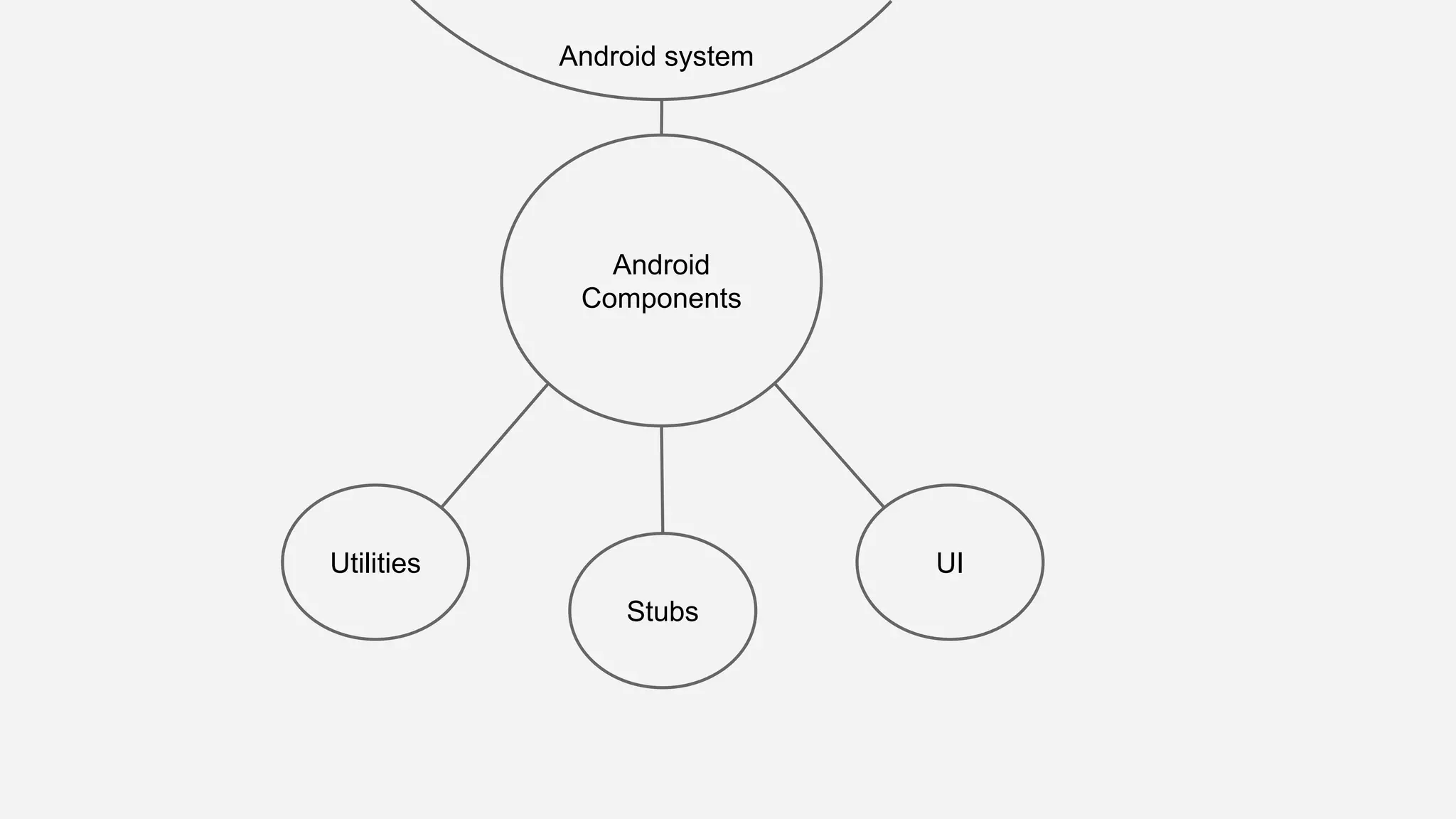
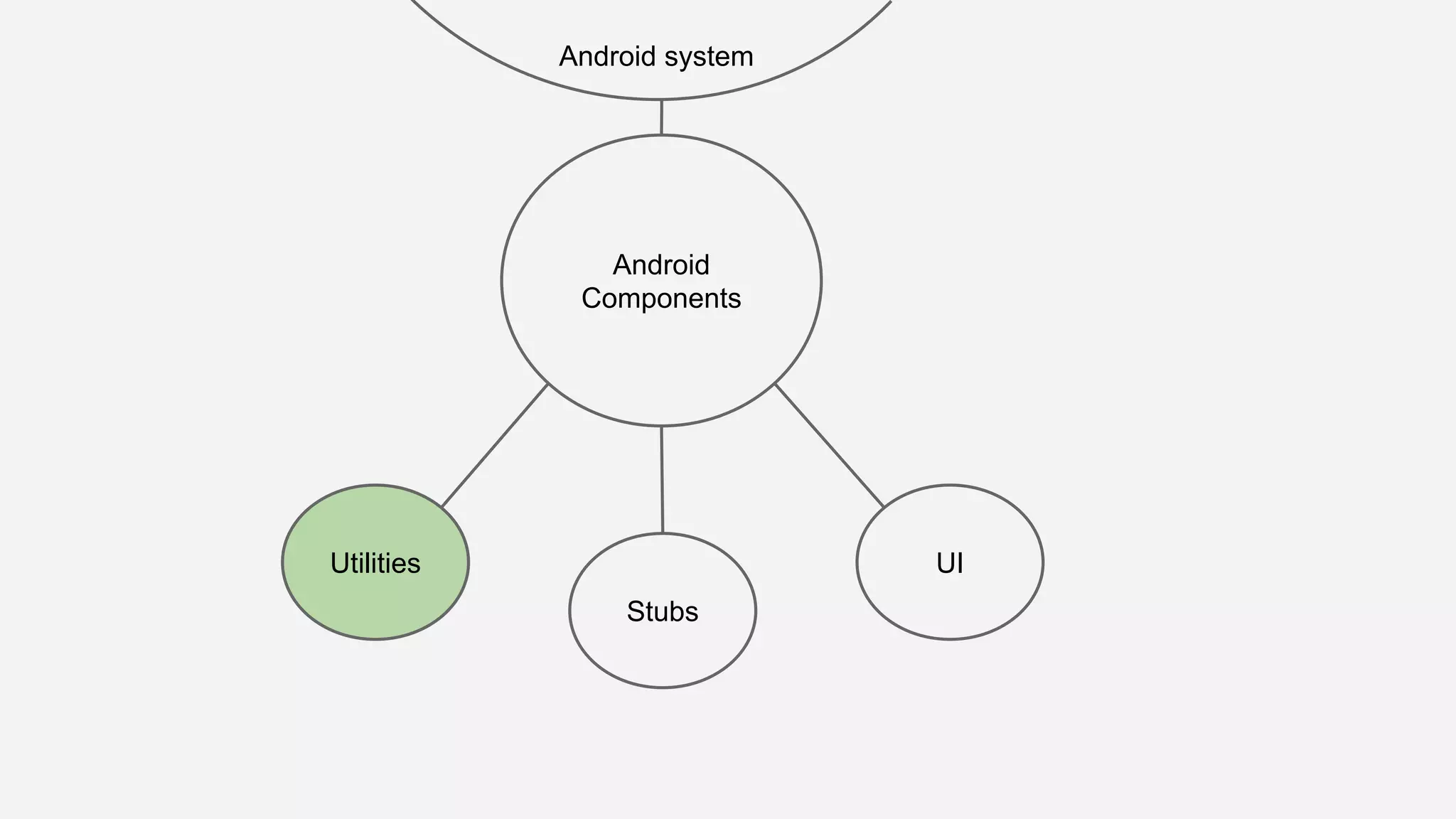
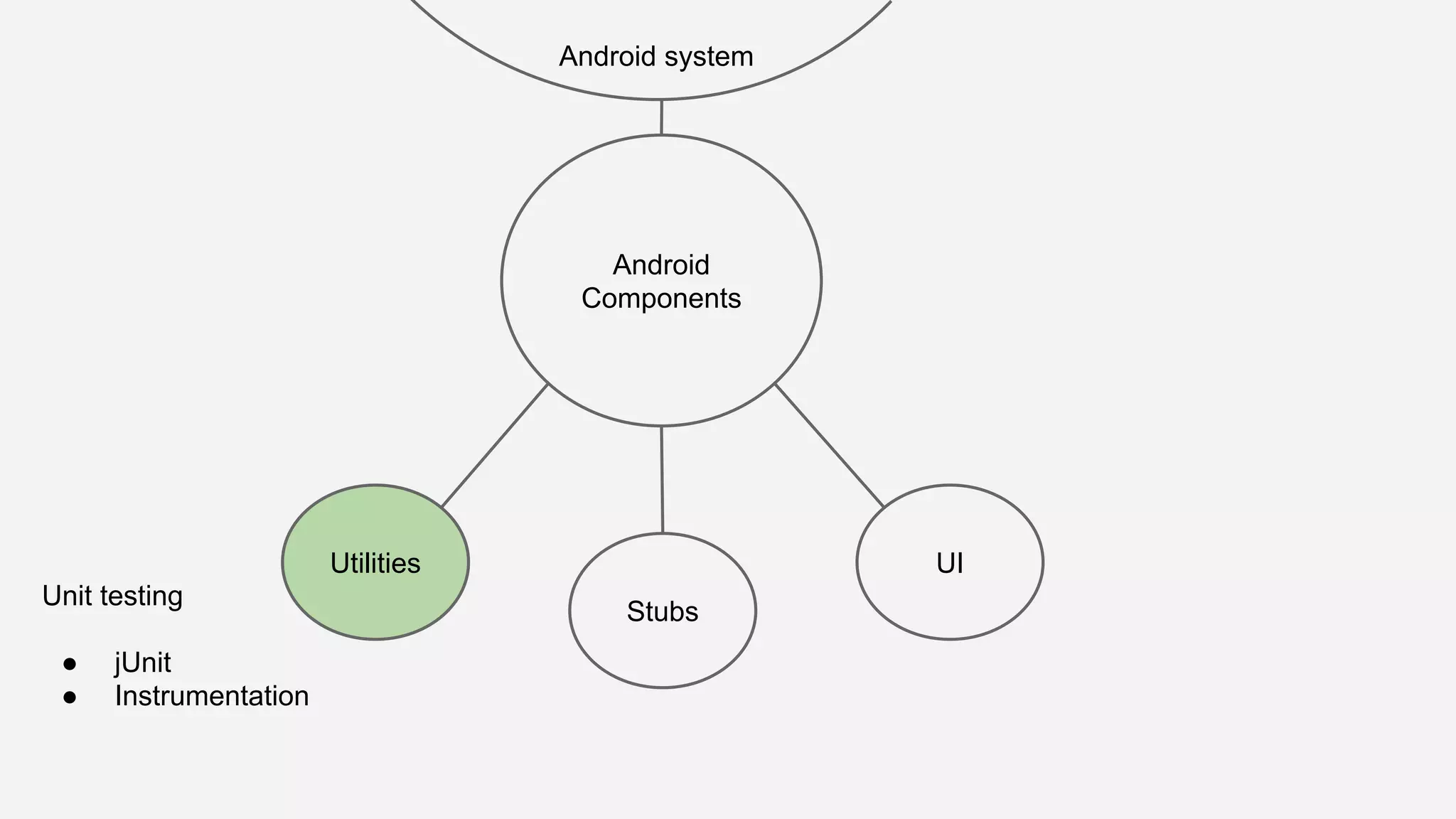
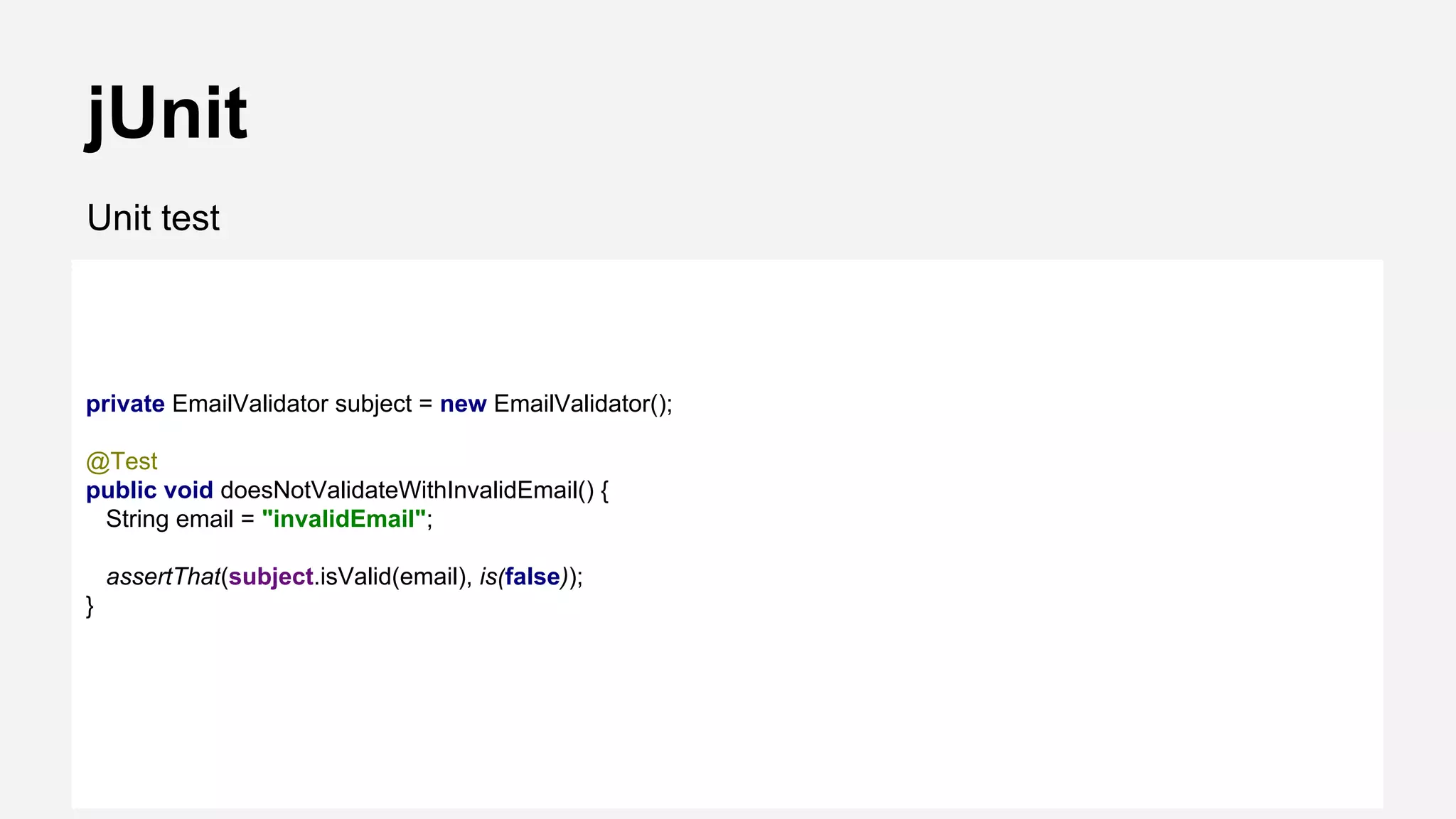
