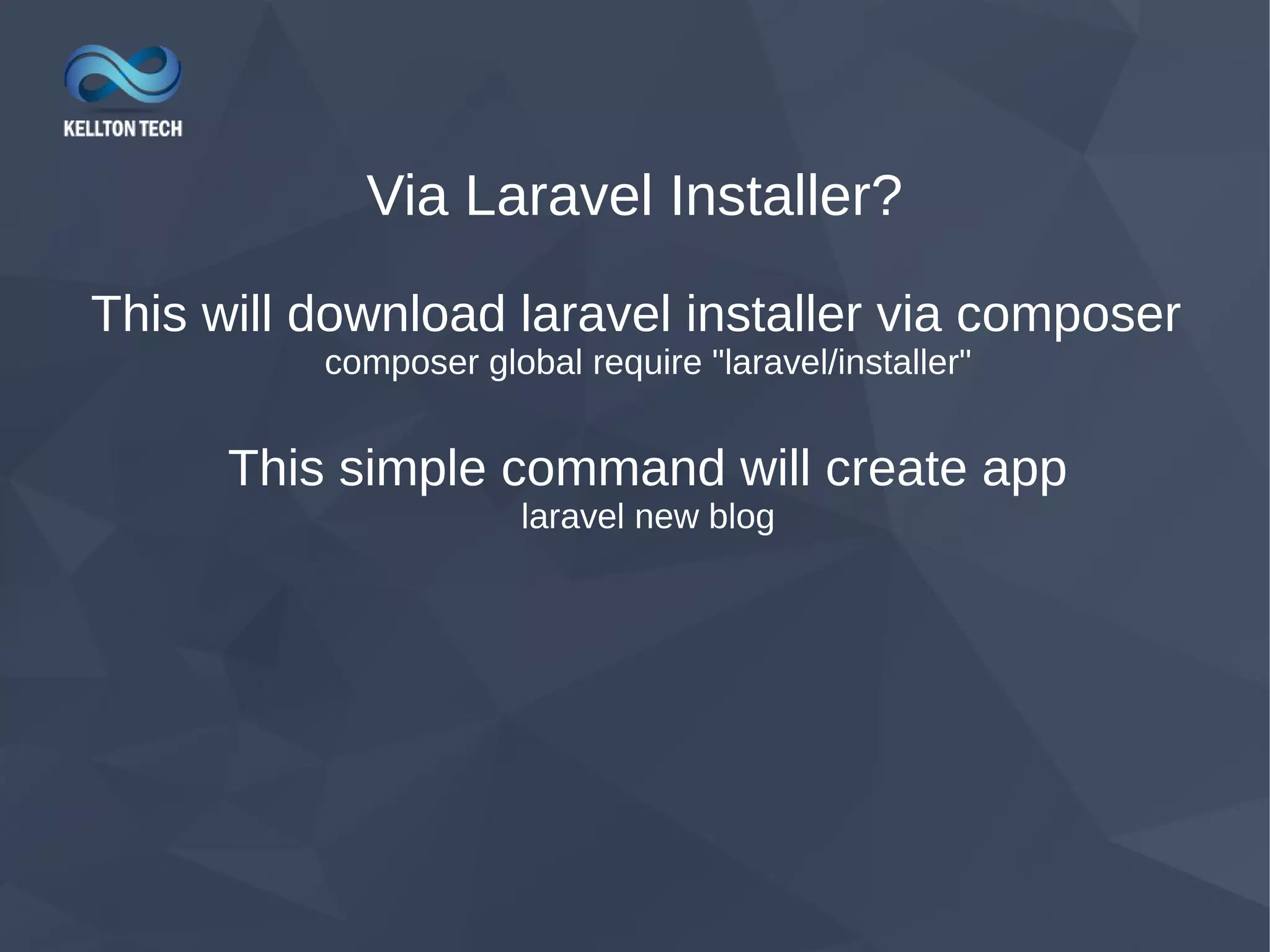
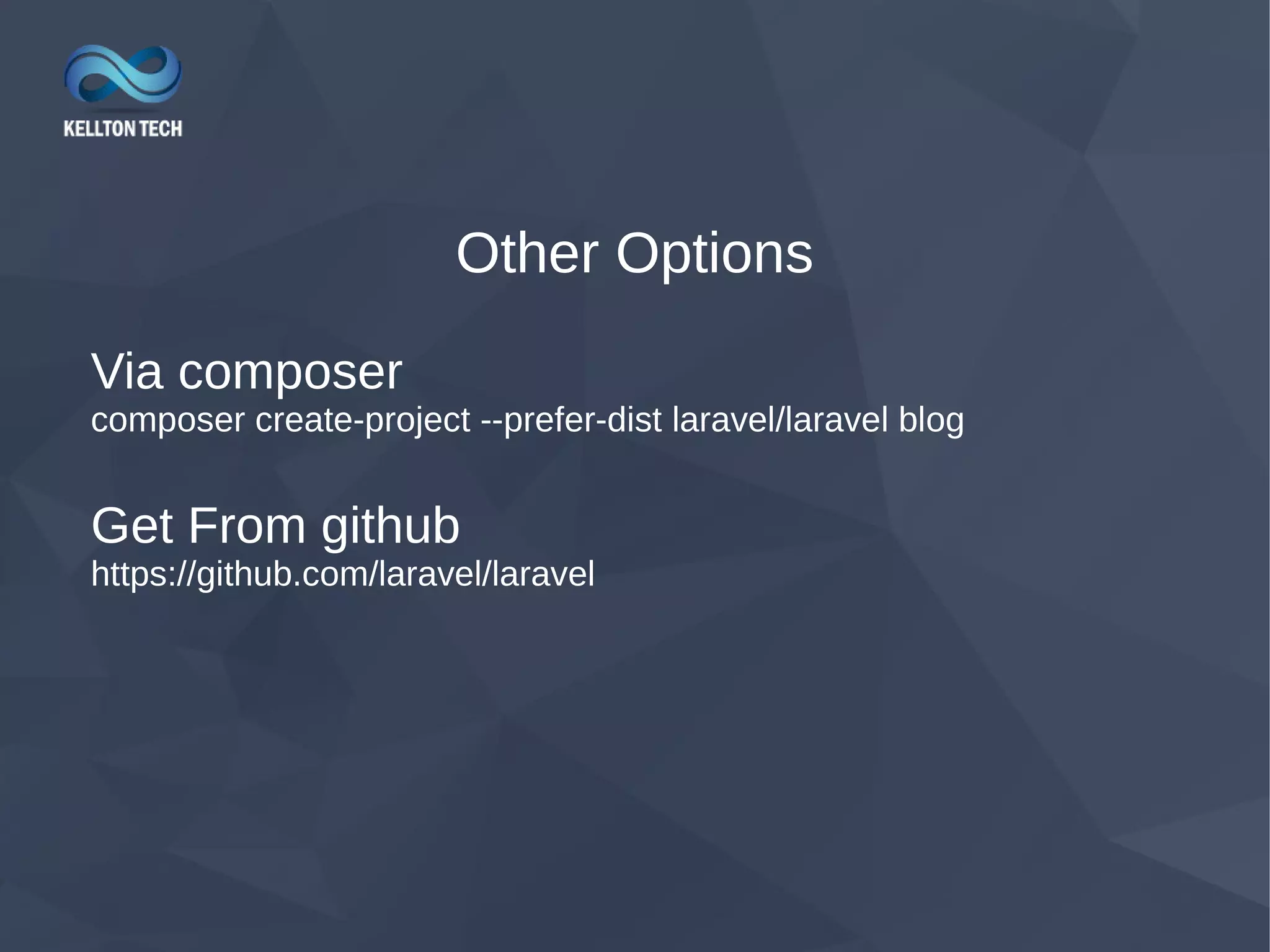
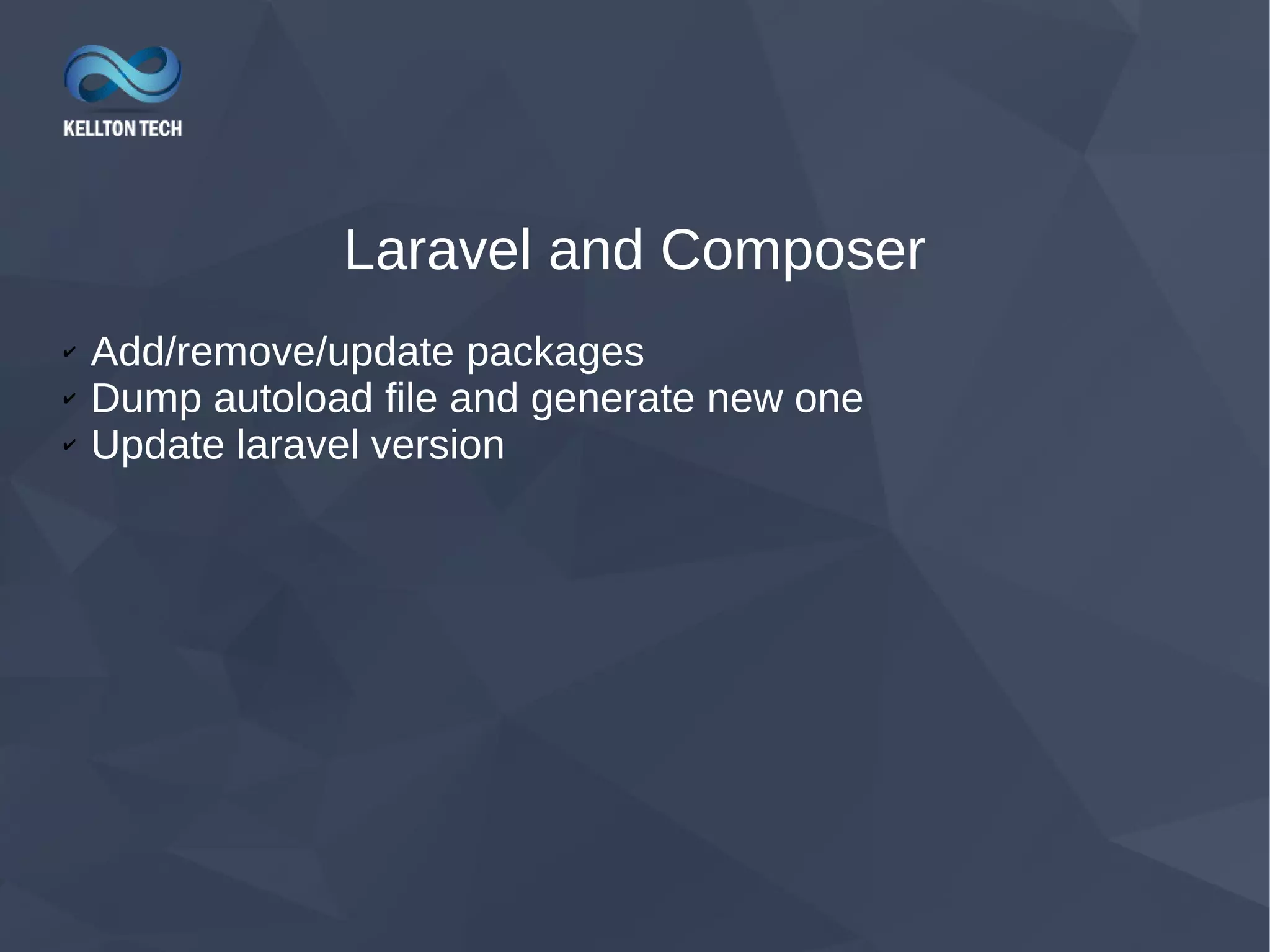
This document provides an overview of Laravel, a PHP web framework. It discusses how to install Laravel via Composer or from GitHub. The directory structure and core components like routing, controllers, models and views are explained. Key Laravel features like middleware, magic commands via Artisan, and request lifecycle are also summarized. The document aims to help developers get started with Laravel and understand its basic architecture and functionality.






![Laravel Routes Route::get('foo', callback); Route::get('/welcome/{name?}', function($name = null){ return 'Name comes from paramatere >> '.$name; })->where('name', '[A-Za-z]+'); Route::group(['prefix' => 'name'], function () { Route::get('/user/profile', function () { return 'name with profile.'; }); });](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/laravel5-170522132002/75/Laravel-5-3-Web-Development-Php-framework-12-2048.jpg)





![Models ✔ Models are located under app/ directory. ✔ php artisan make:model Userkelltontech. ✔ Table convention is "snake cased" flights for Flight Model. ✔ Protect mass update protected $fillable = ['name'];/ guarded ✔ AppFlight::findOrFail(1); ✔ FindOrFail(1); ✔ Flight::popular()->women()->orderBy('created_at')->get(); Enable soft Delete ✔ Add deleted_at ✔ use IlluminateDatabaseEloquentSoftDeletes; ✔ Use trait SoftDeletes;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/laravel5-170522132002/75/Laravel-5-3-Web-Development-Php-framework-18-2048.jpg)