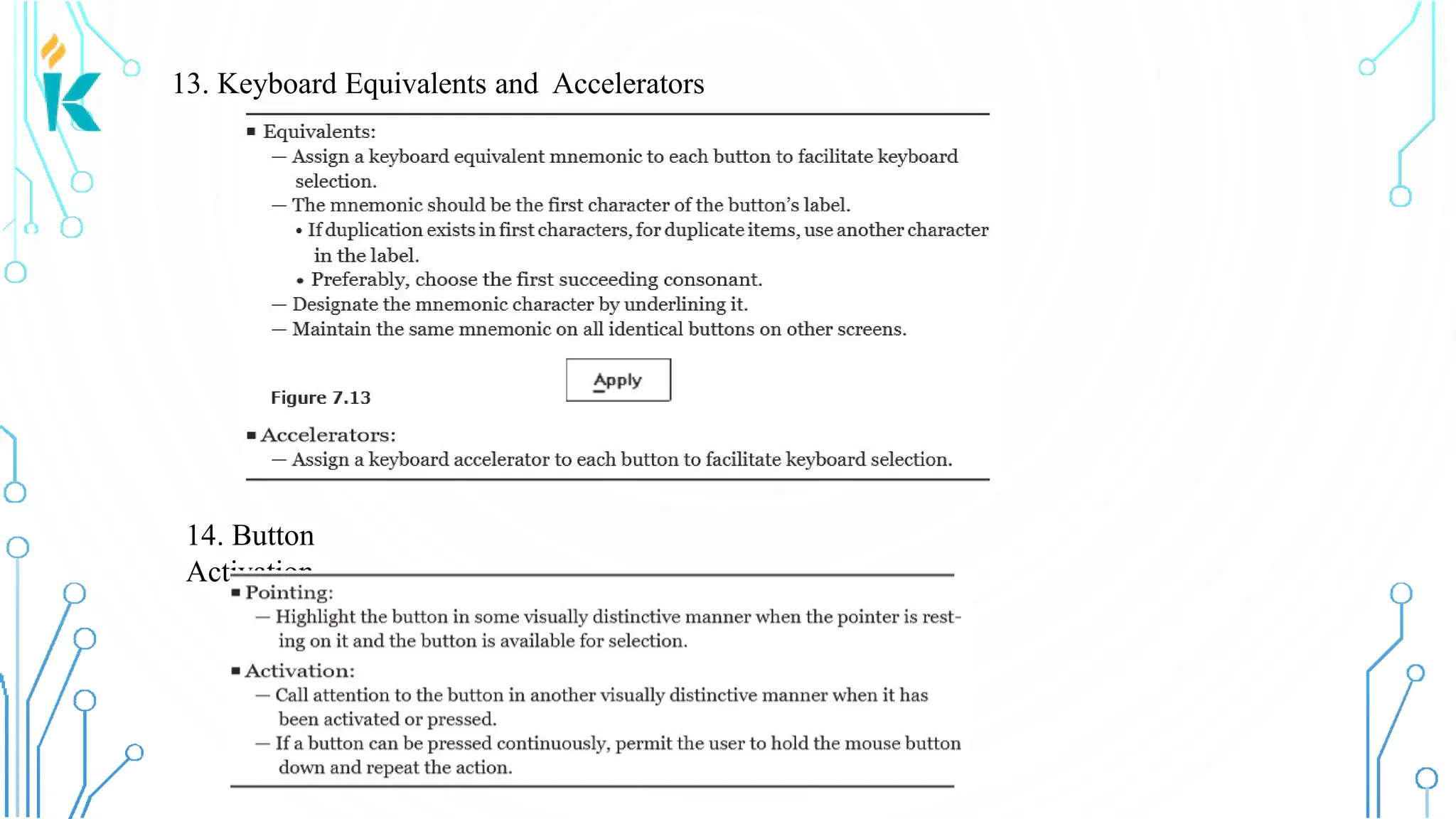
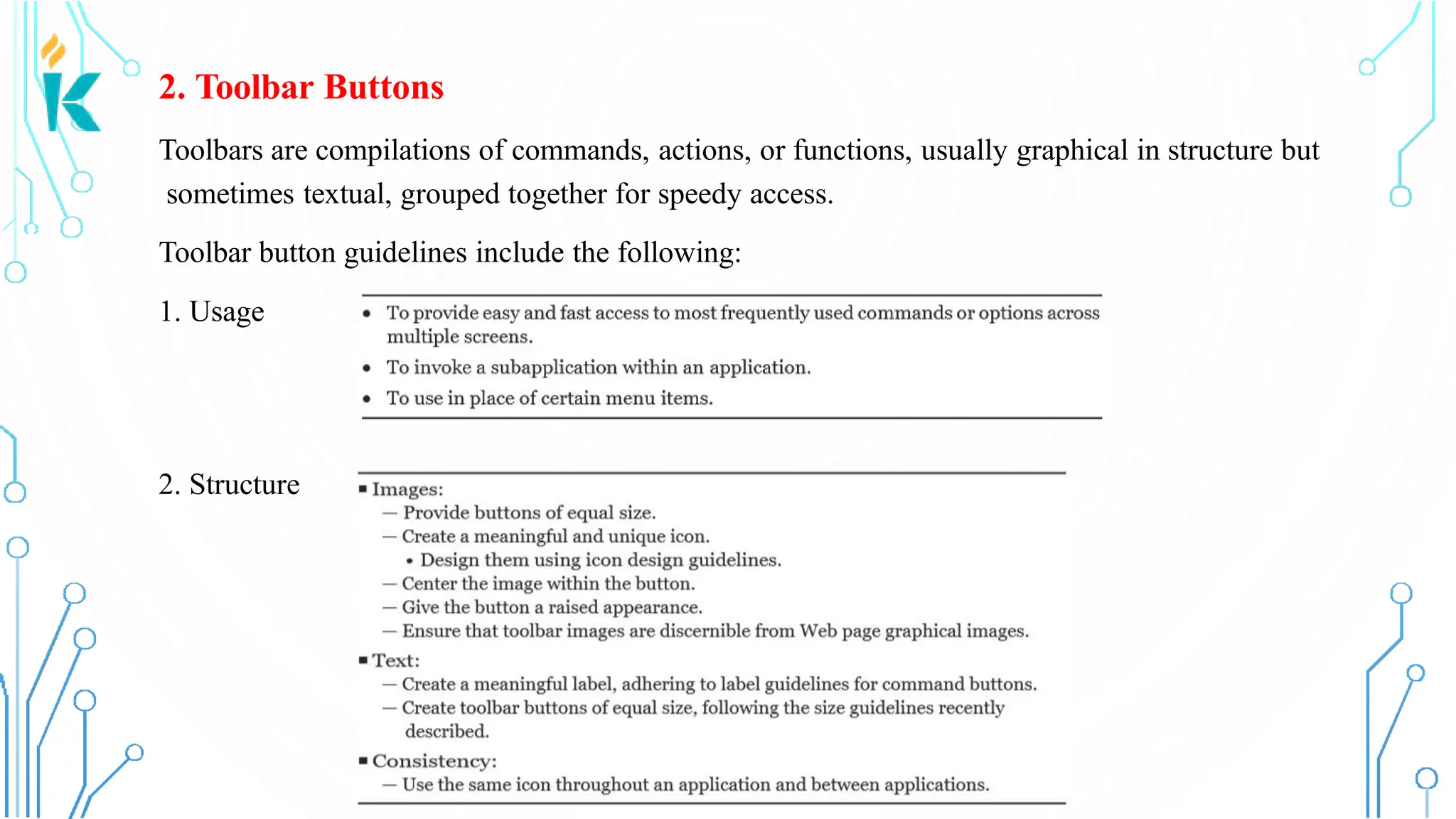
