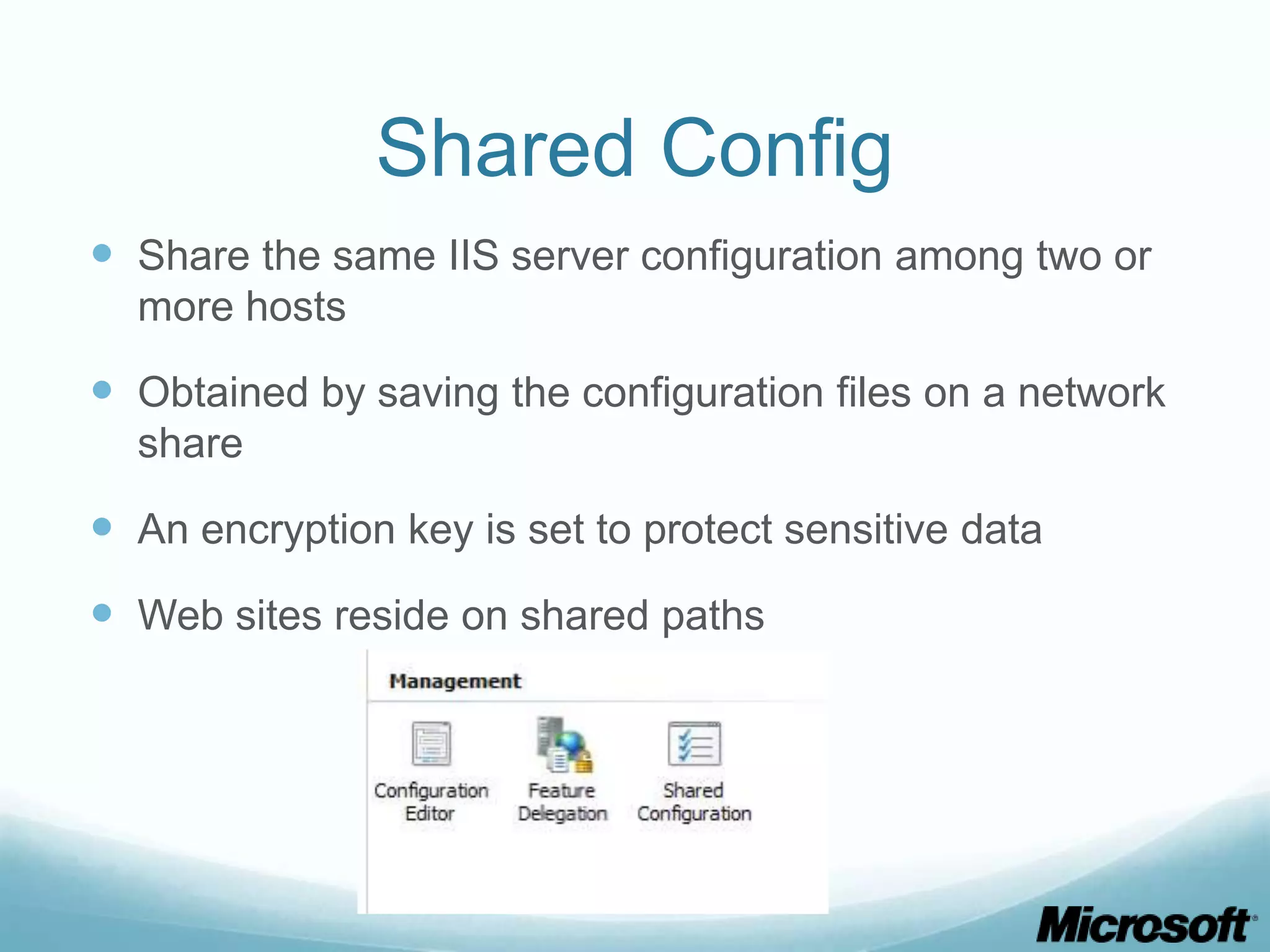