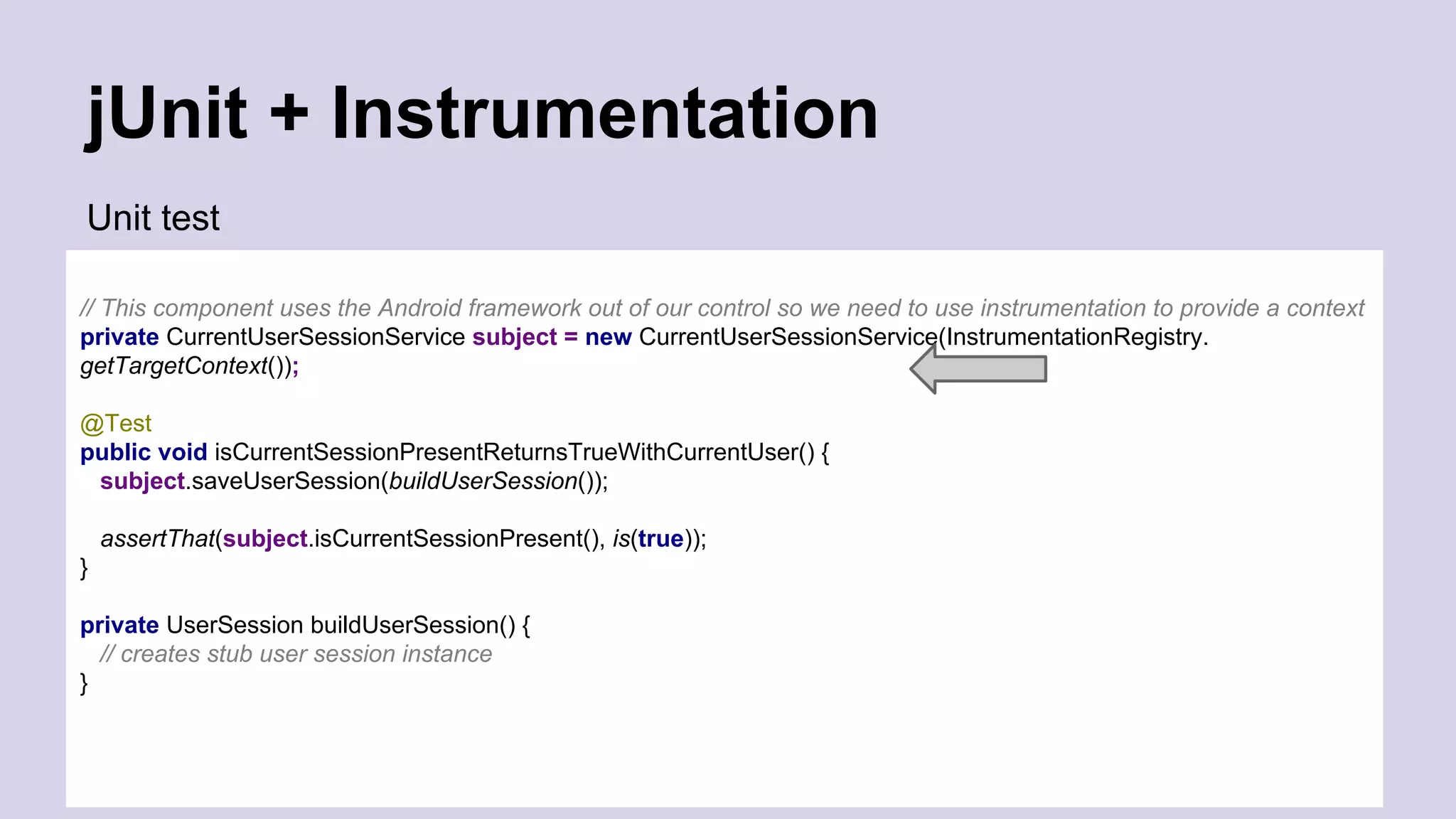
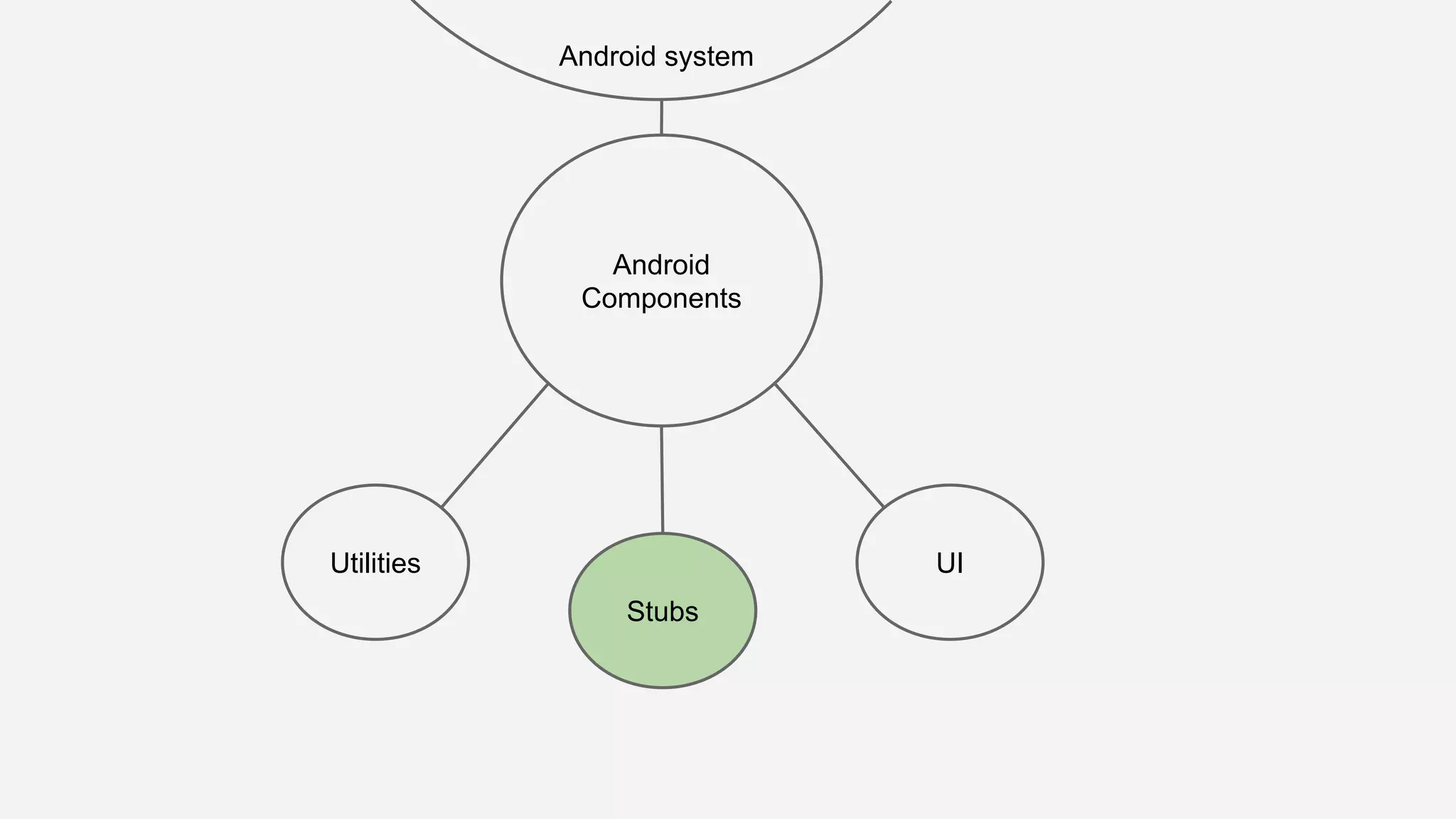
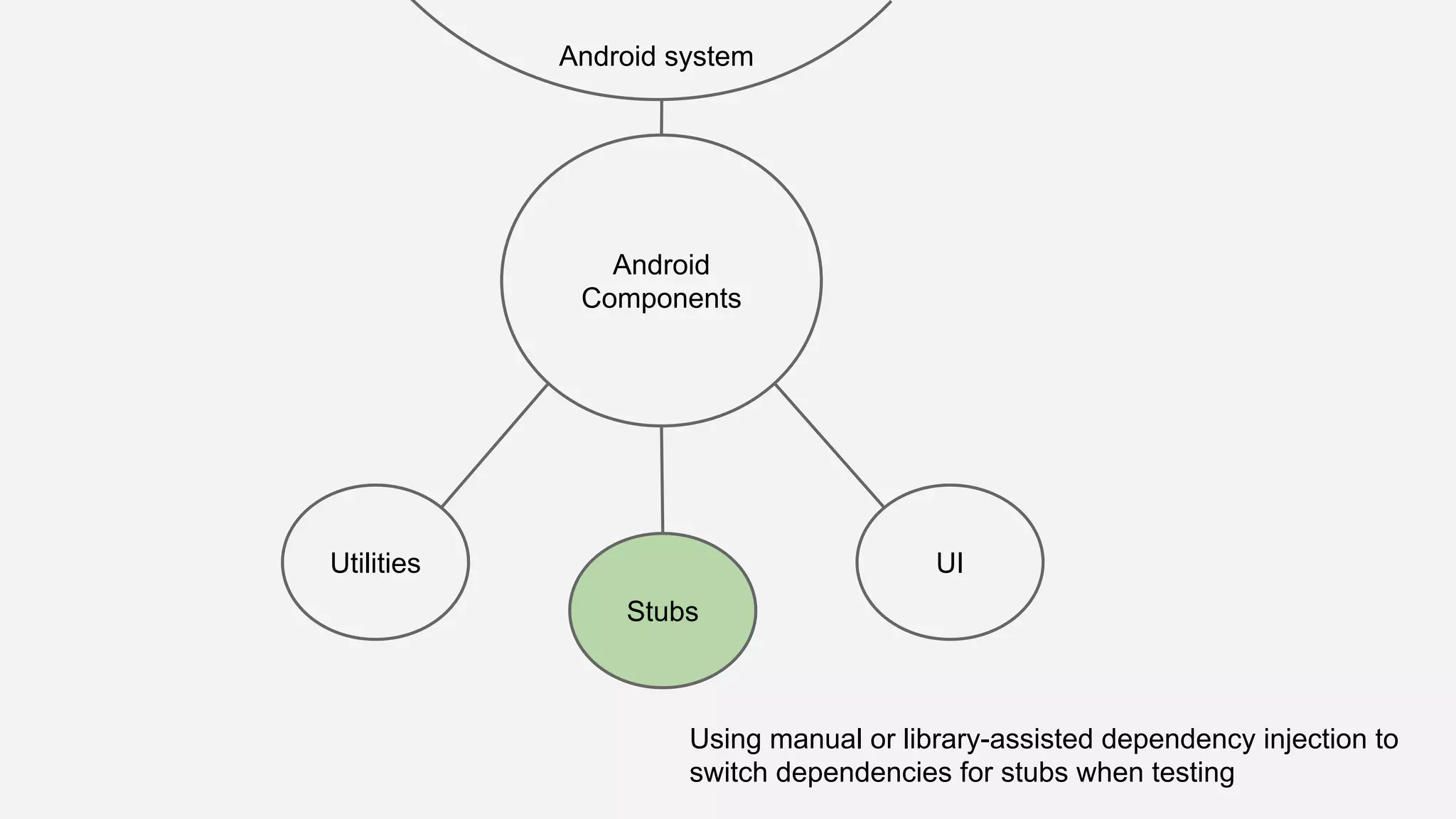
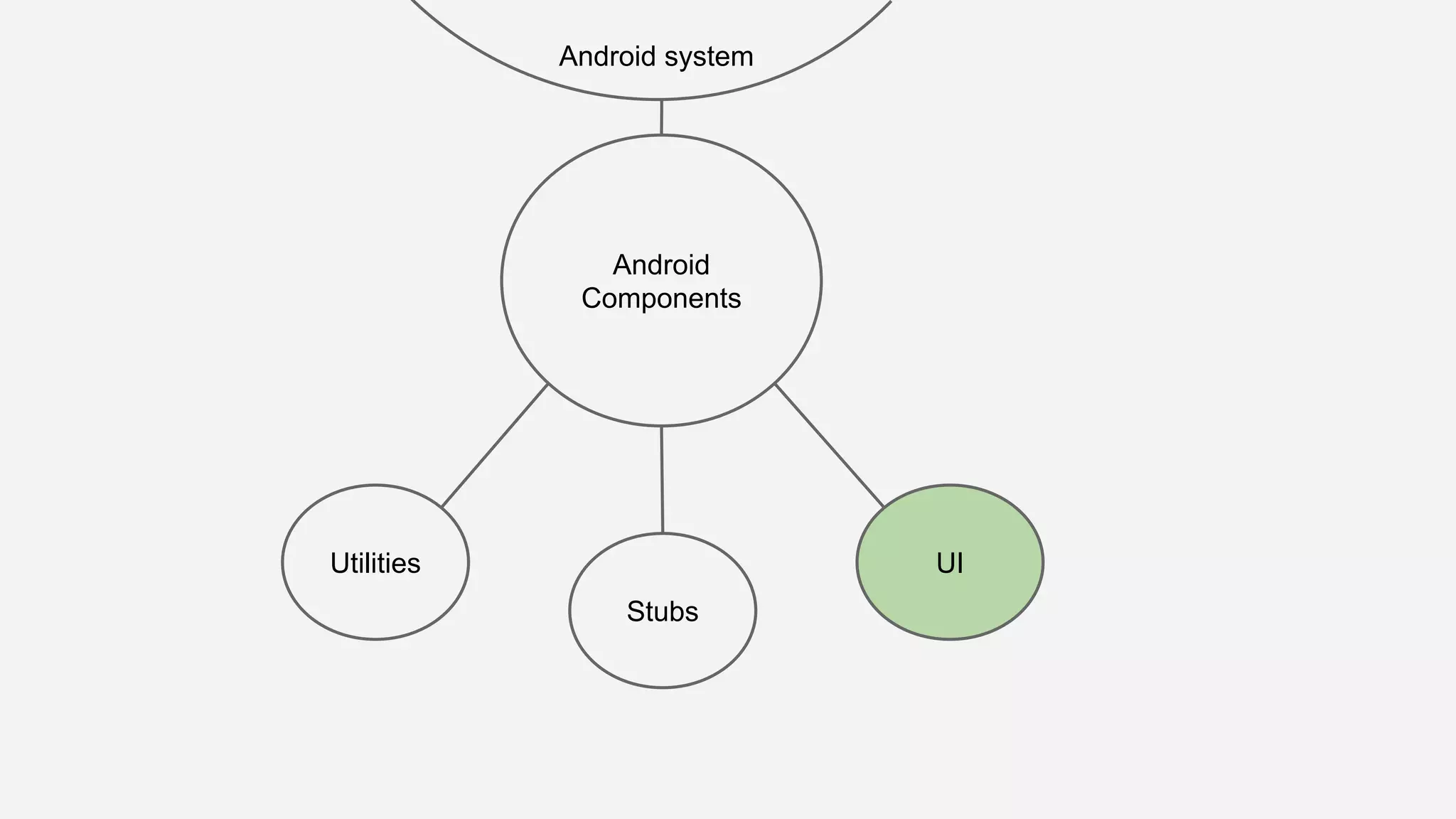
