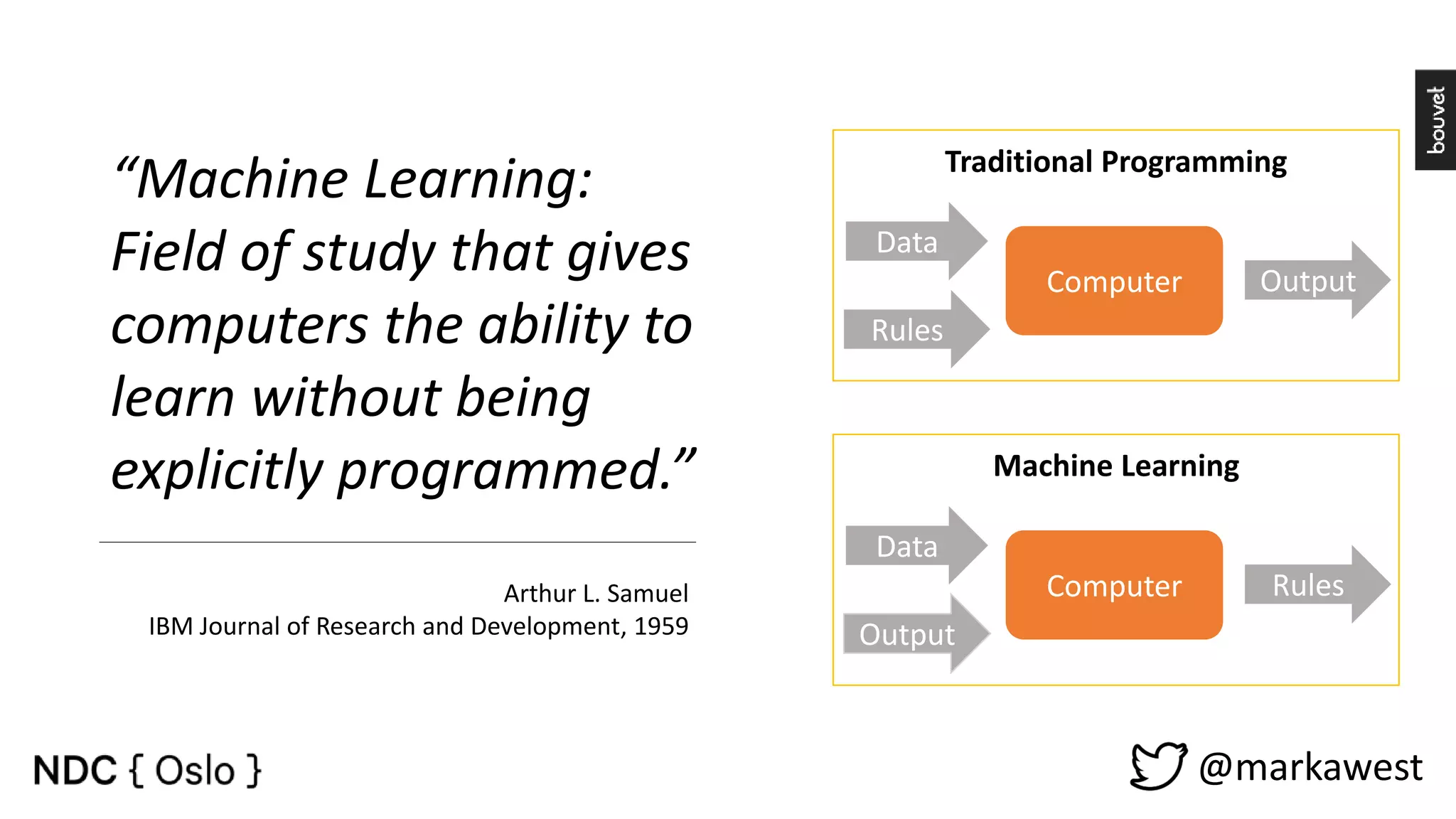
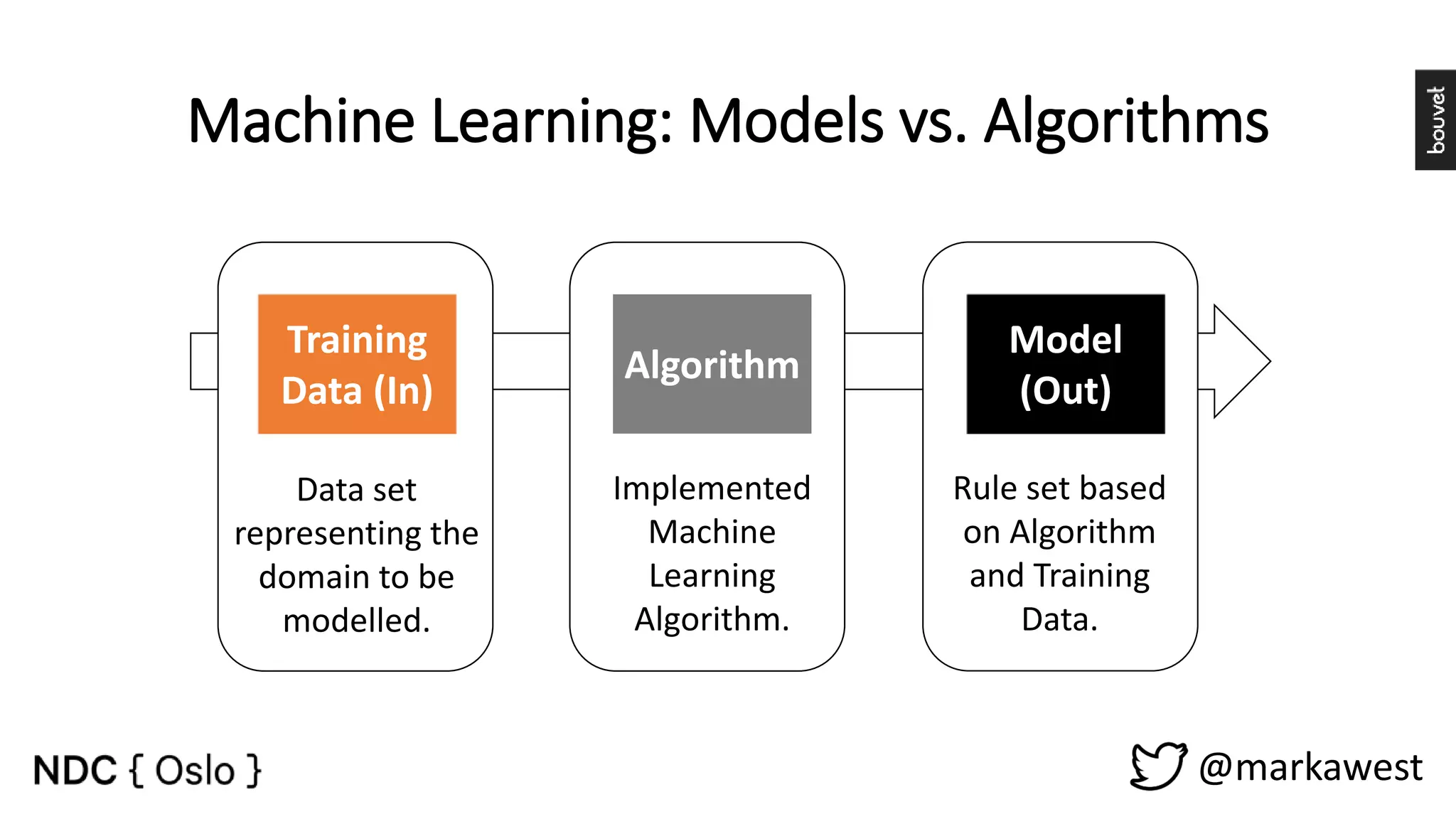
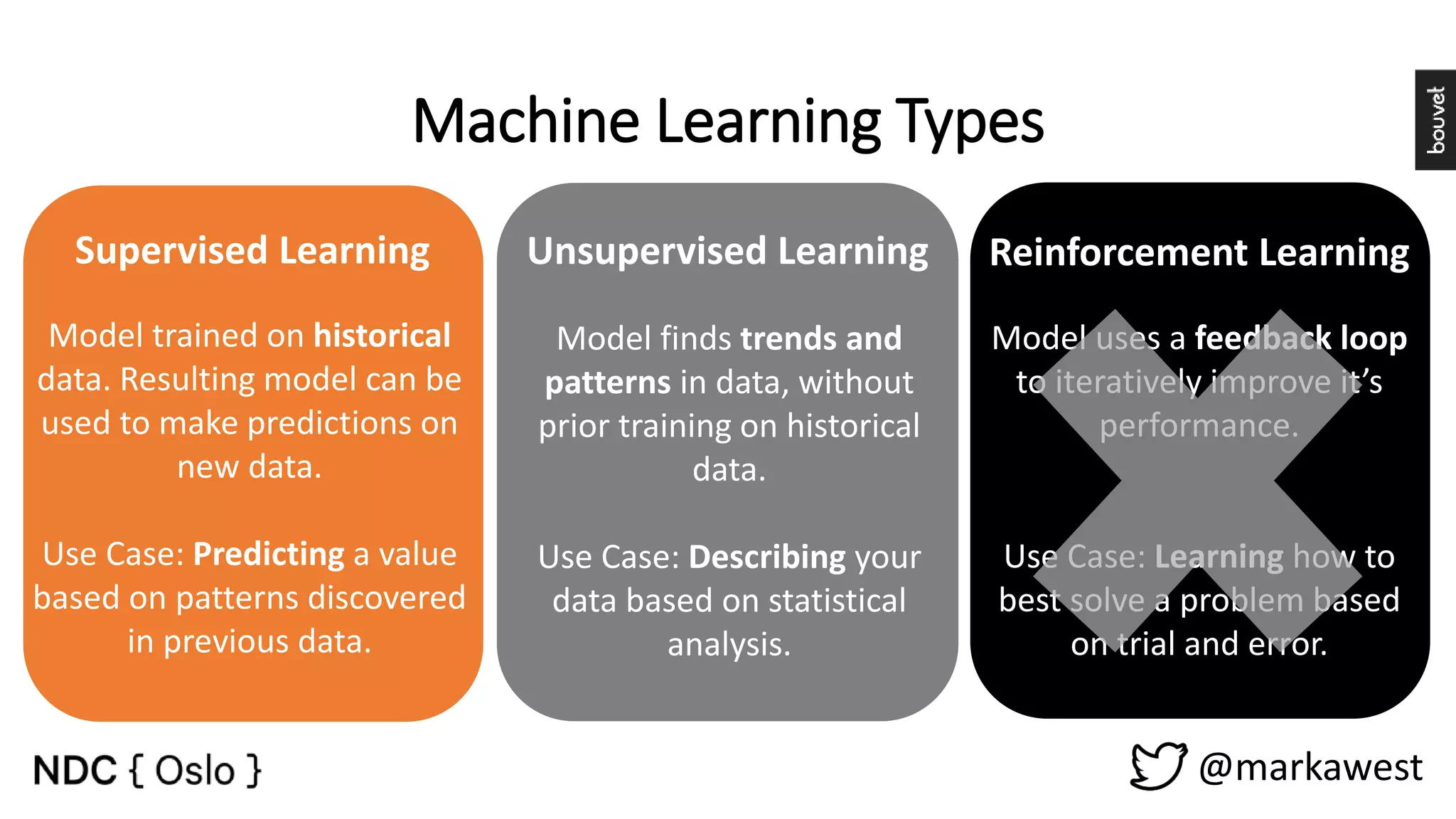
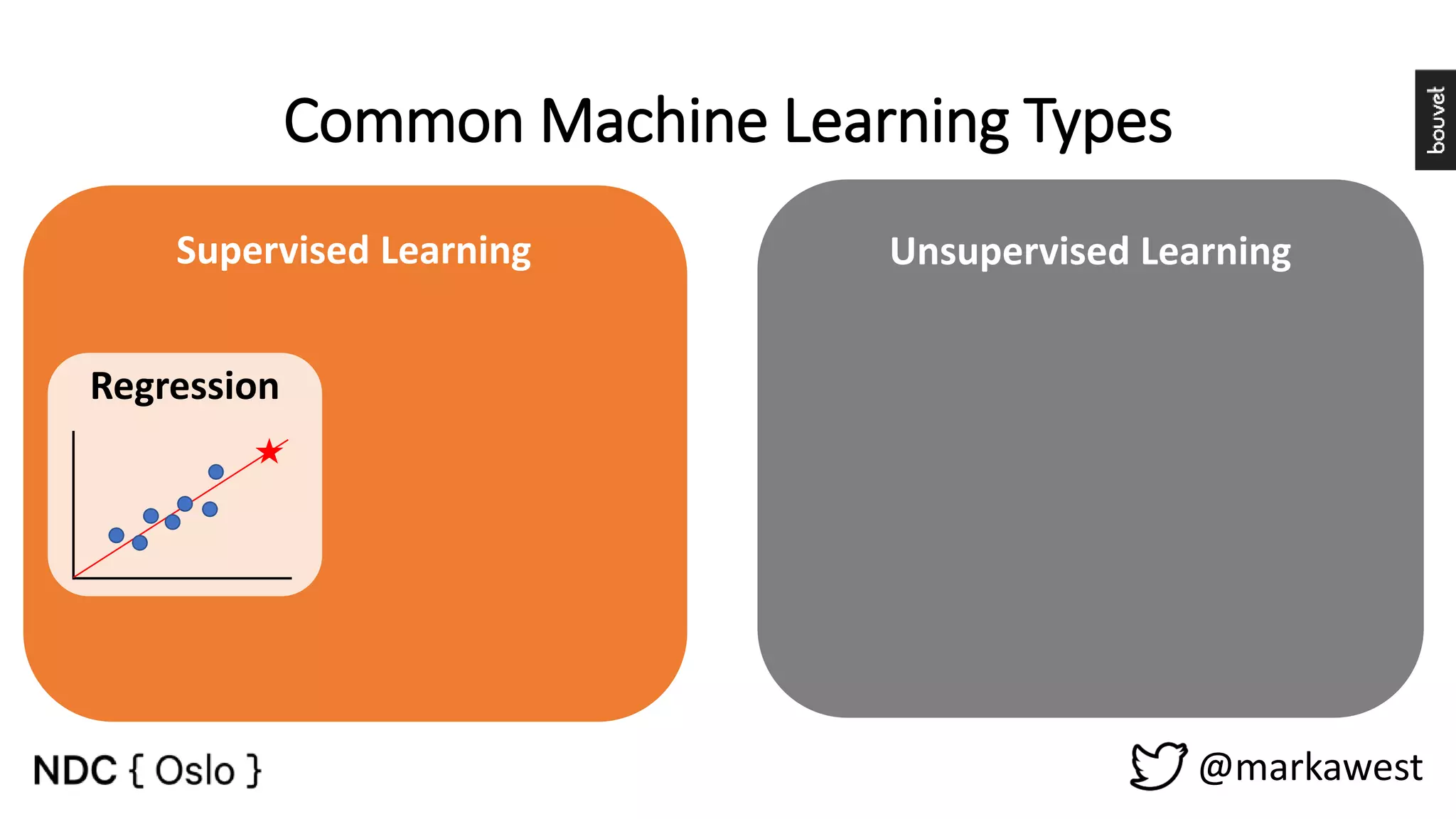
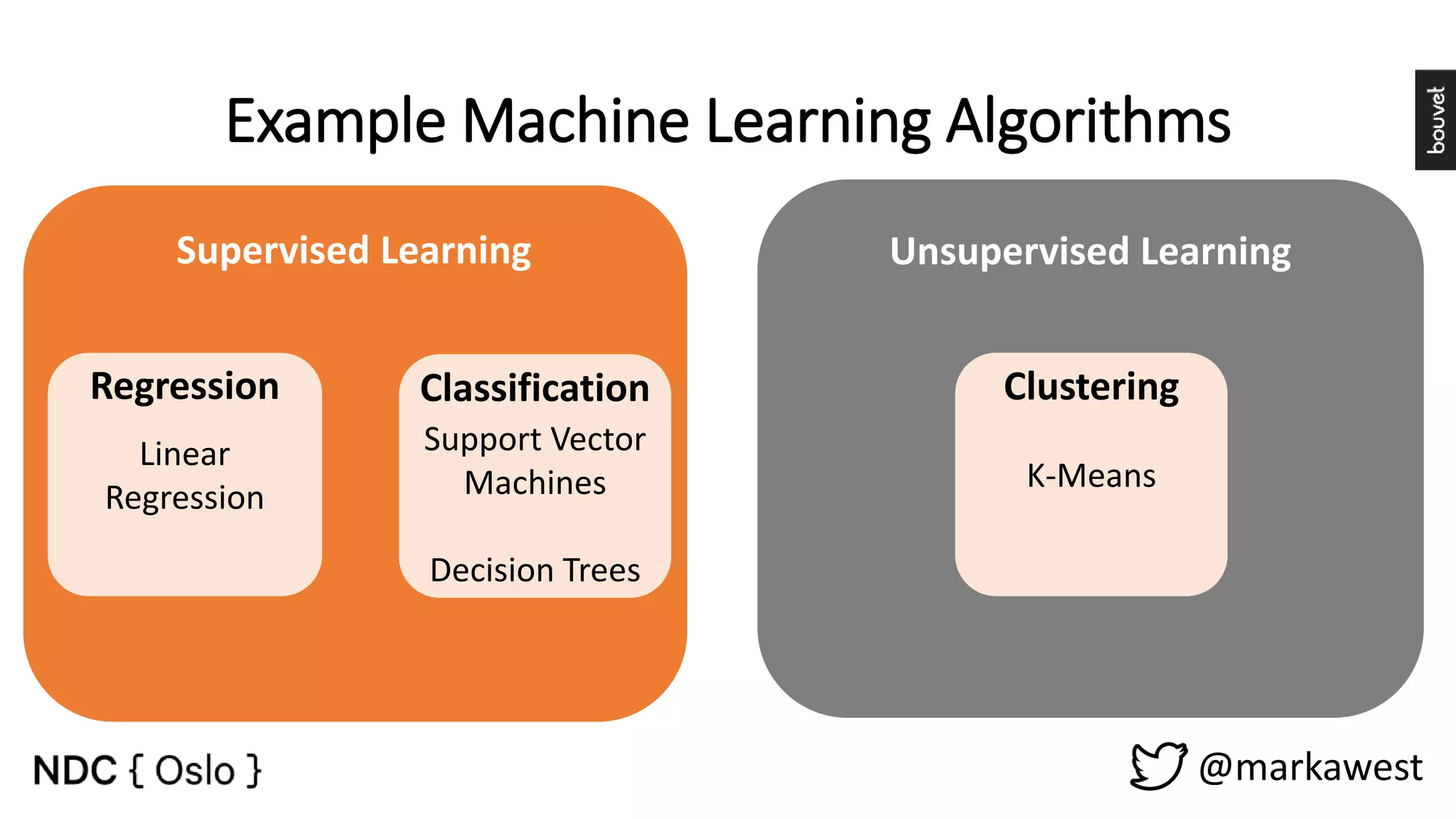
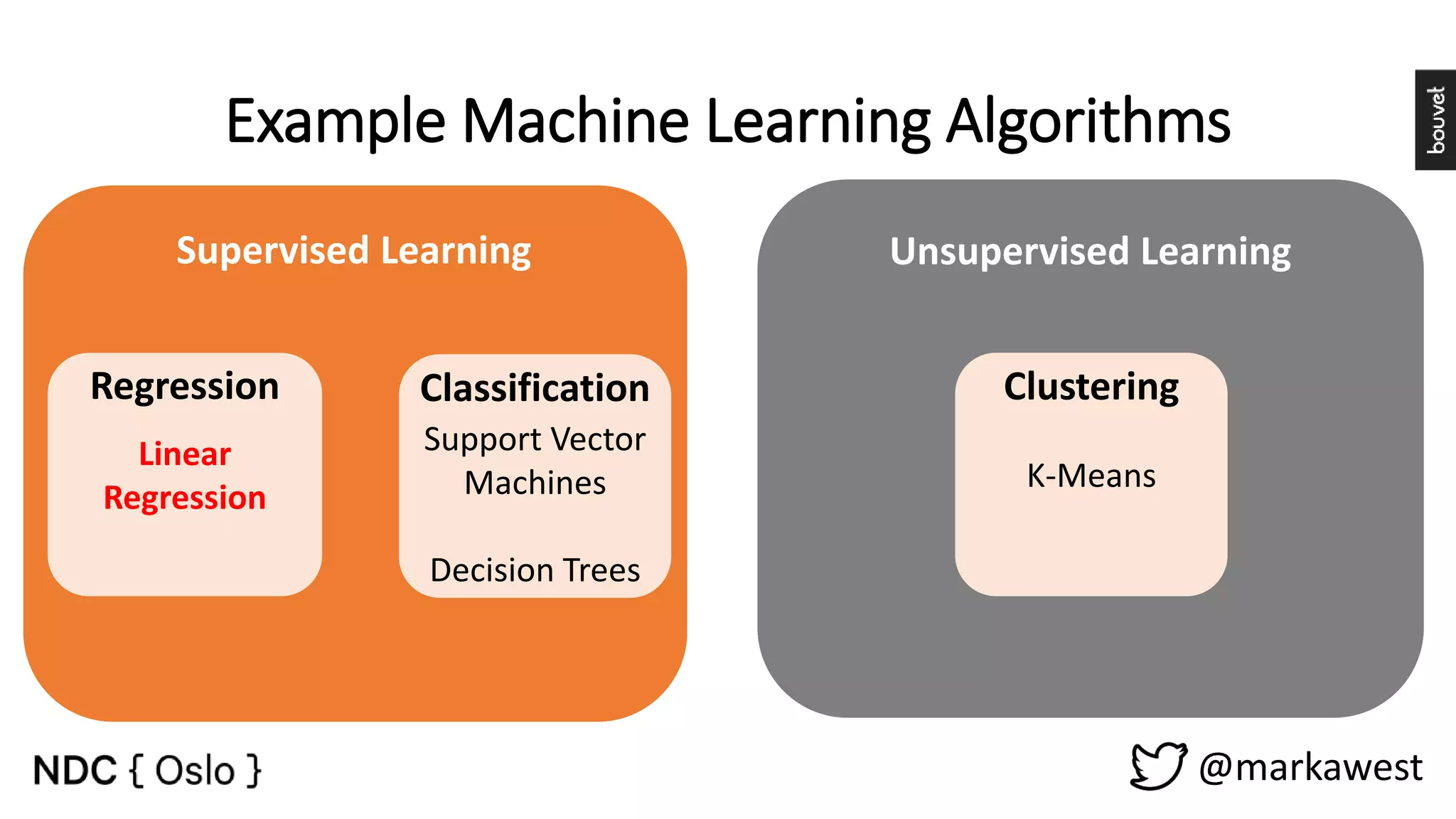