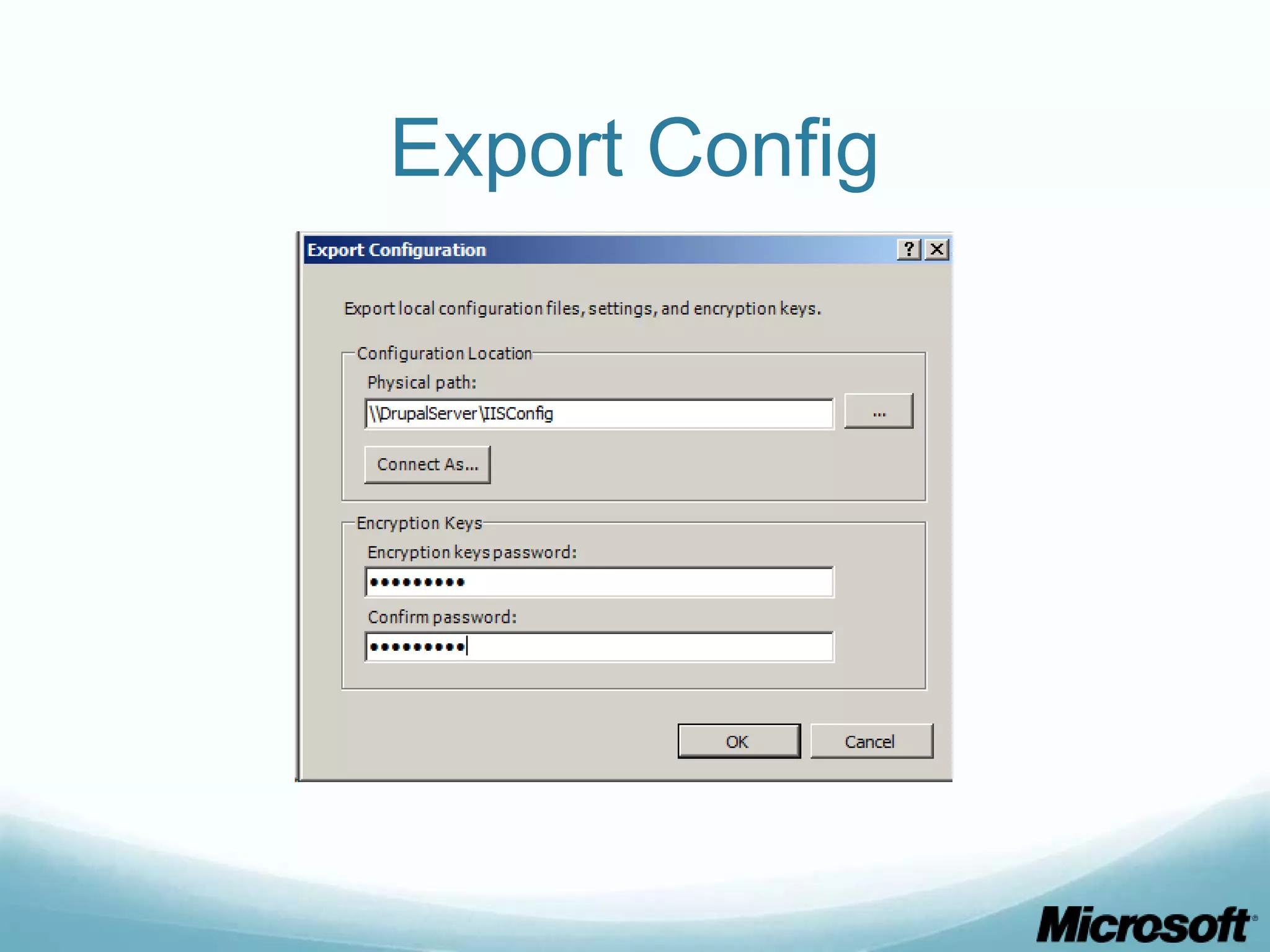
