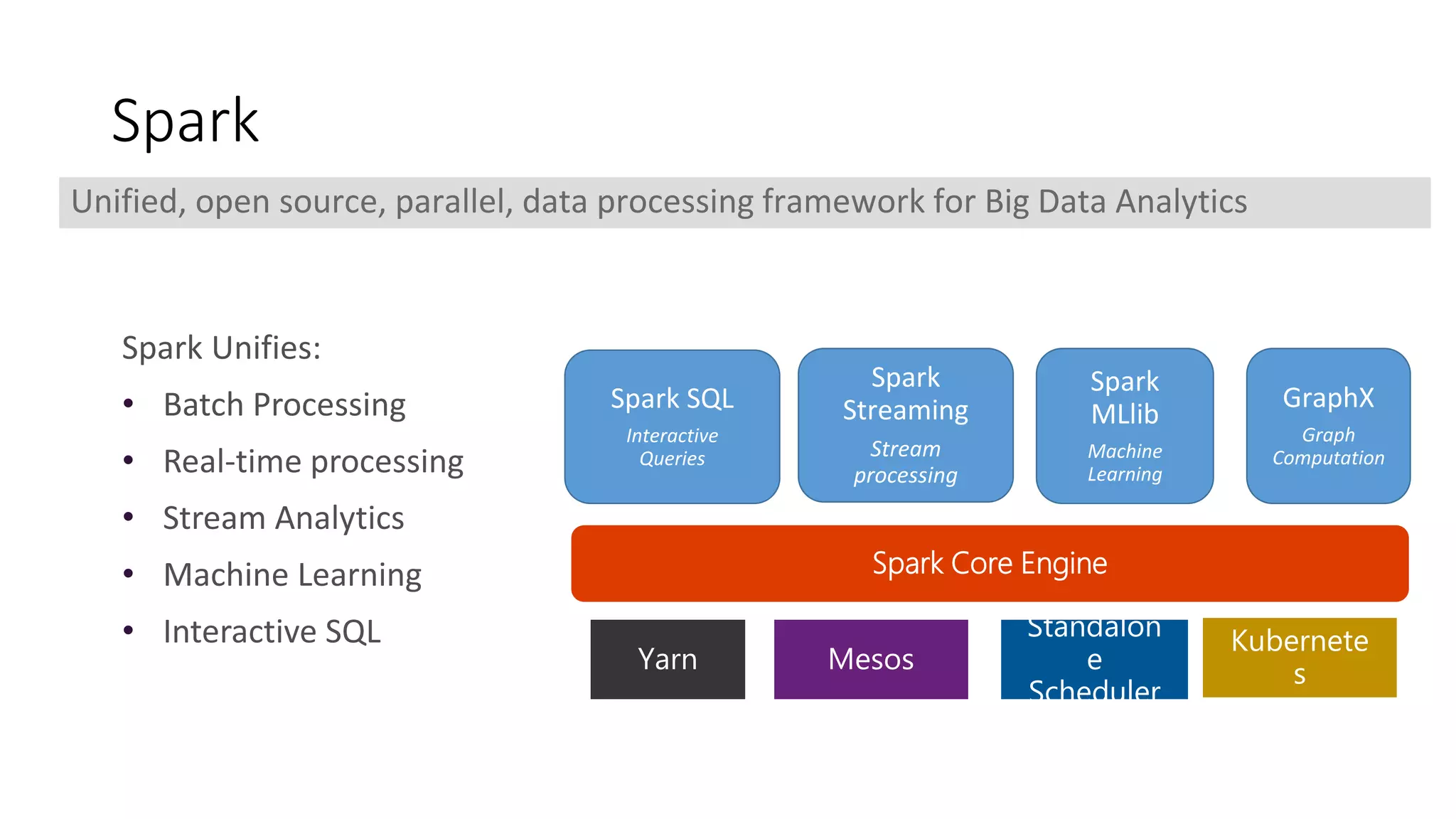
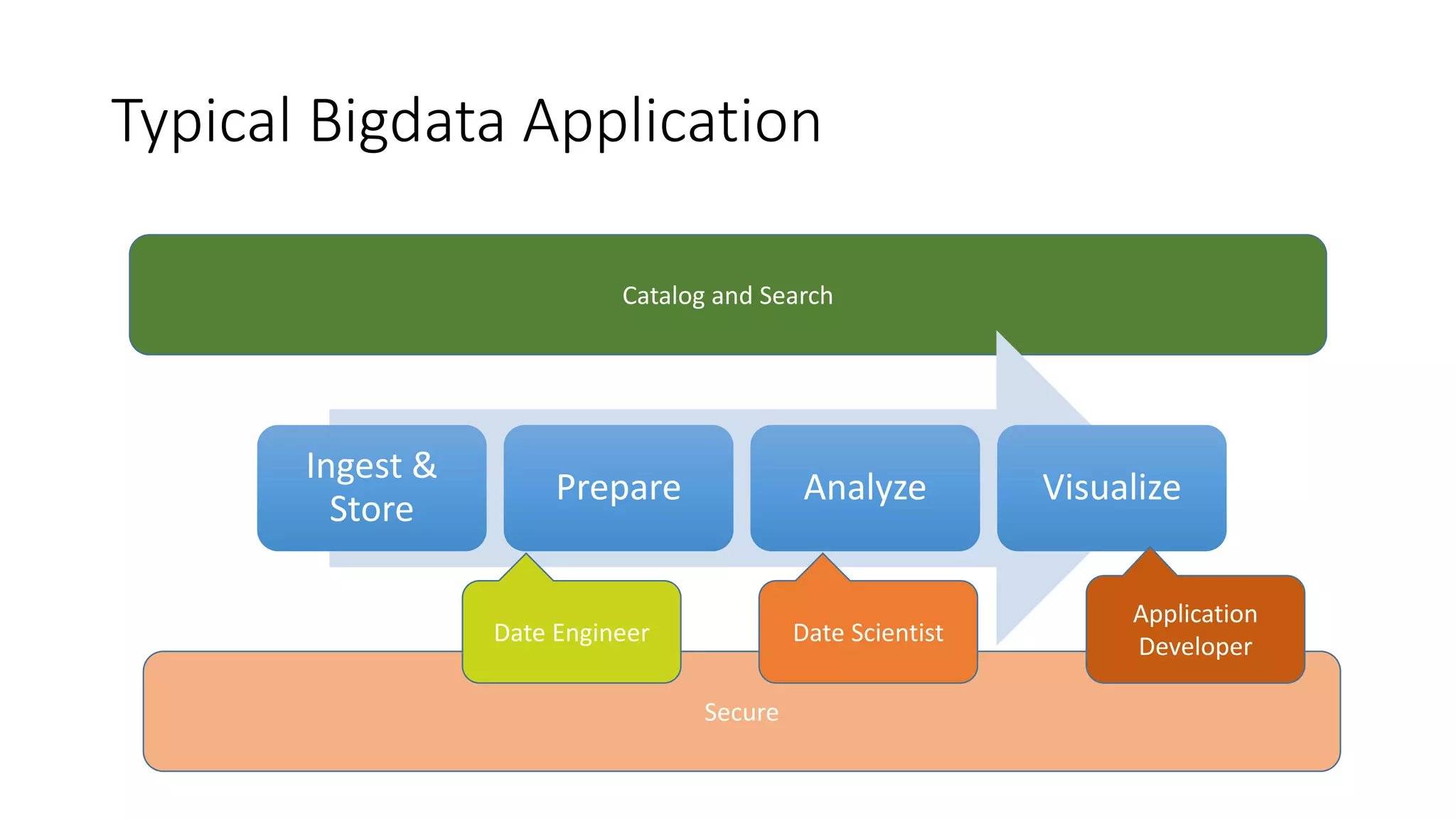
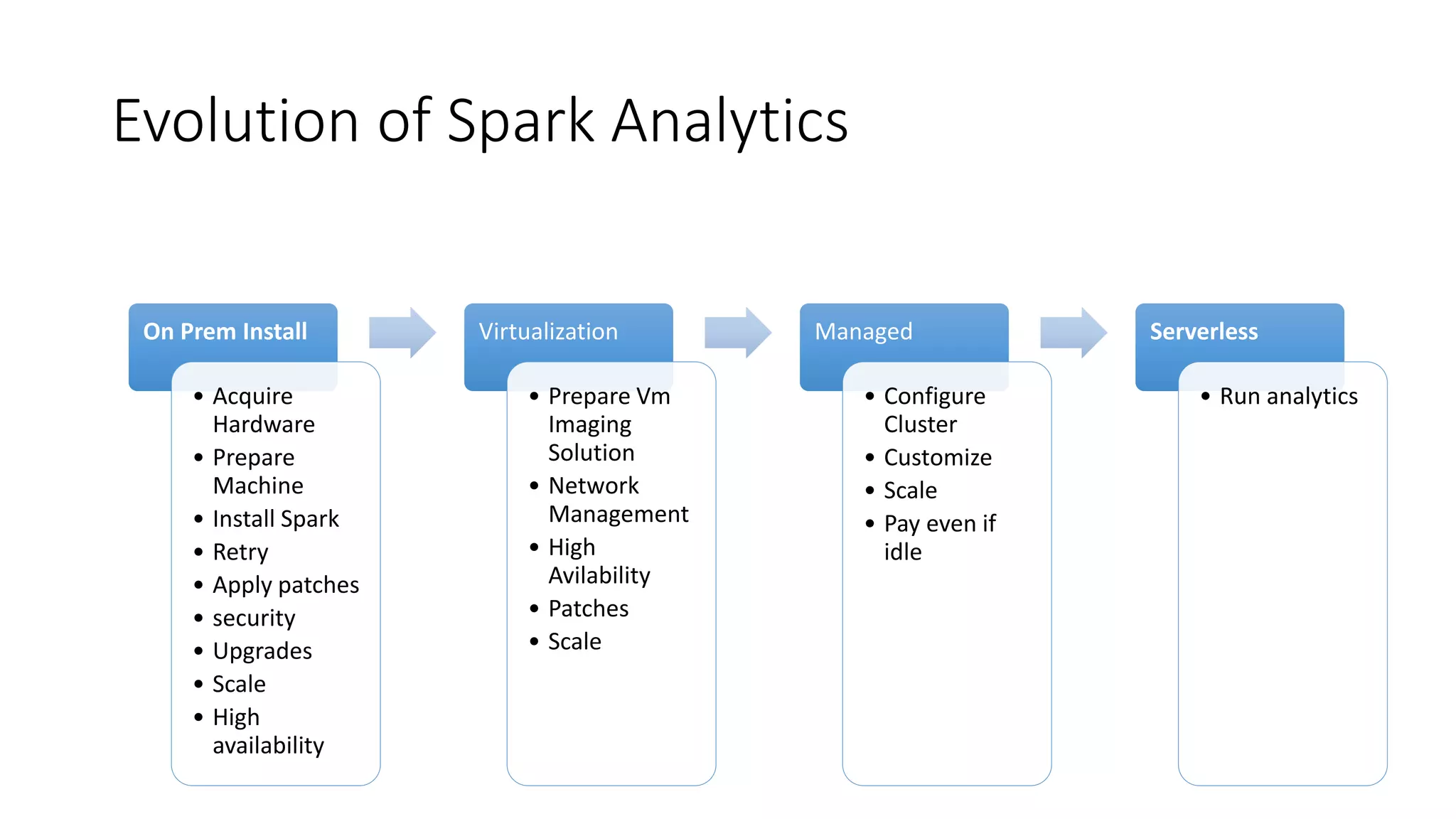