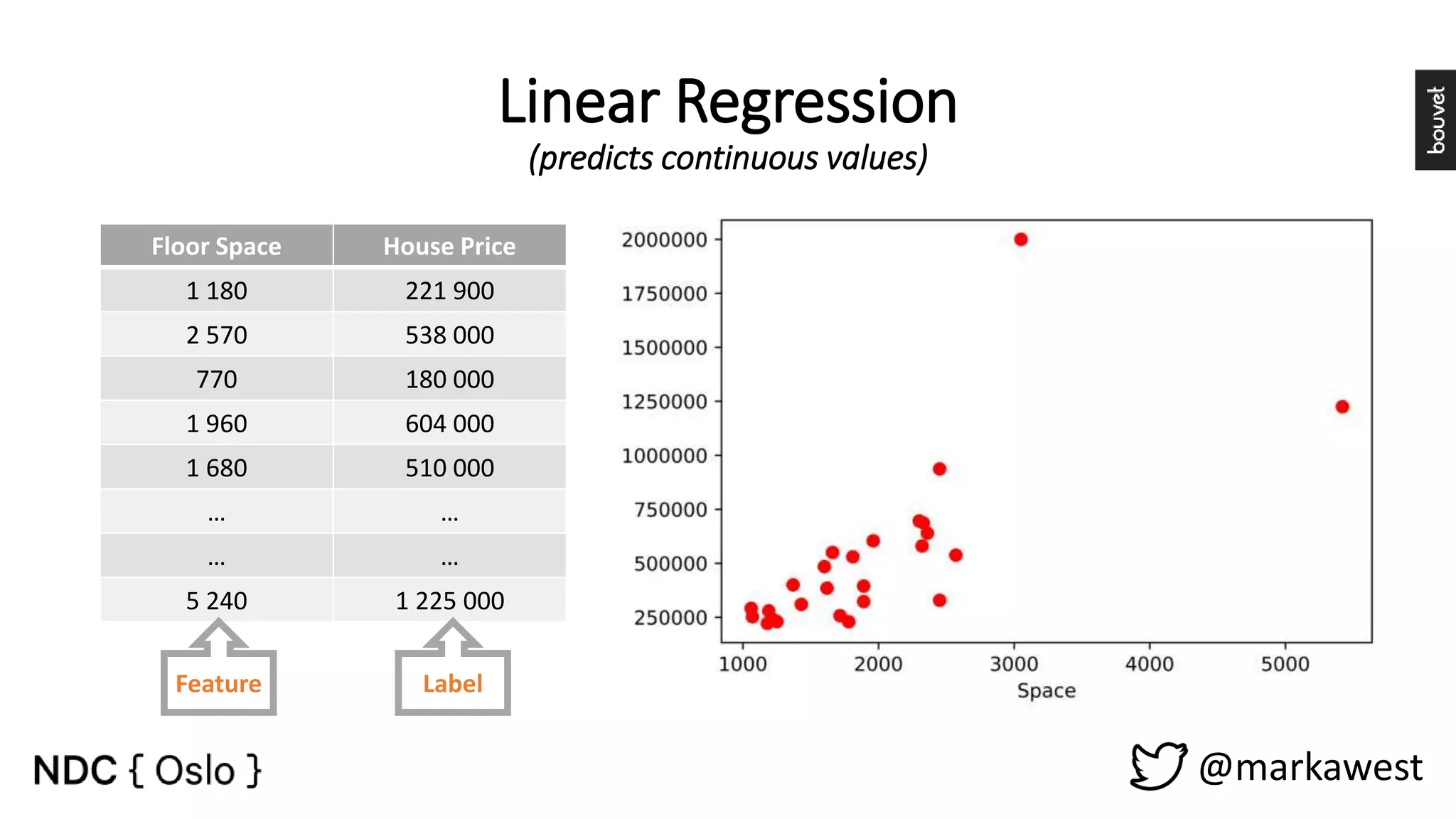
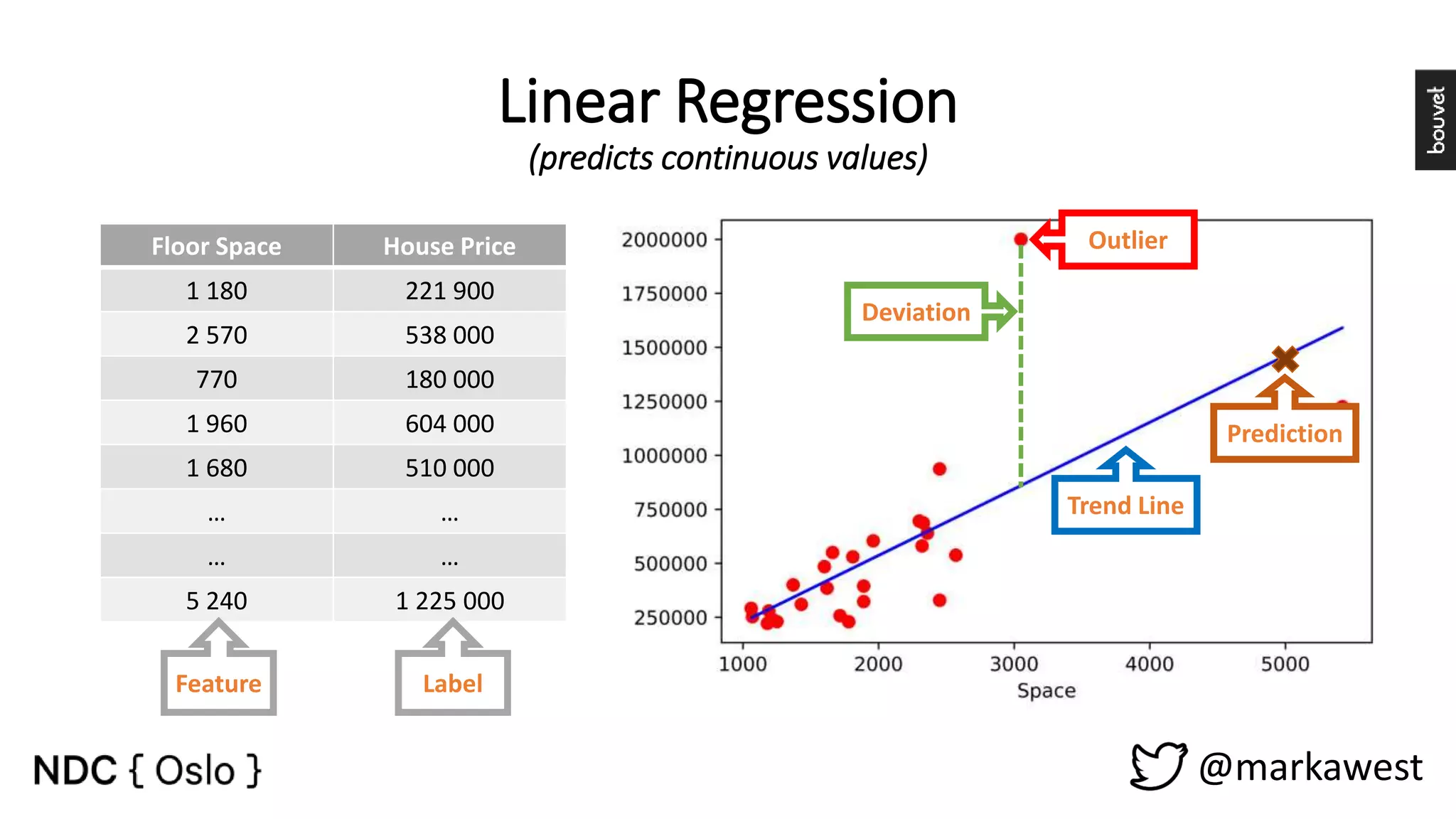
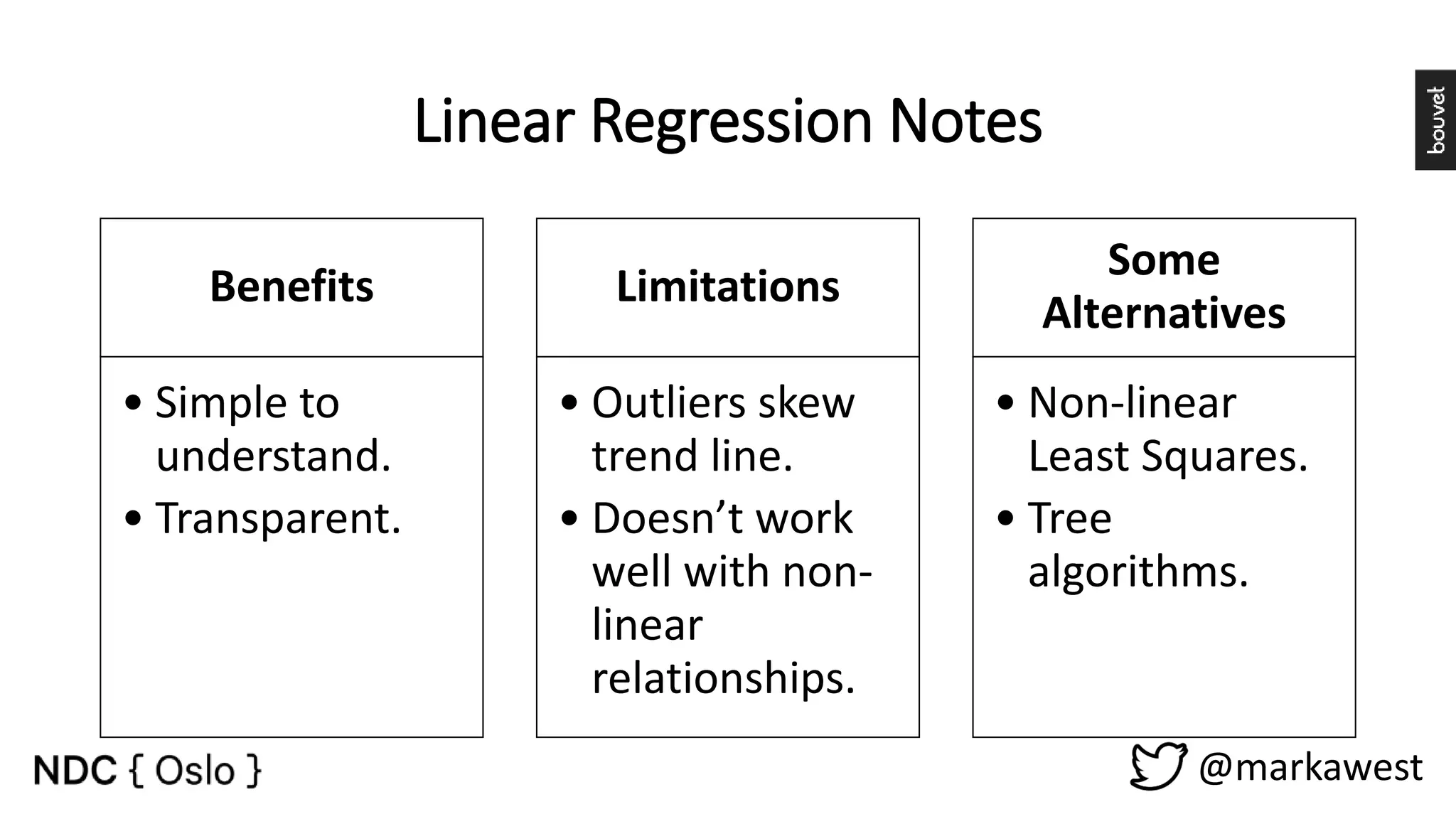
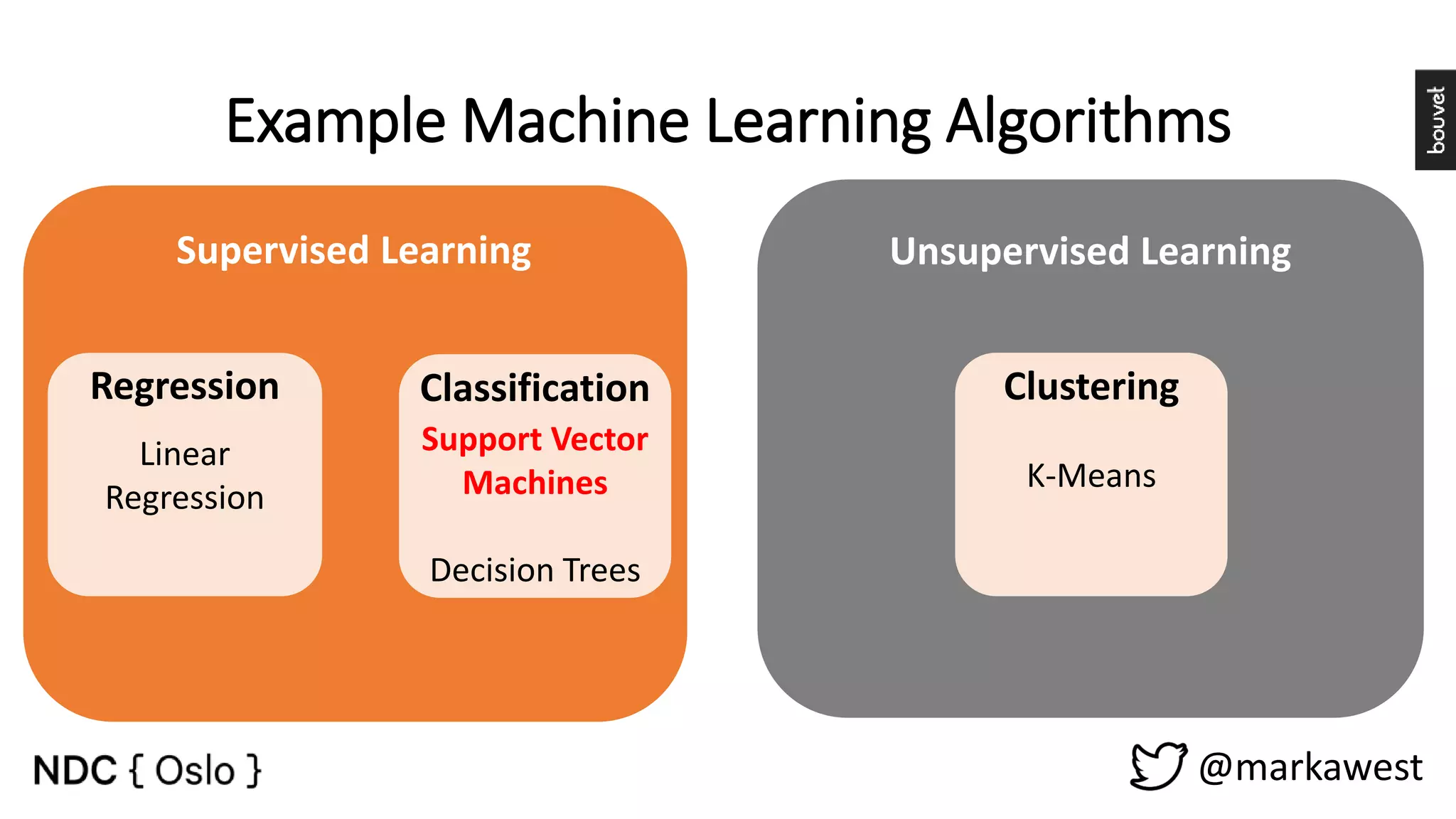
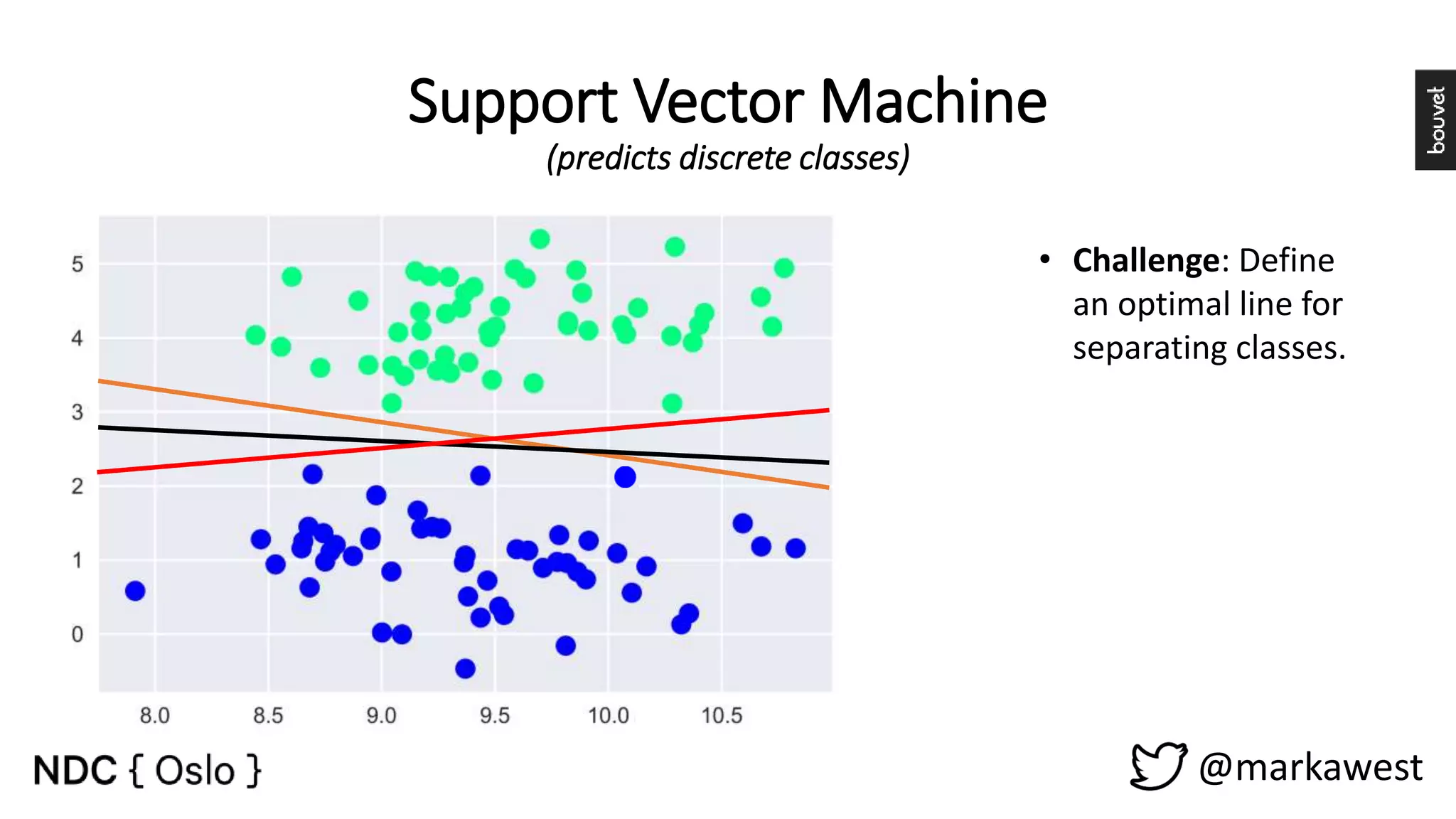
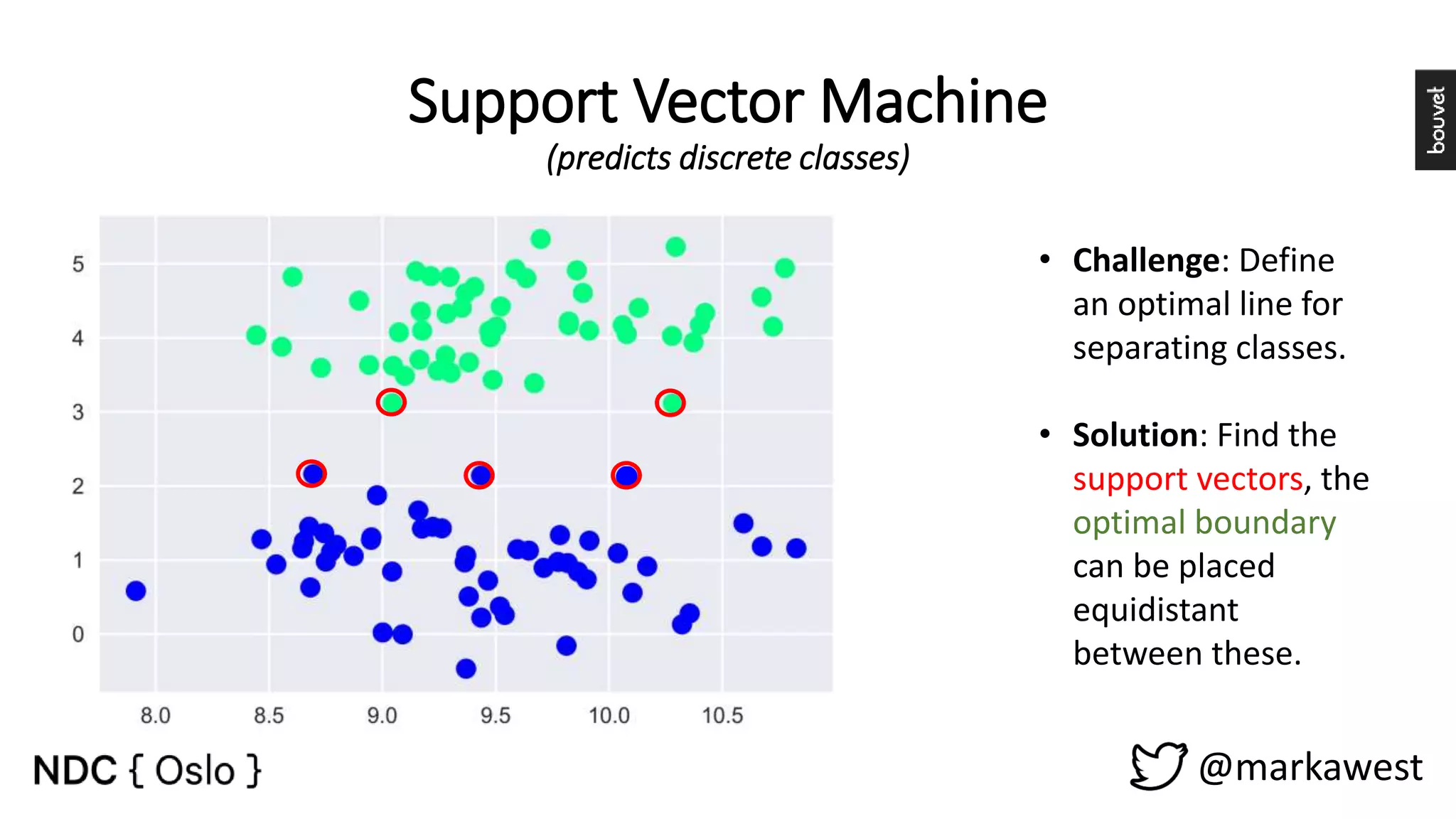
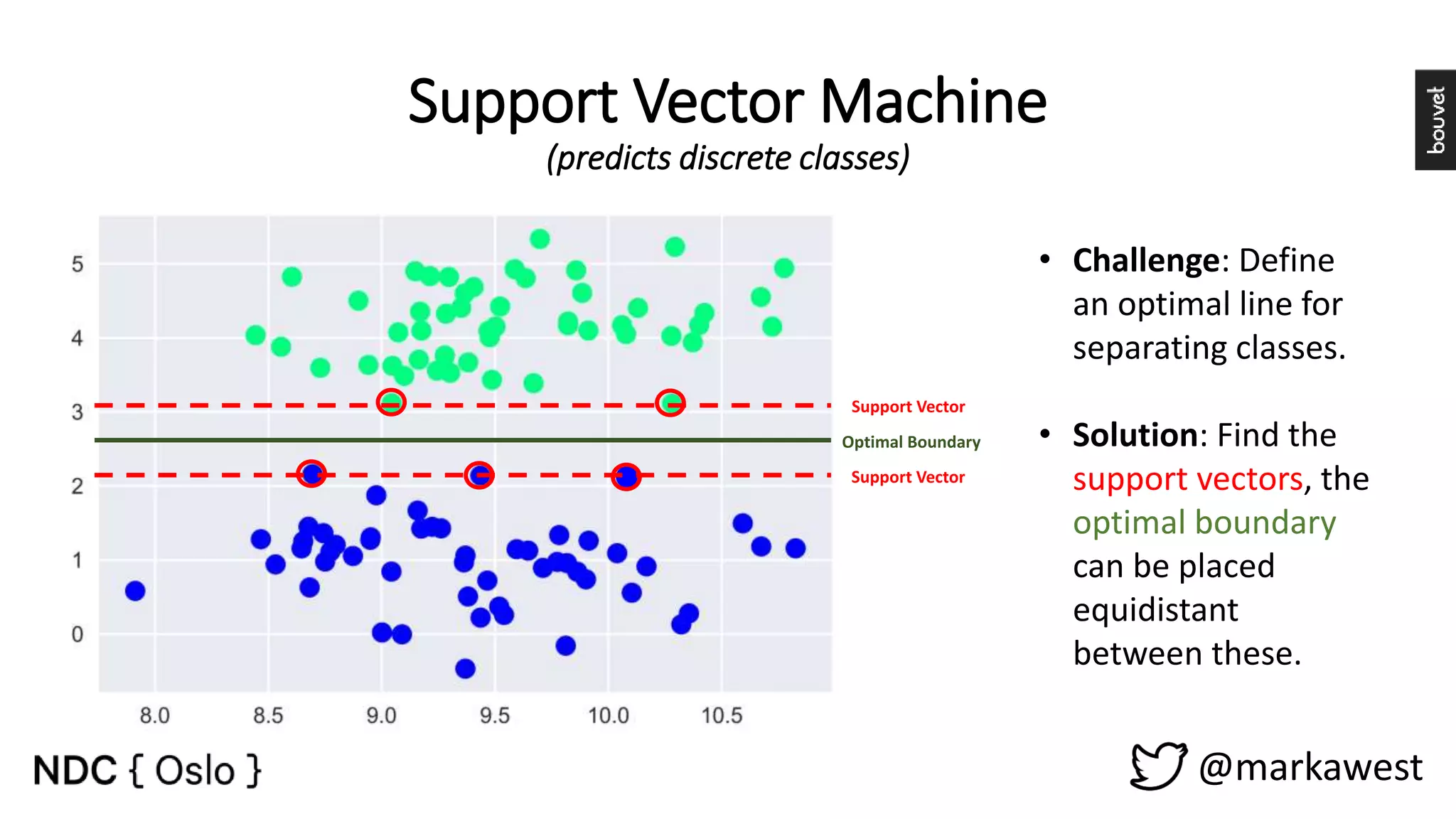