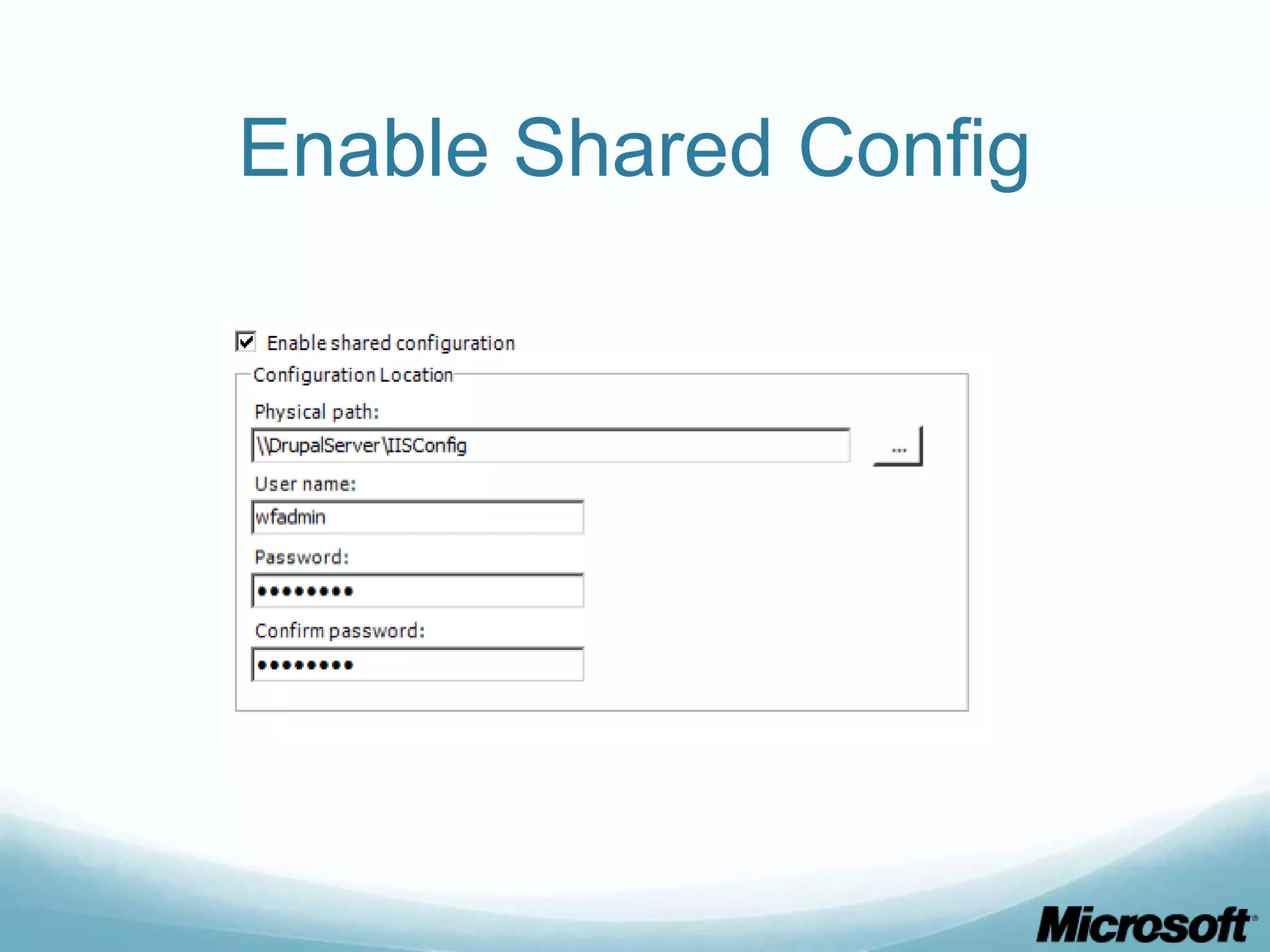
