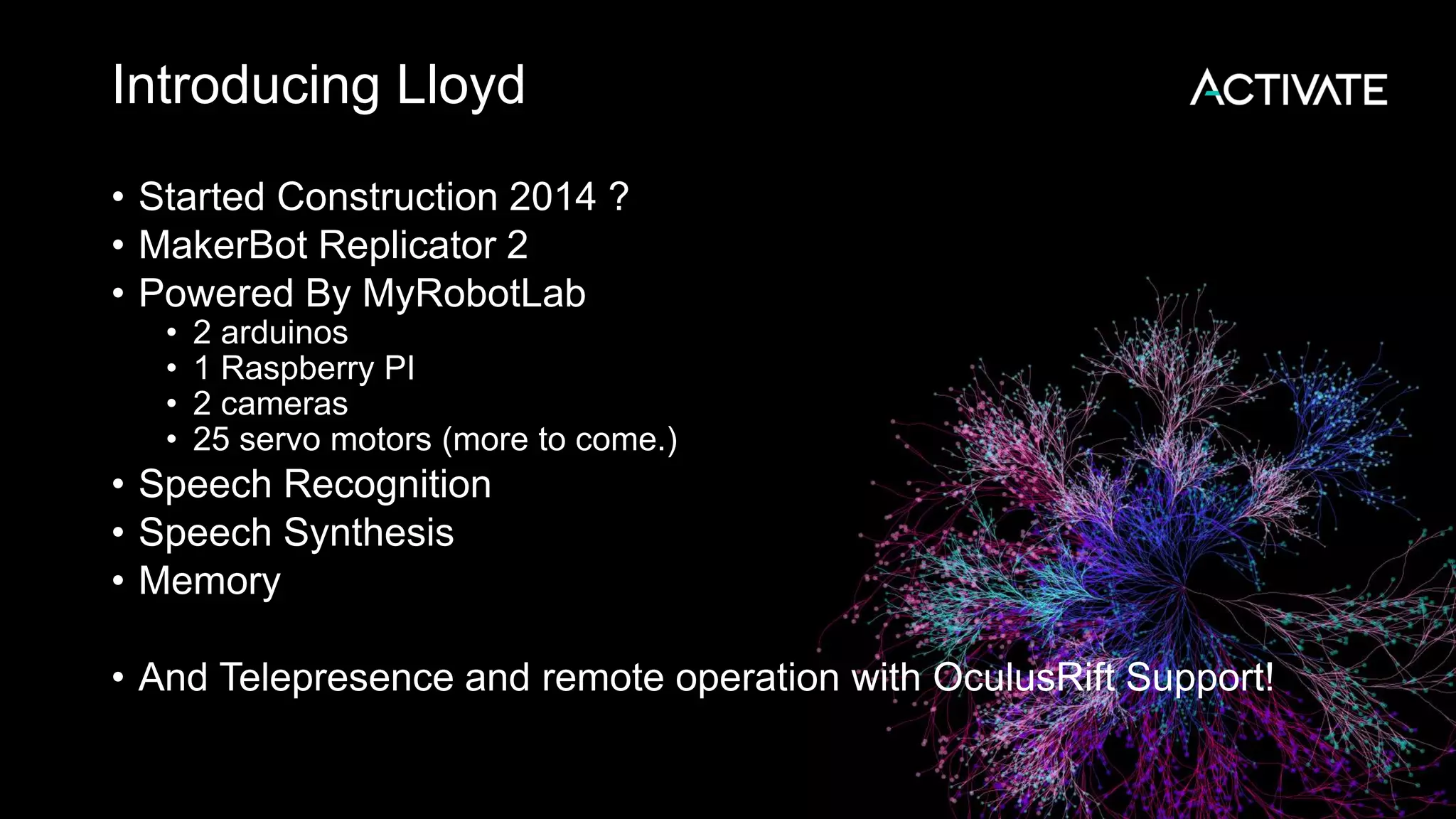
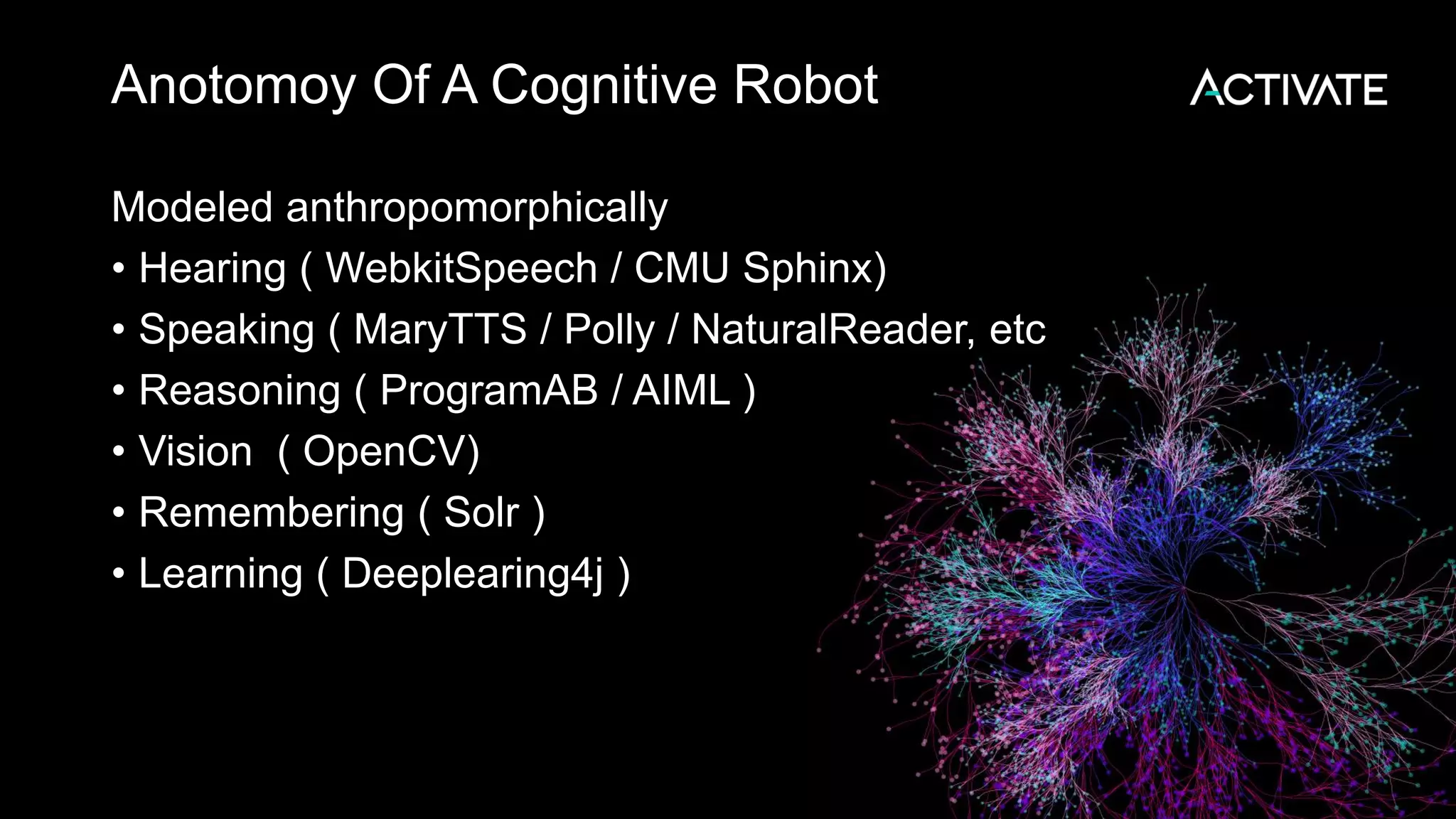
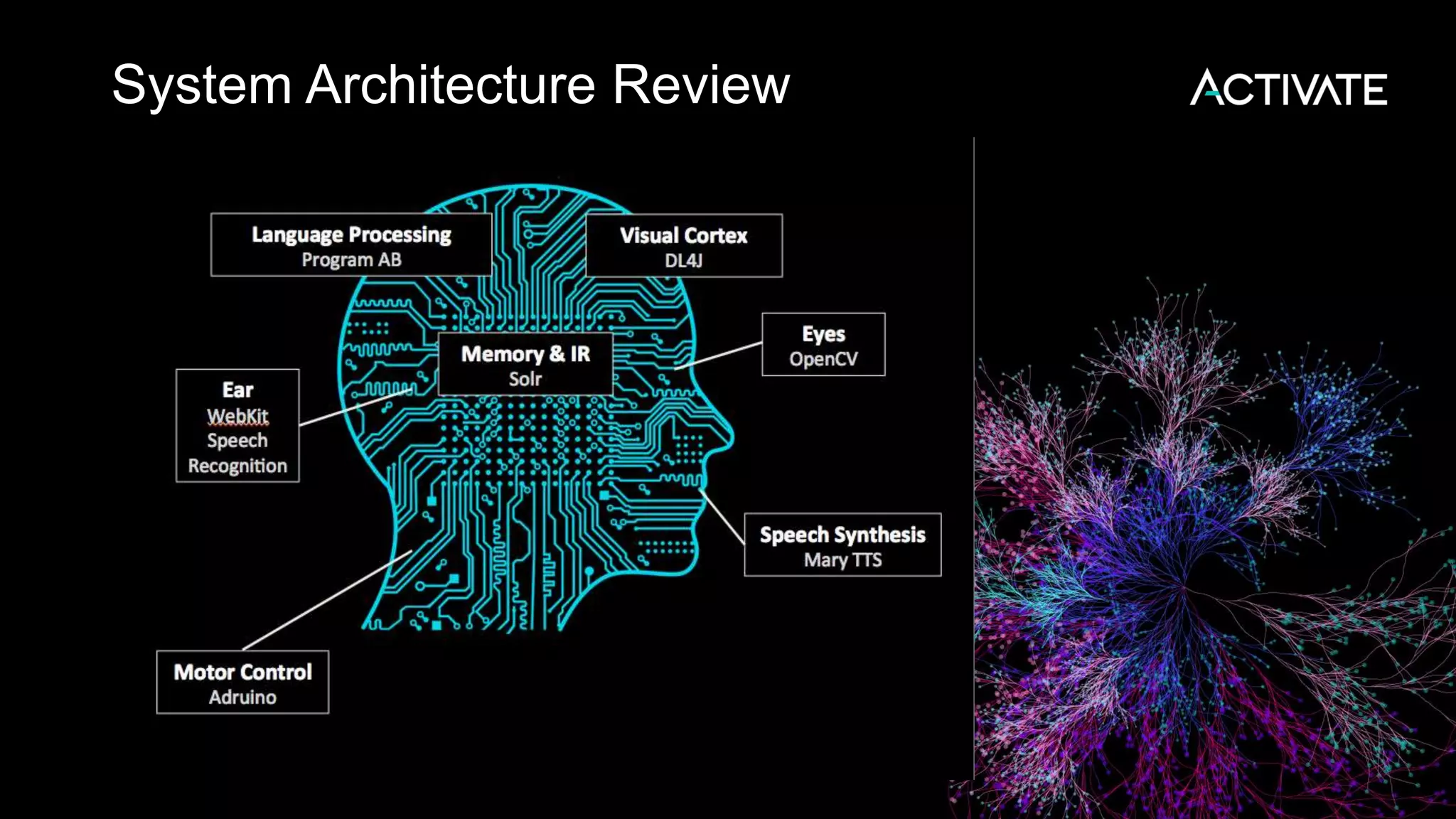
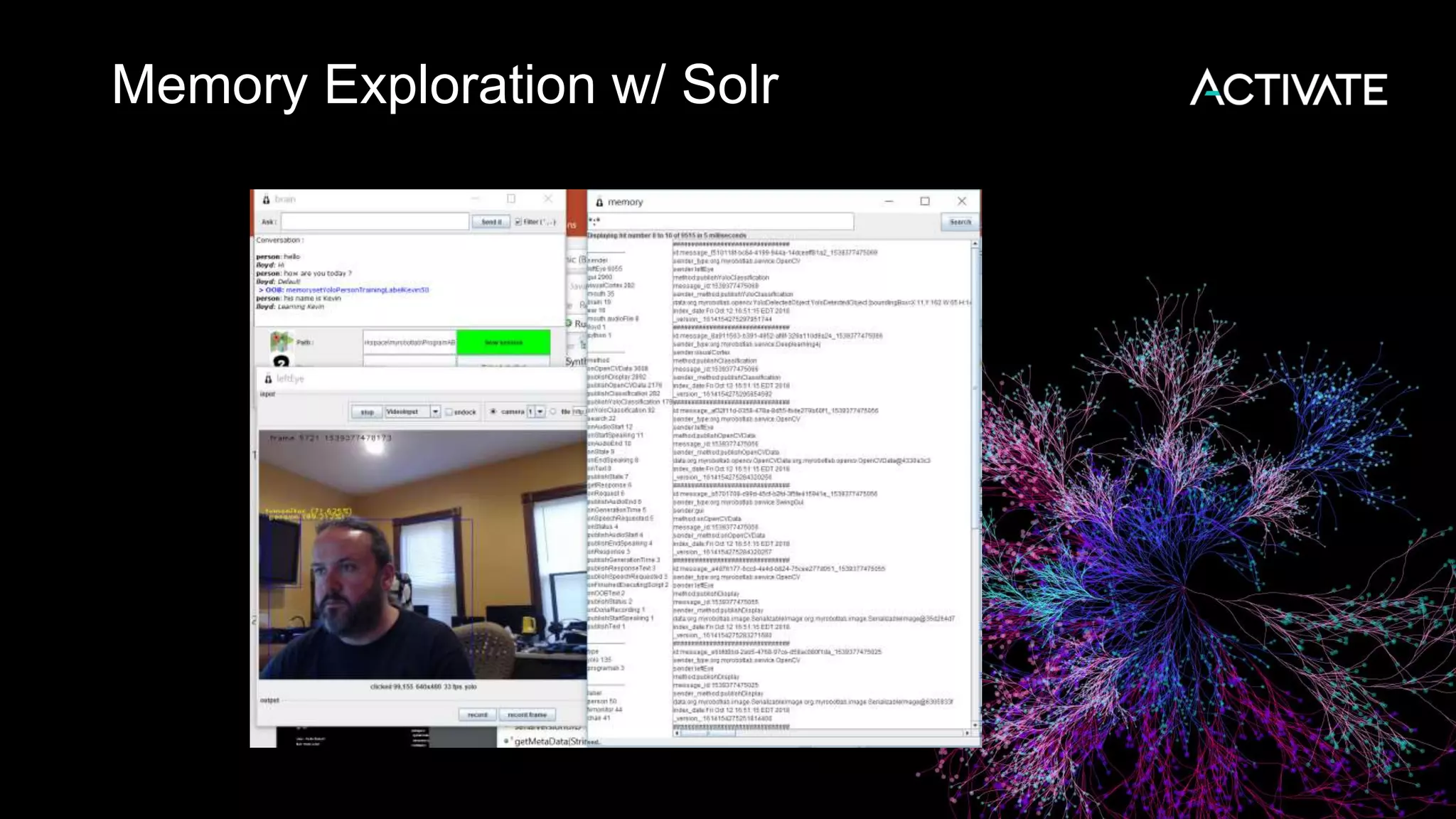