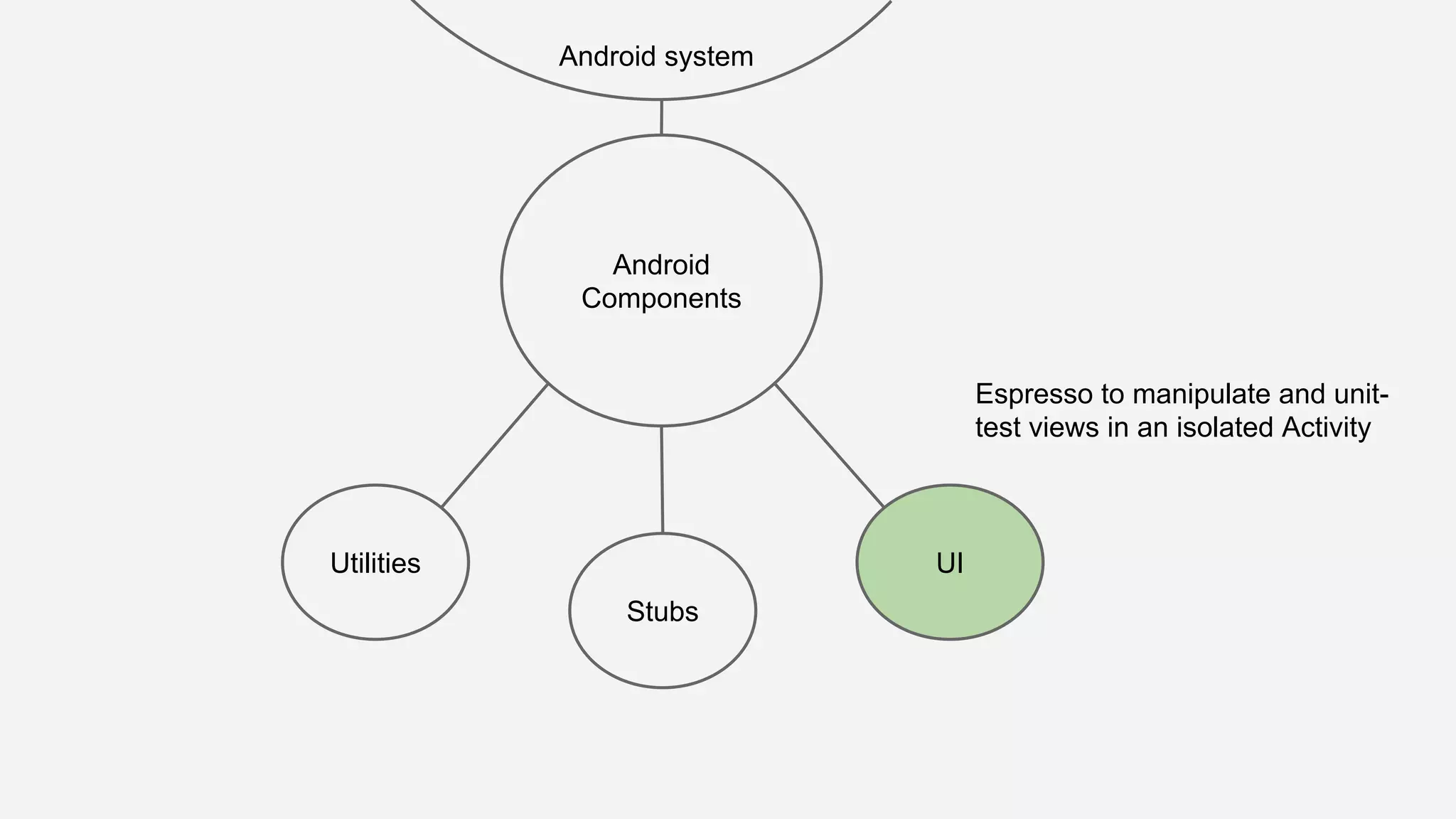
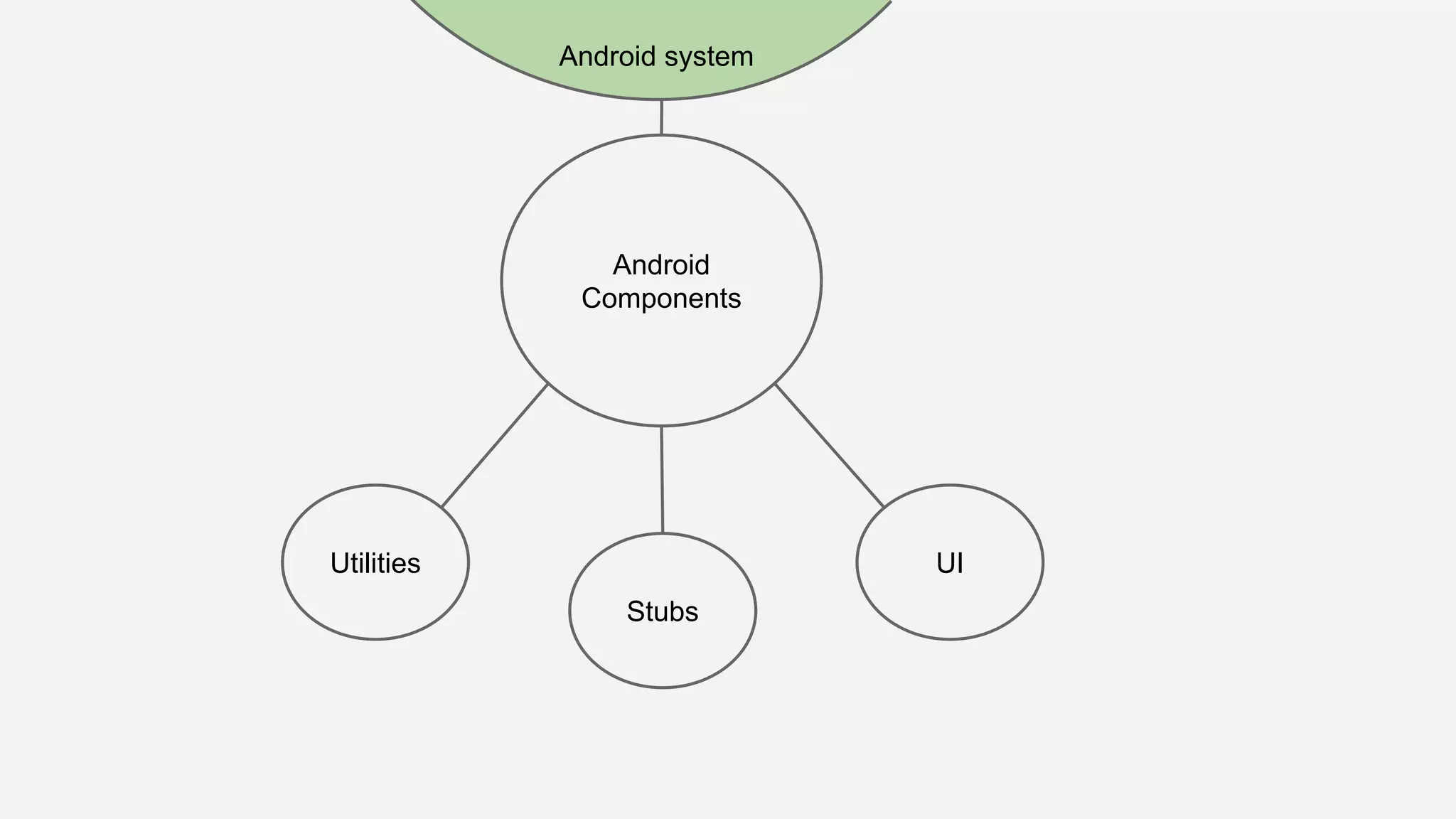
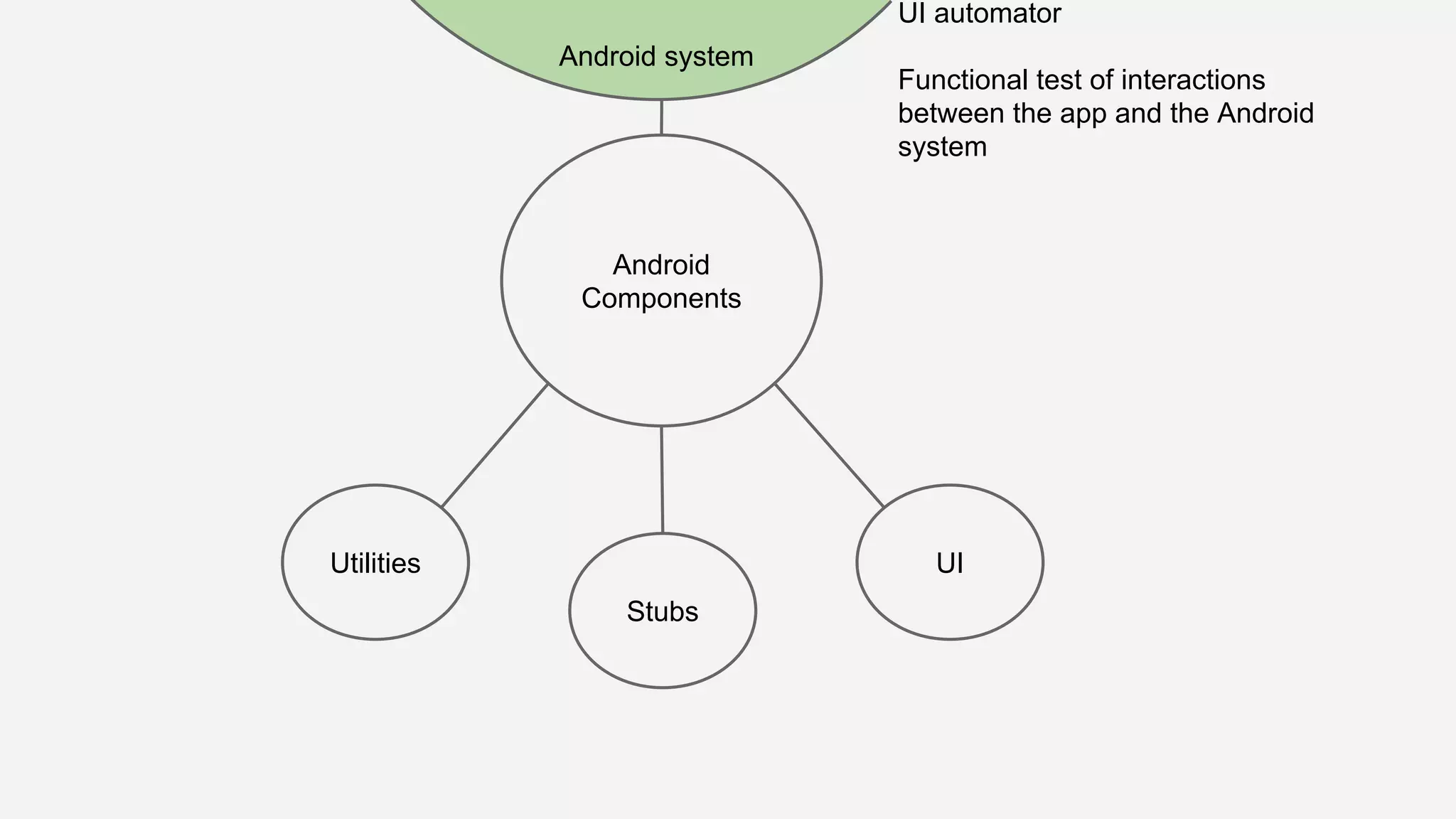
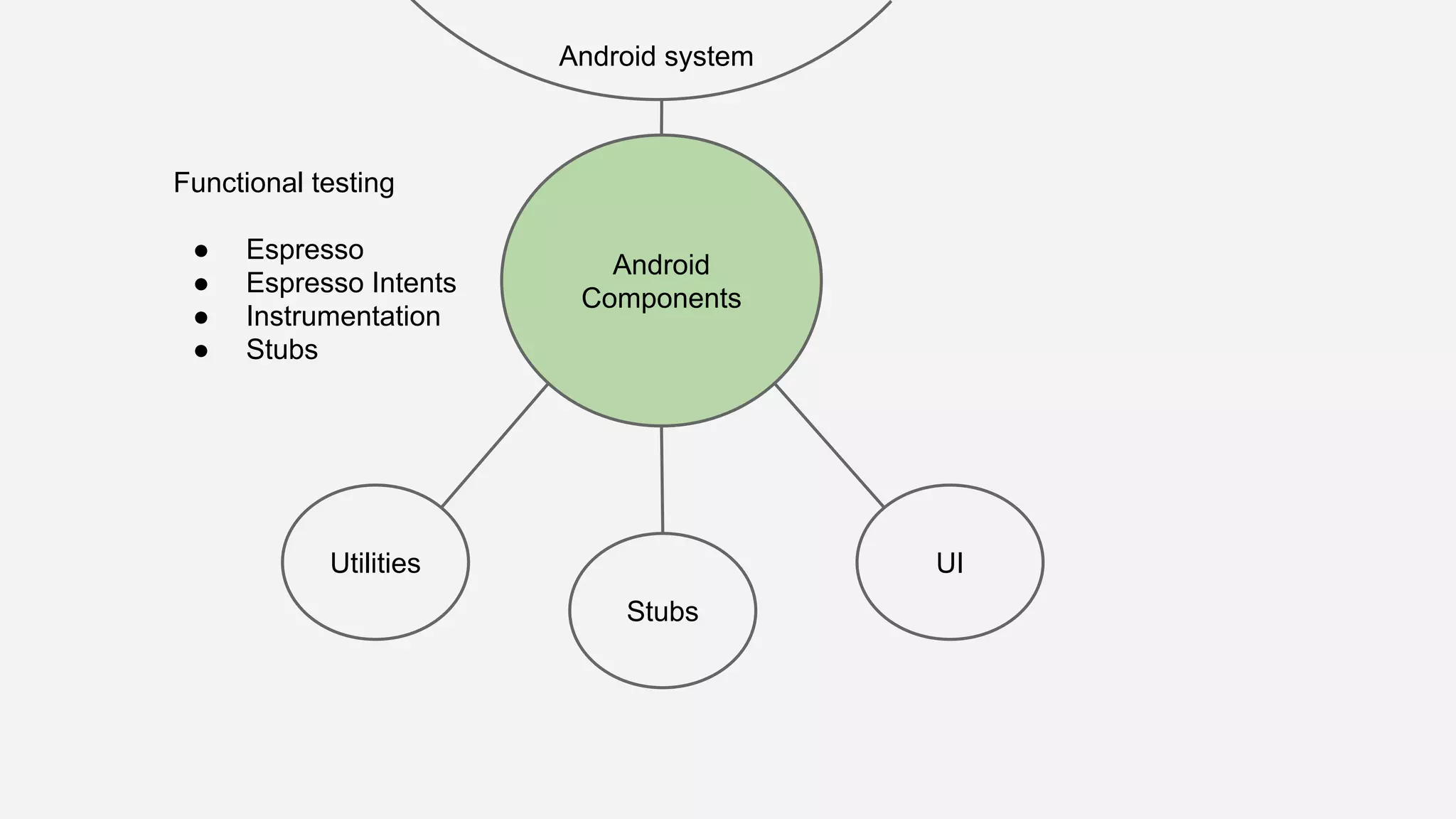
