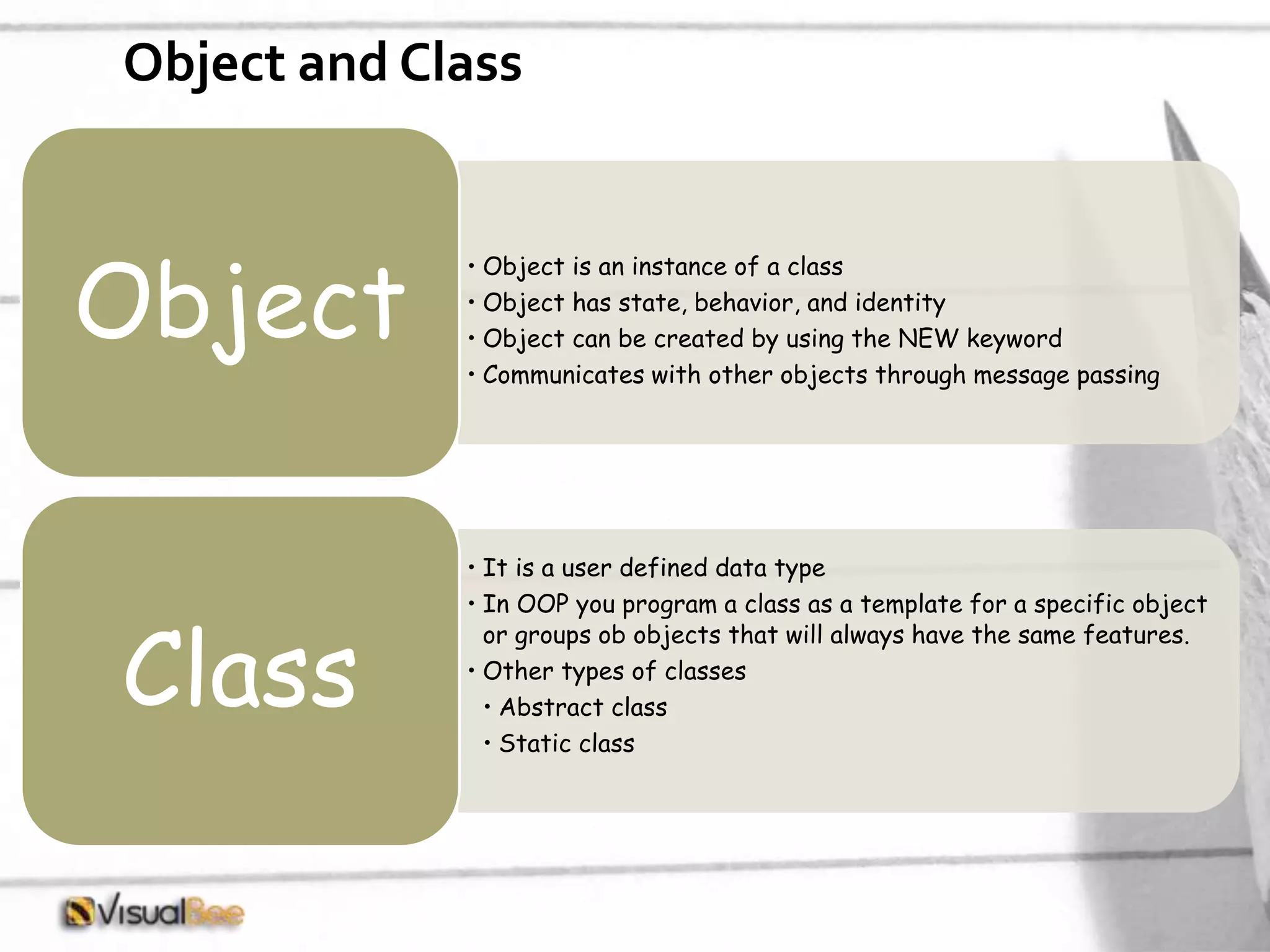
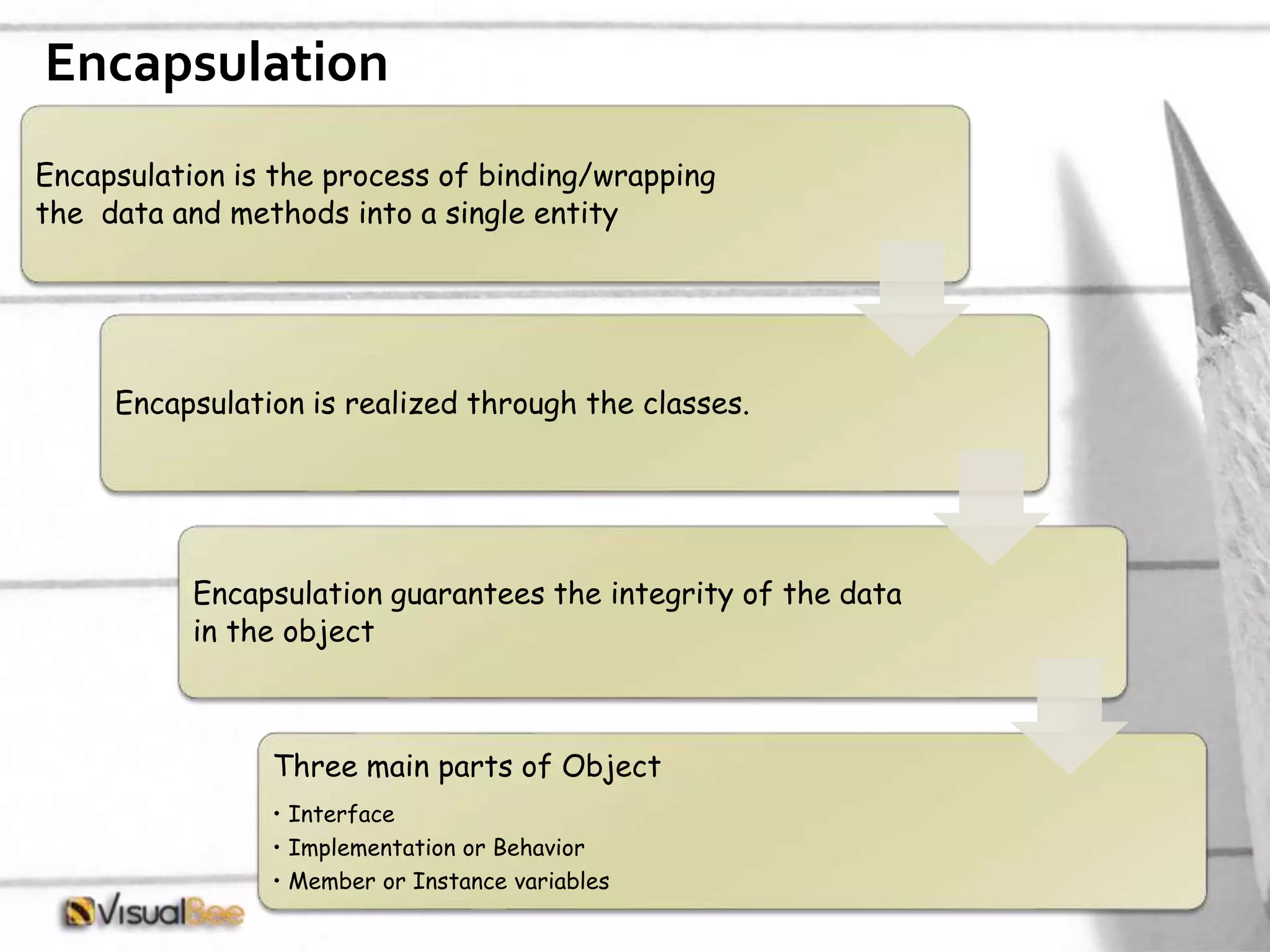
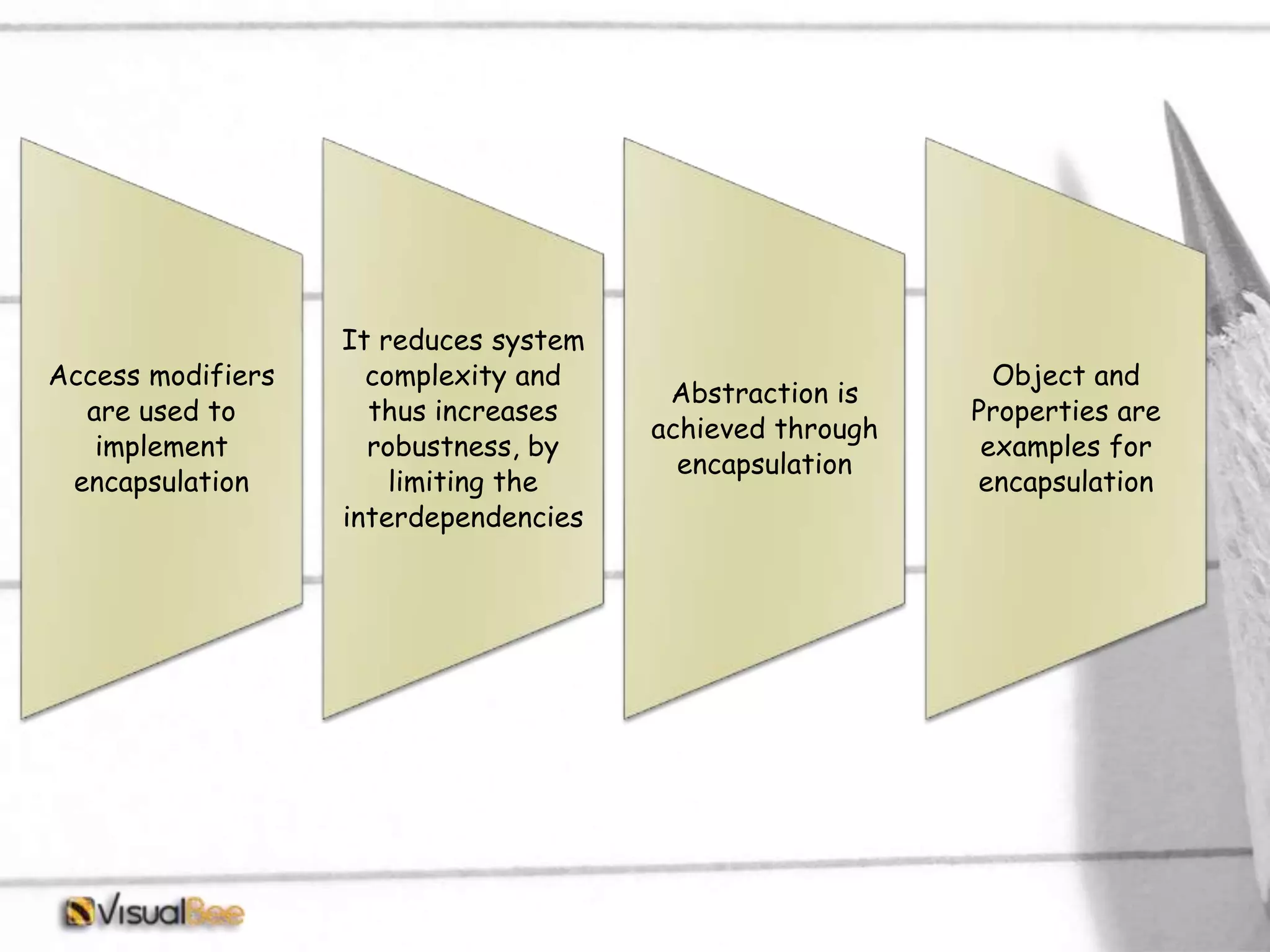
