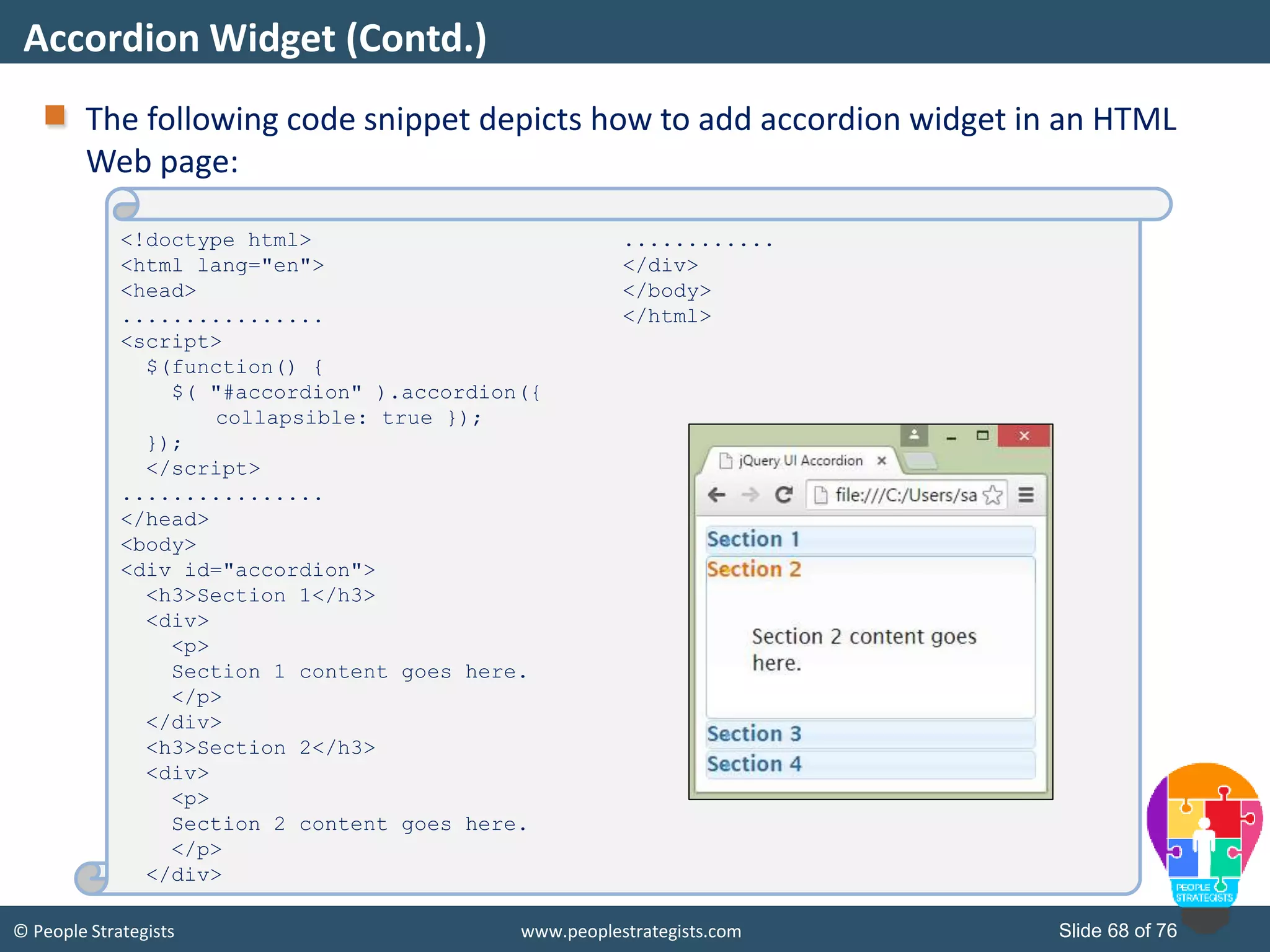
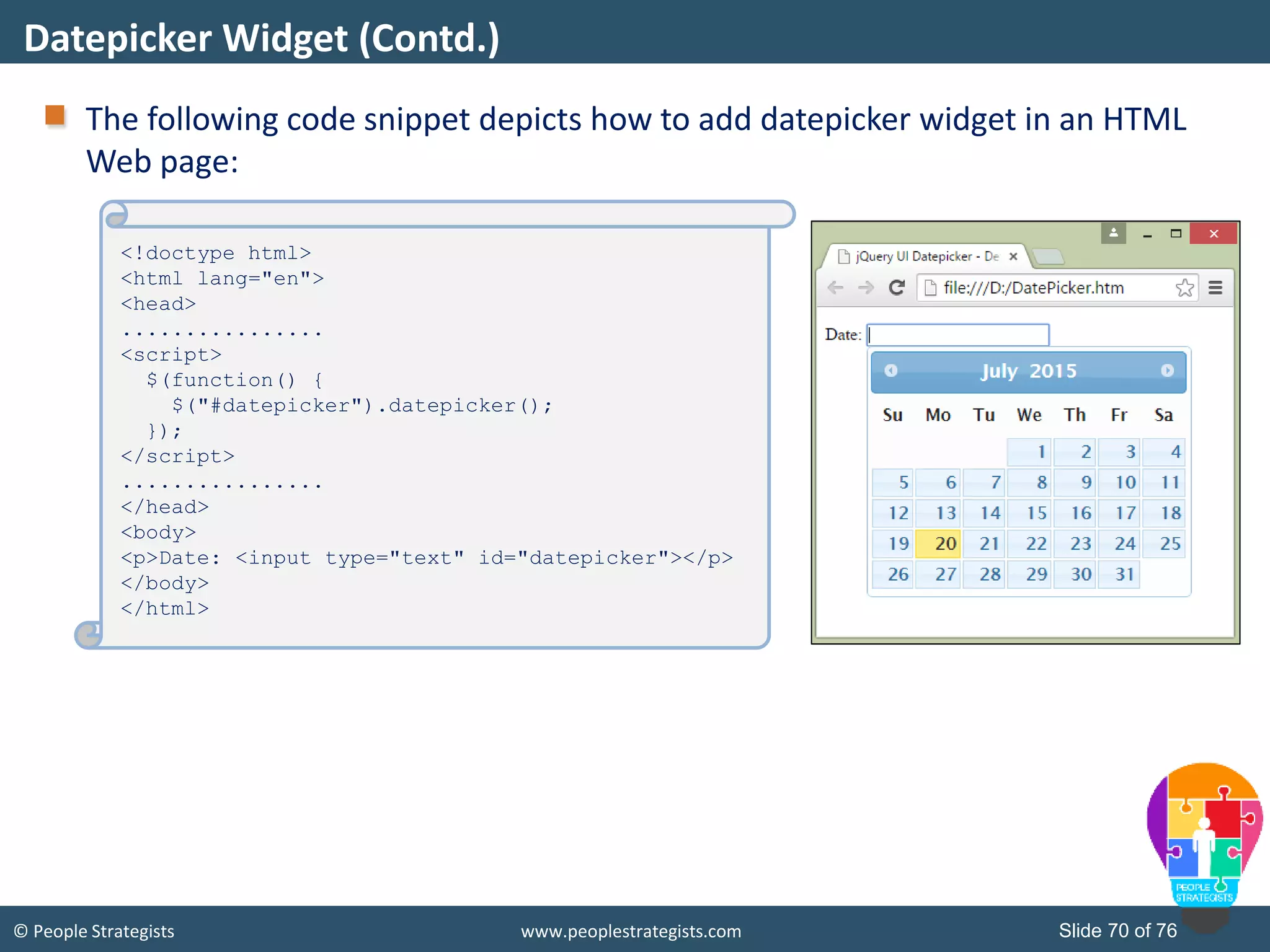
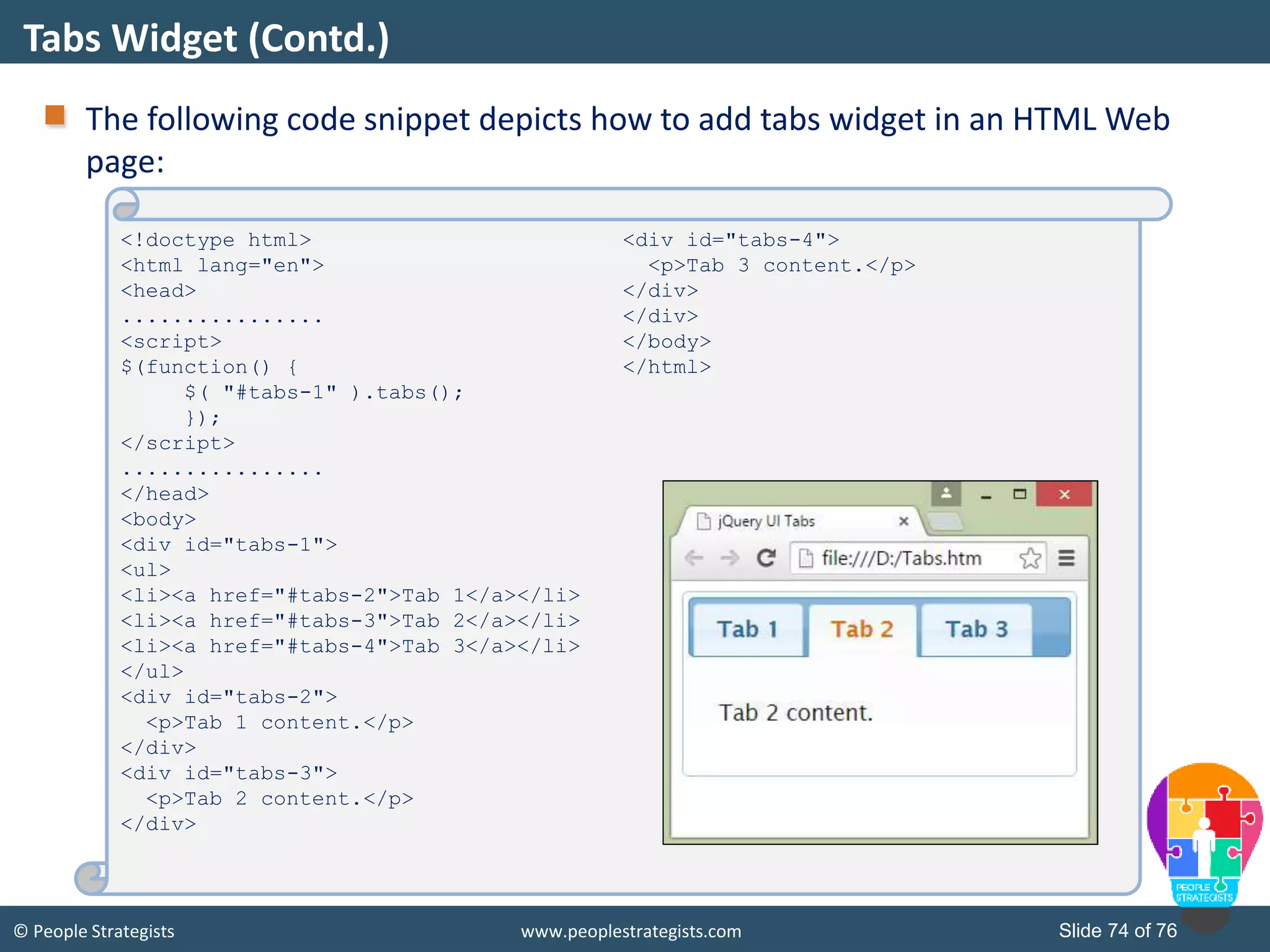
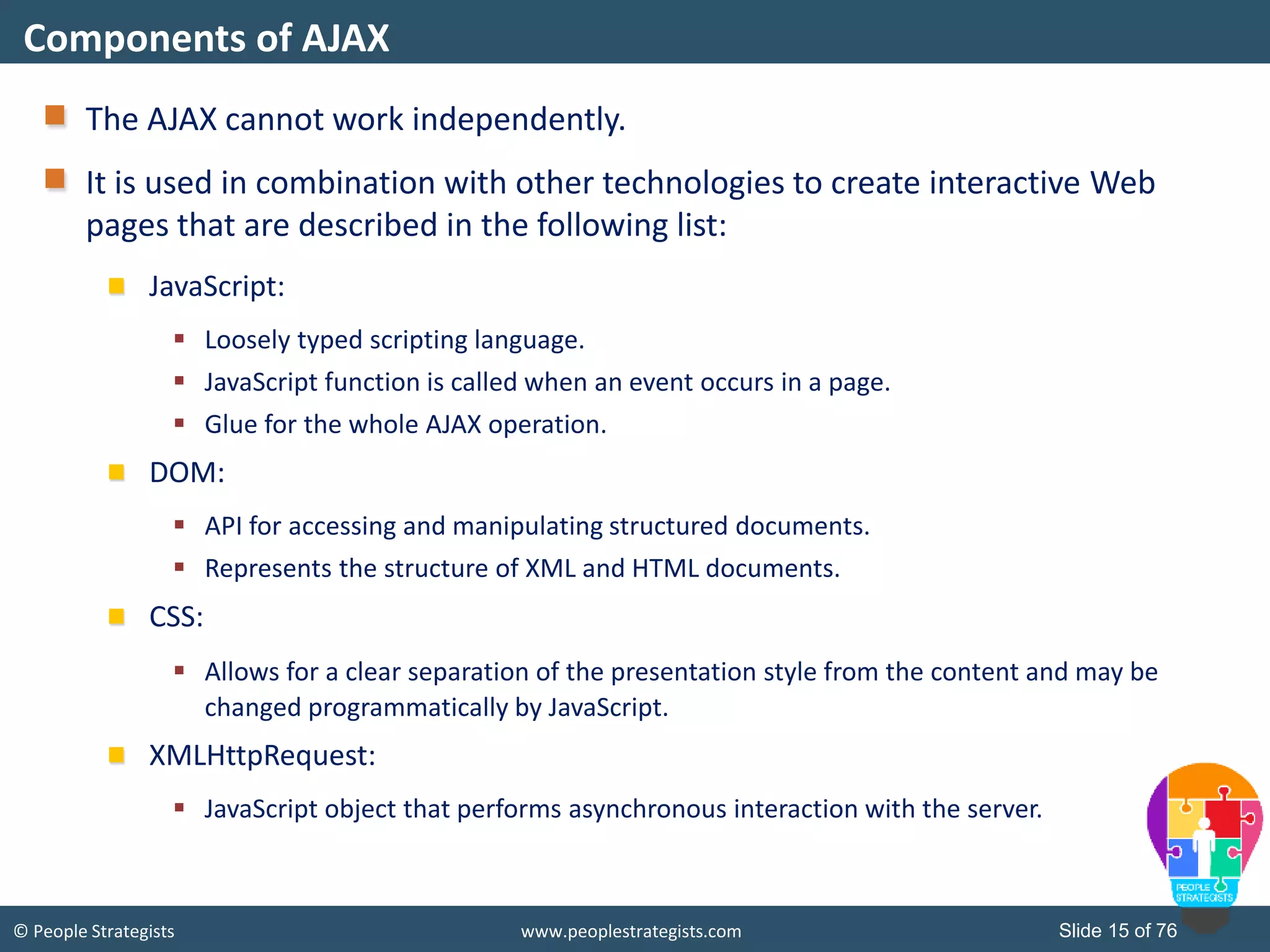
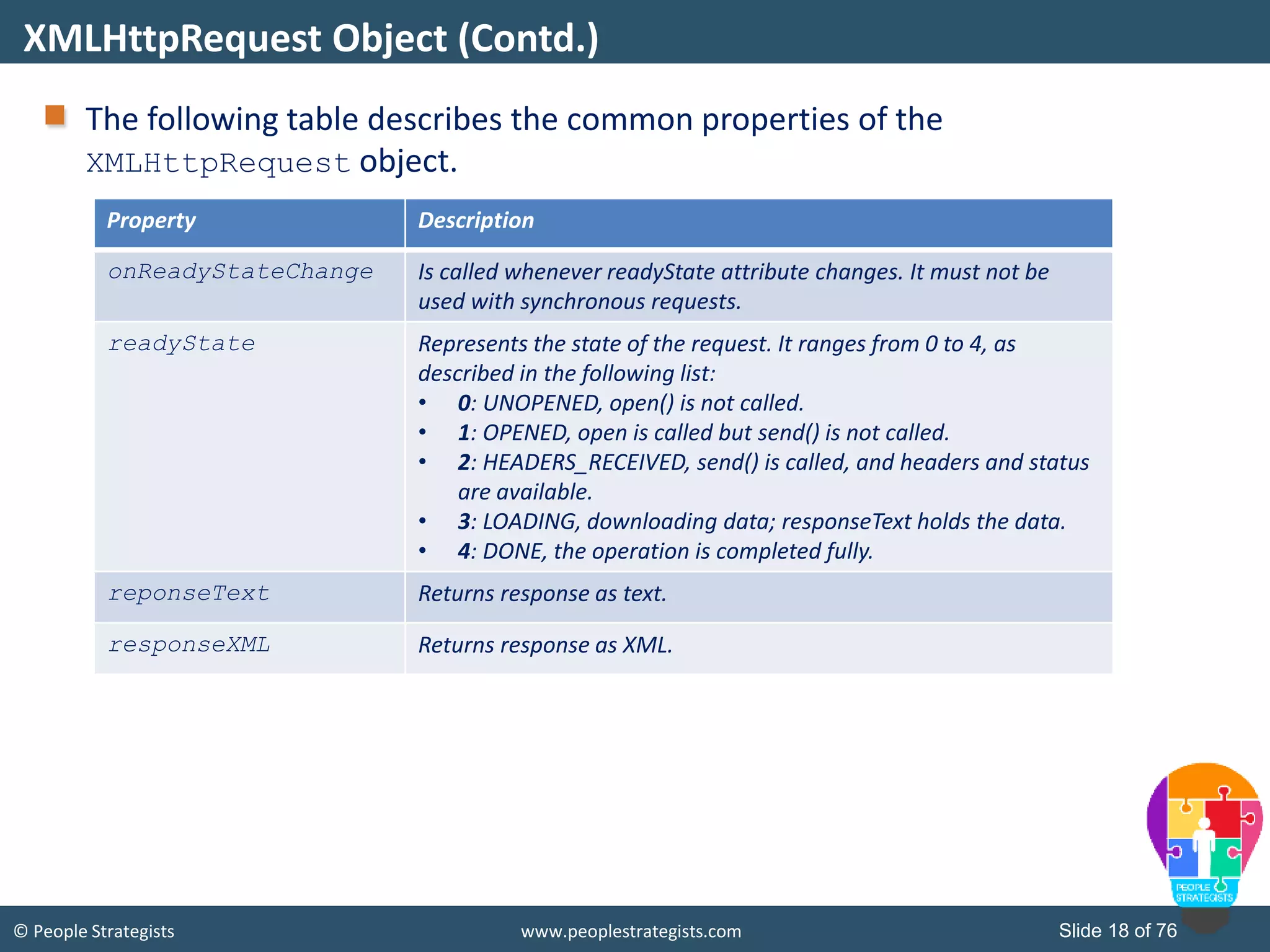
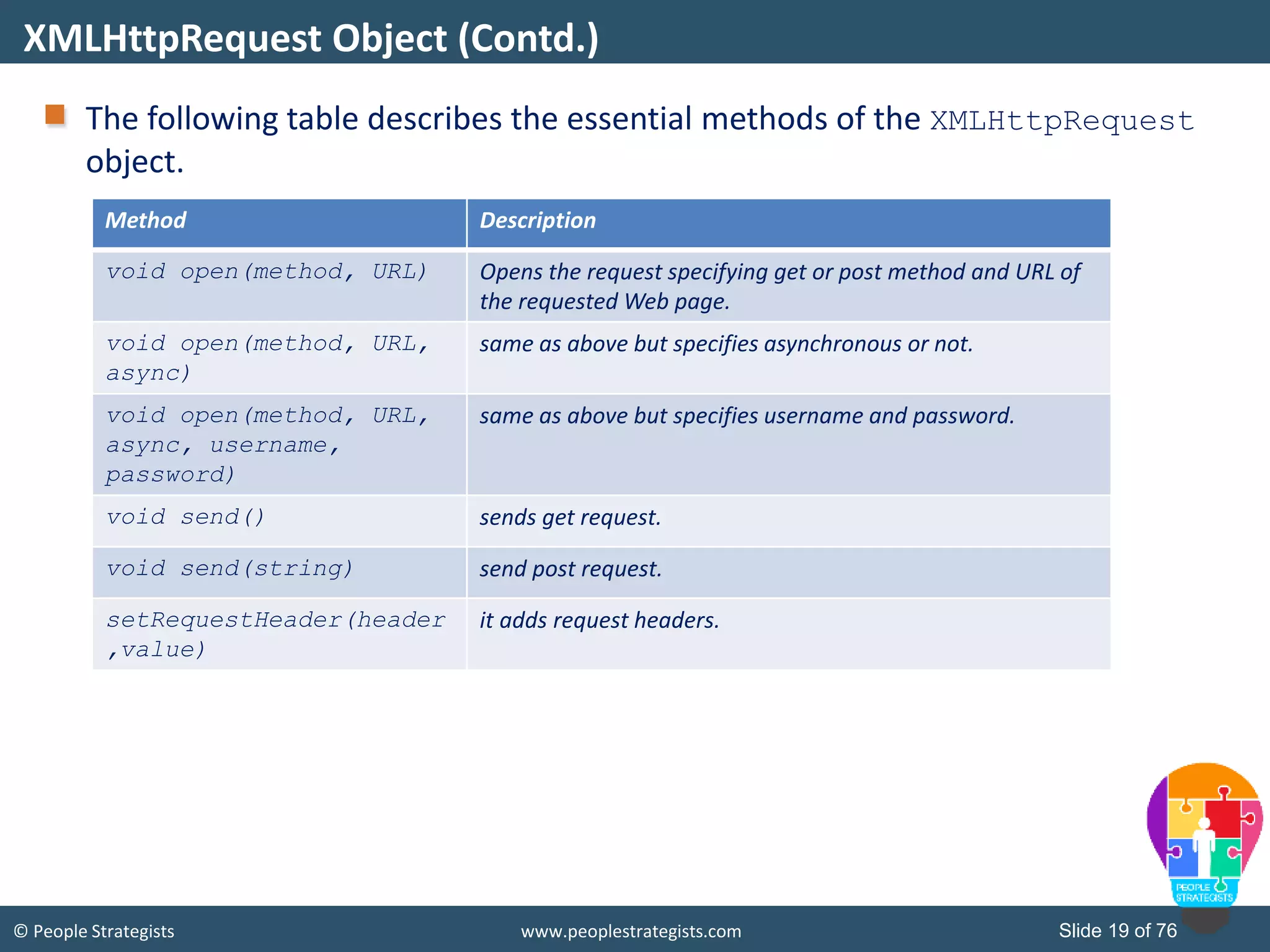
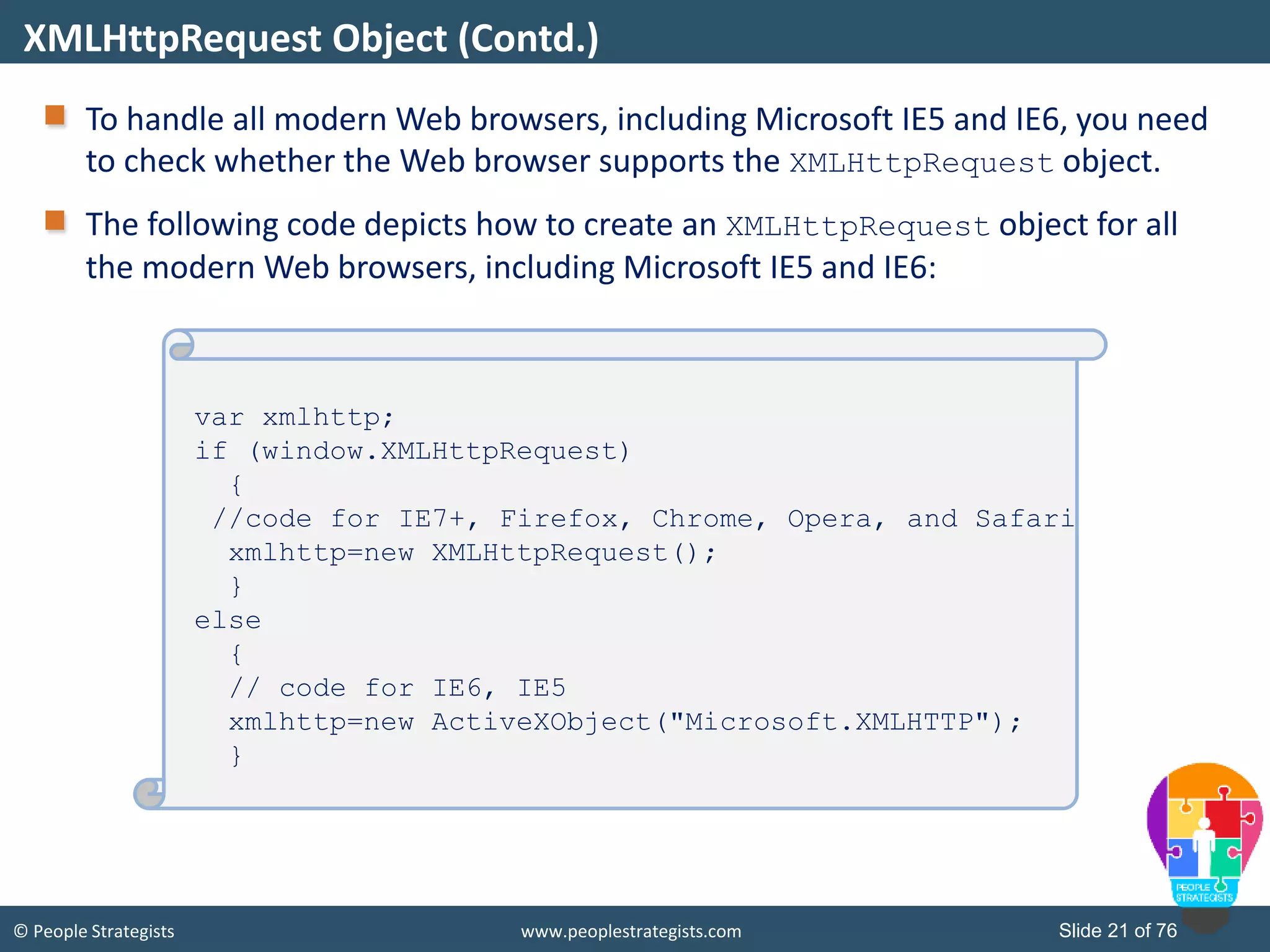
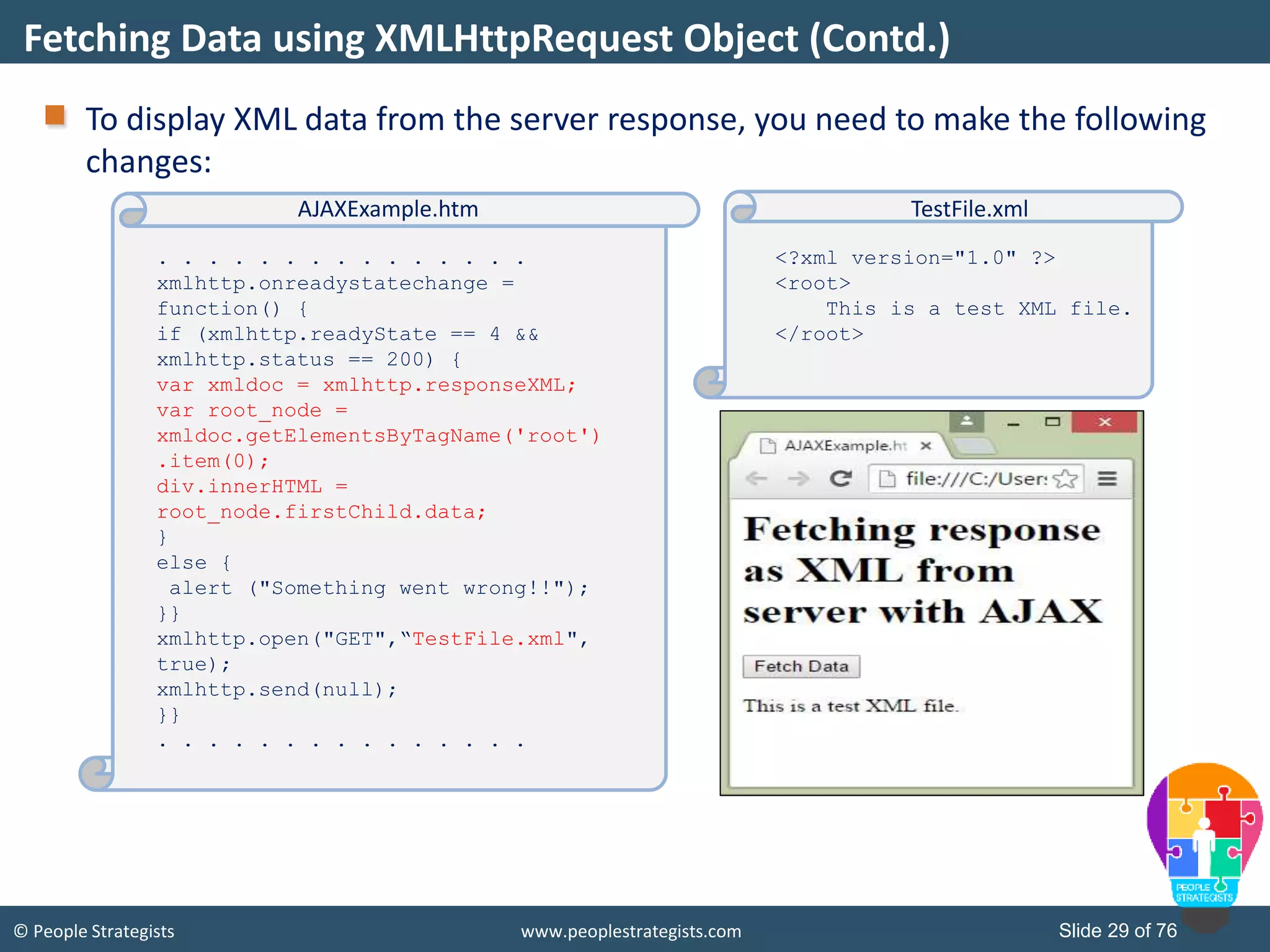
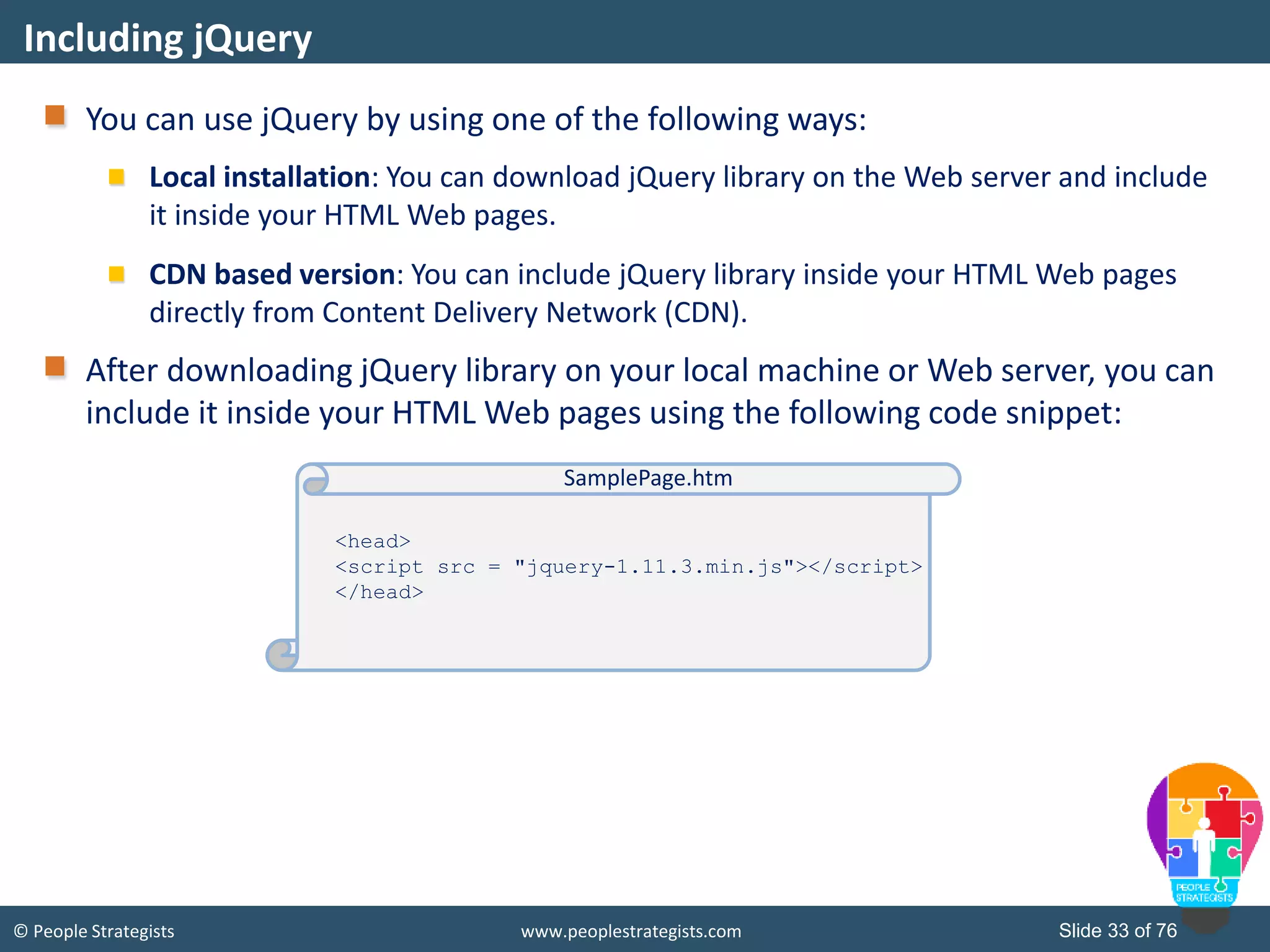
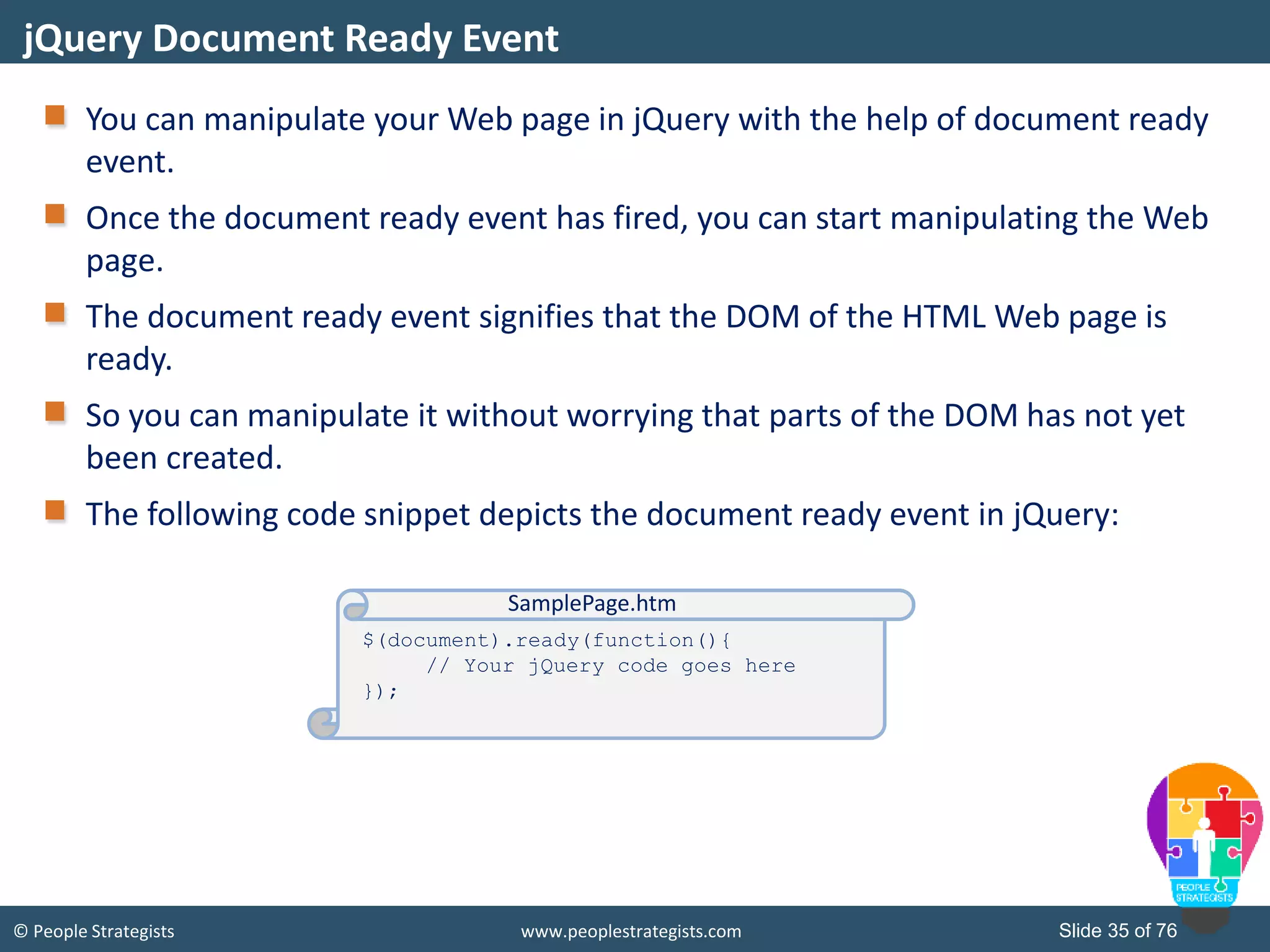
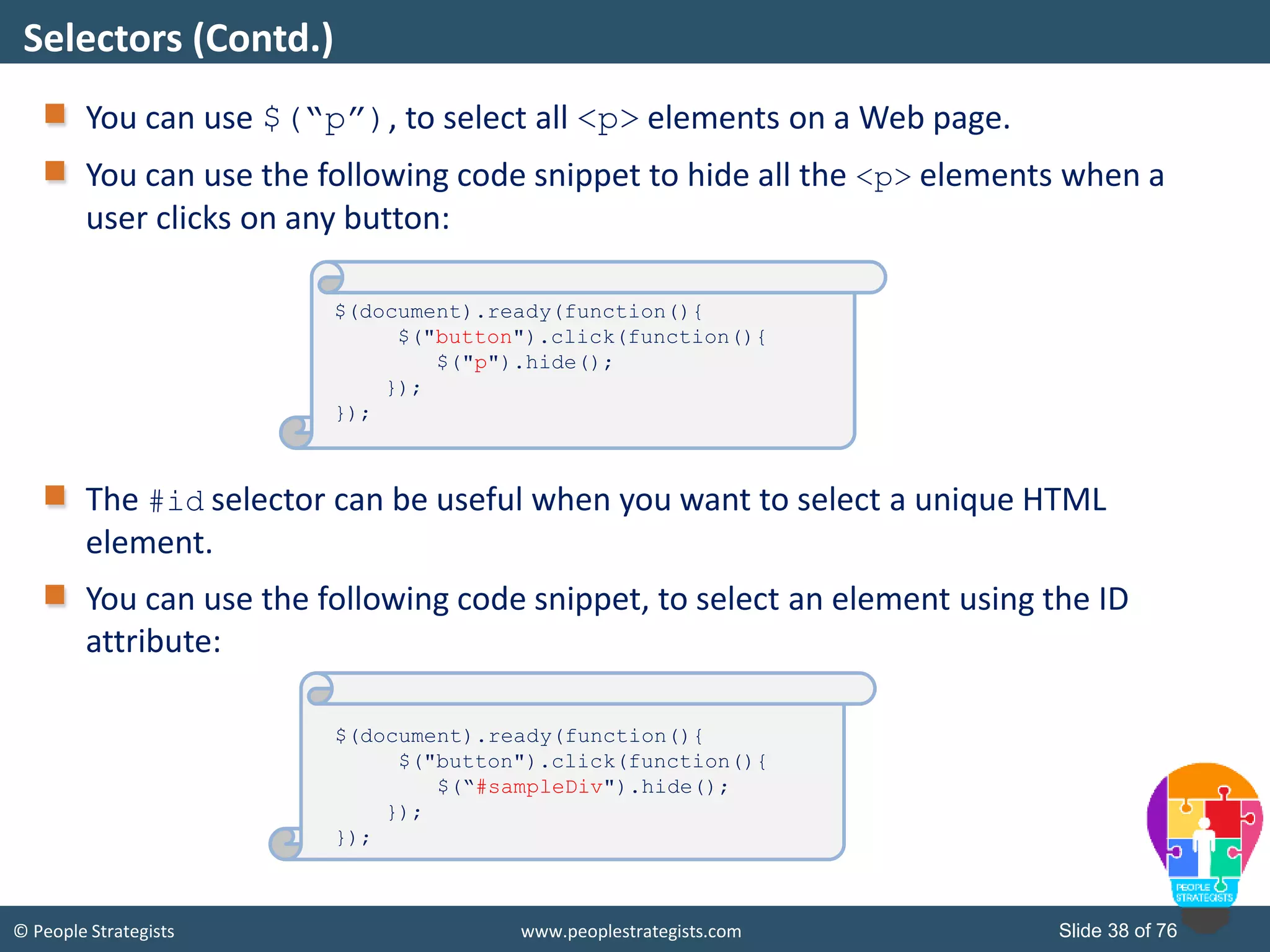