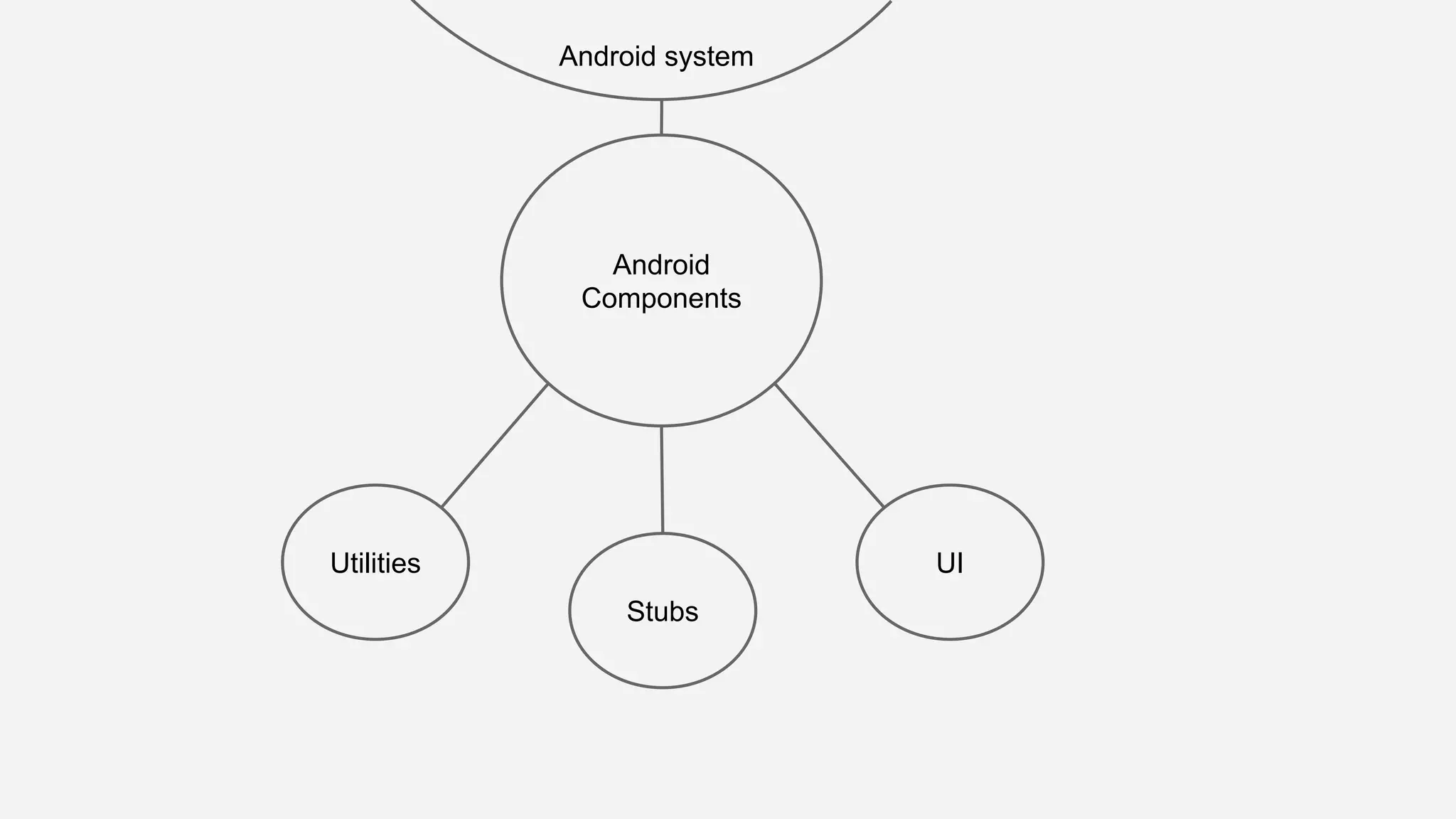
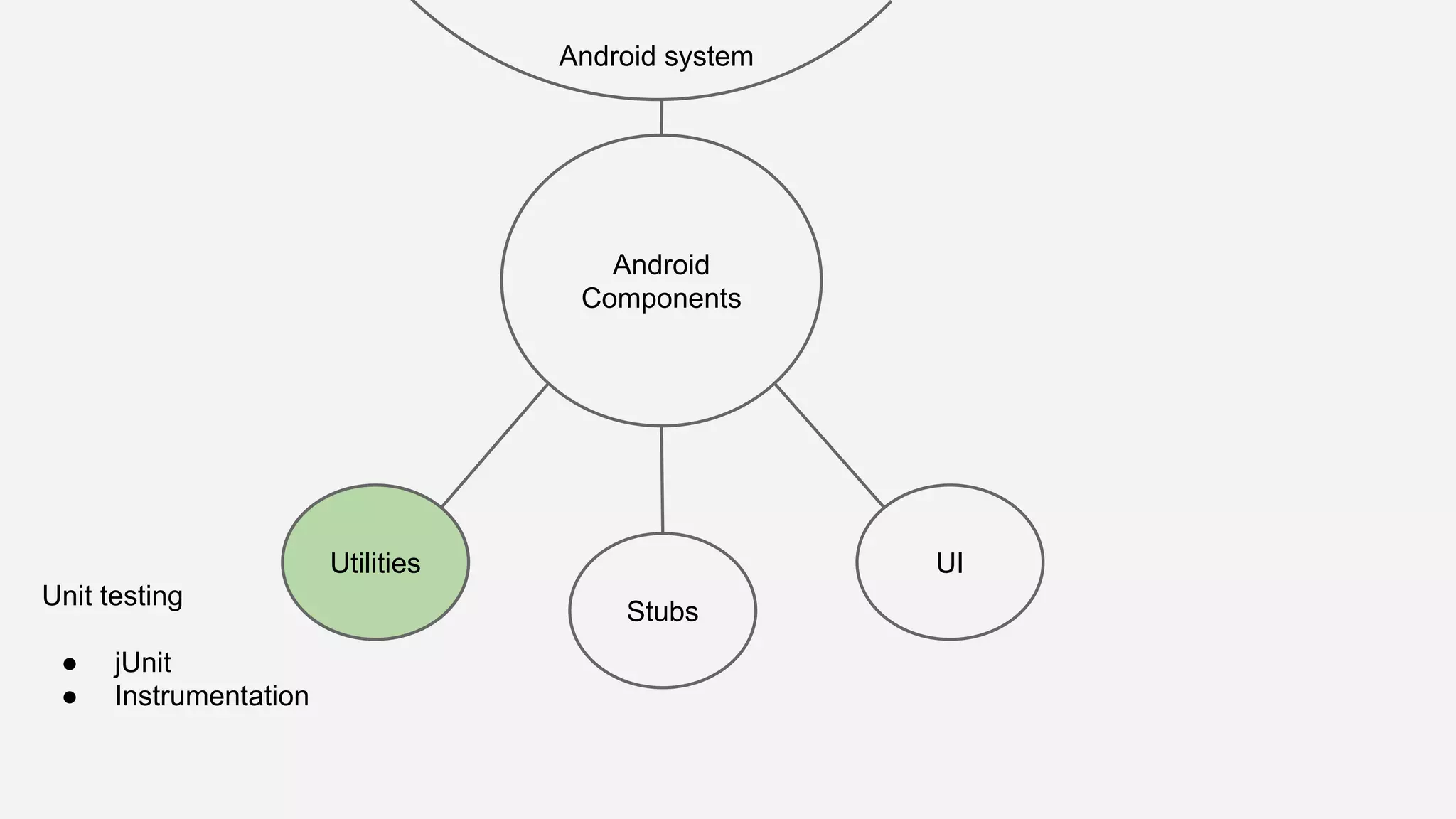
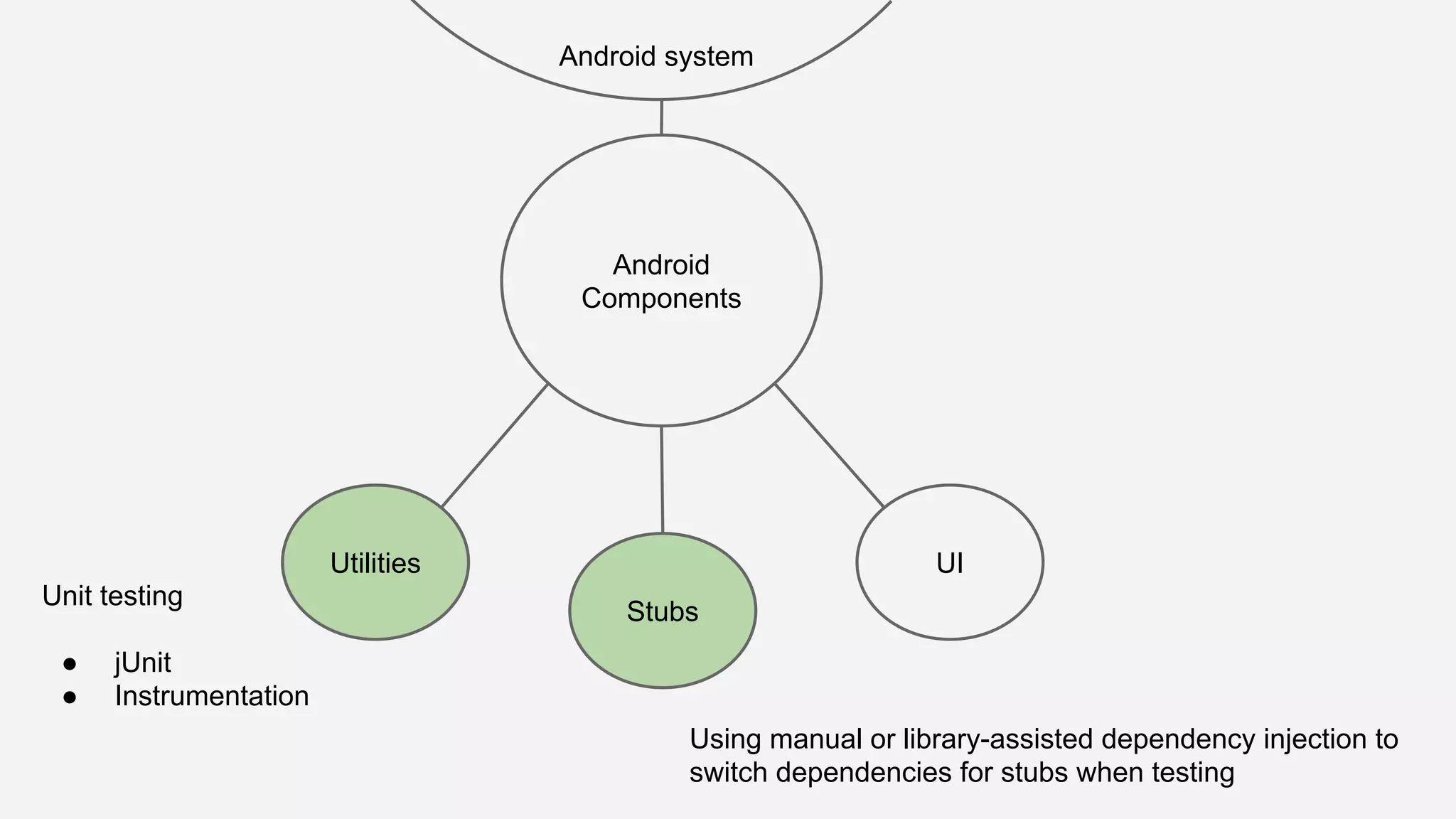
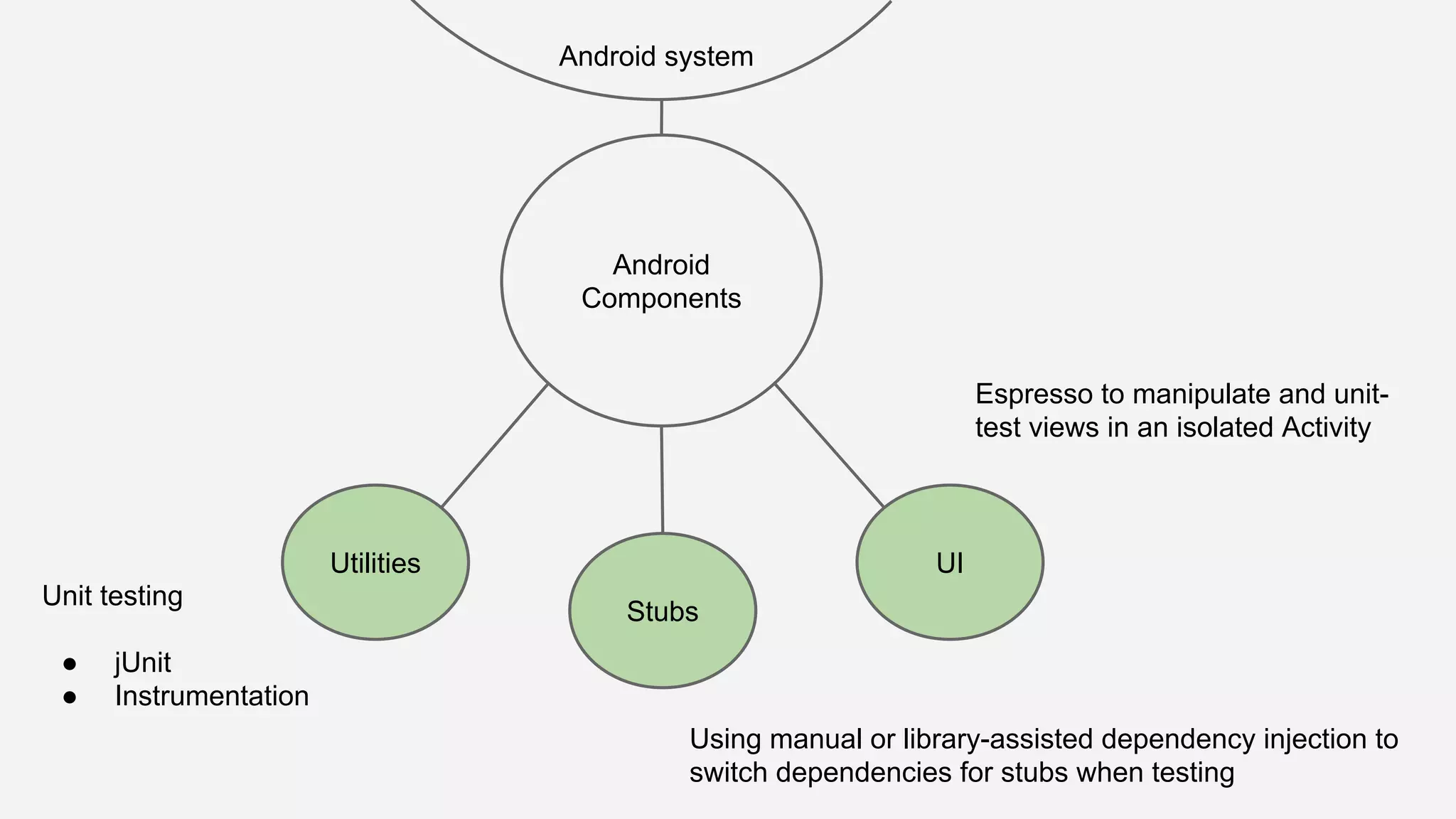