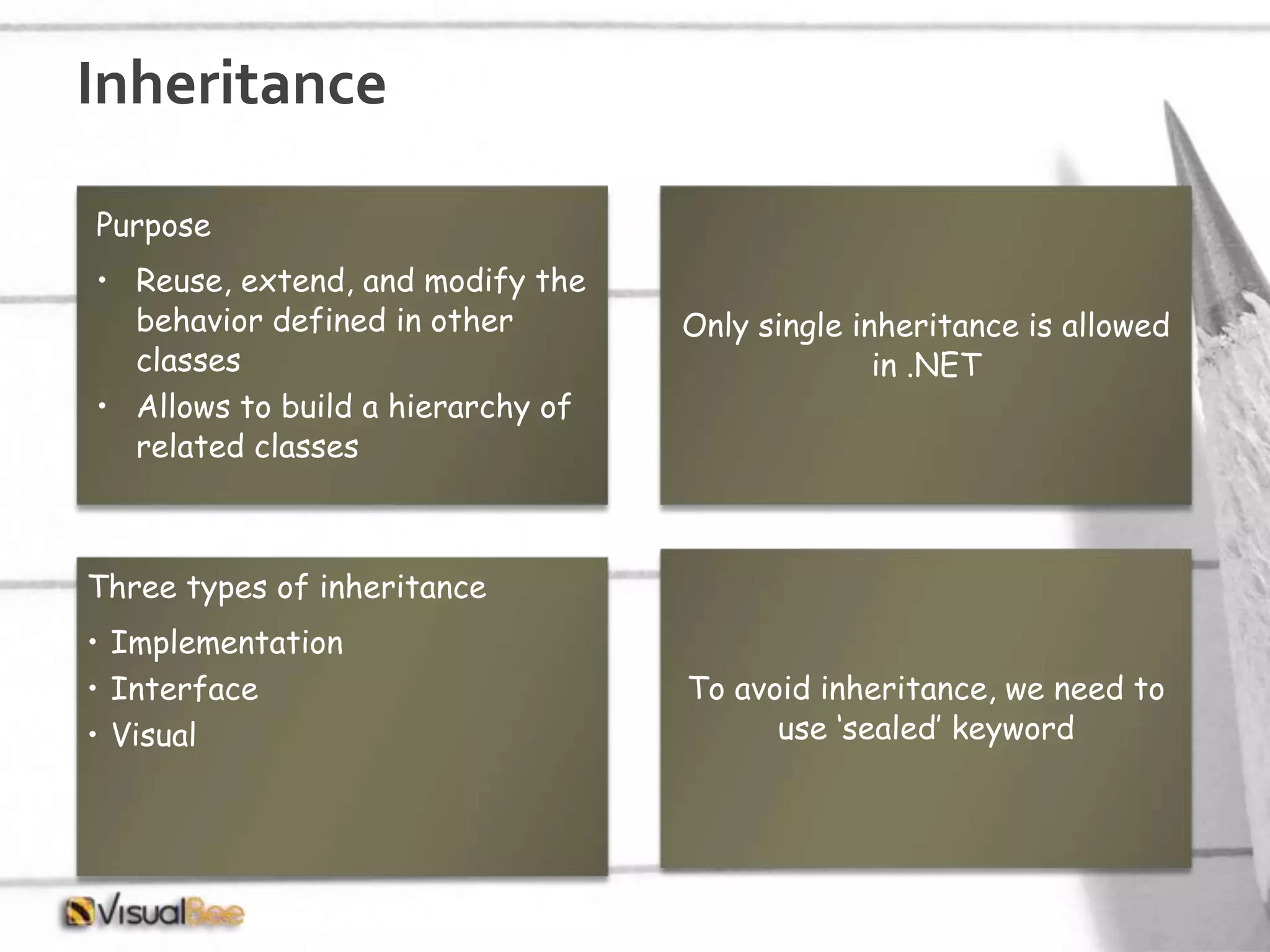
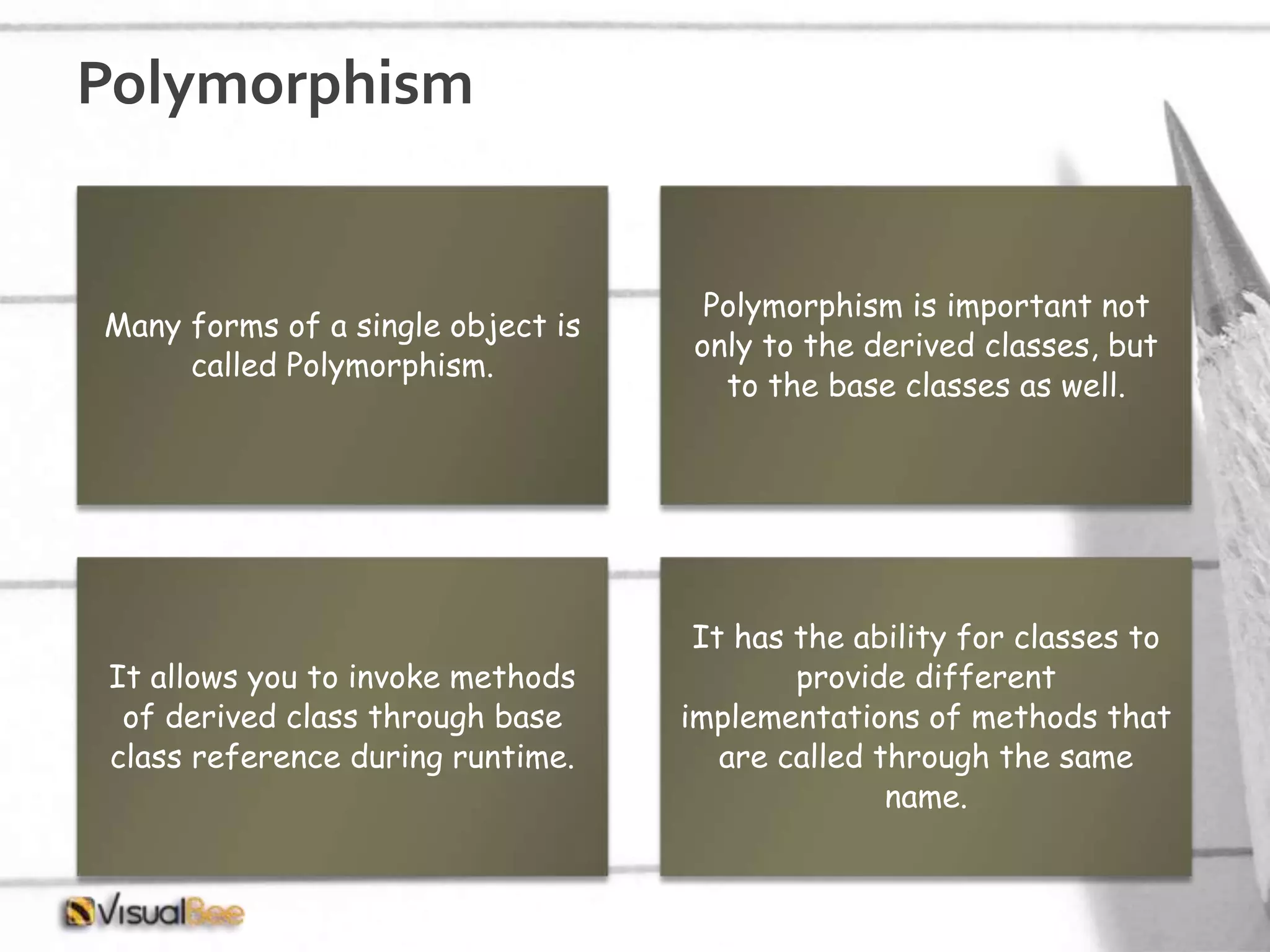
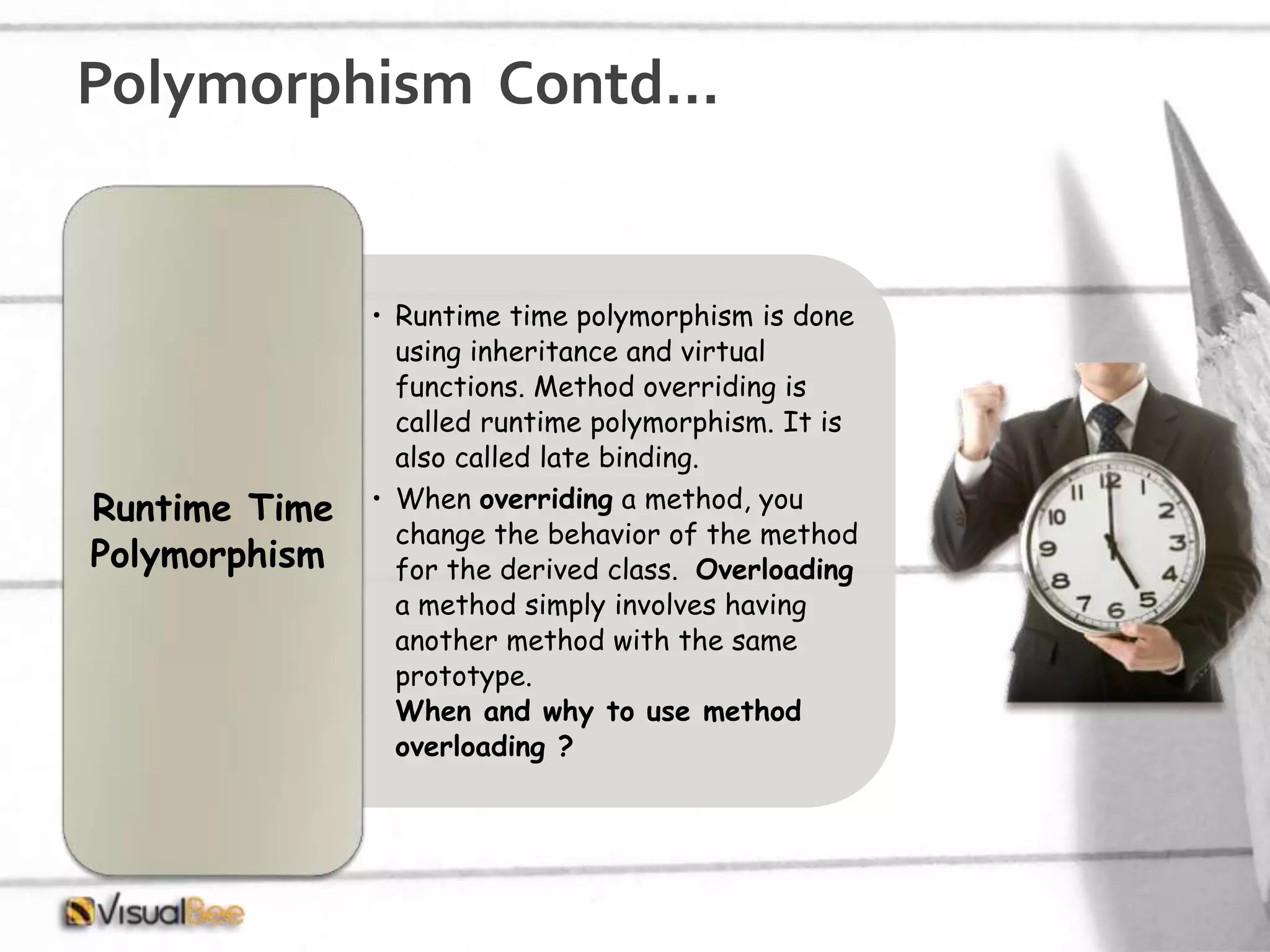