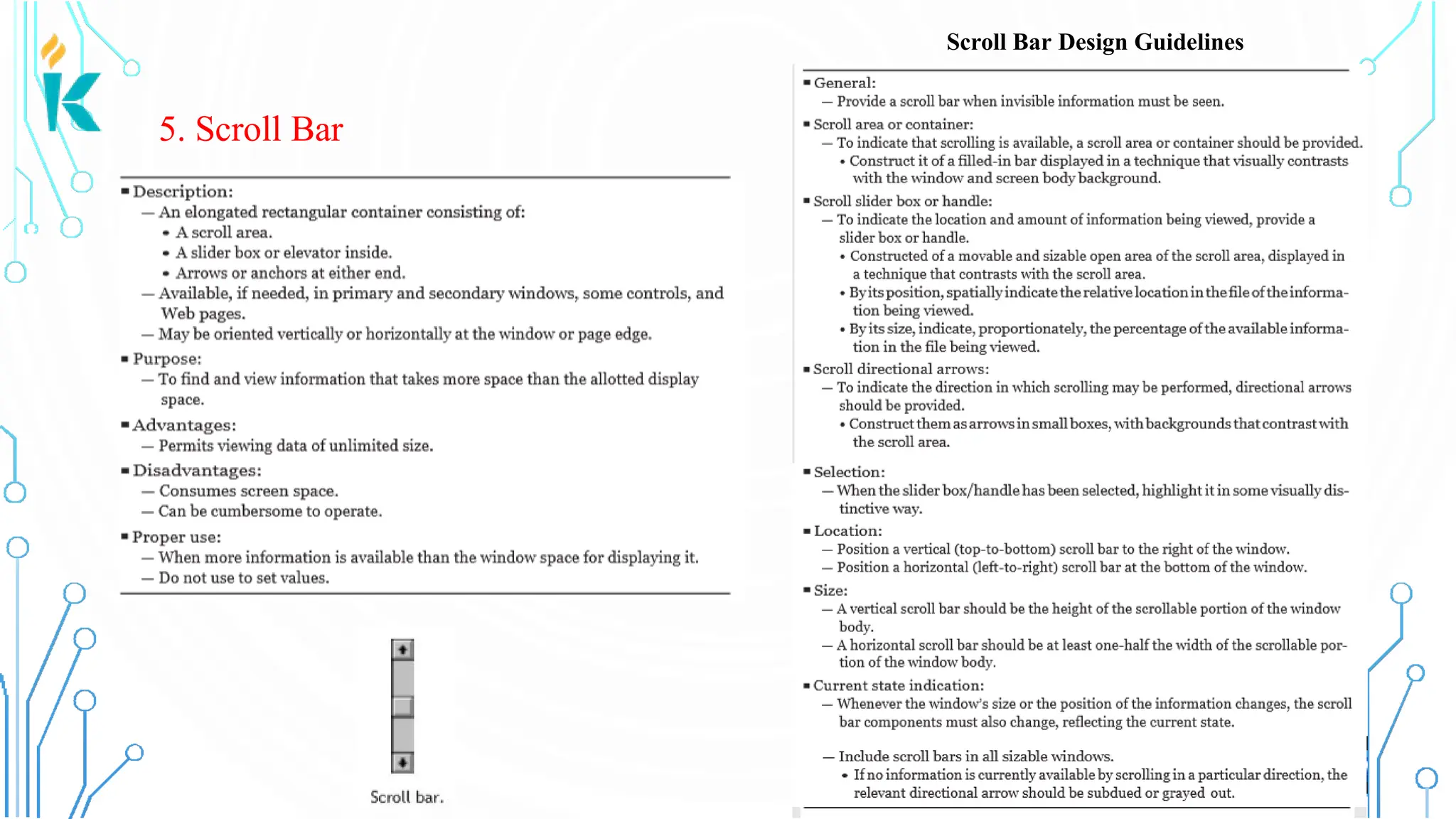
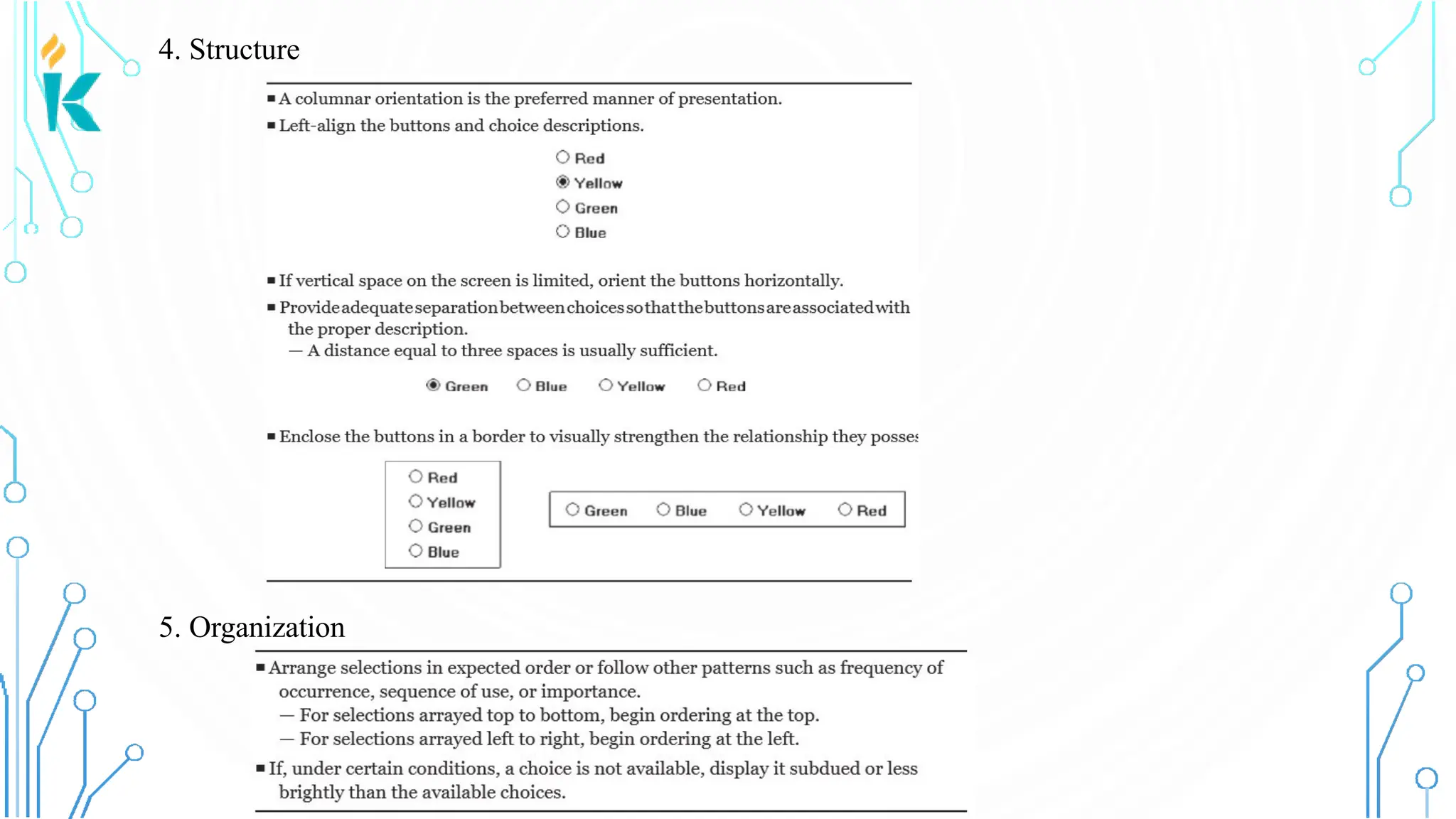
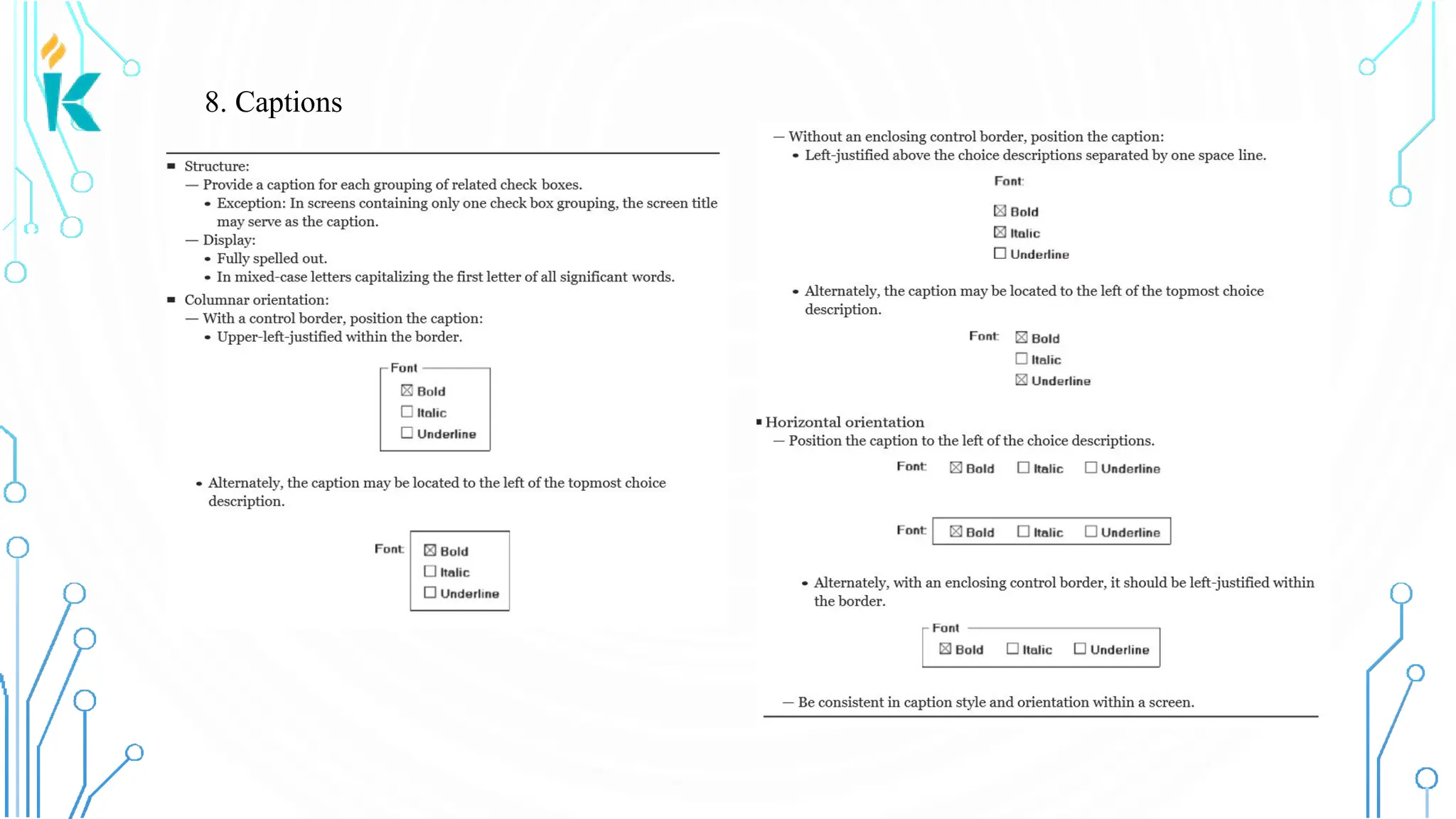