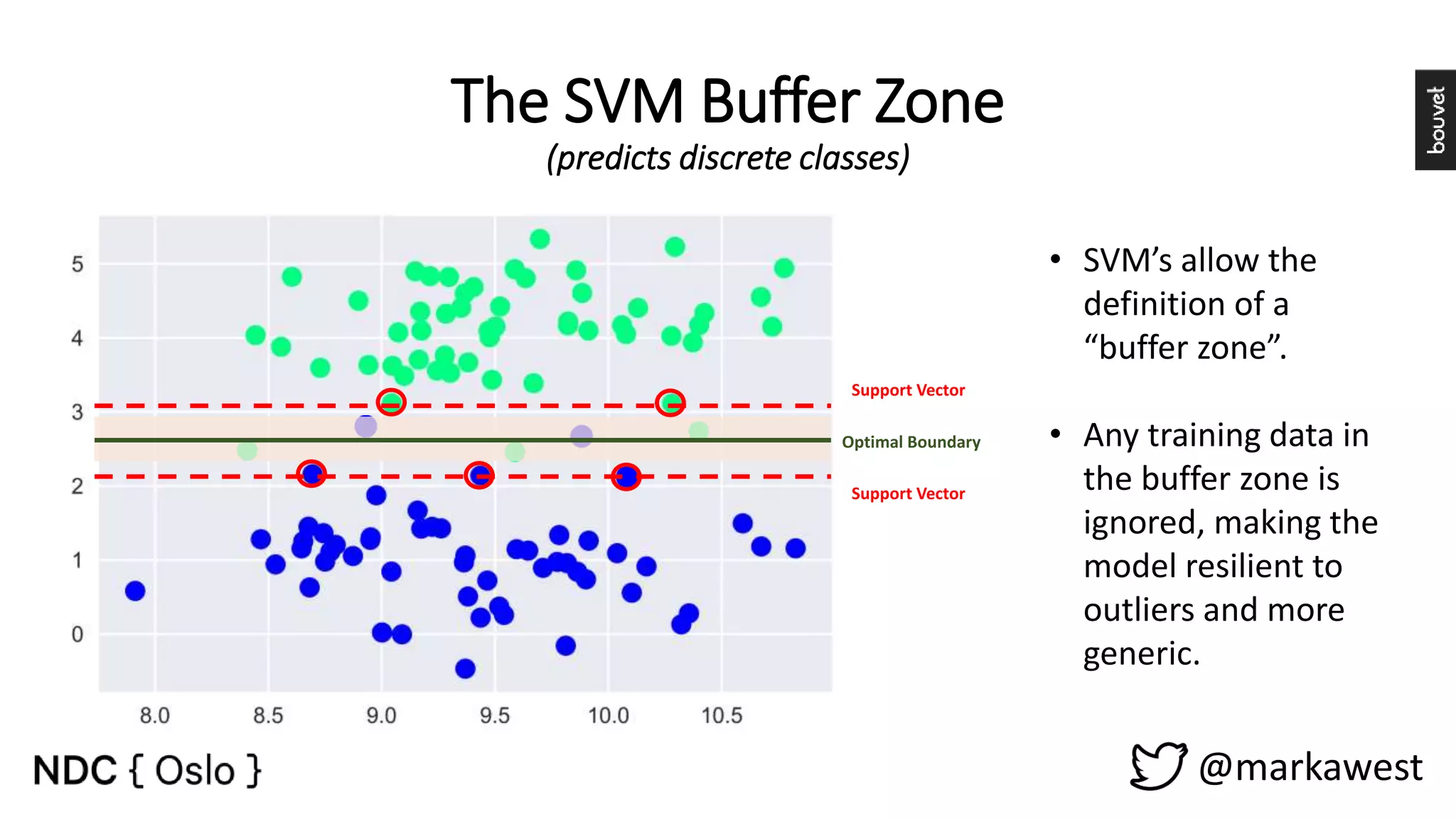
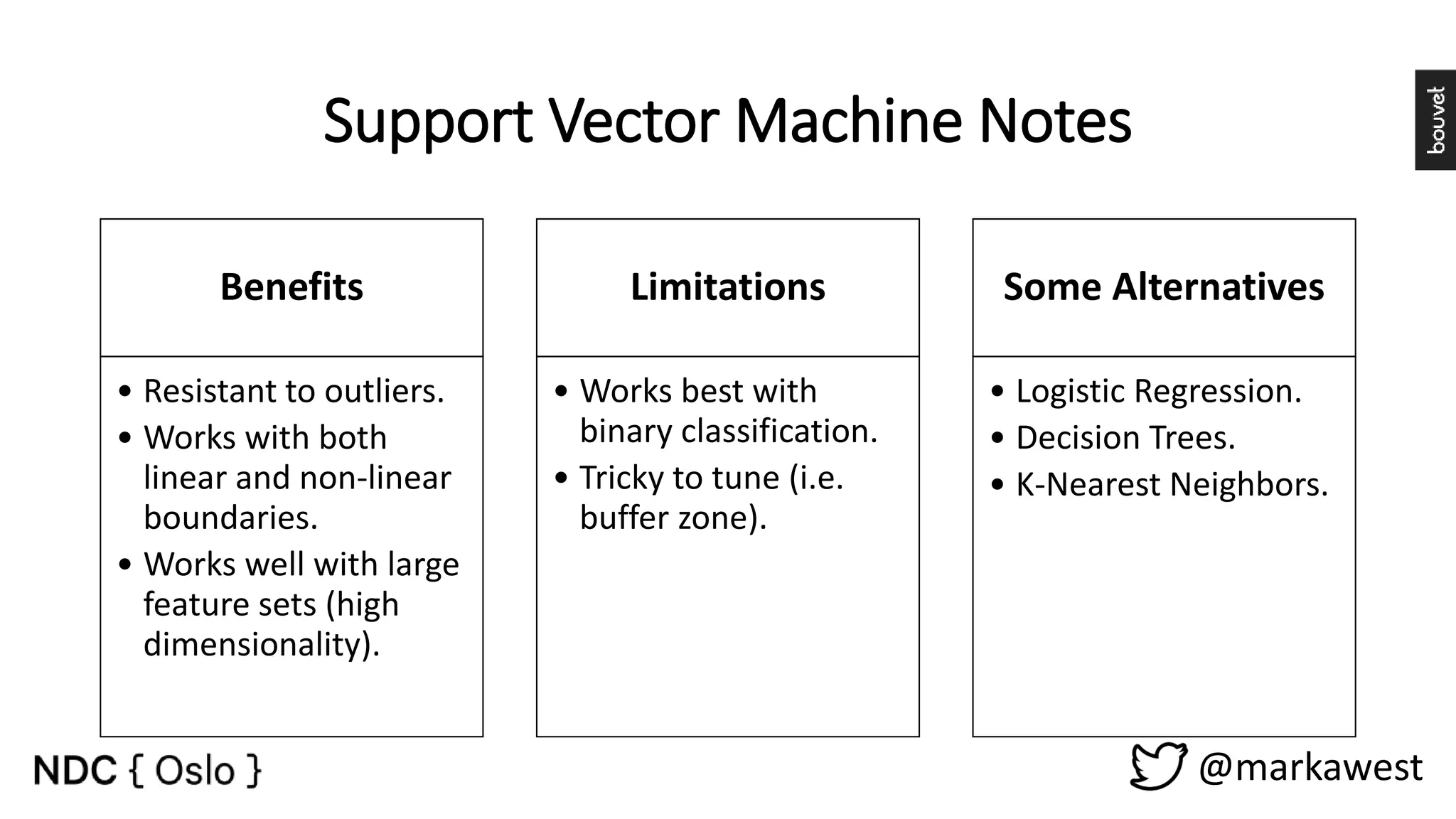
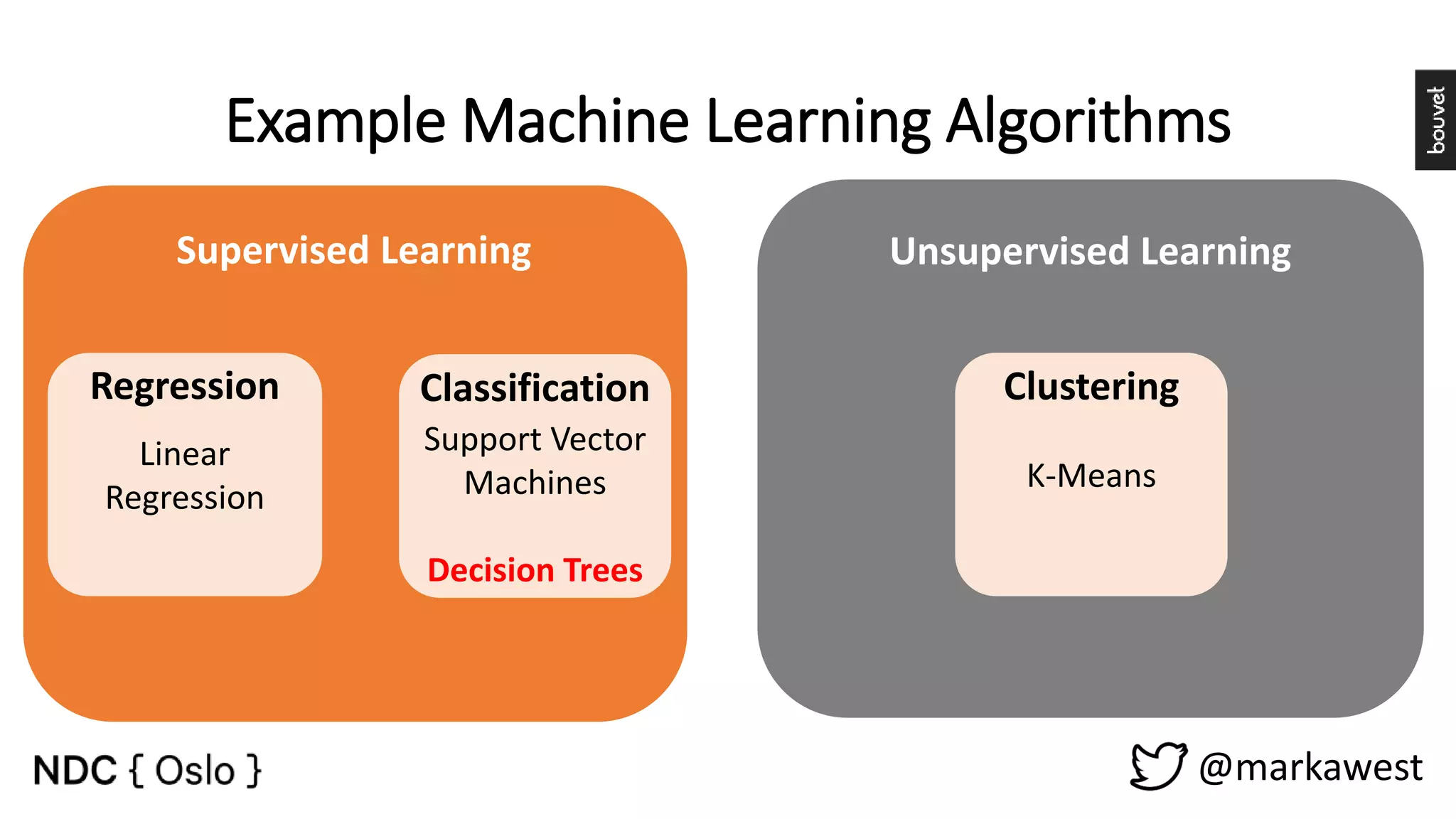
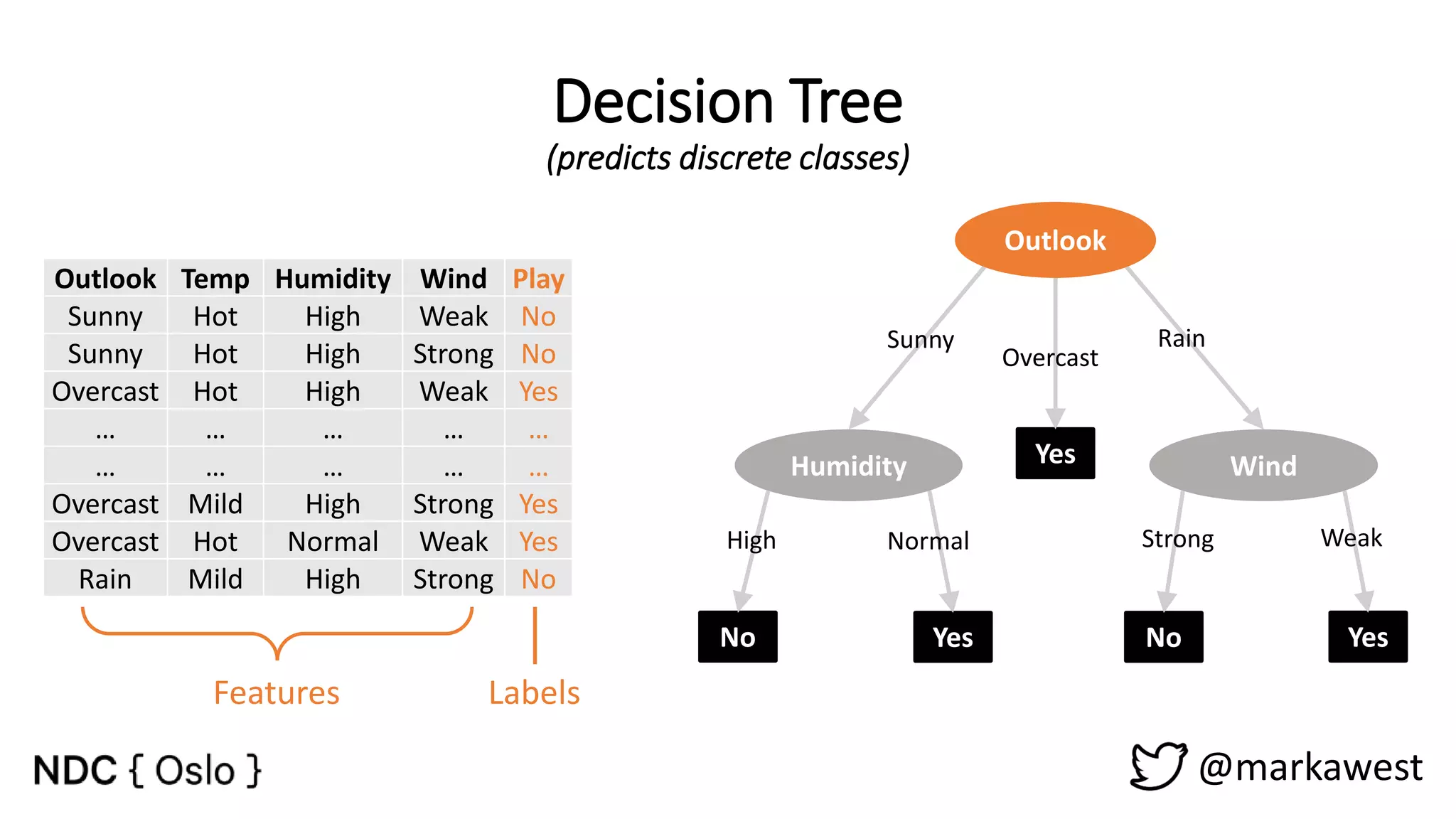
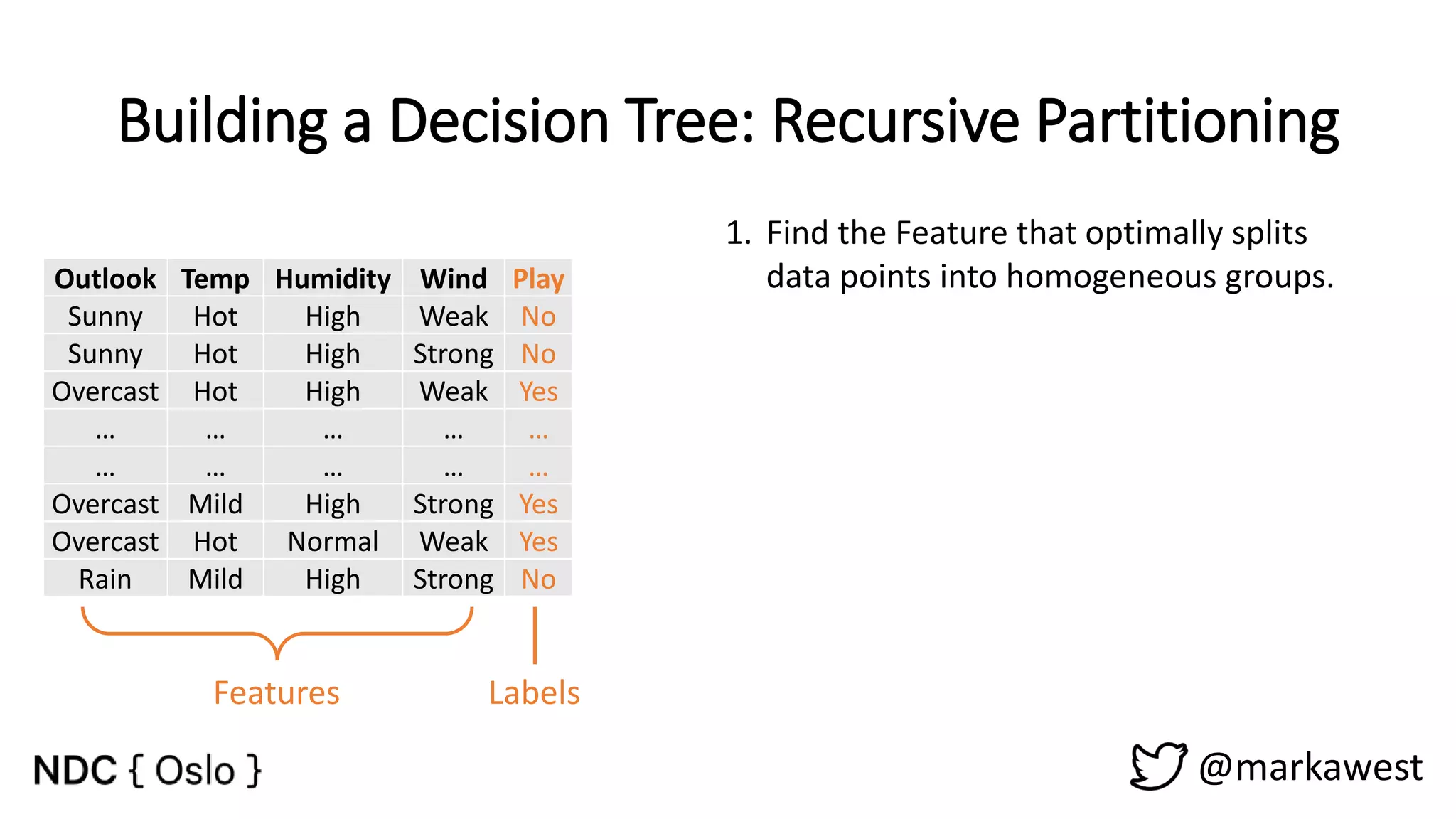
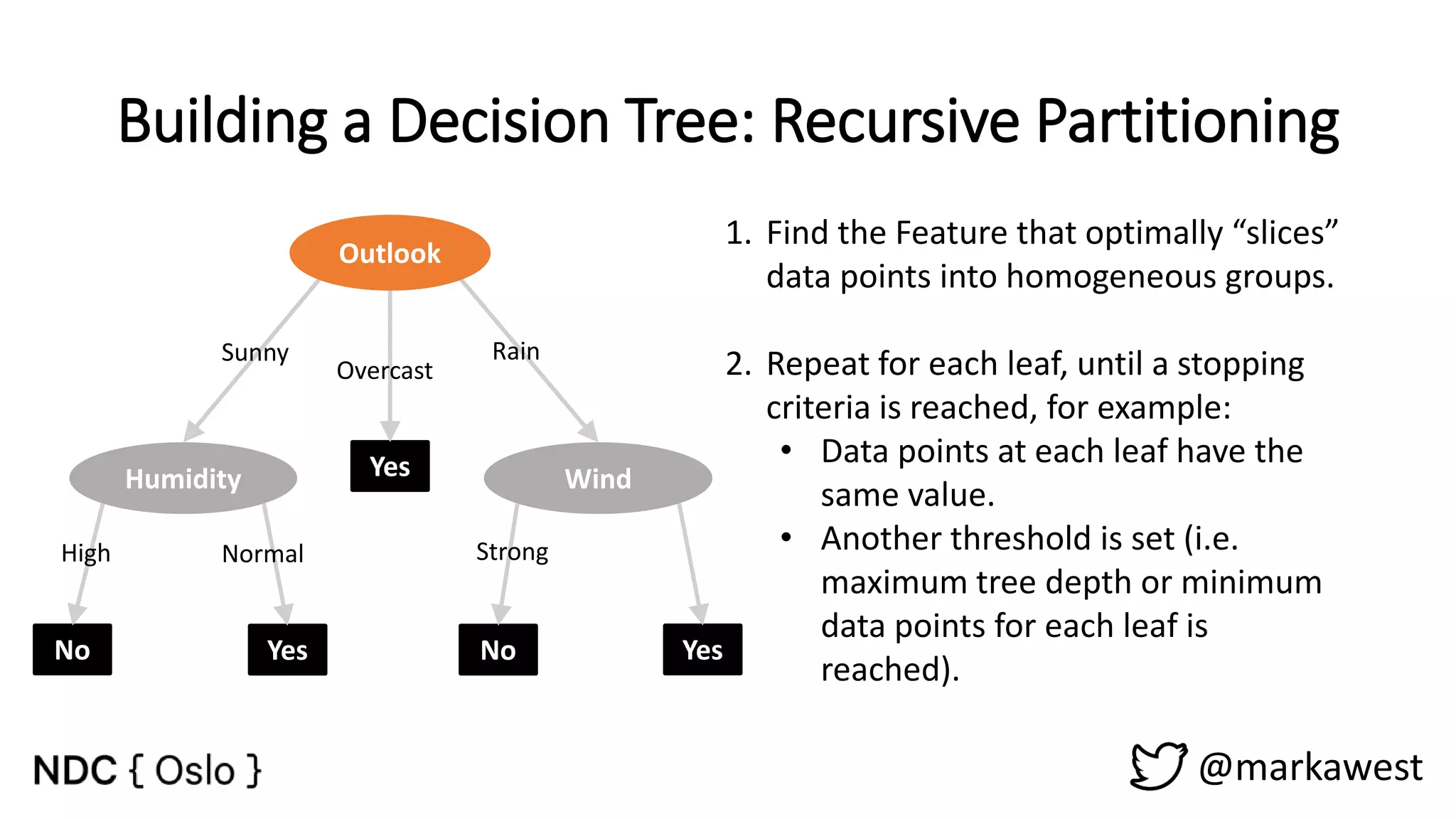