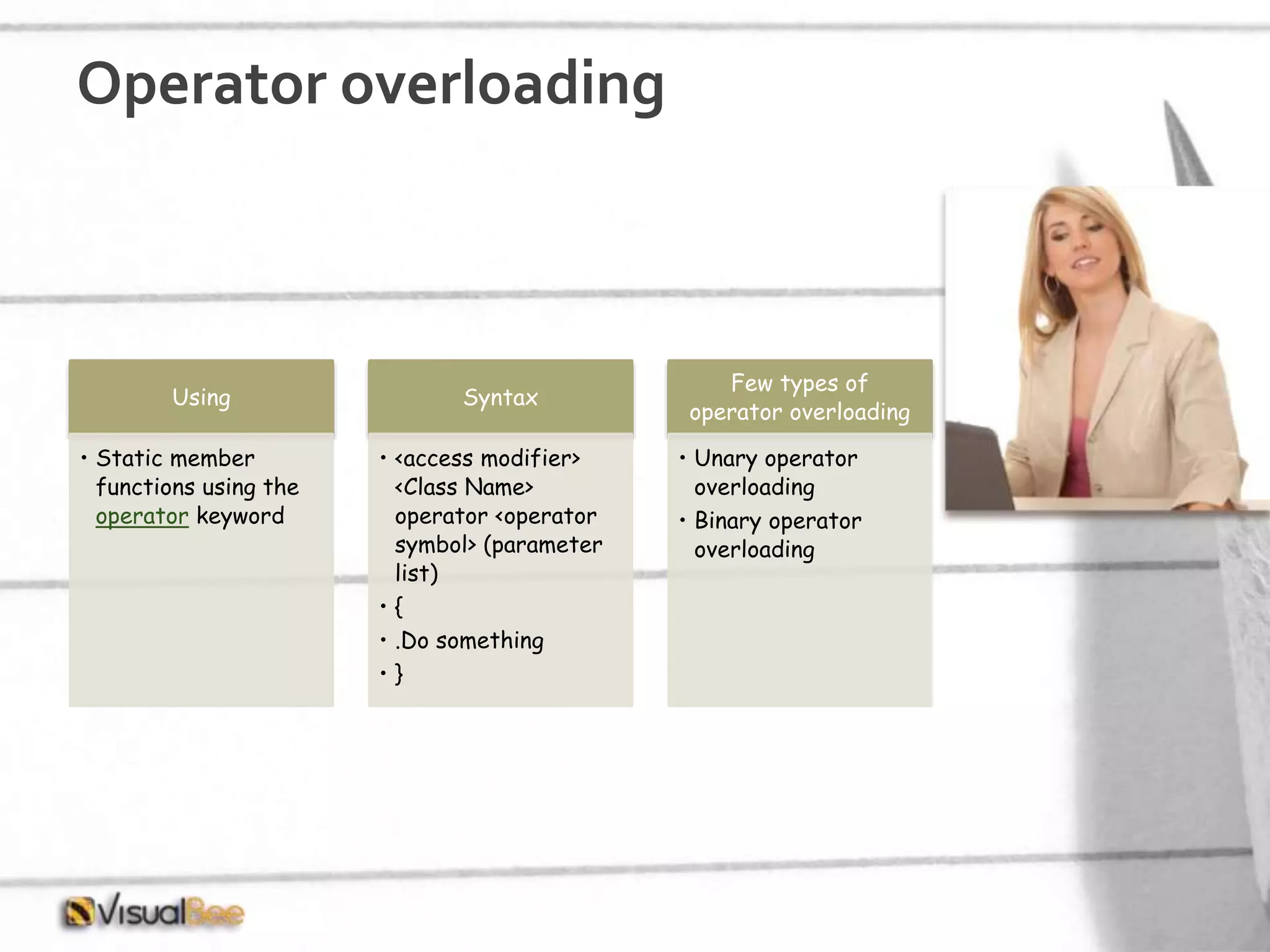
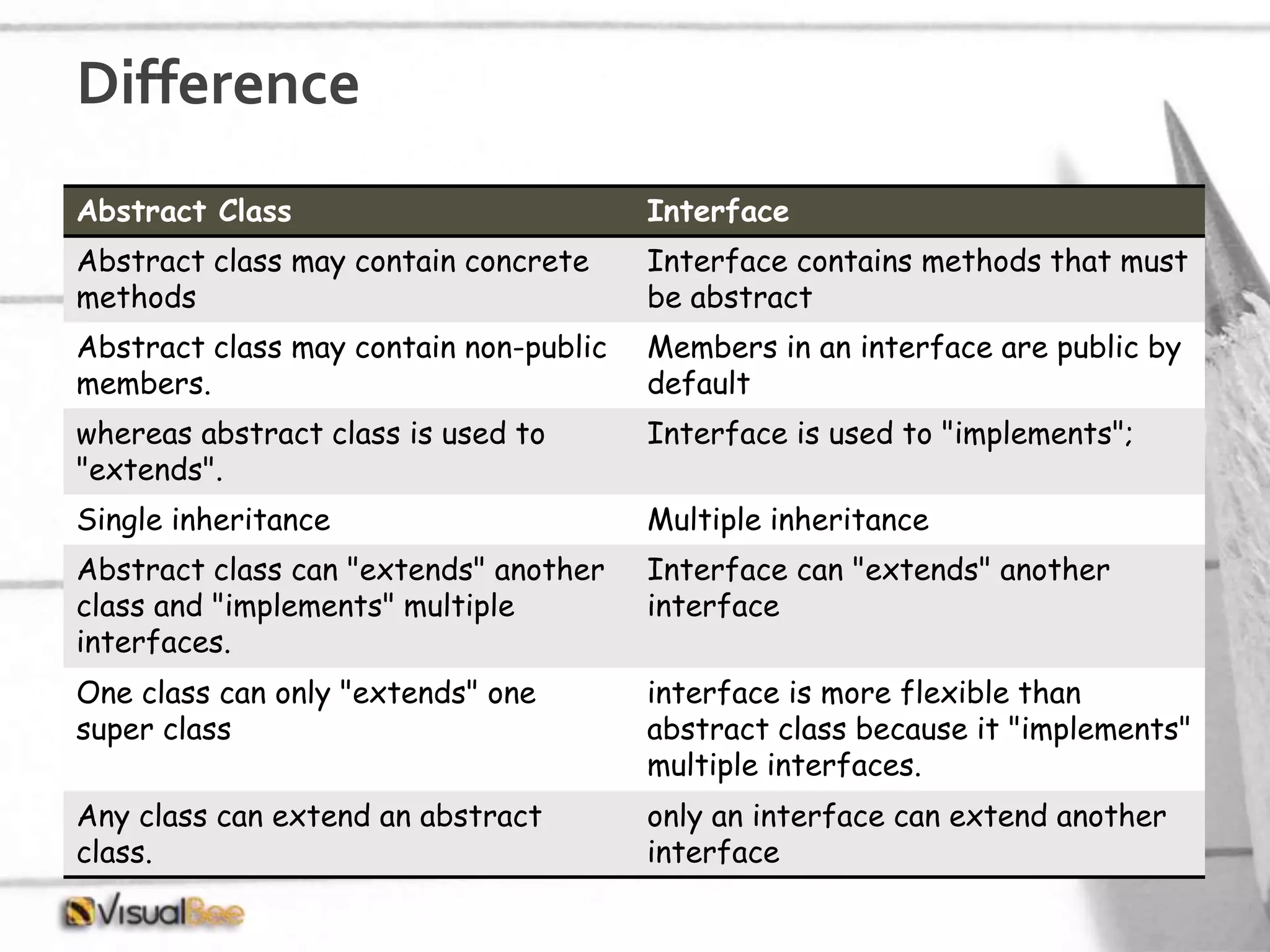
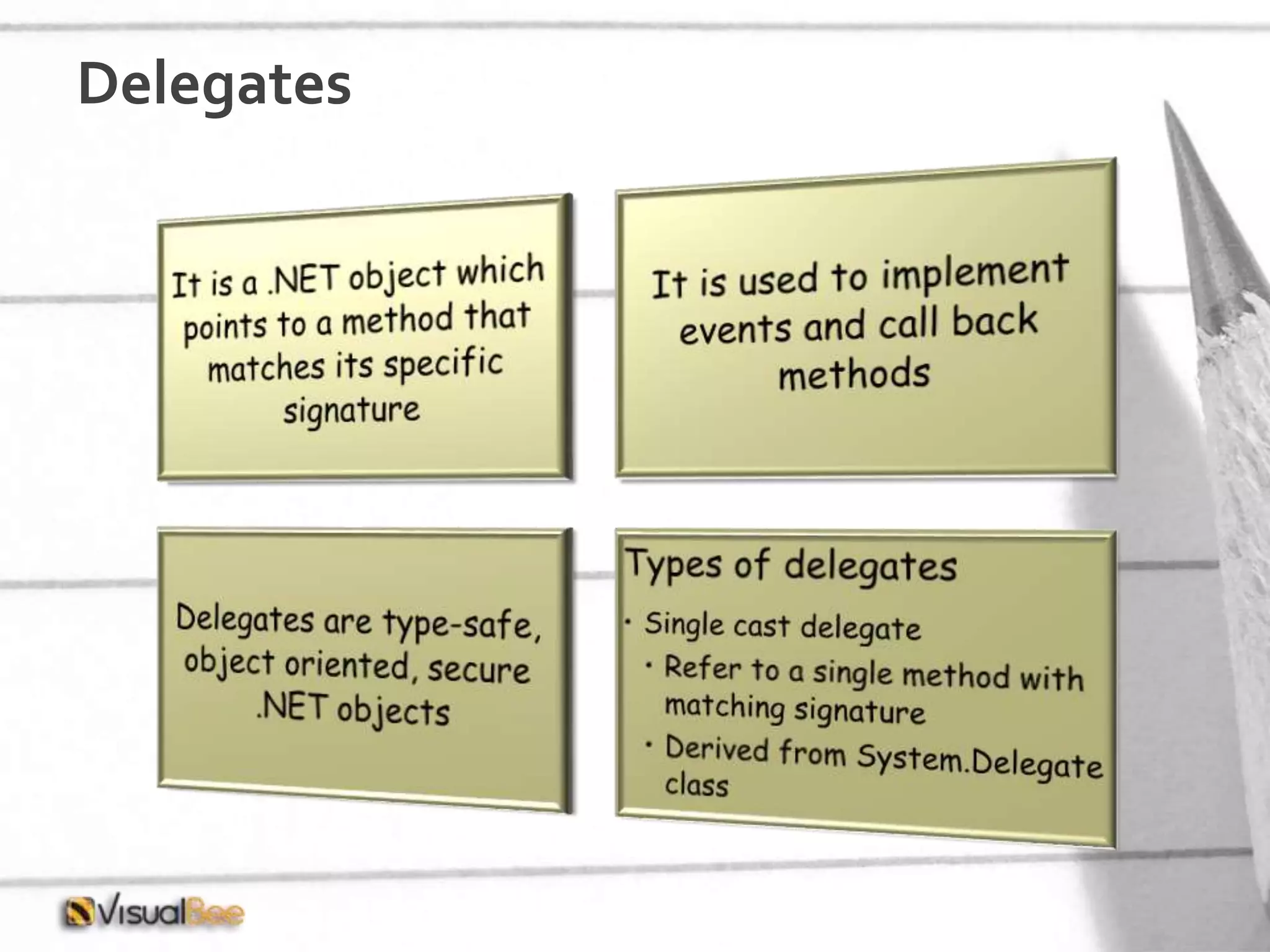
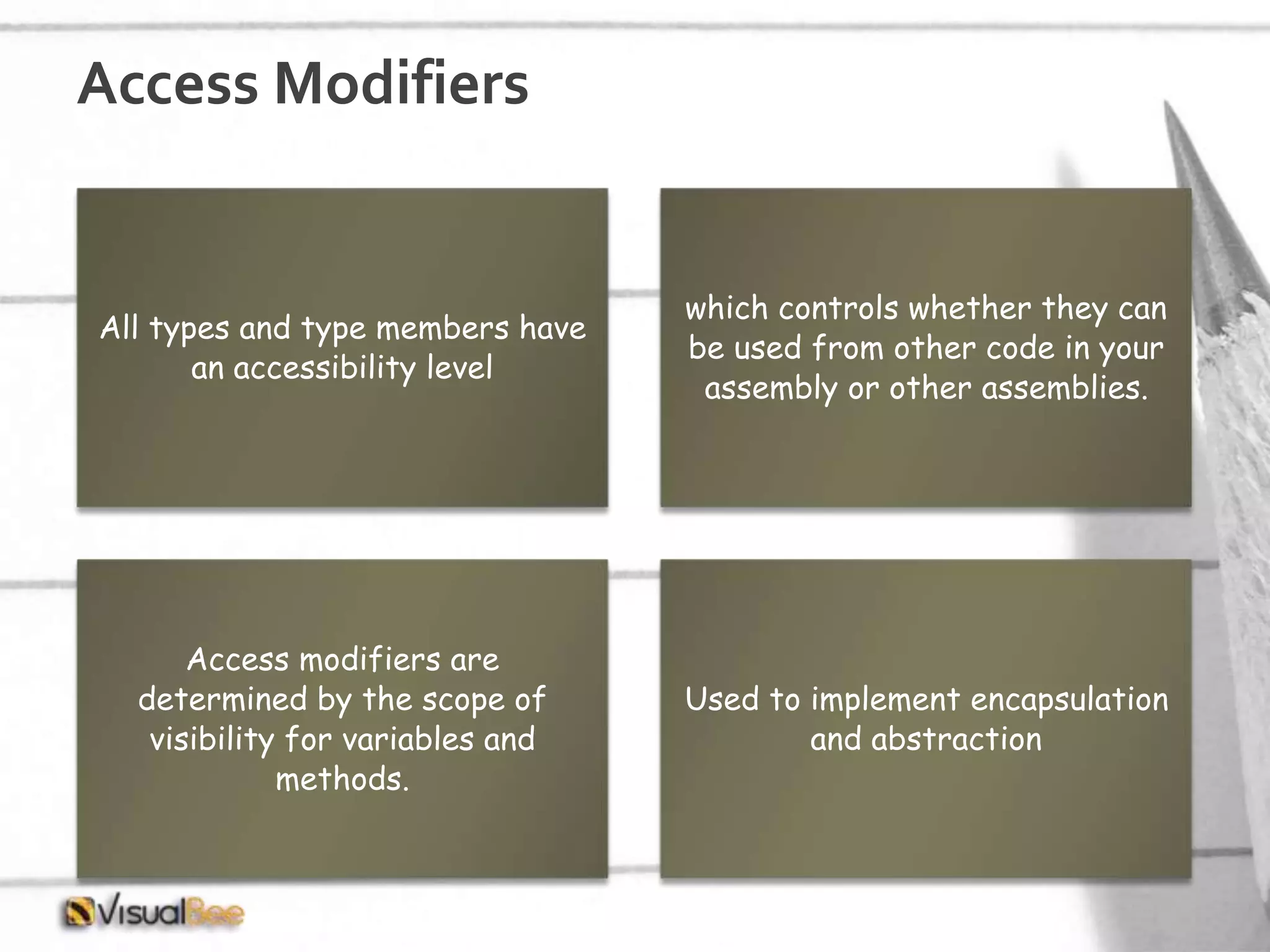