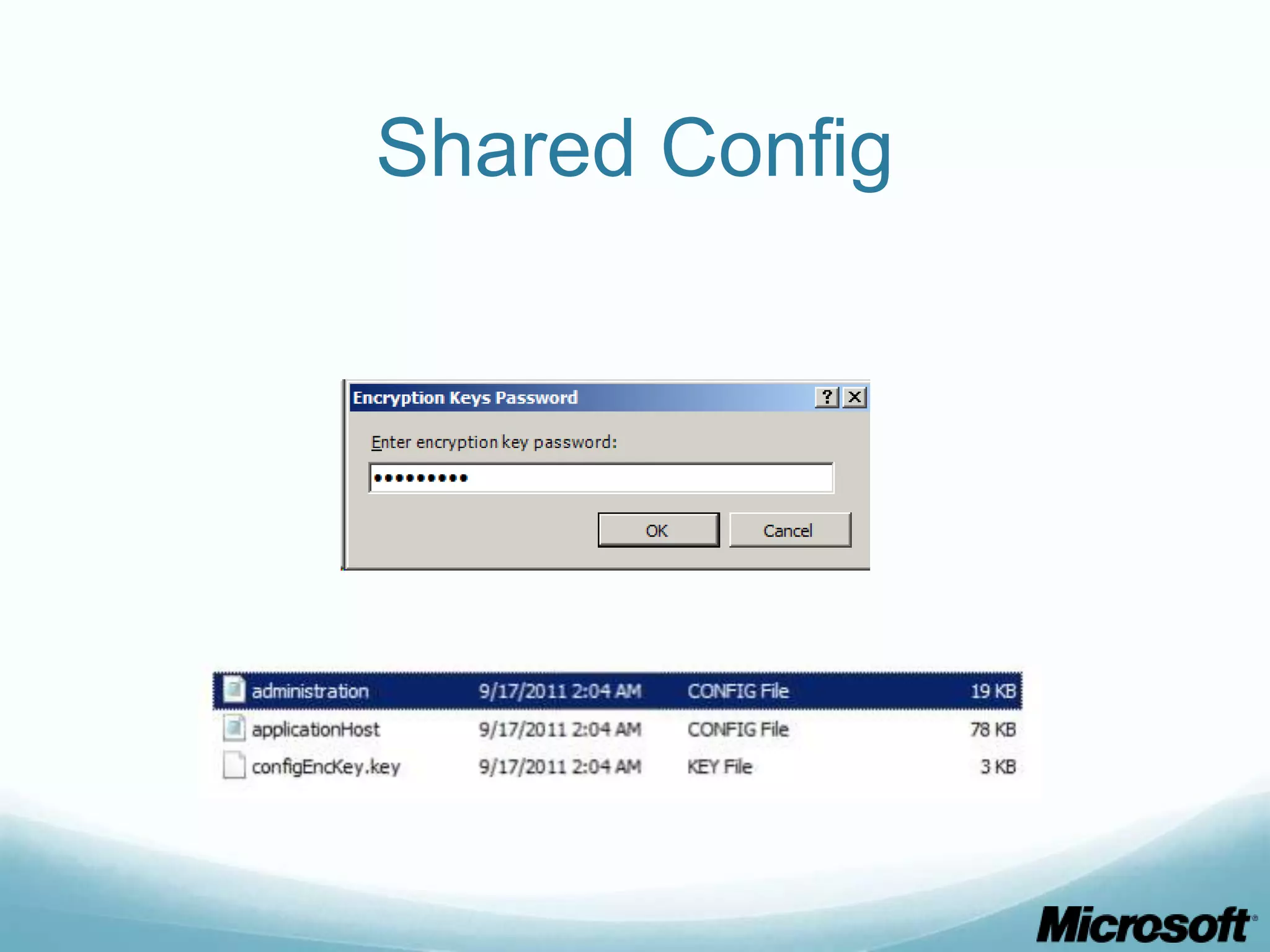