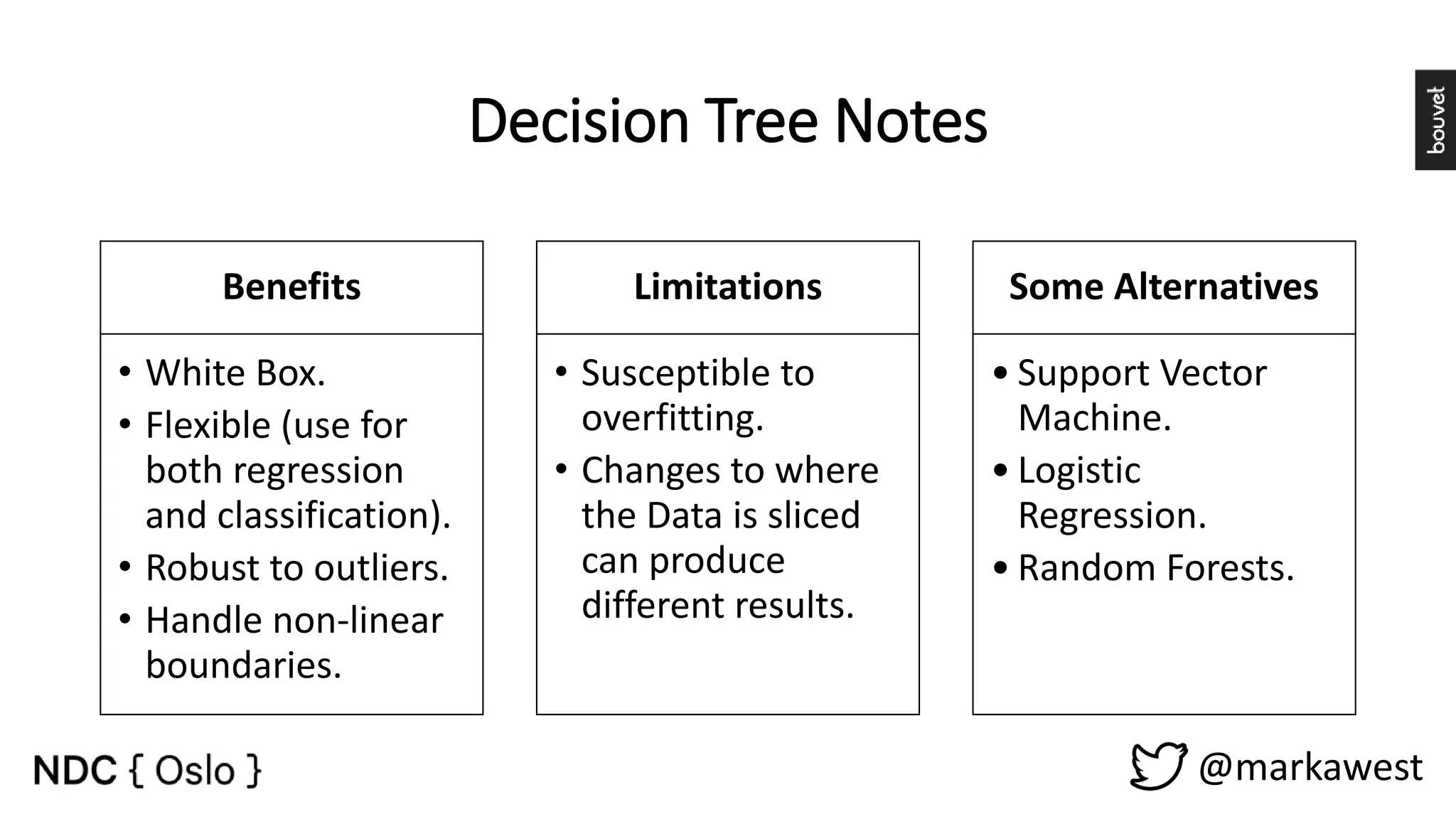
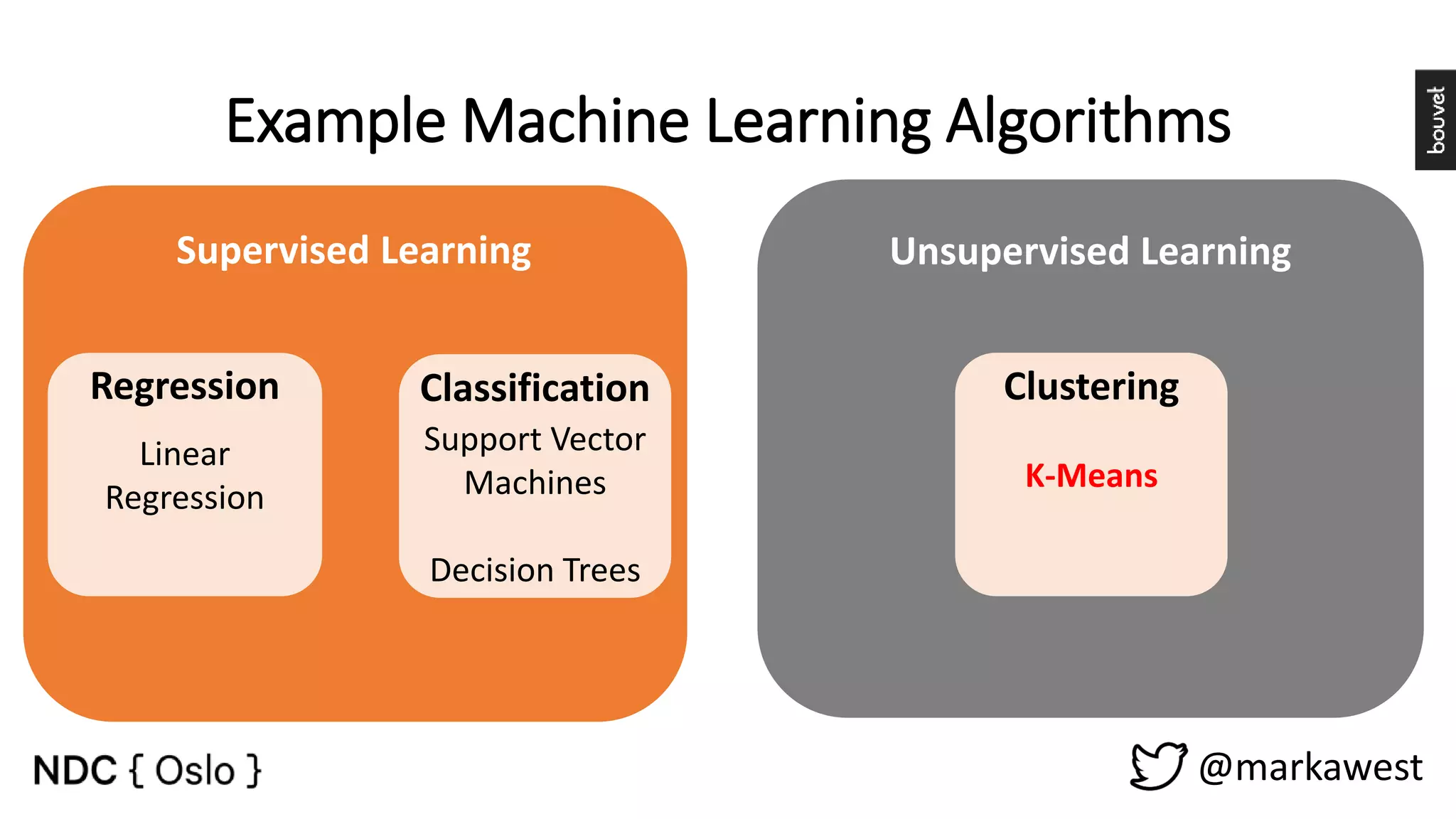
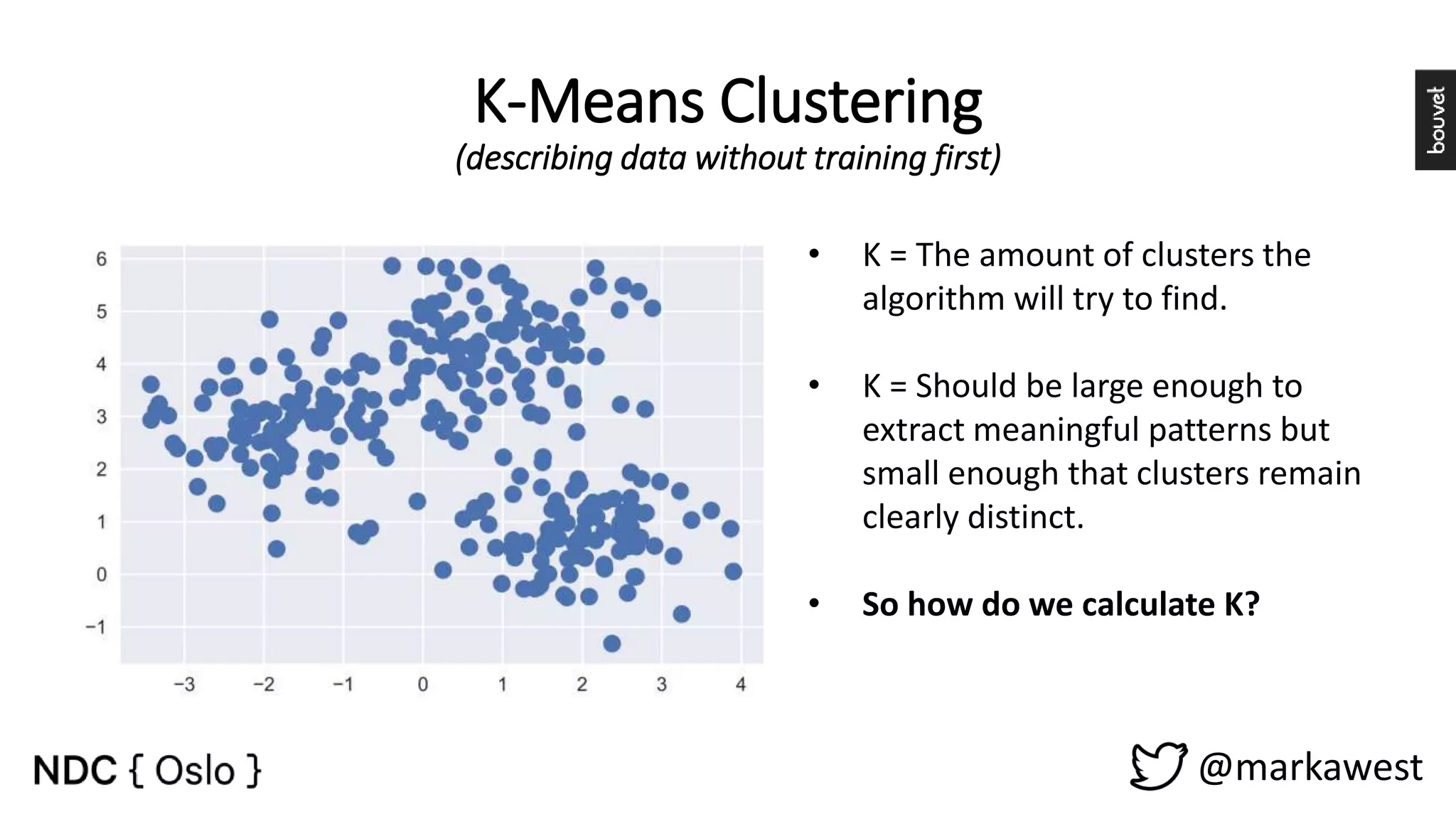
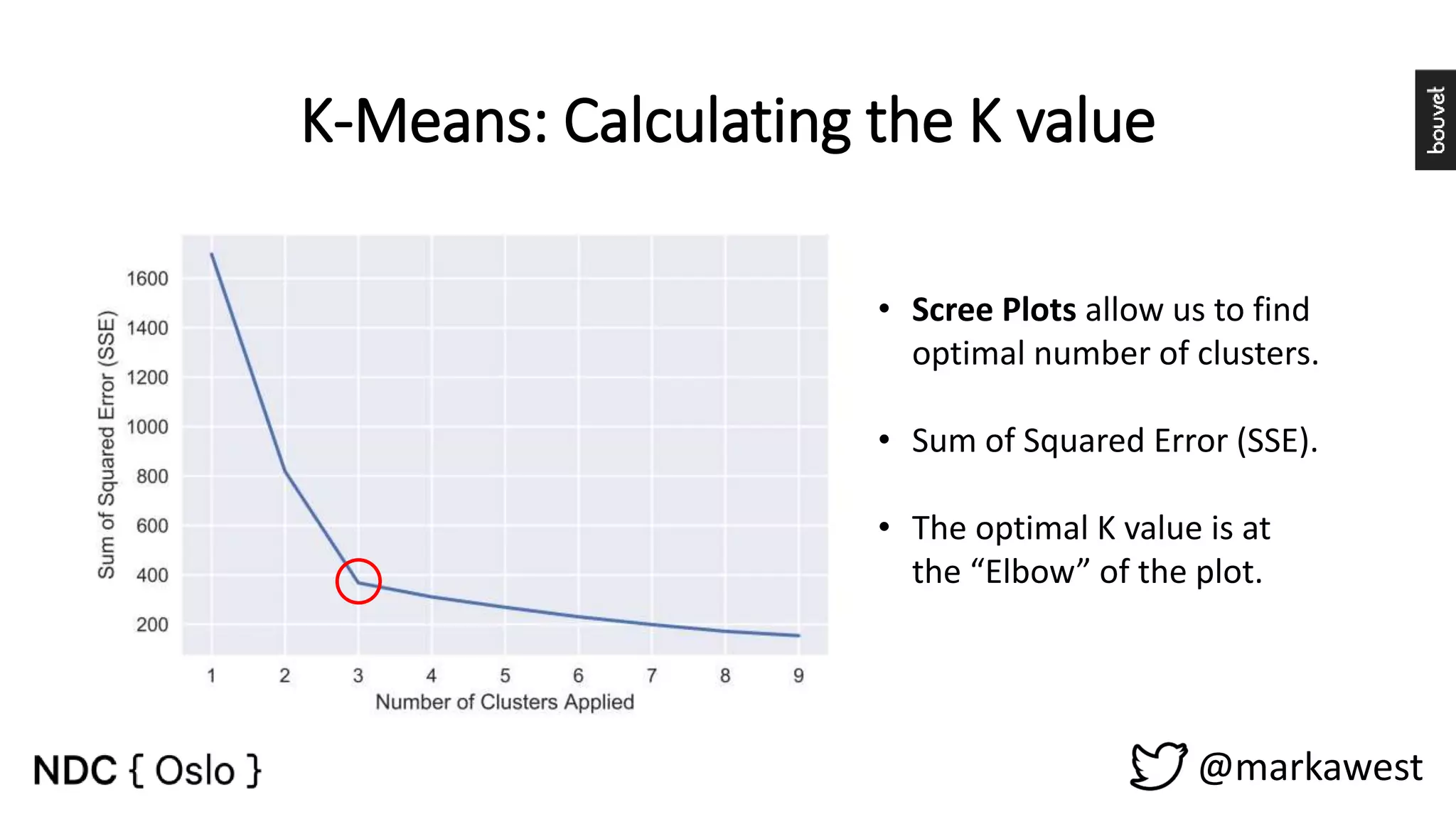
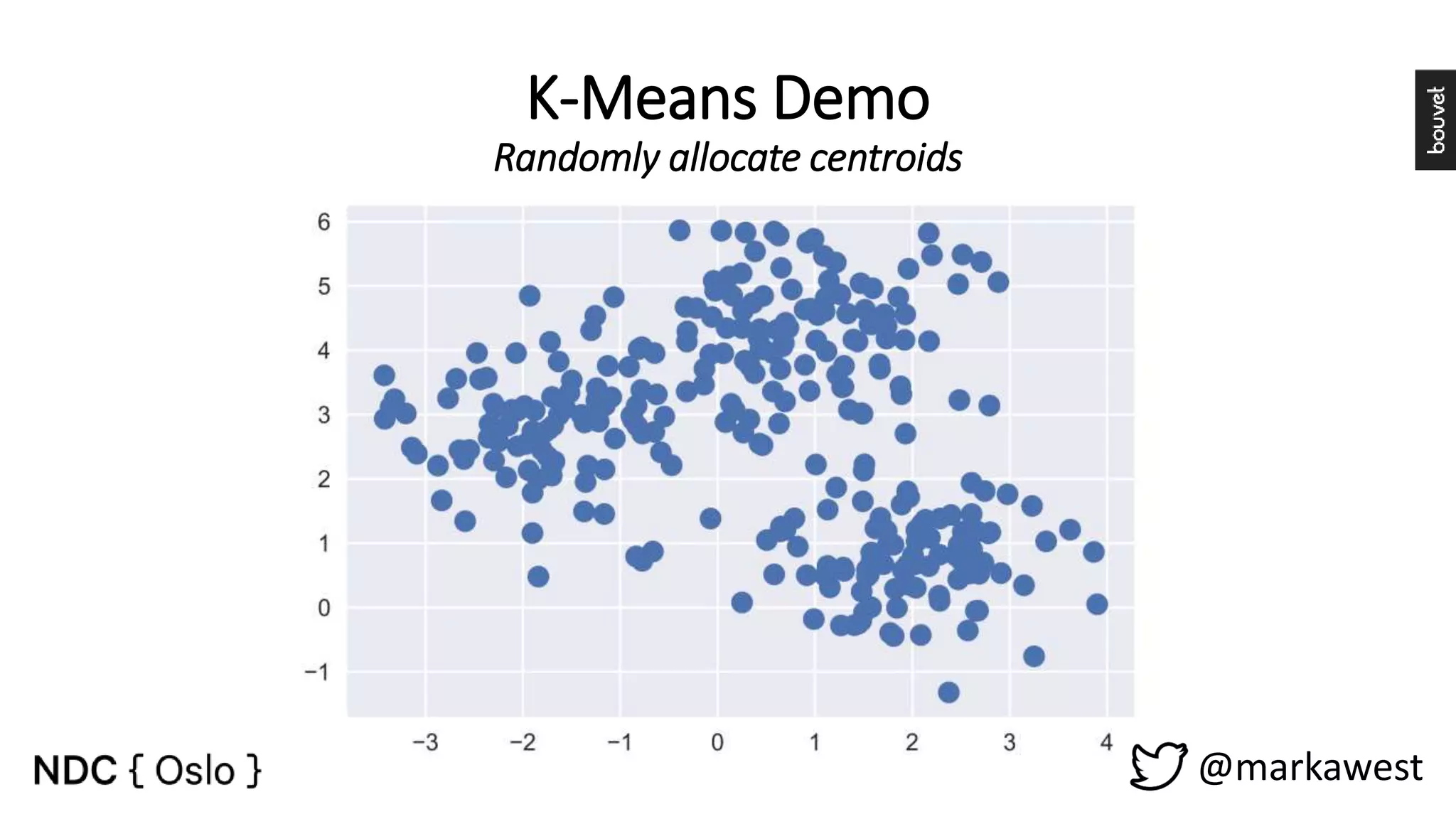
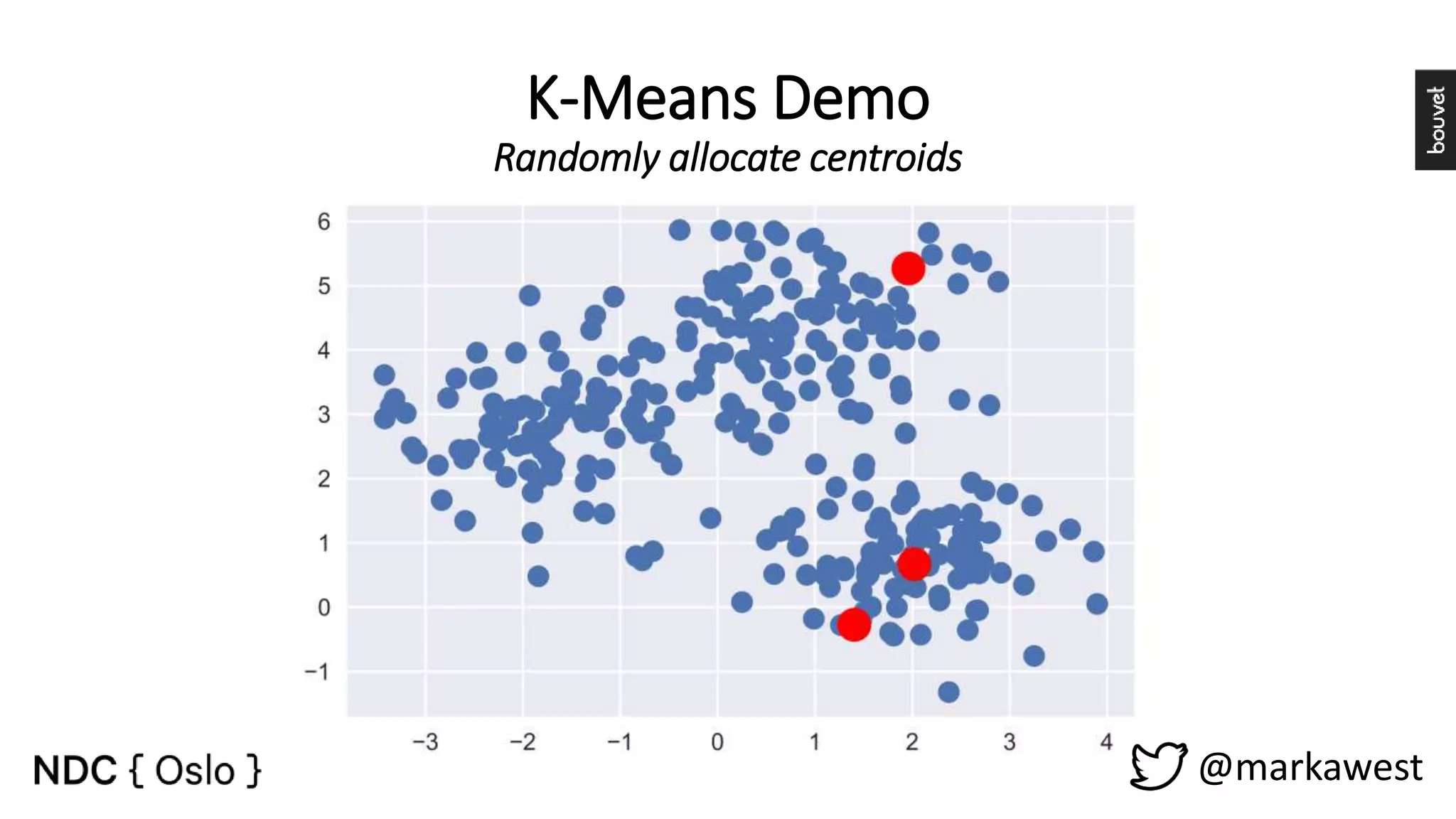