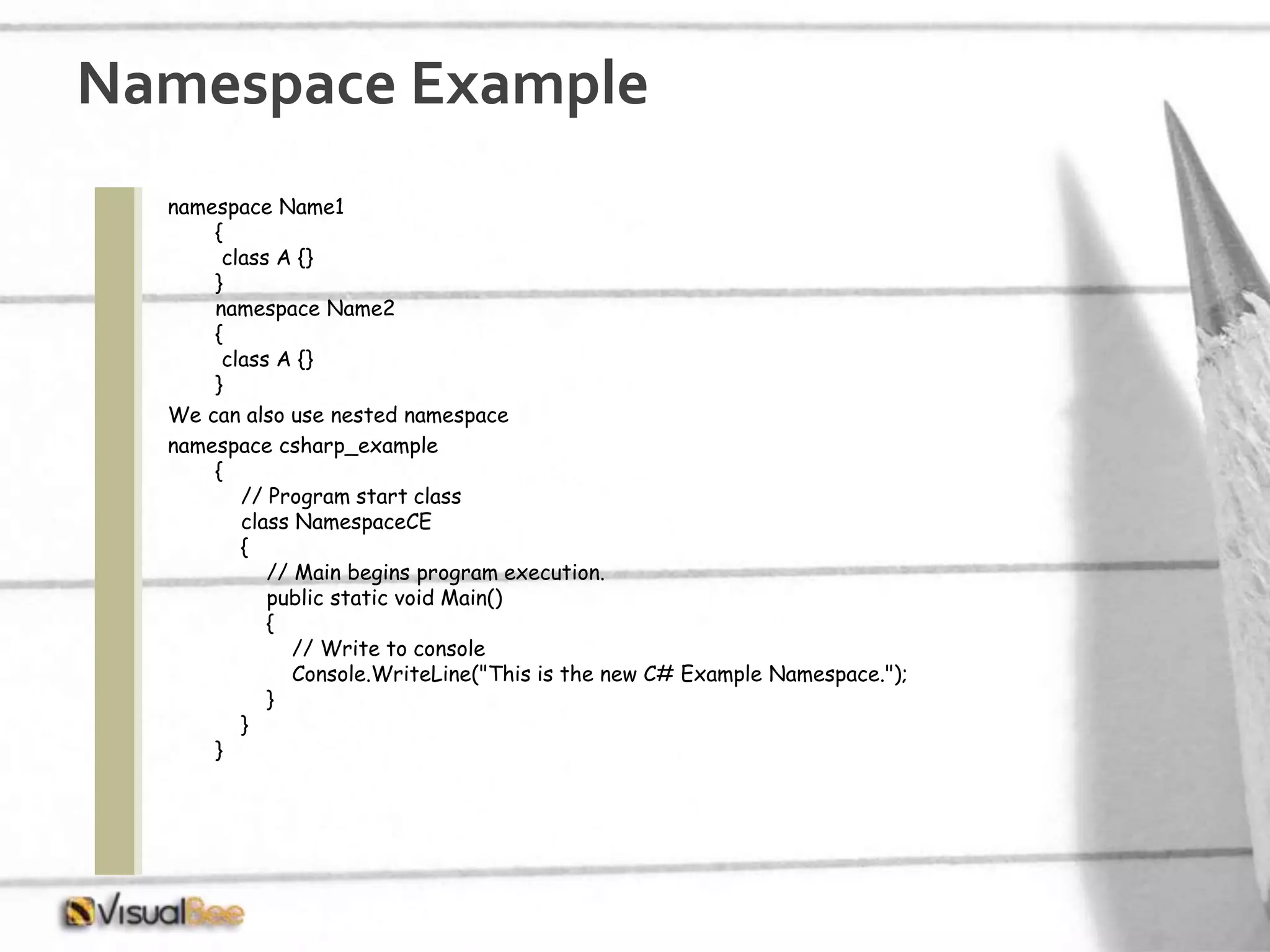
This document provides an overview of object-oriented programming (OOP) concepts including class and object, encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, interfaces, delegates, and access modifiers. It discusses how classes define objects, encapsulation binds data and methods into entities, inheritance creates new classes from existing ones, polymorphism allows different implementations of methods, interfaces define groups of related functionalities, delegates refer to methods, and access modifiers control visibility. Namespaces are used to organize code into unique scopes.