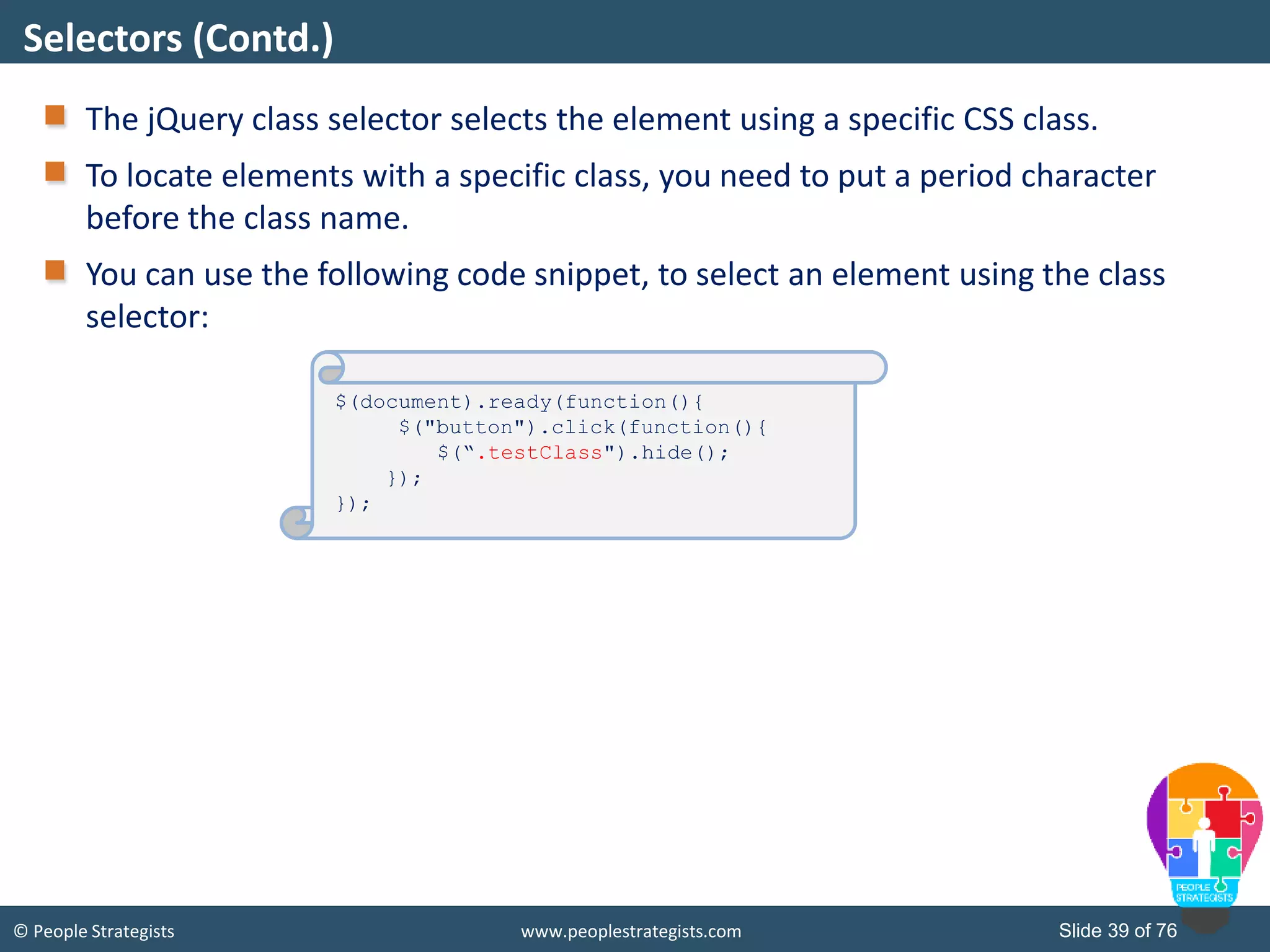
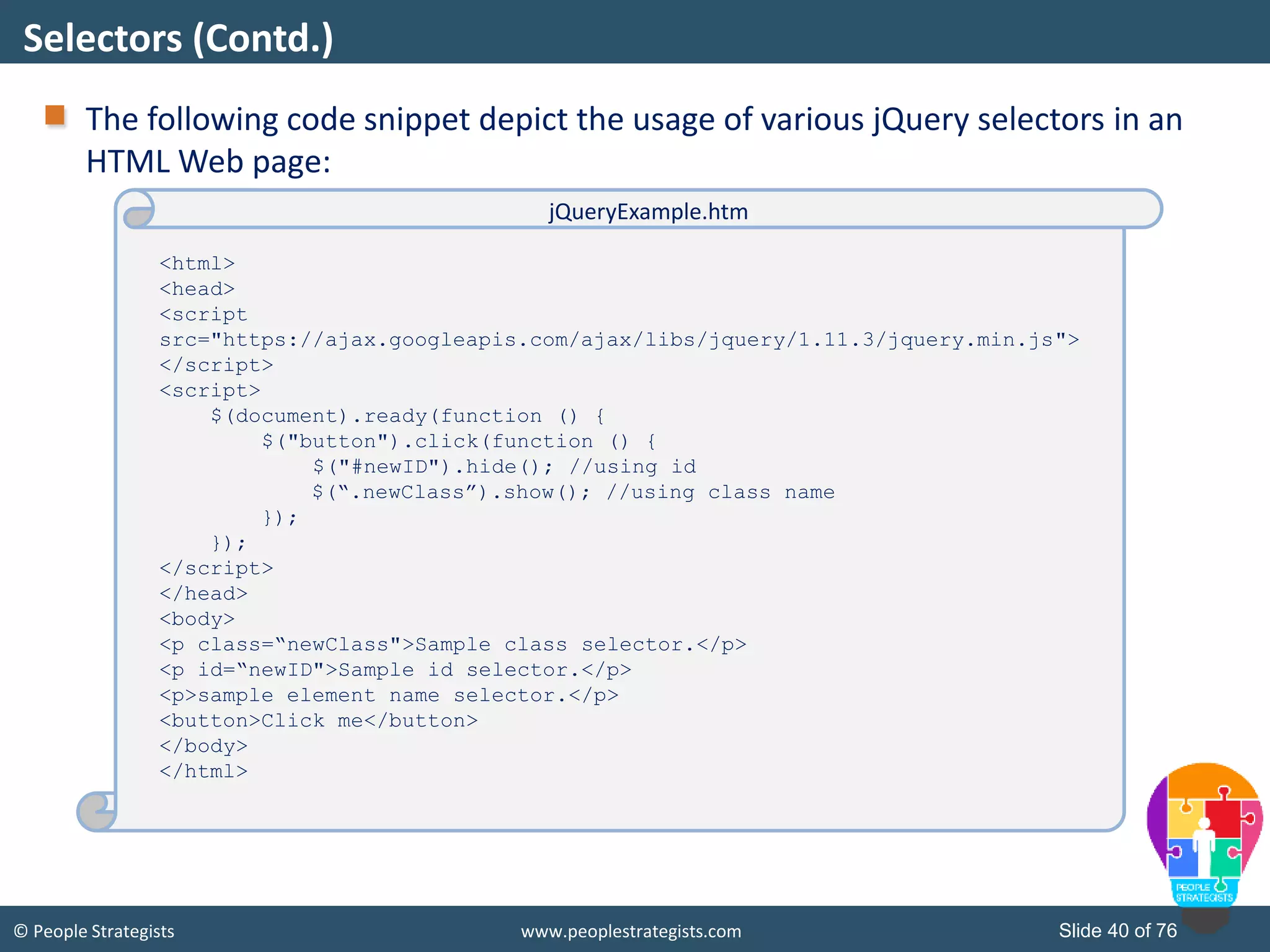
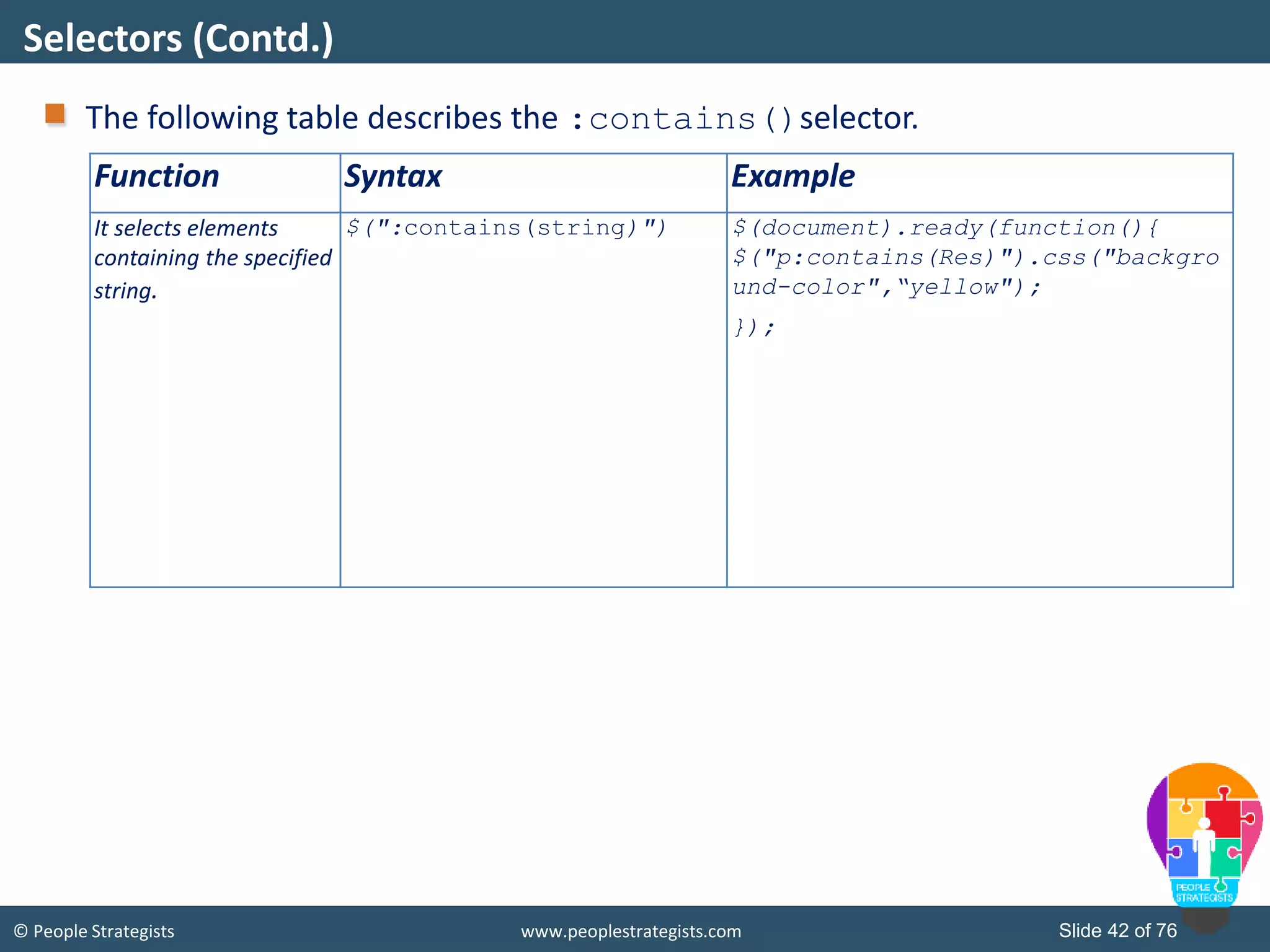
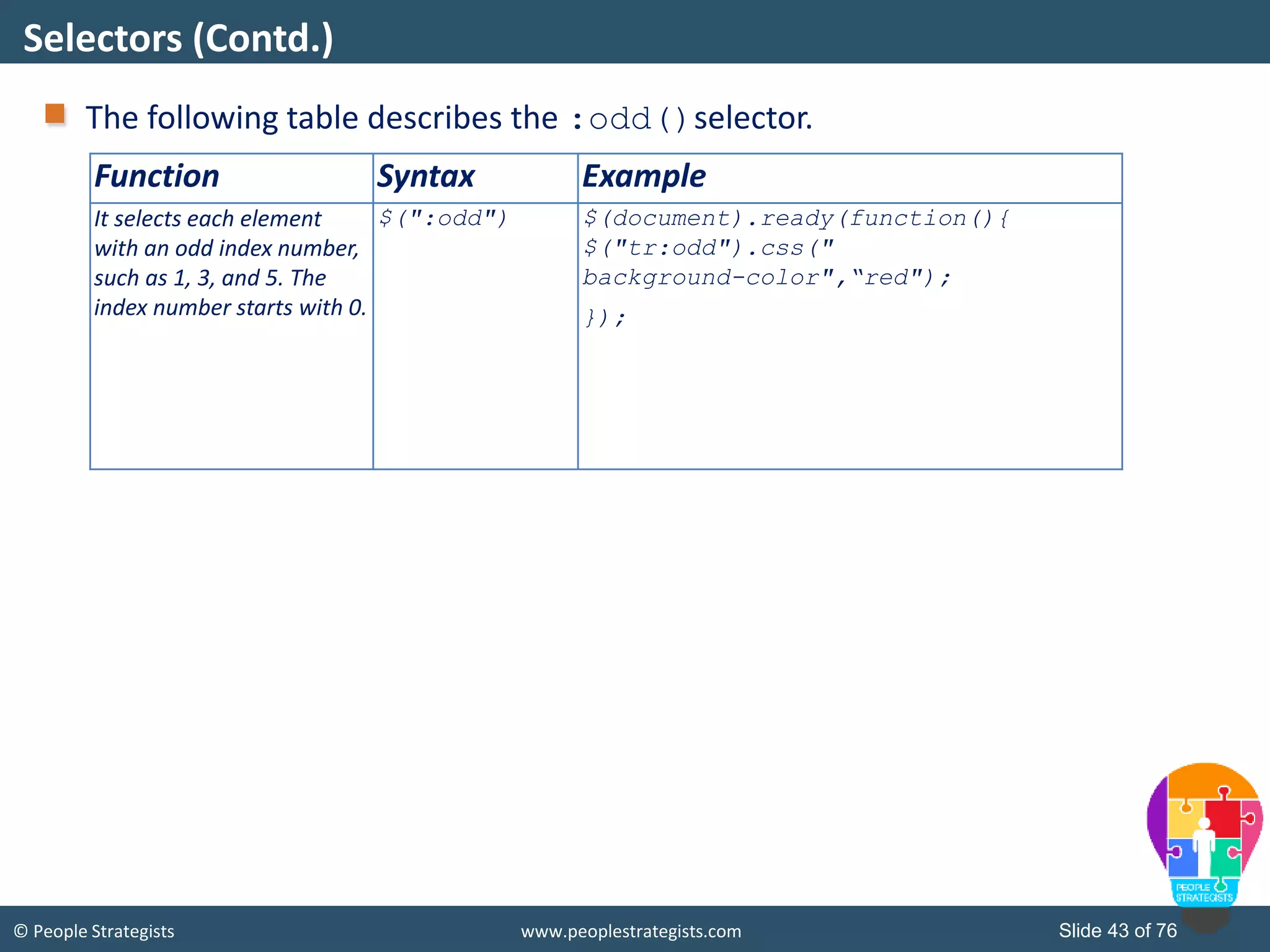
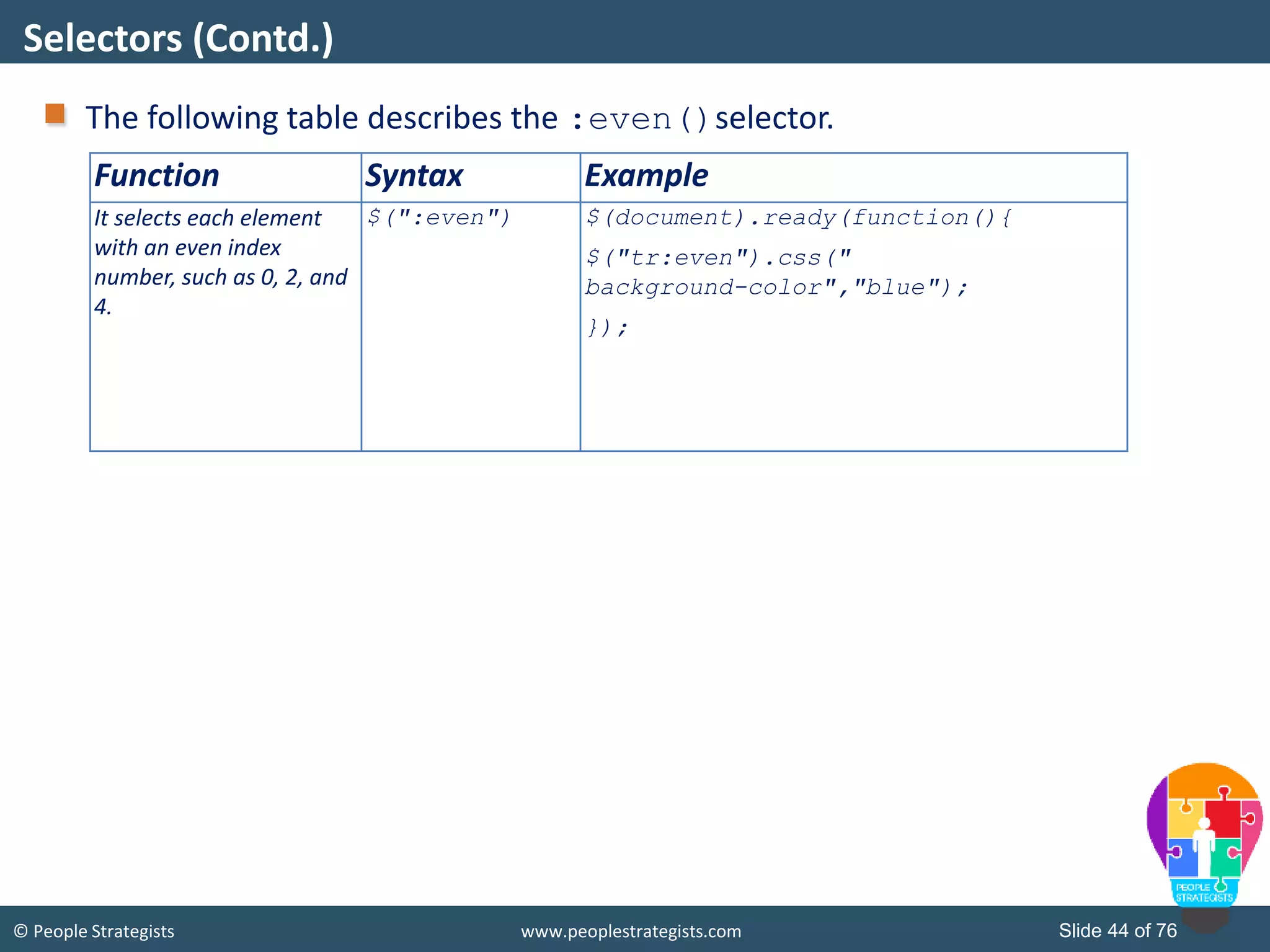
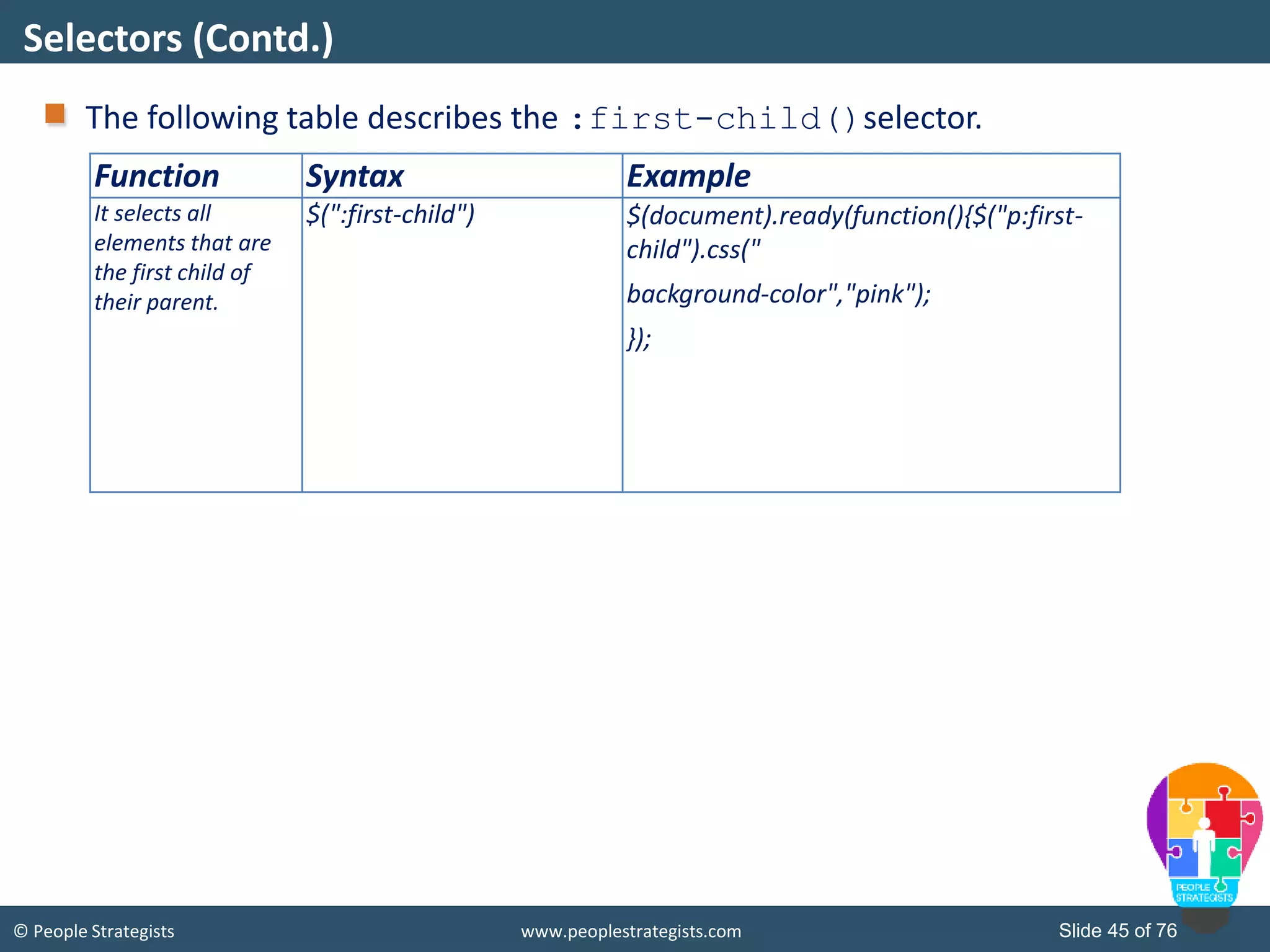
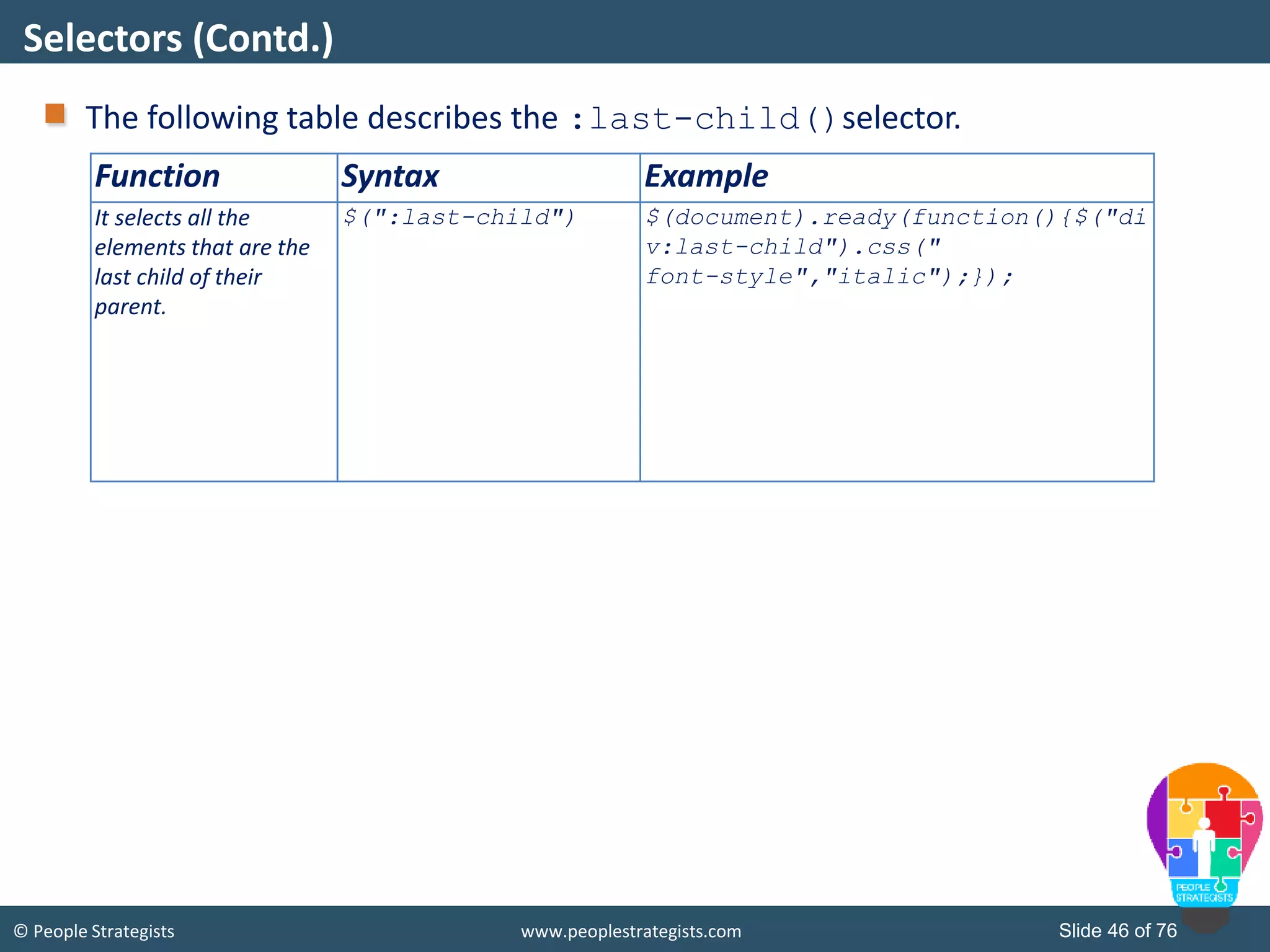
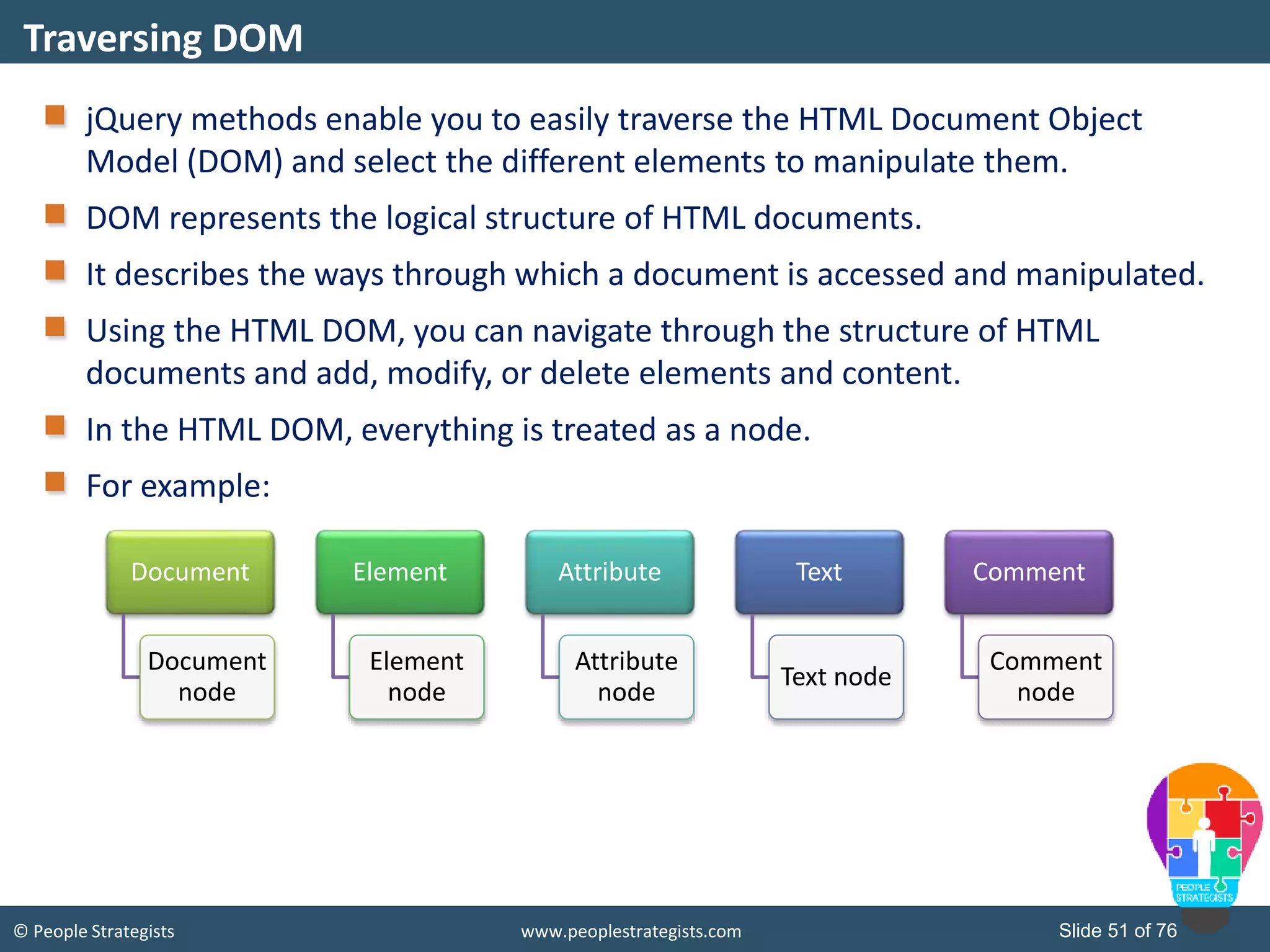
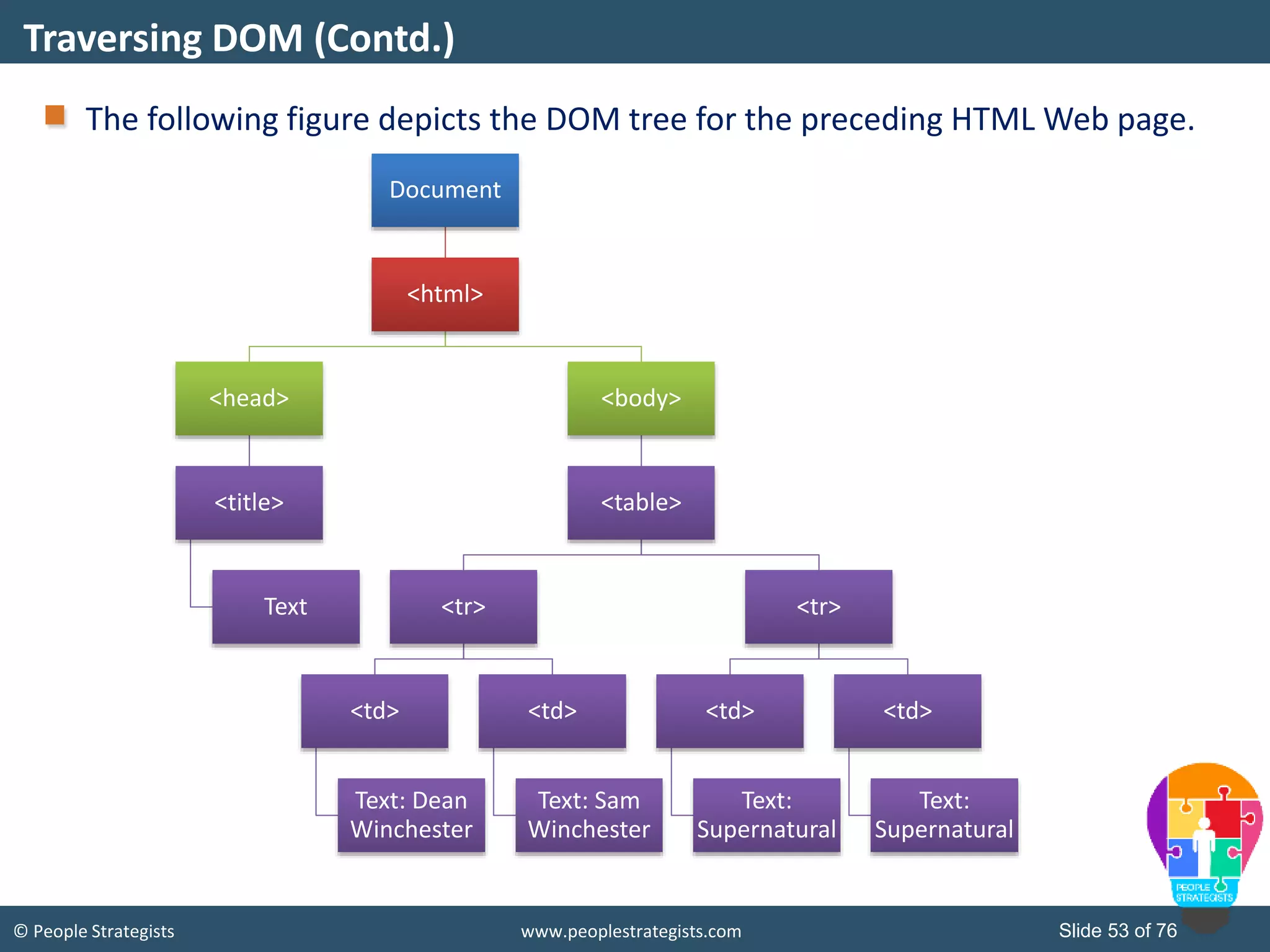