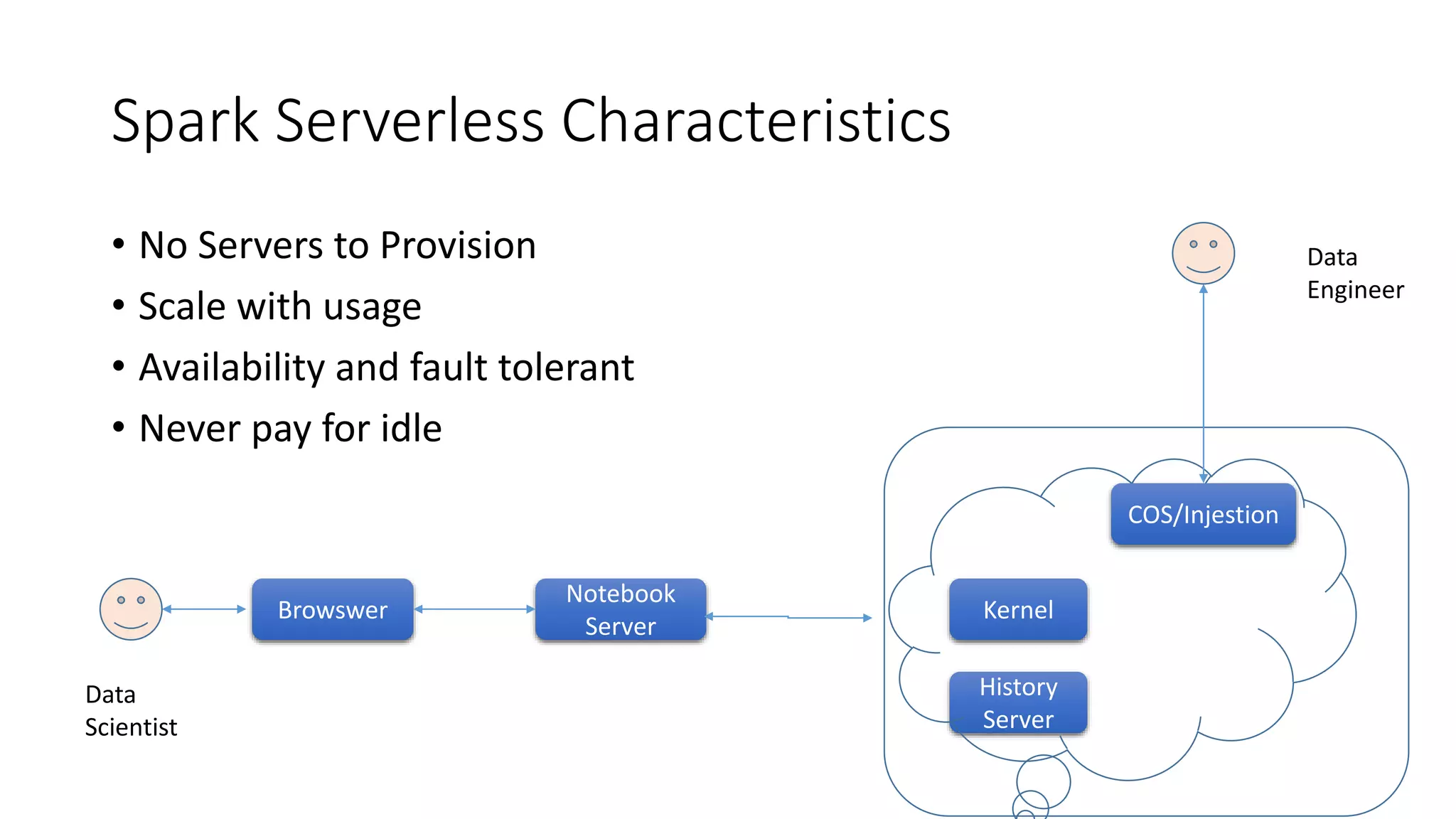
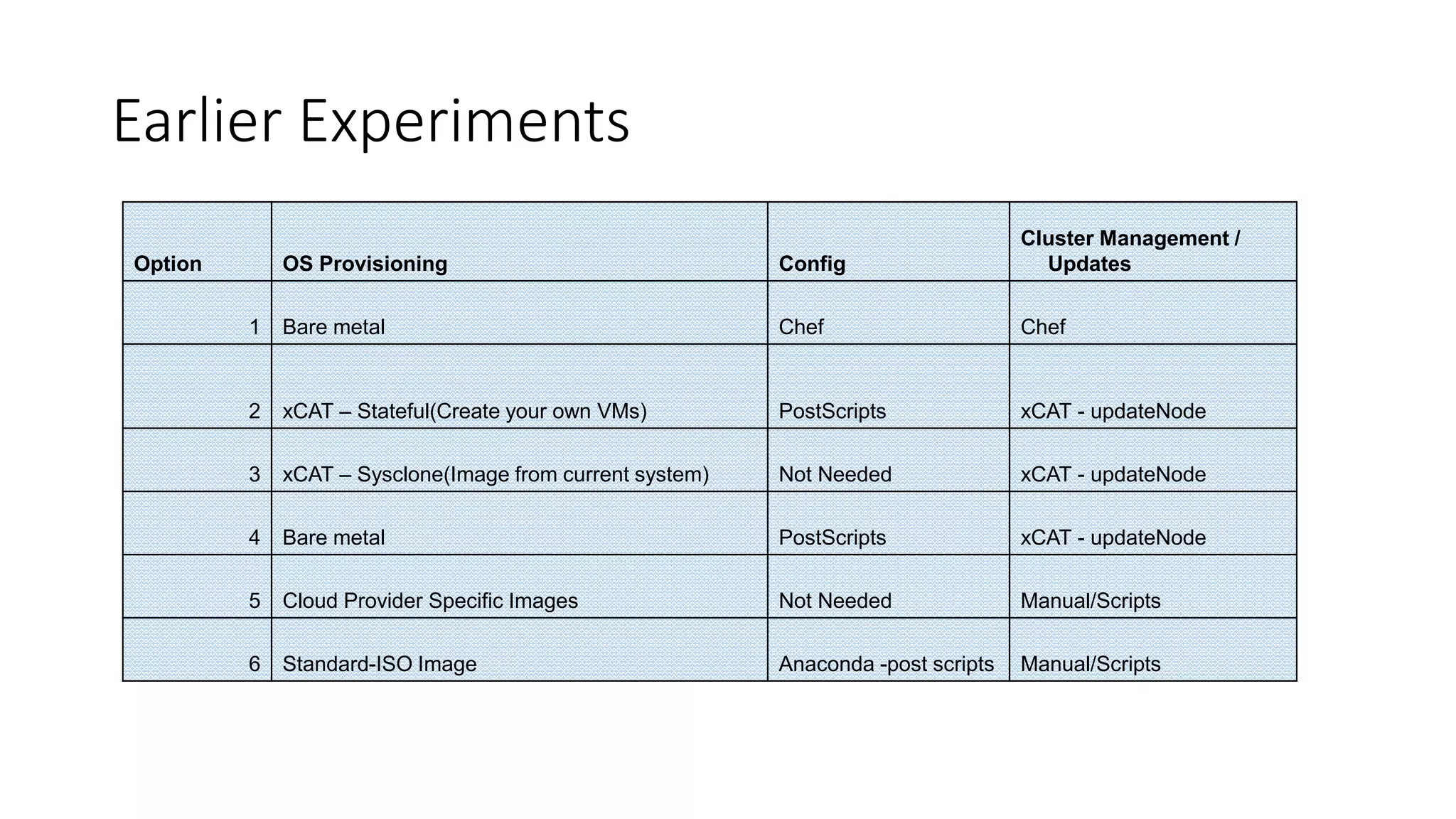
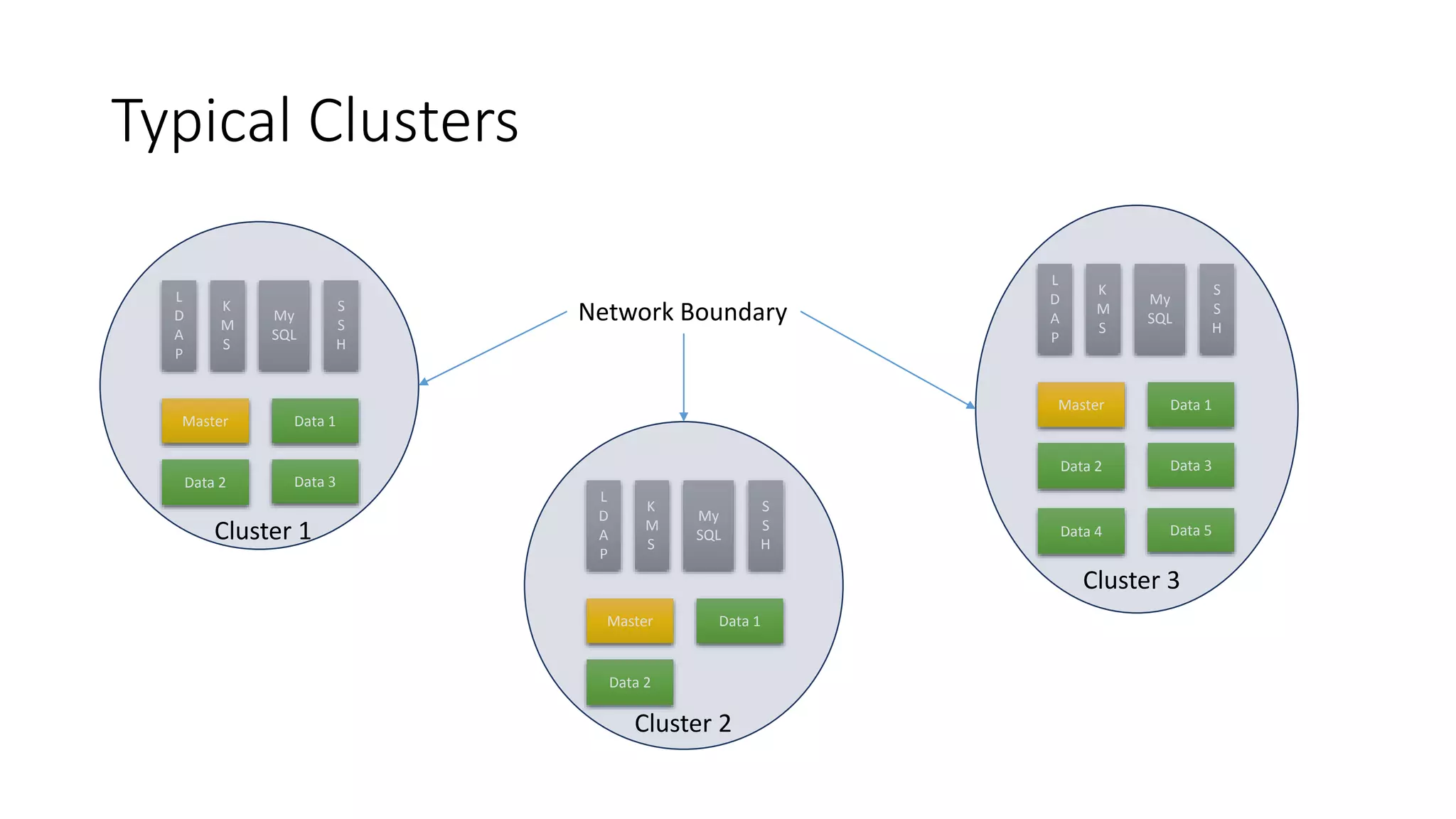
