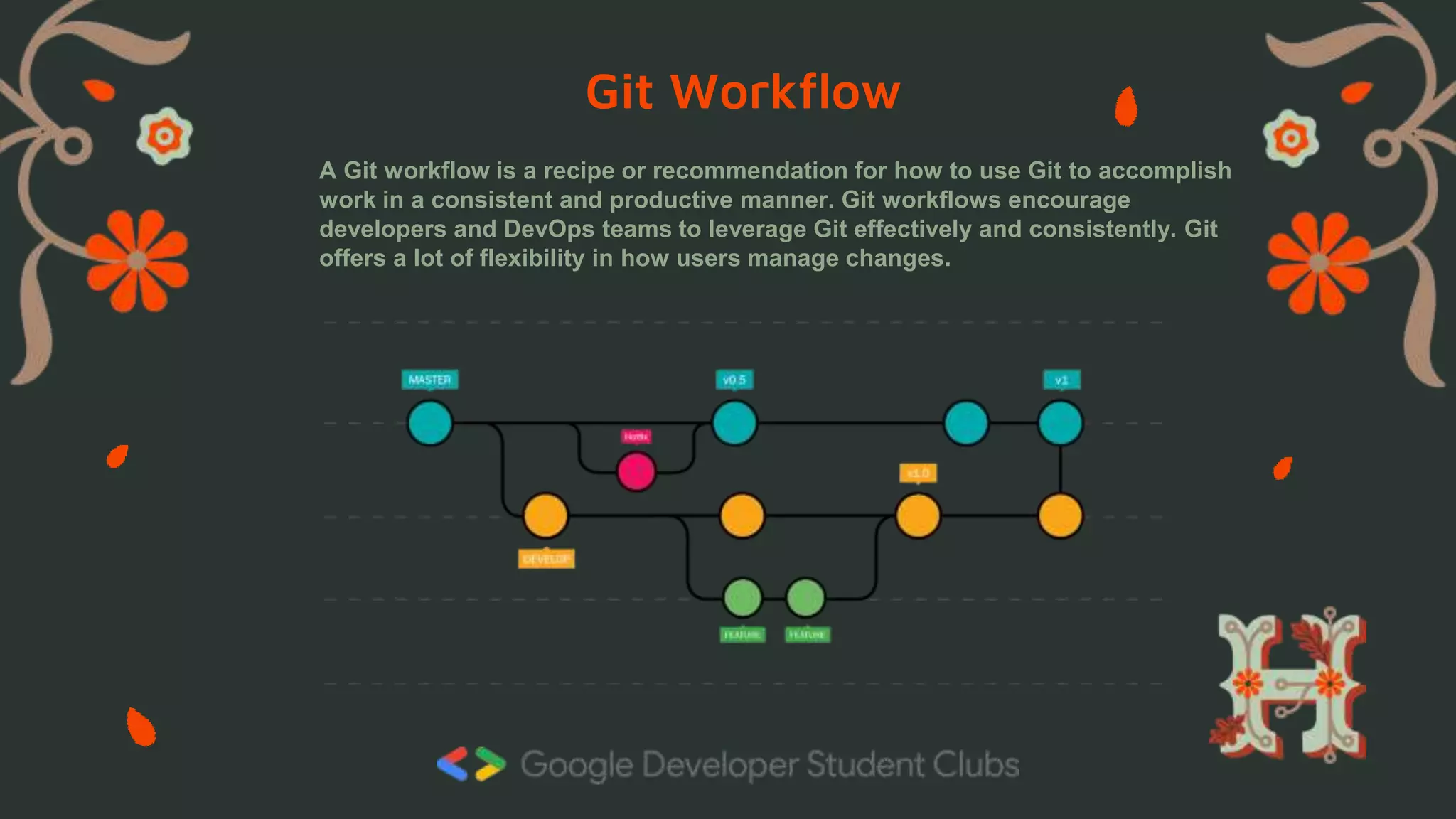
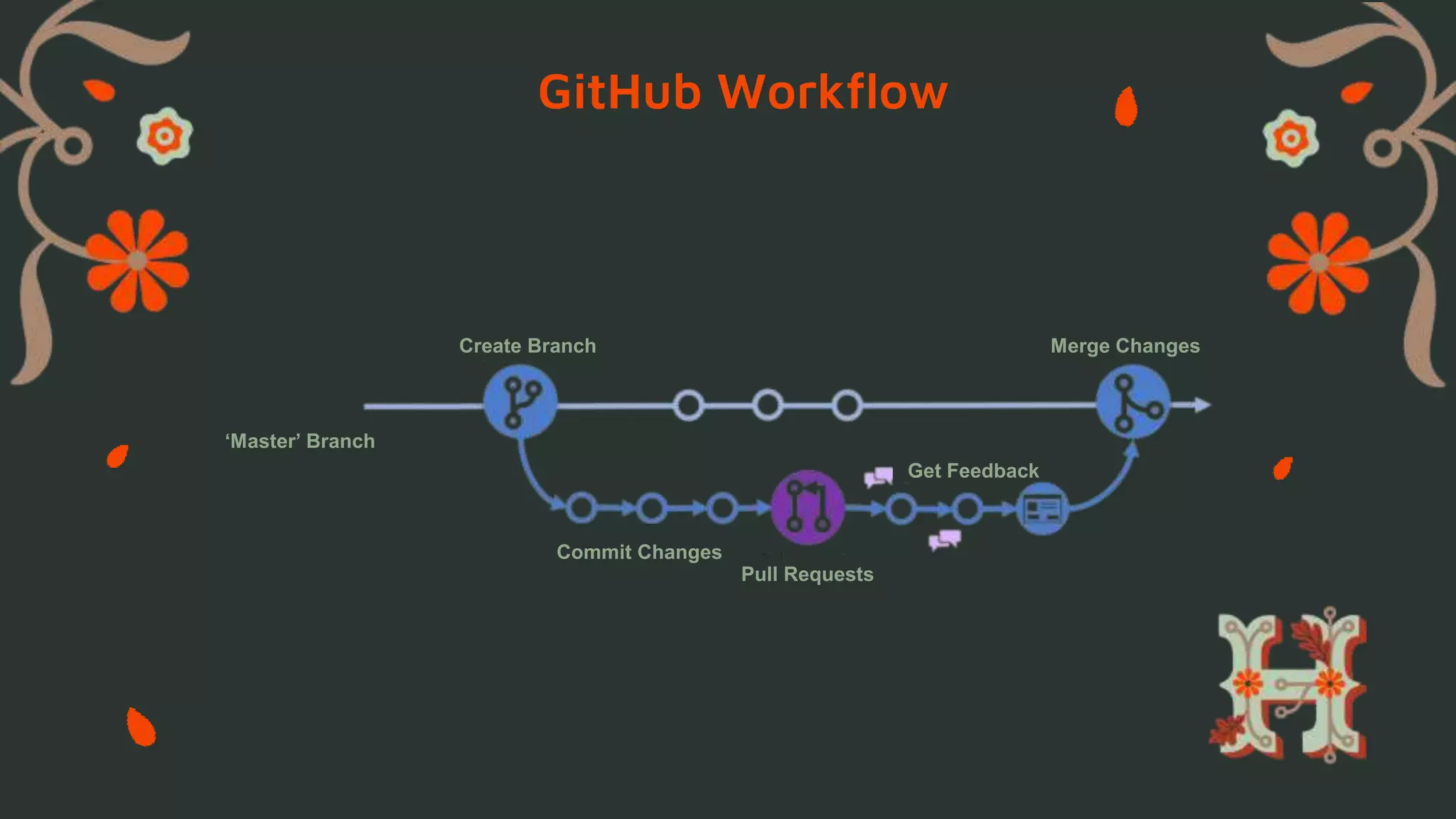
This document provides an overview of Git and GitHub for contributing to open source projects during Hacktoberfest. It defines version control systems and how Git is a distributed VCS that allows developers to work asynchronously. Key Git commands and GitHub workflows are described, including creating branches, committing changes, and submitting pull requests. The steps for contributing to projects during Hacktoberfest via forking repositories and making pull requests are also outlined.