This document provides an overview of AJAX and jQuery. It begins by stating the objectives of the document, which are to identify the AJAX web application model, work with AJAX and jQuery, implement selectors, manipulate the DOM, implement jQuery UI widgets. It then provides information on introducing AJAX, including how it allows asynchronous updating of web pages. It describes the components that AJAX uses, including XMLHttpRequest, JavaScript, DOM, and CSS. It also provides examples of how AJAX is used in real-life scenarios and browsers that support AJAX.























![© People Strategists www.peoplestrategists.com Slide 50 of 76 To highlight the names of those employees who’s productivity is more than 85% in yellow color, use the following code snippet: In the preceding code snippet, the <ul> element that has the value of the class attribute as Greater_eightyfive is selected and the background color, yellow, is applied to it. Selectors (Contd.) $(document).ready(function () { var res = $('ul[class="Greater_eightyfive"]'); res.css("background-color", "yellow"); });](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ajaxandjquery-150723055256-lva1-app6892/75/Ajax-and-Jquery-50-2048.jpg)


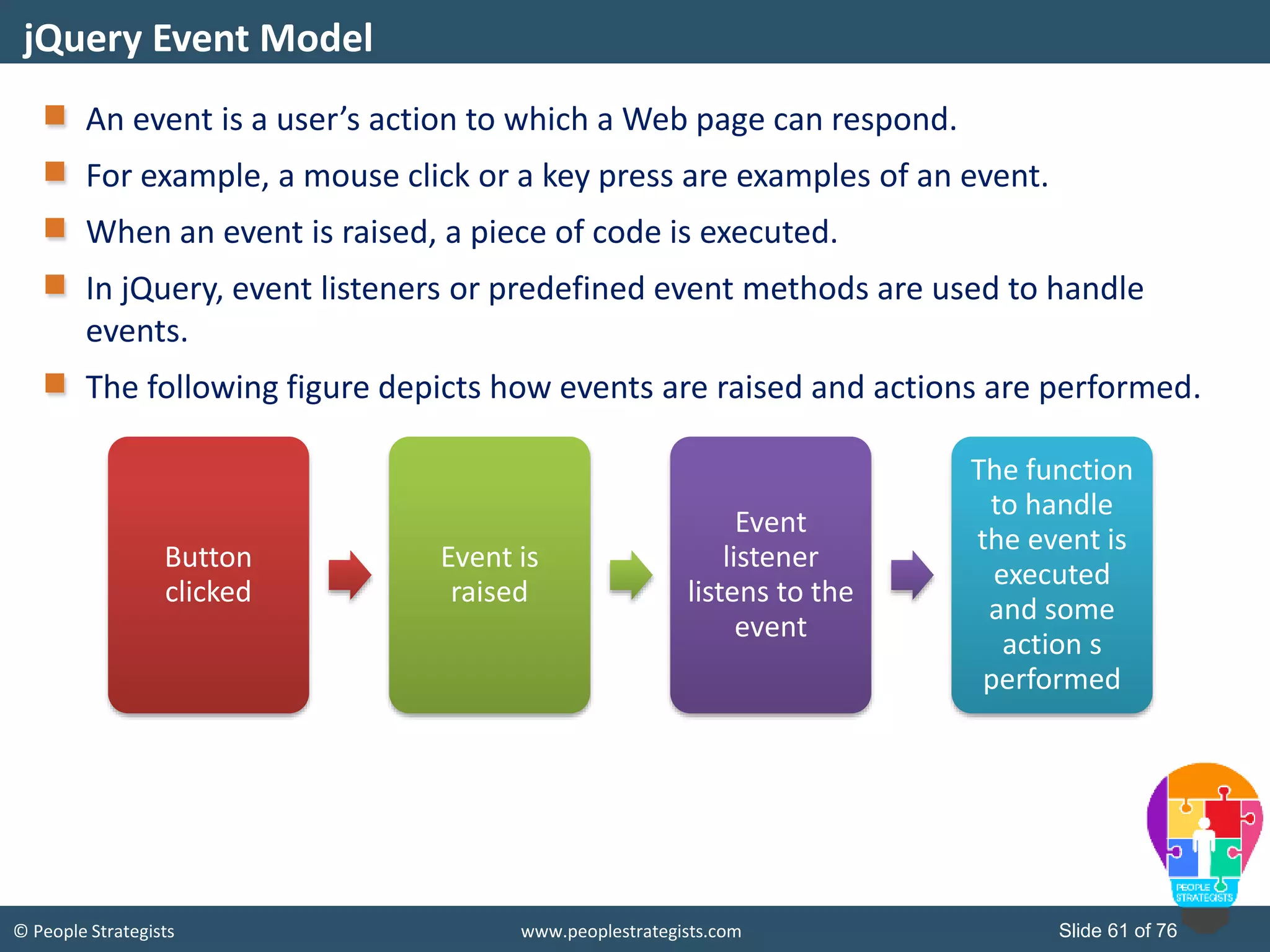
![© People Strategists www.peoplestrategists.com Slide 62 of 76 jQuery provides you the following methods to attach event handler to multiple events of a selected element(s): bind() on() The bind()method: Is used to attach one or more event handlers for the selected elements. Can be invoked by using the following syntax: To attach an event handler to a single event, you can use the following code snippet: To attach an event handler to multiple events, you can use the following code snippet: Binding Events $(selector).bind(event[,data],function $("p").bind("click",function(){ alert(" Click event raised"); }); $("#btn").bind("mouseover mouseout",function(){ $("#btn").toggleClass(“demo"); });](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ajaxandjquery-150723055256-lva1-app6892/75/Ajax-and-Jquery-62-2048.jpg)
![© People Strategists www.peoplestrategists.com Slide 63 of 76 The on()method can be used to attach one or multiple event handlers for the selected and their child elements. The following figure depicts the syntax to use the on()method. The following code snippet can be used to attach the click event to the <p> element at the click even of a button: Binding Events (Contd.) $(selector).on(event[,childSelector][,data],function [,map]) $("div").on("click","p",function(){ $(this).hide(); });](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ajaxandjquery-150723055256-lva1-app6892/75/Ajax-and-Jquery-63-2048.jpg)