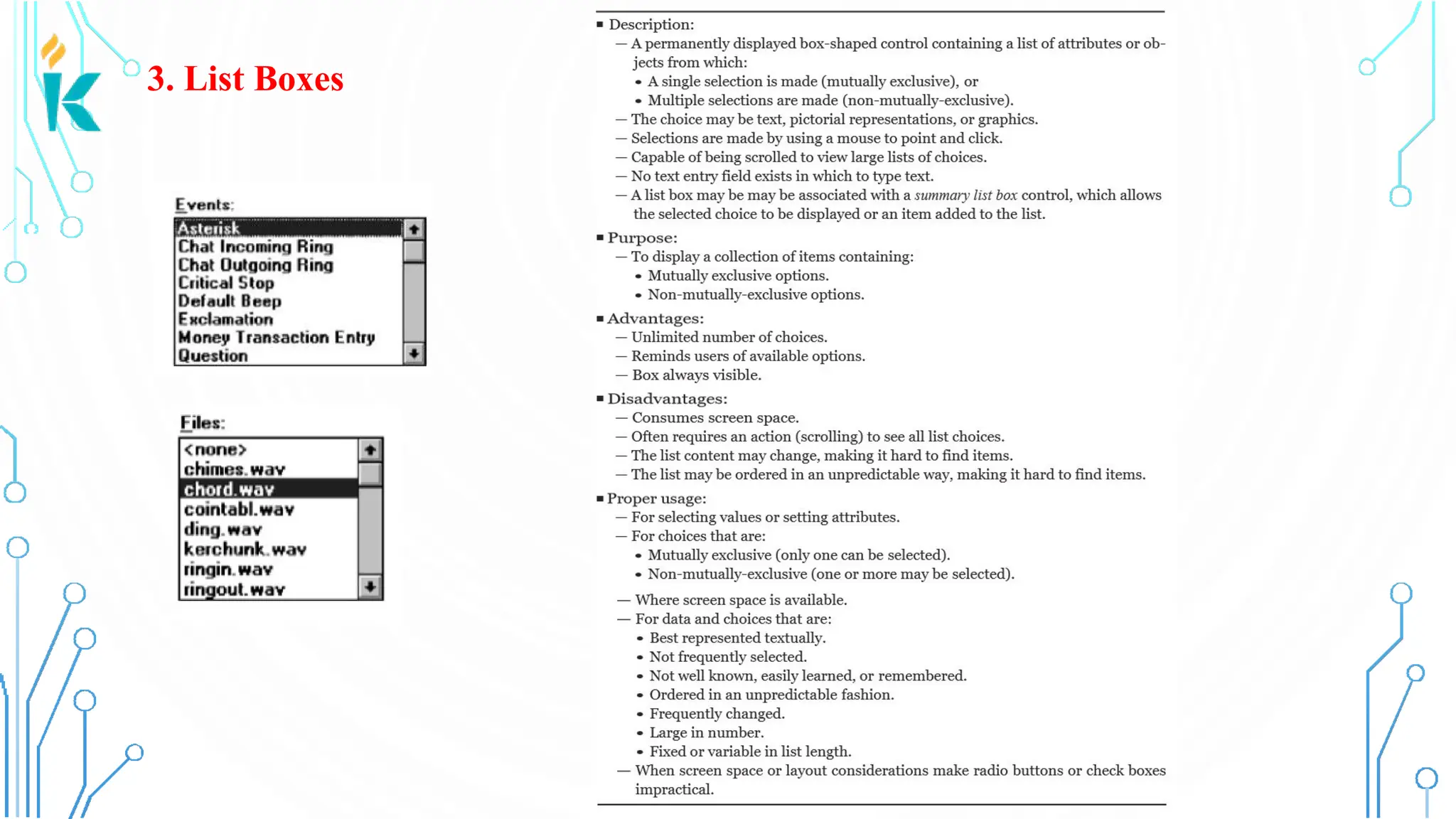
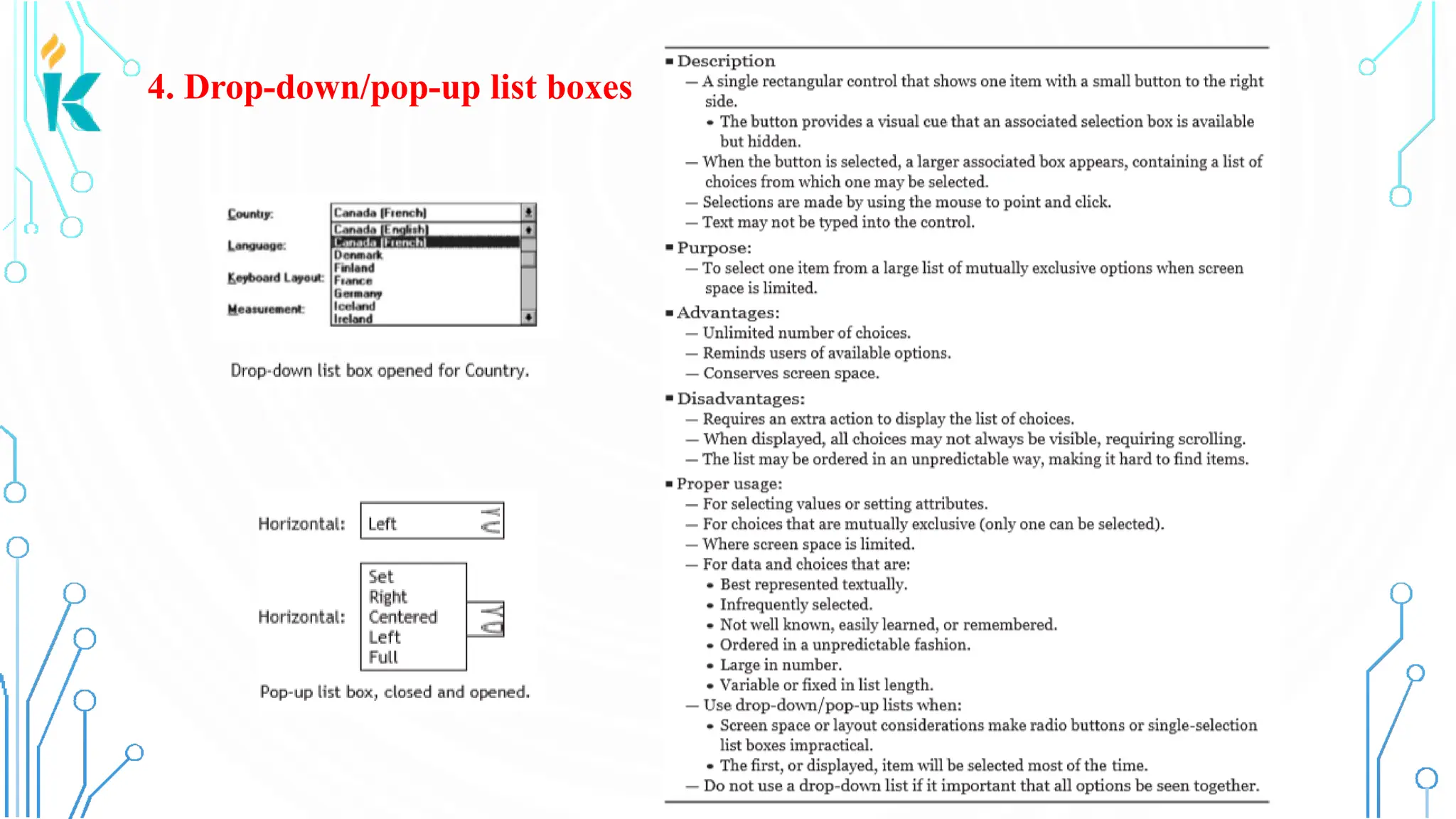