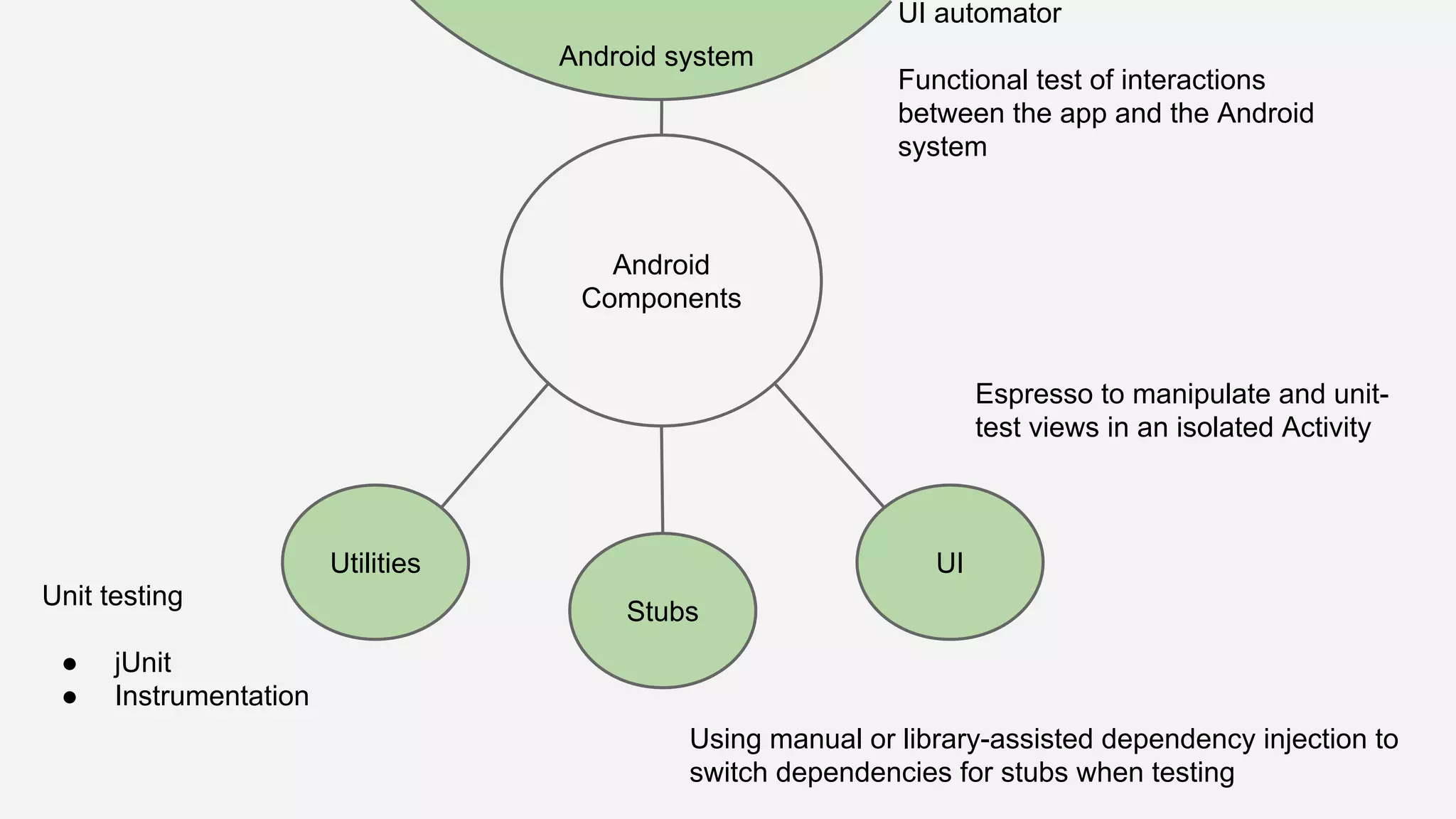
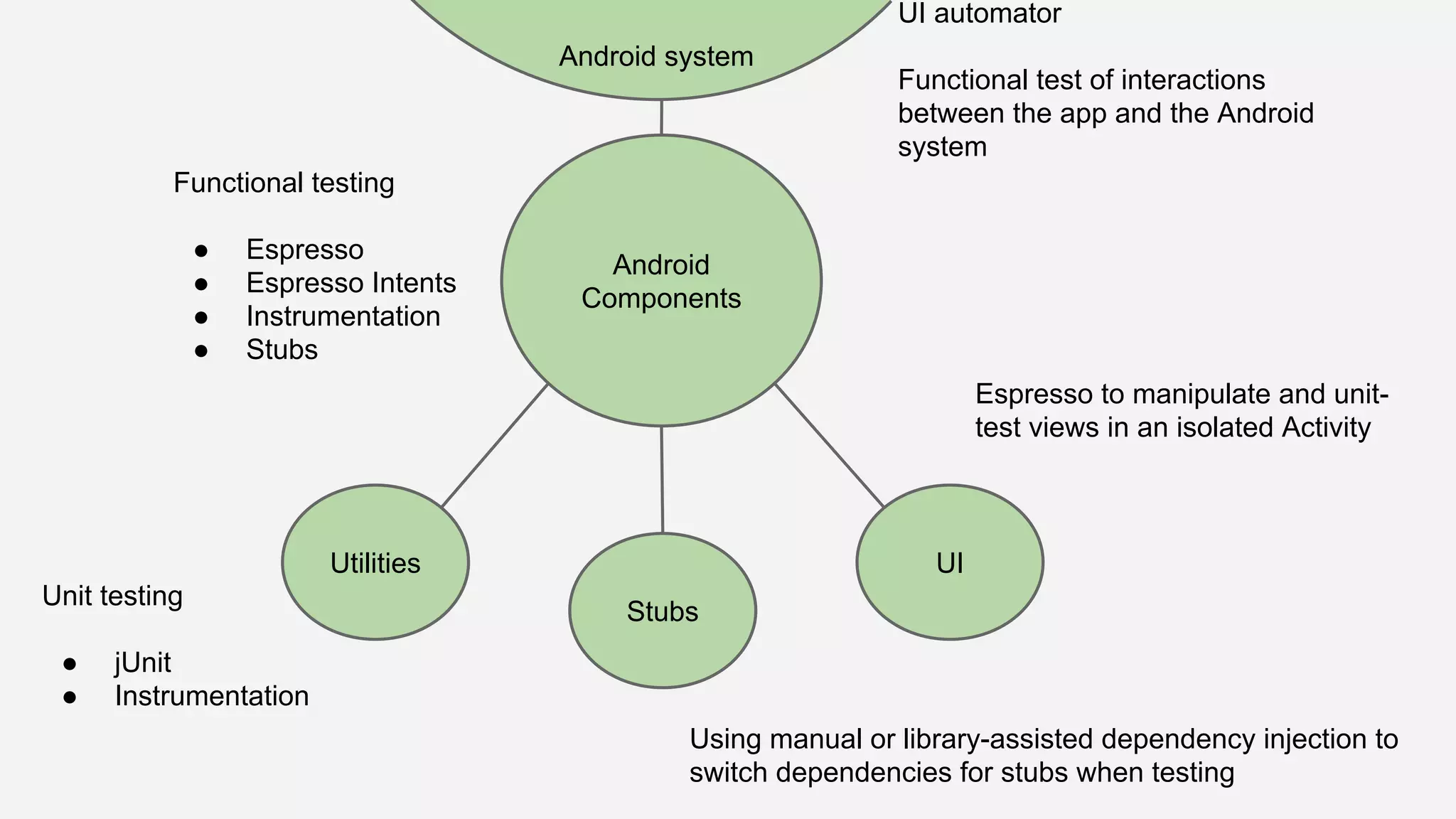
The document discusses best practices for automated Android testing, including testing utilities, Android components, the UI, and expected user behavior. It recommends using support libraries like Instrumentation, Android JUnit Runner, Espresso, and UIAutomator for testing. Espresso allows testing UI interactions within an app, while UIAutomator can test interactions between apps and the system. Tests should be decoupled and use stubs for dependencies that can't be controlled. Everything that could cause errors, like getter/setters, should be tested.