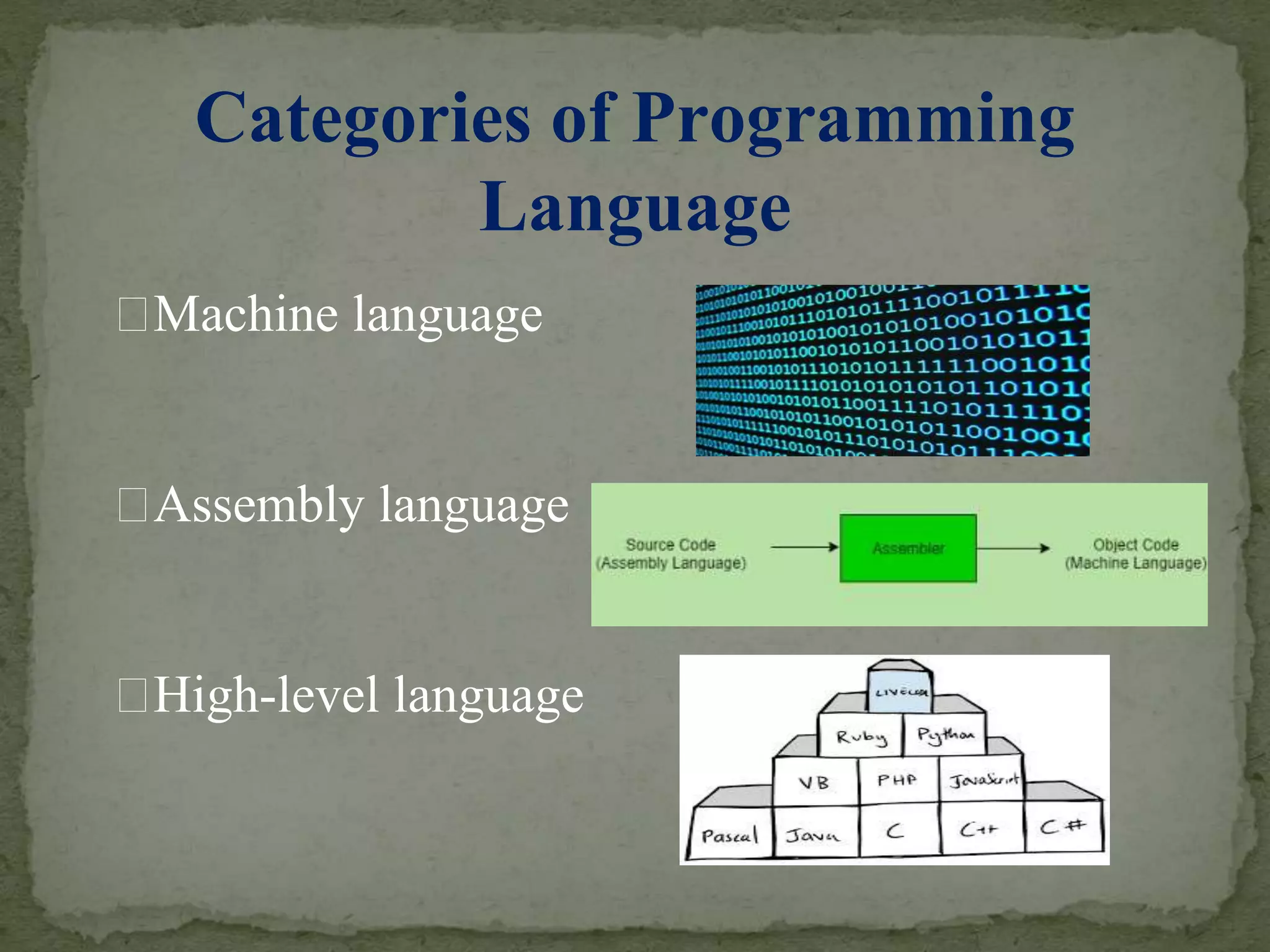
The document explains the concept of computer programming, detailing its evolution, the categories of programming languages (machine, assembly, and high-level languages), and the programming process. It outlines the definition of a computer program as a set of instructions for the CPU, elaborates on the syntax and operational characteristics of different programming languages, and introduces programming tools essential for software development. Additionally, it describes the systems development life cycle, emphasizing the lifecycle of programs within information systems.
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programminglanguageandprocess-190406074828/75/Programming-language-and-process-1-2048.jpg)