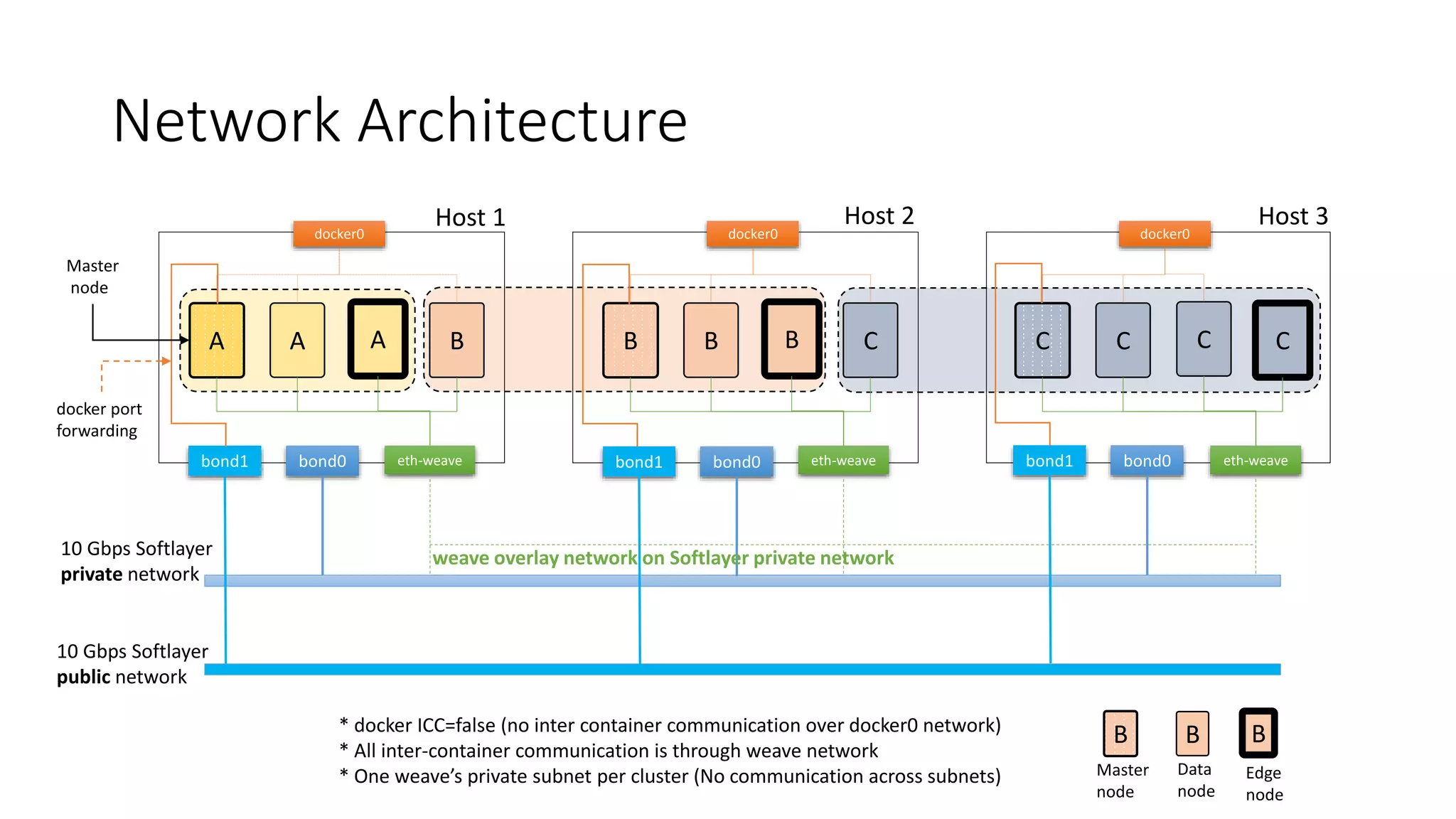
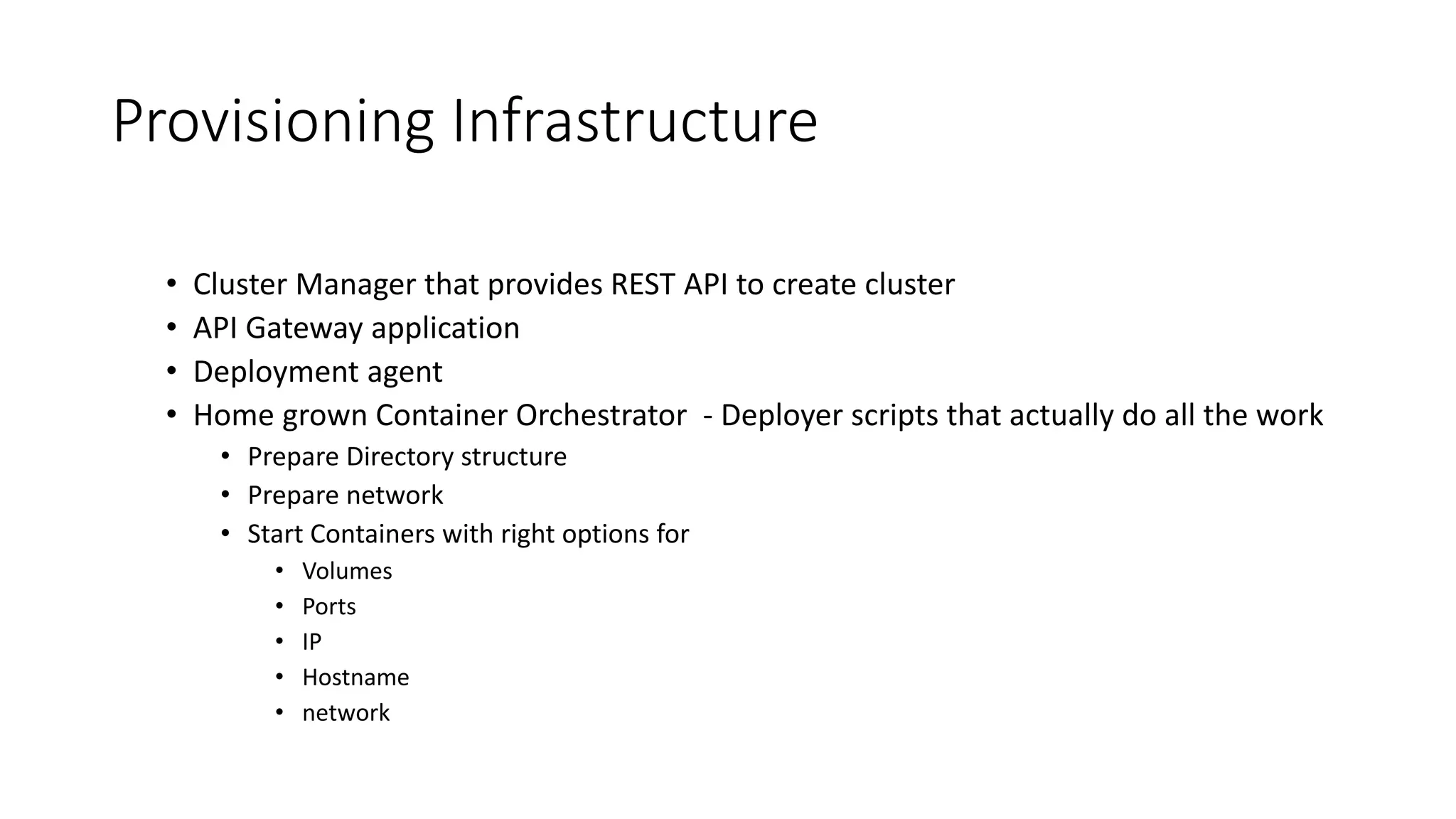
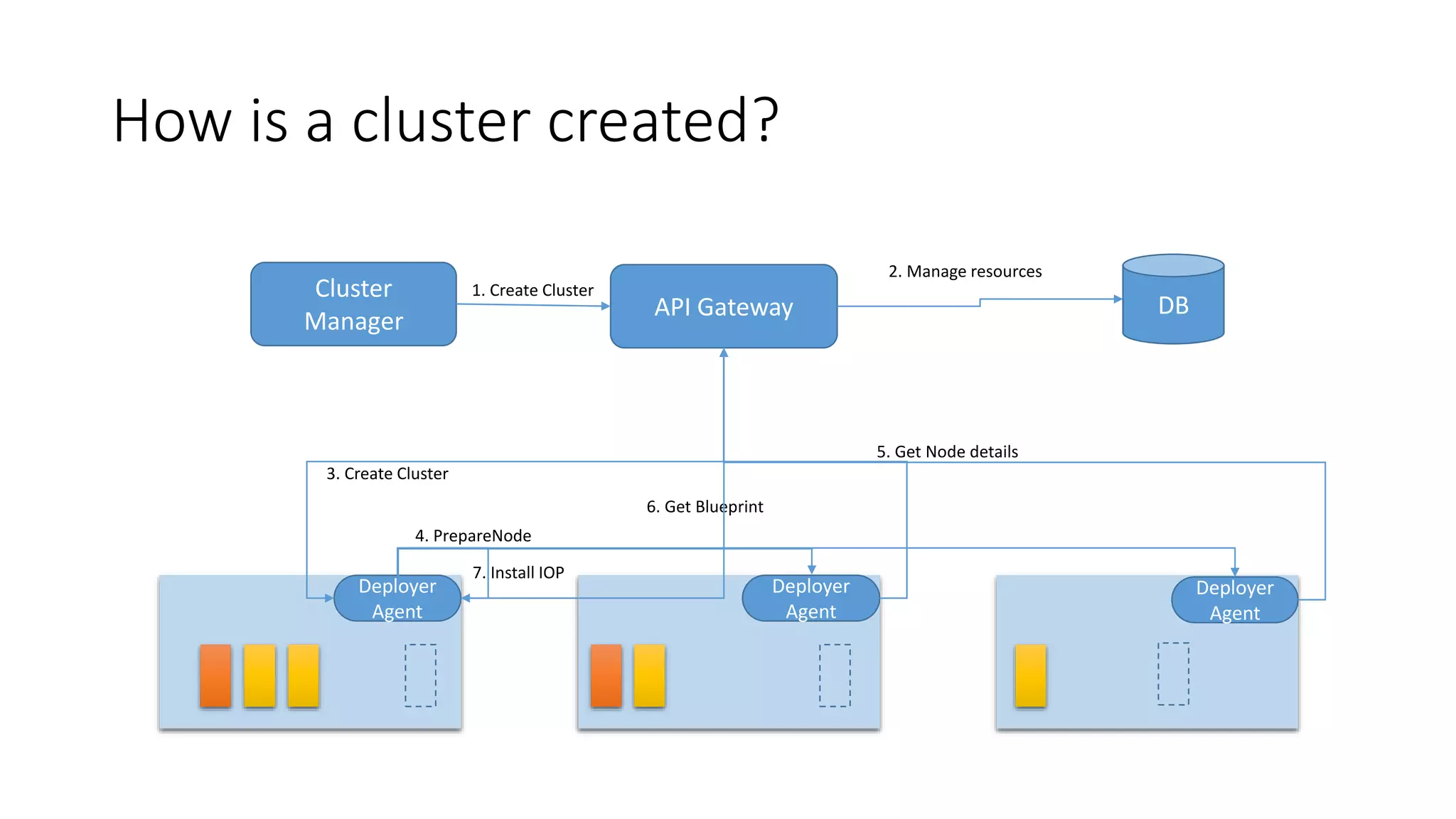