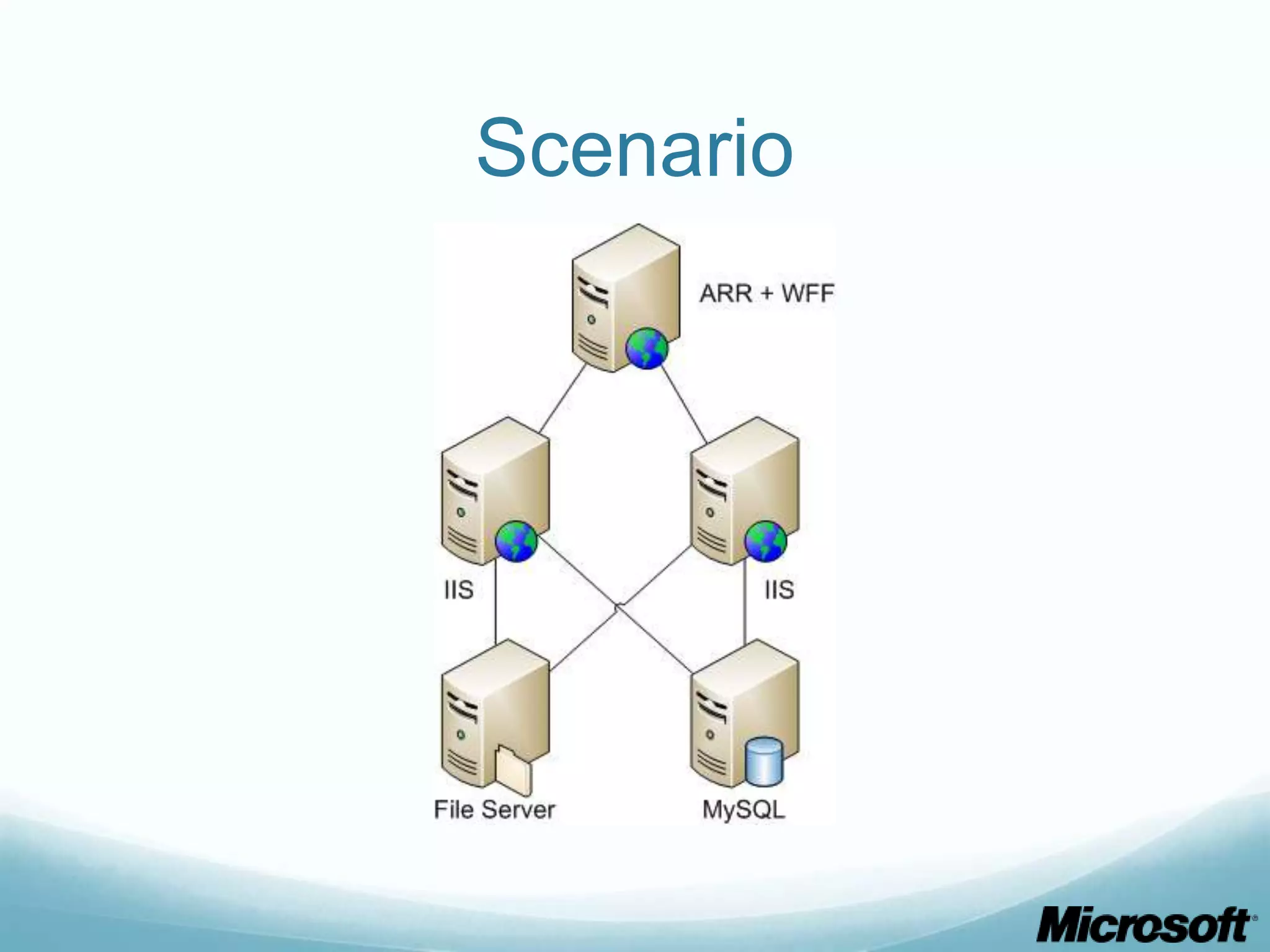