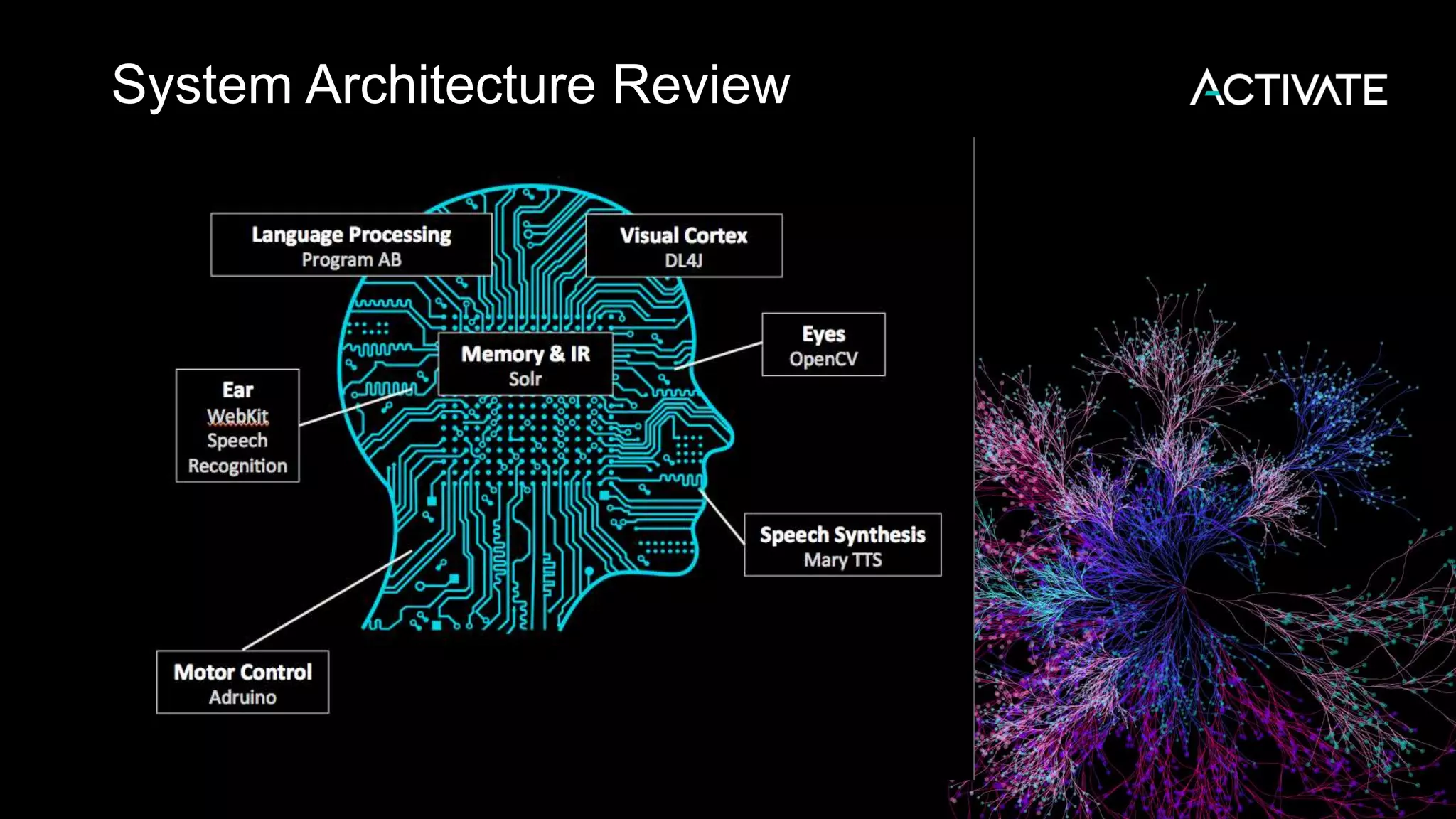
This document discusses using robots, search, and AI technologies together. It summarizes demonstrating a humanoid robot that can learn from its surroundings and interact with humans naturally. The robot will learn to recognize people by being introduced to them, just as humans meet and remember each other. The agenda includes introducing the InMoov robot platform and MyRobotLab framework, and demonstrating how to make a cognitive robot using technologies like speech recognition, computer vision, natural language understanding, memory storage in Solr, and deep learning with Deeplearning4j.