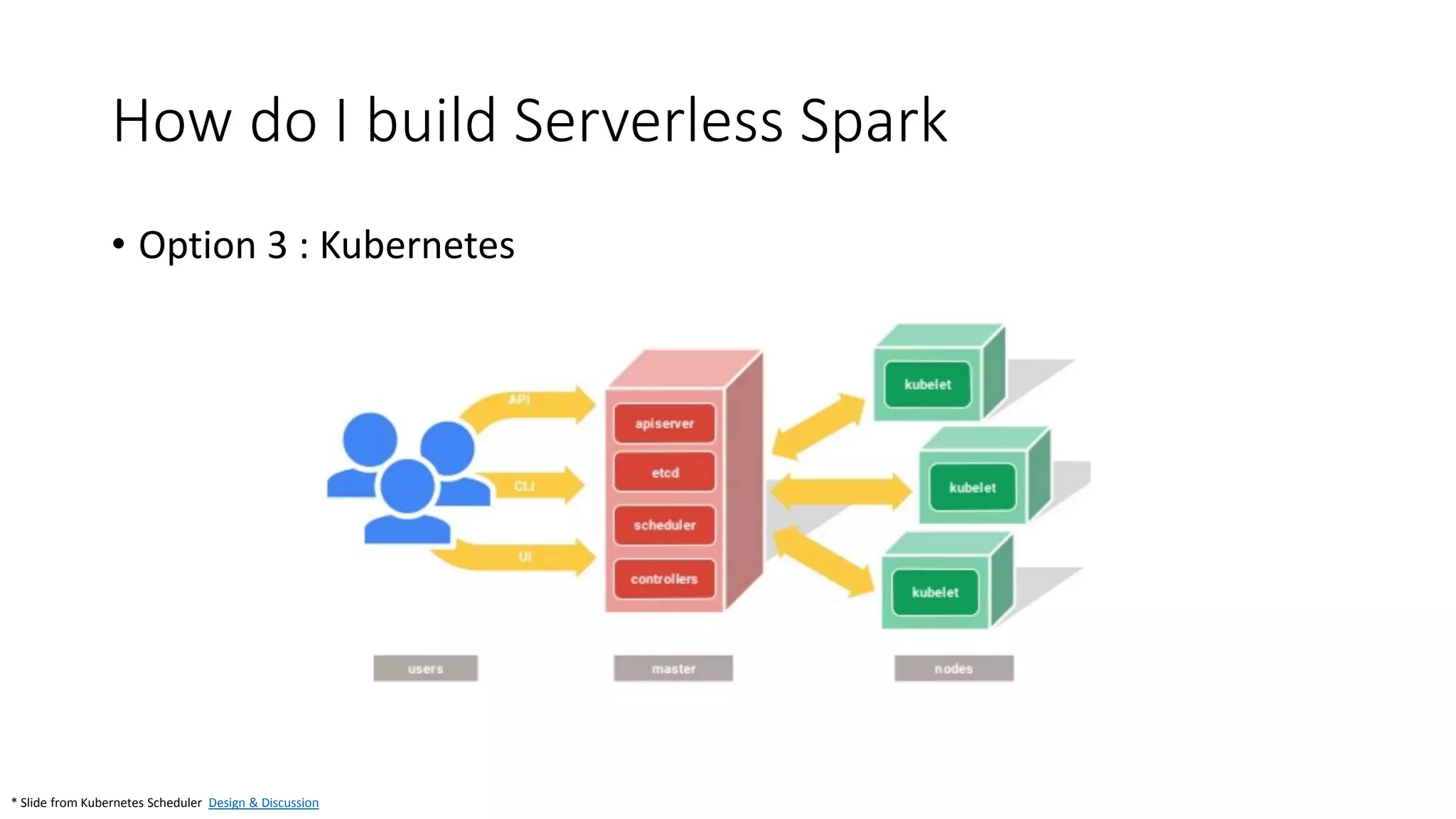
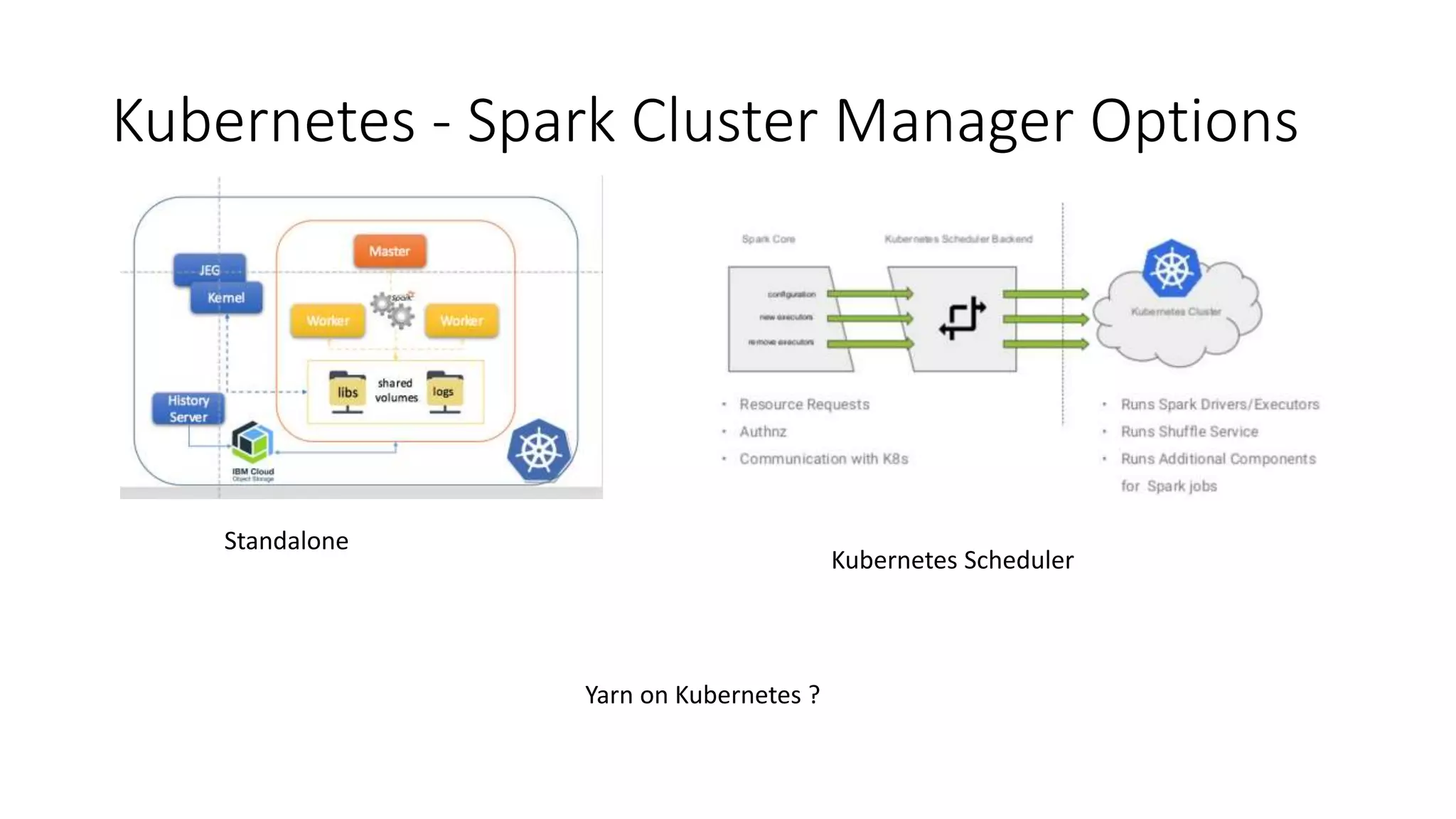
The document discusses the advantages of using Kubernetes as a container orchestrator for running Spark clusters in the cloud, emphasizing its benefits such as automation, high availability, and resource flexibility. It outlines the challenges of traditional Spark analytics setups and highlights the efficacy of serverless architecture with Kubernetes for data scientists. Additionally, it provides insights into the deployment and management of Spark on Kubernetes while referencing various tools and resources for further exploration.