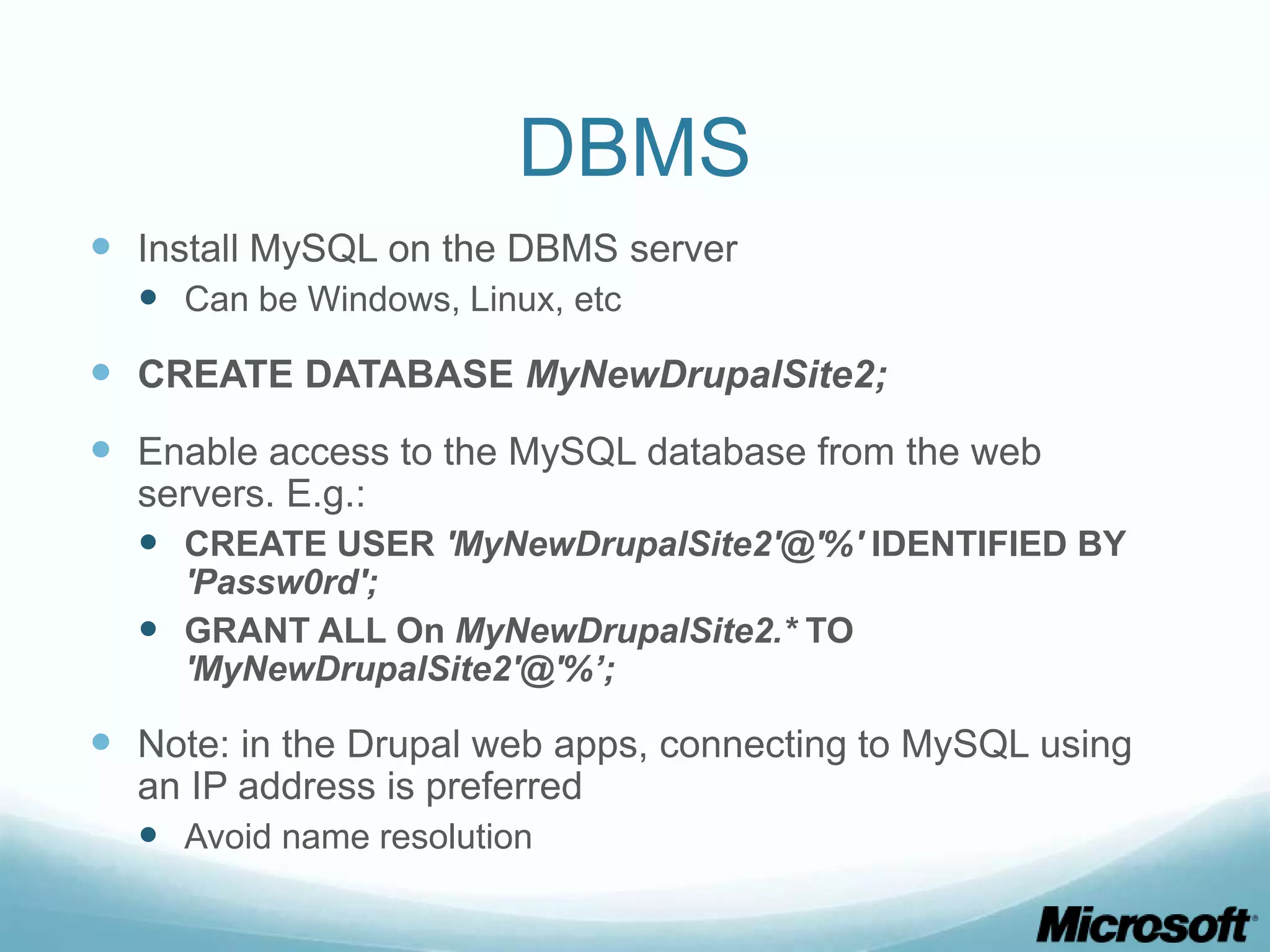