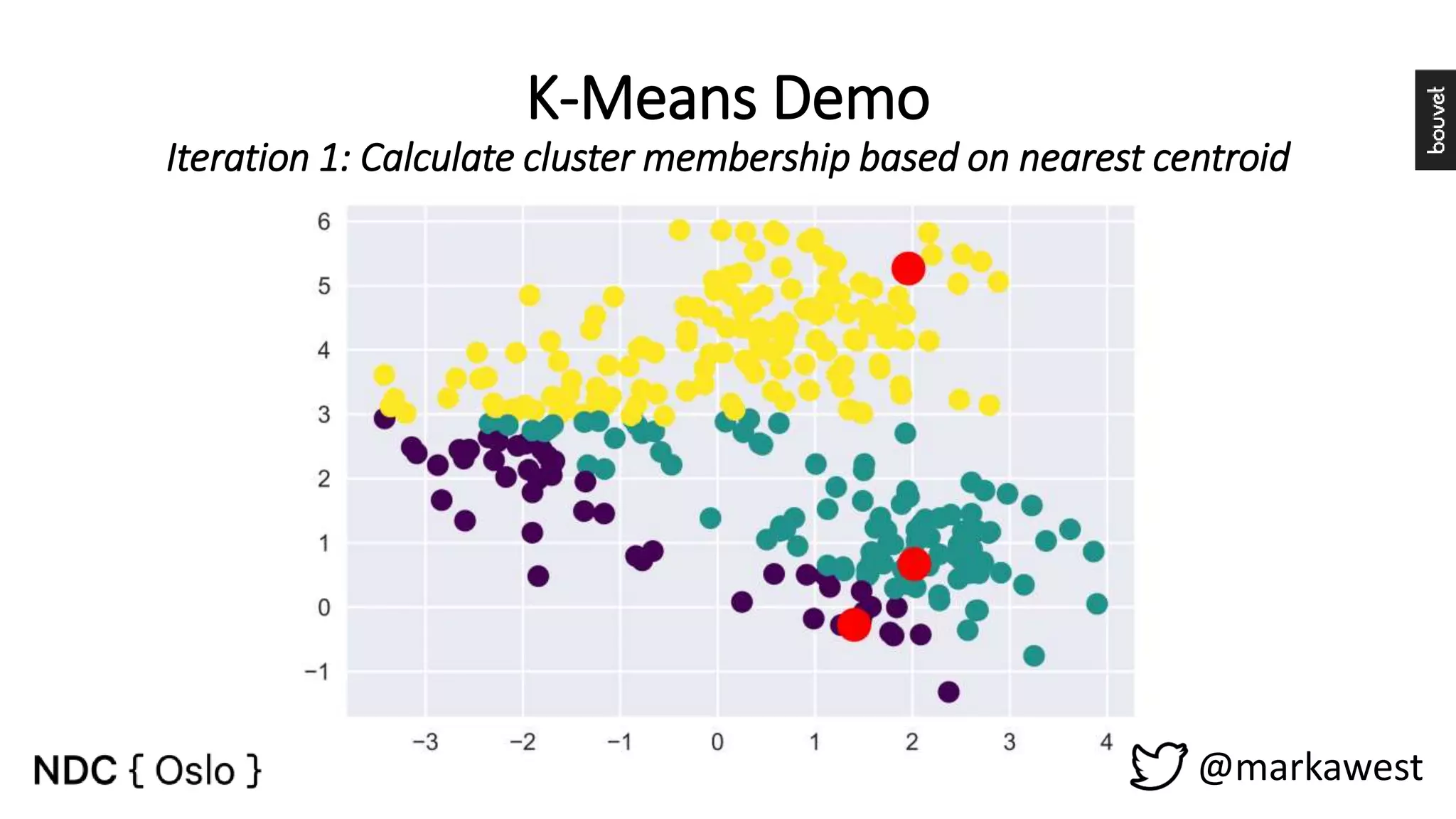
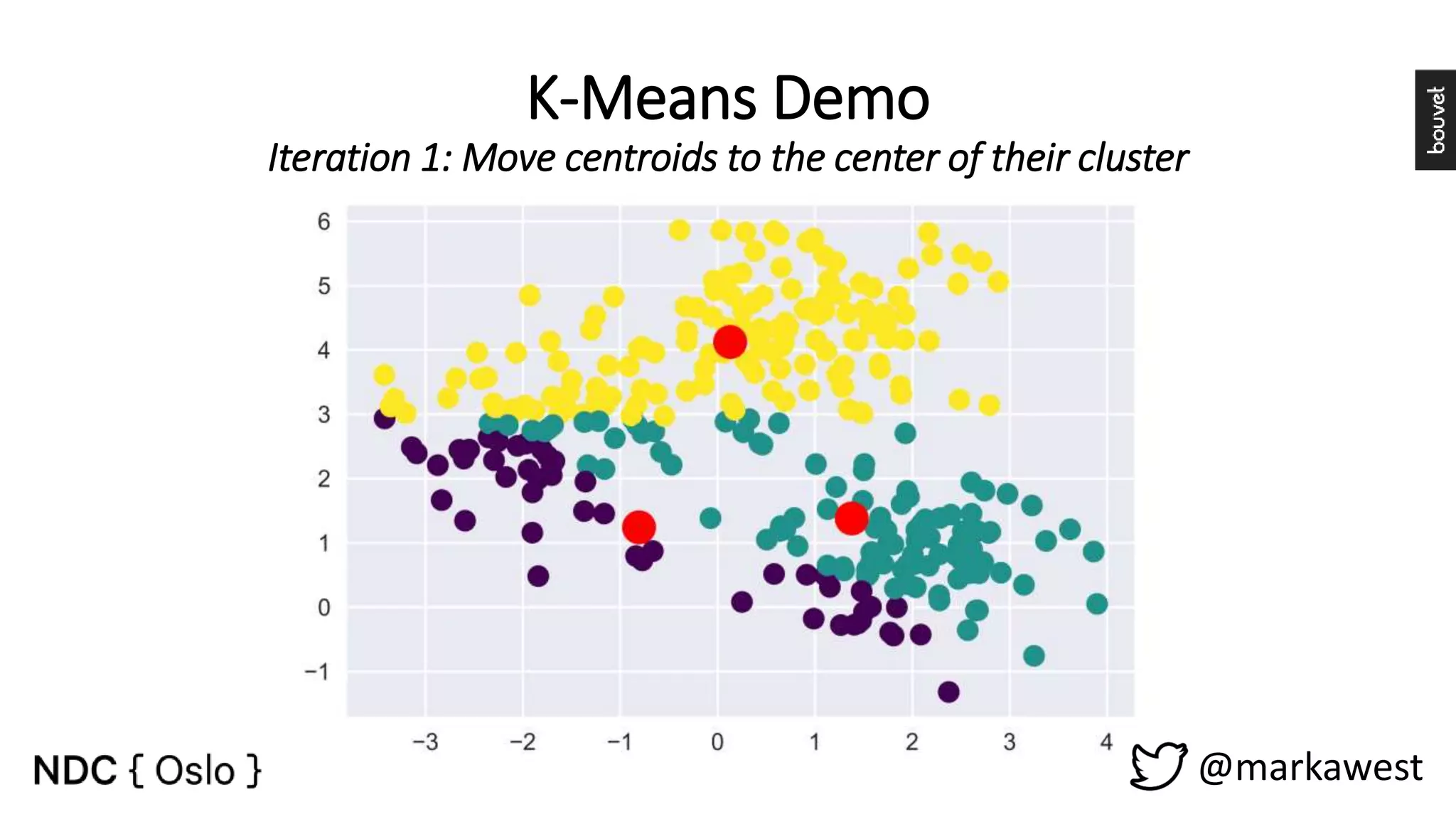
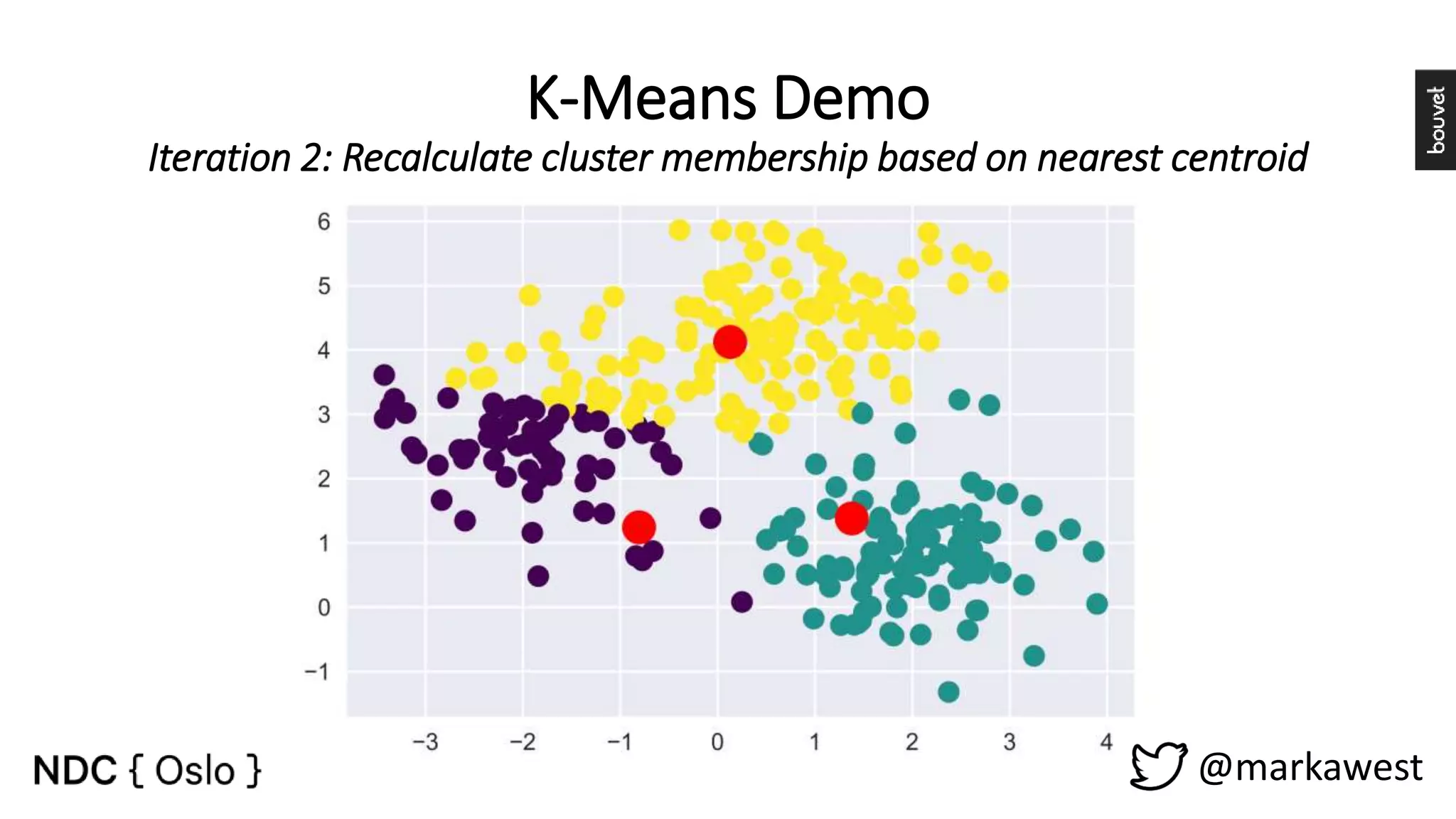
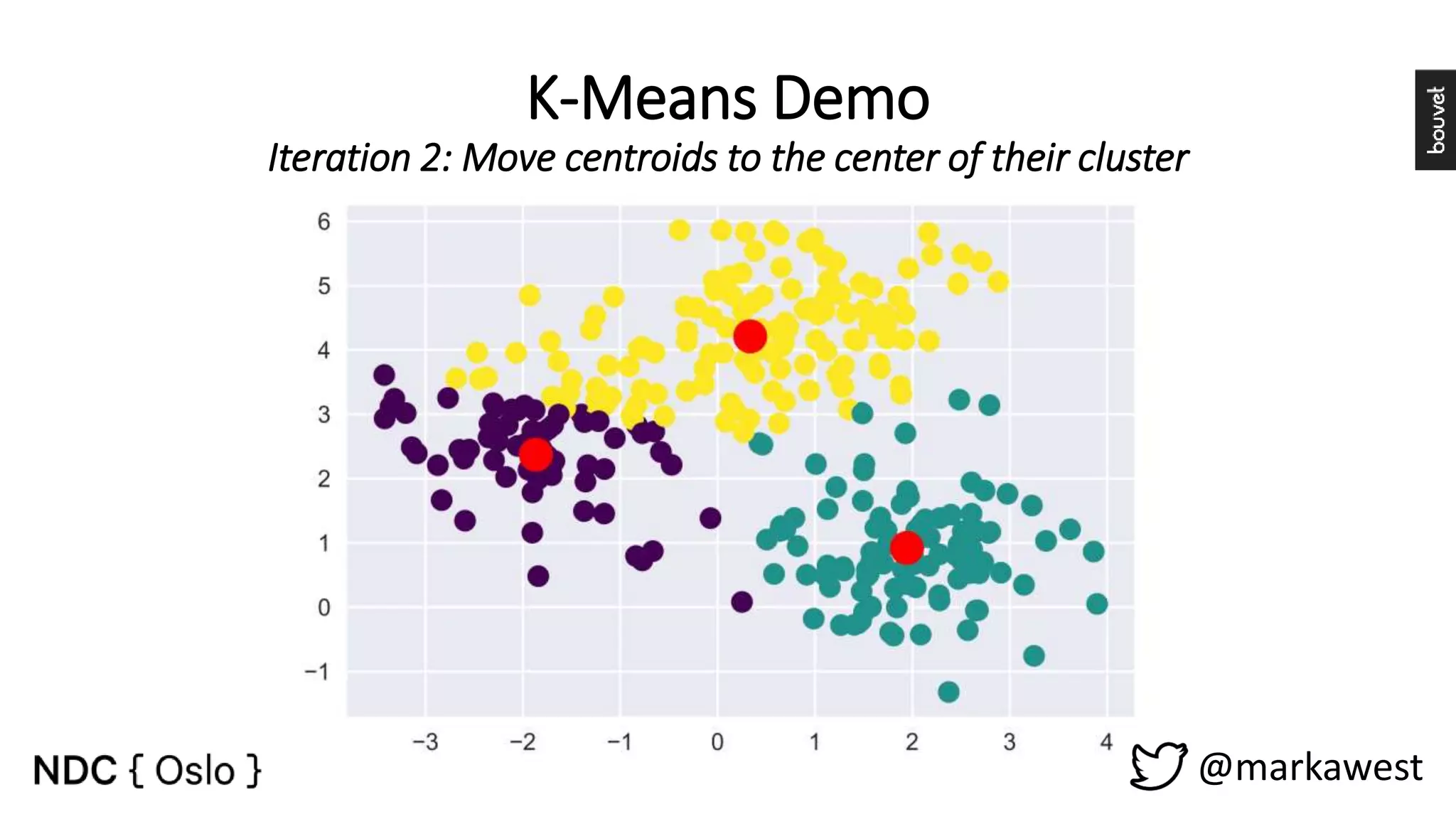
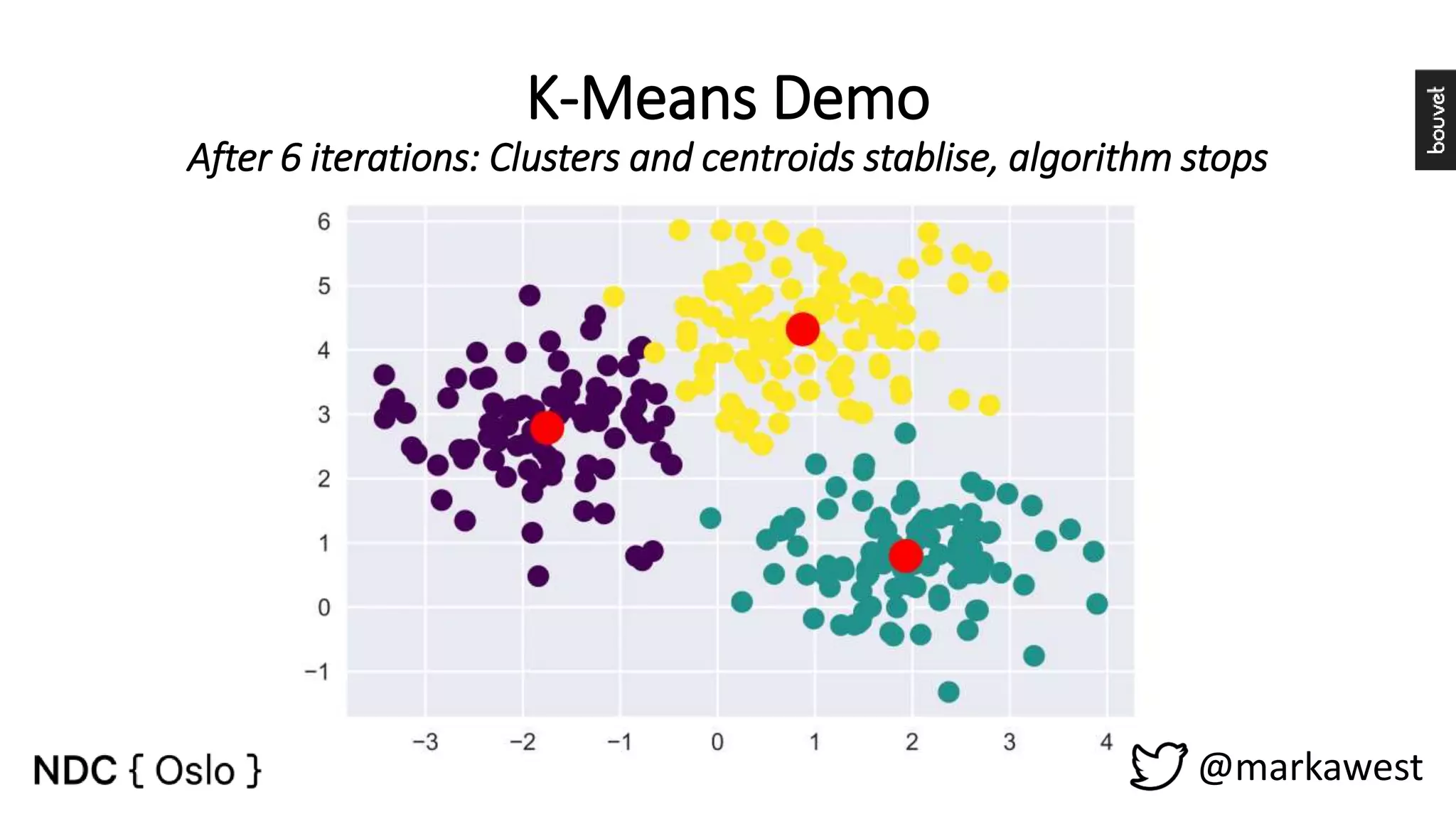
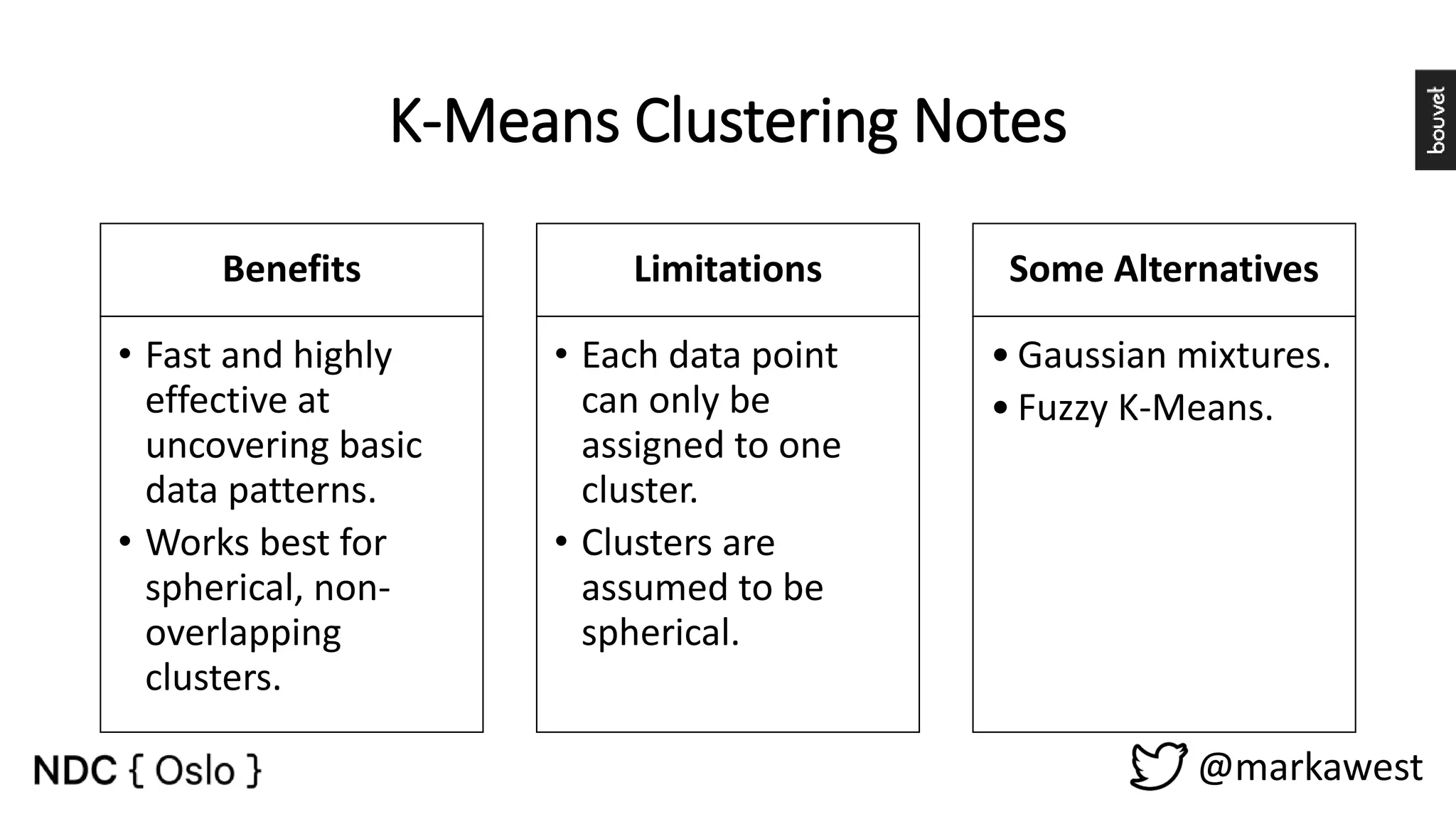
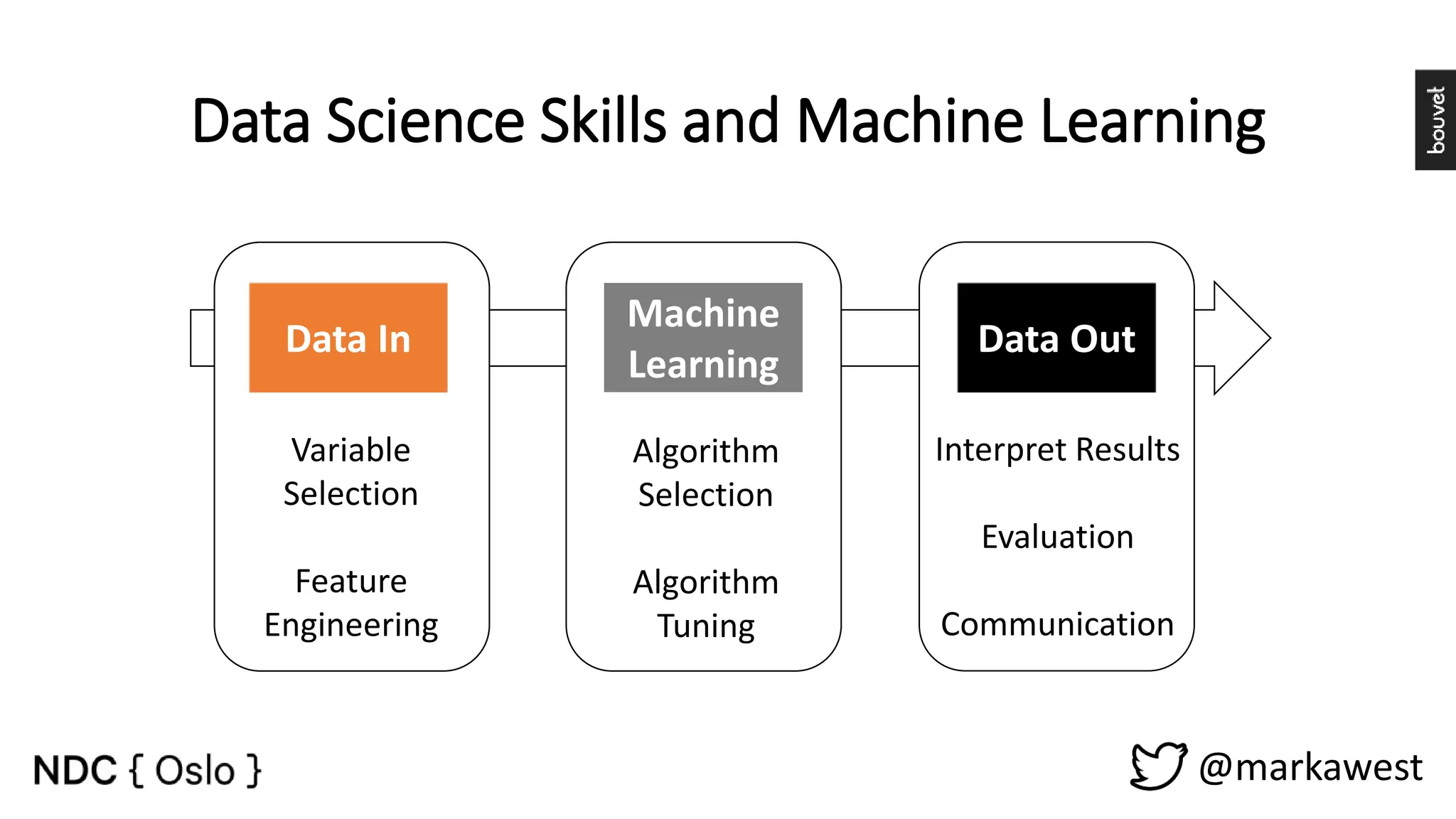