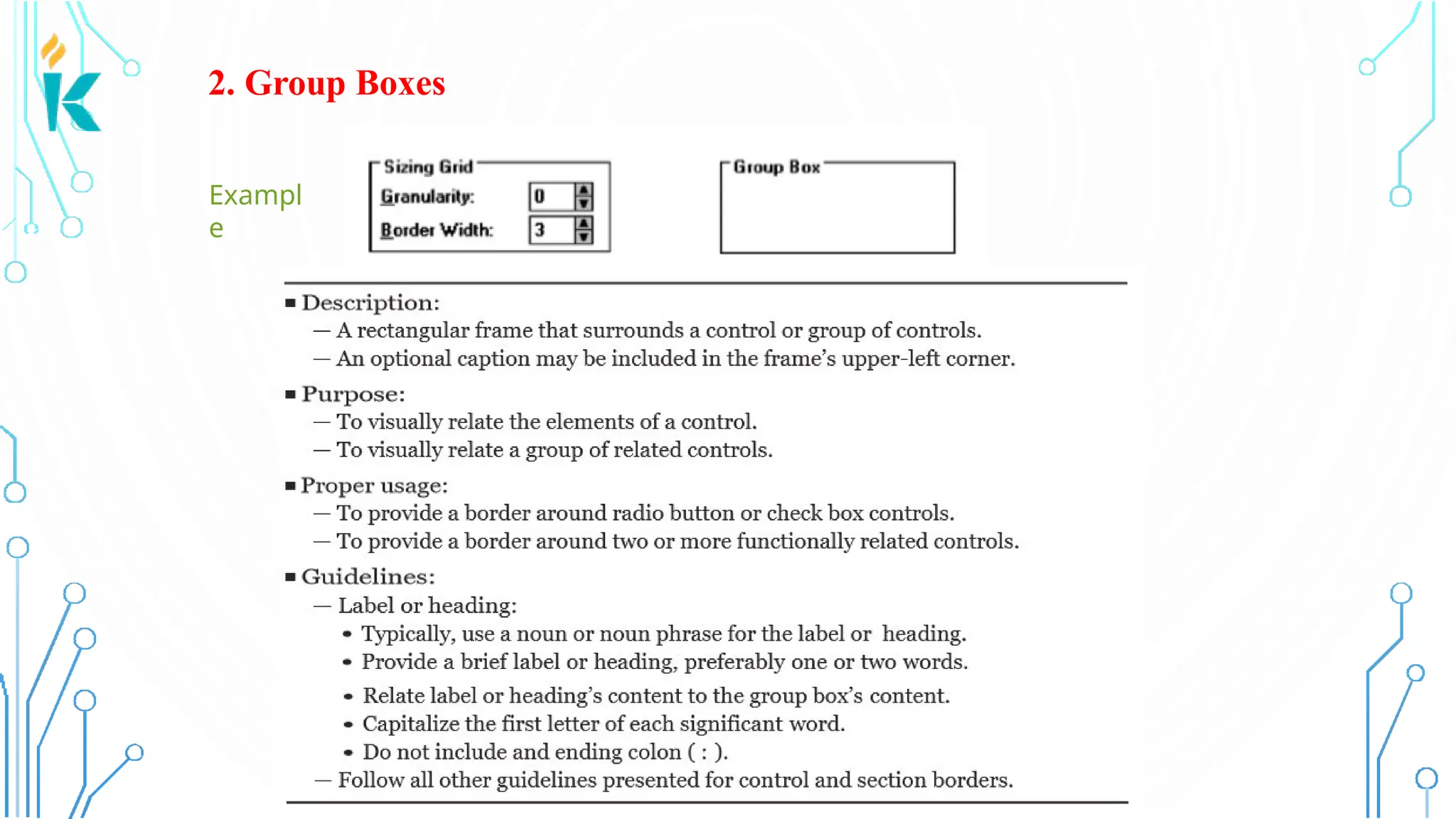
This document discusses screen-based controls or widgets used in user interface design, detailing their types, functionalities, and guidelines for effective usage. It covers operable controls like buttons, sliders, and selection controls, as well as custom and presentation controls that provide informational assistance. Additionally, it addresses prototype testing and various evaluation methods to assess design effectiveness.