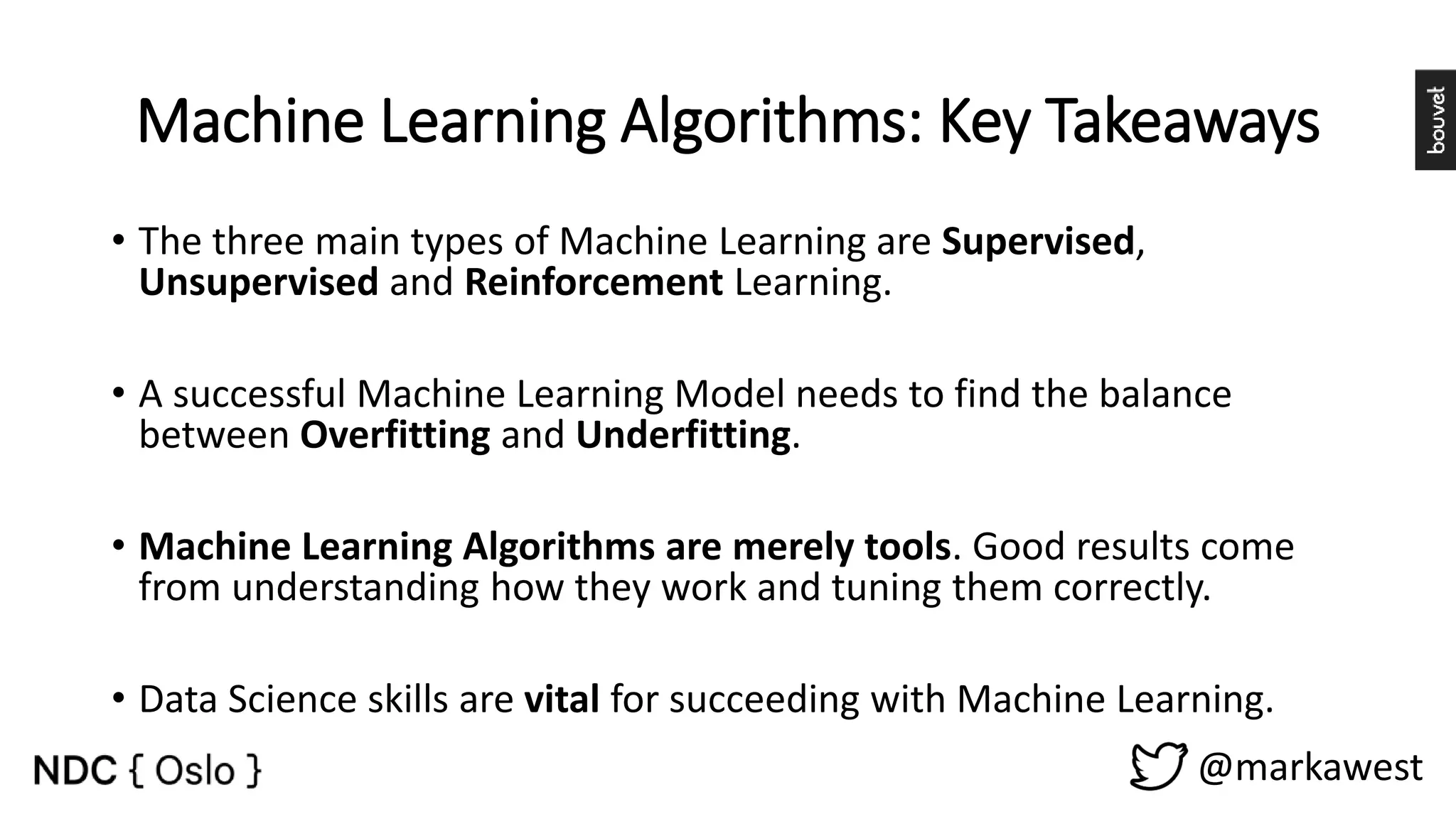
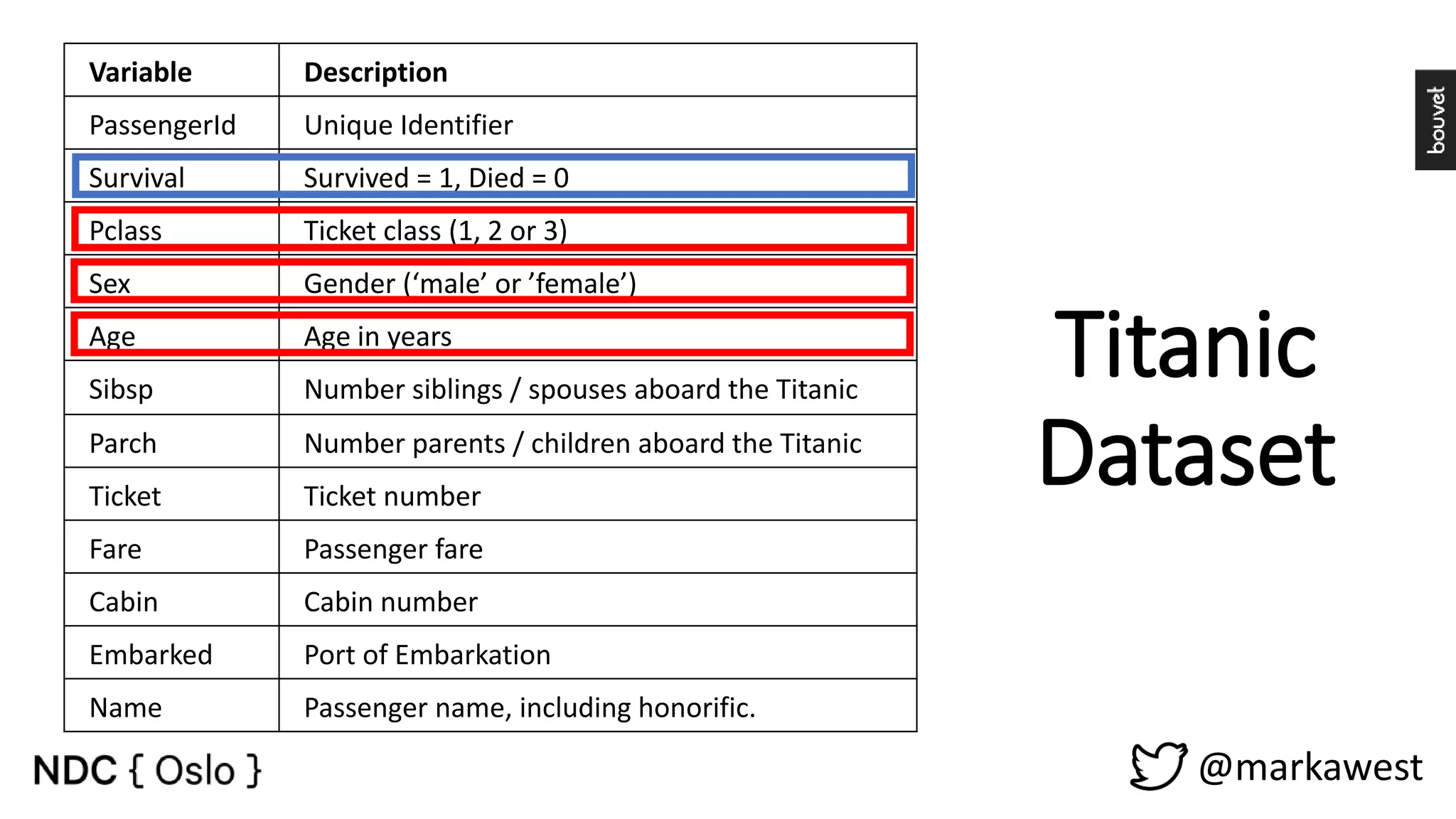
The document provides an overview of data science, highlighting its interdisciplinary nature and the roles involved in data science projects, including data scientists, data engineers, and visualization experts. It emphasizes the importance of machine learning as a tool within data science, discussing various algorithms like supervised and unsupervised learning, as well as practical applications such as predicting Titanic passenger survival. Key takeaways stress that data science requires a blend of mathematical, statistical, and software development skills, and that understanding machine learning algorithms is crucial for achieving successful data-driven outcomes.