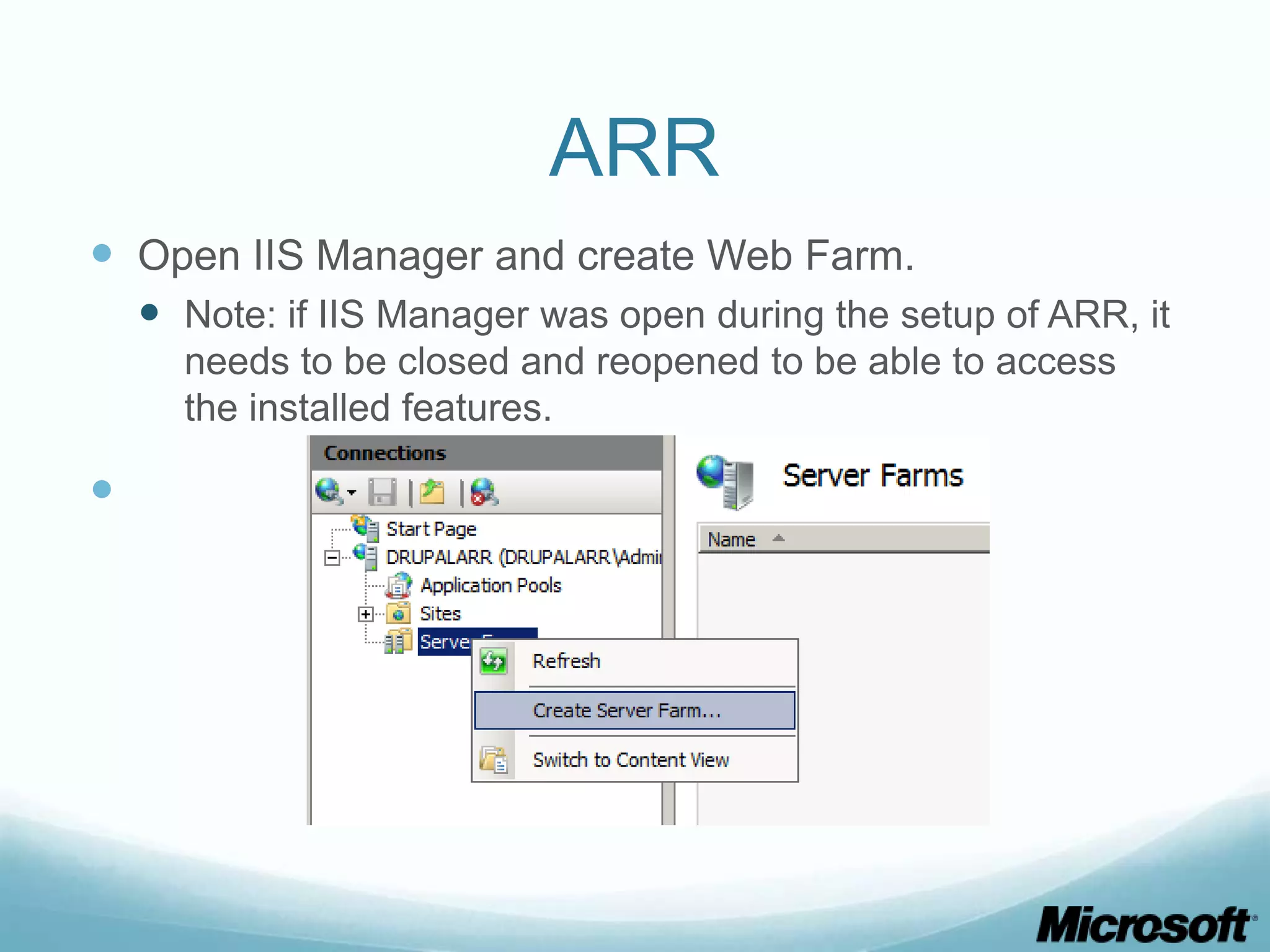
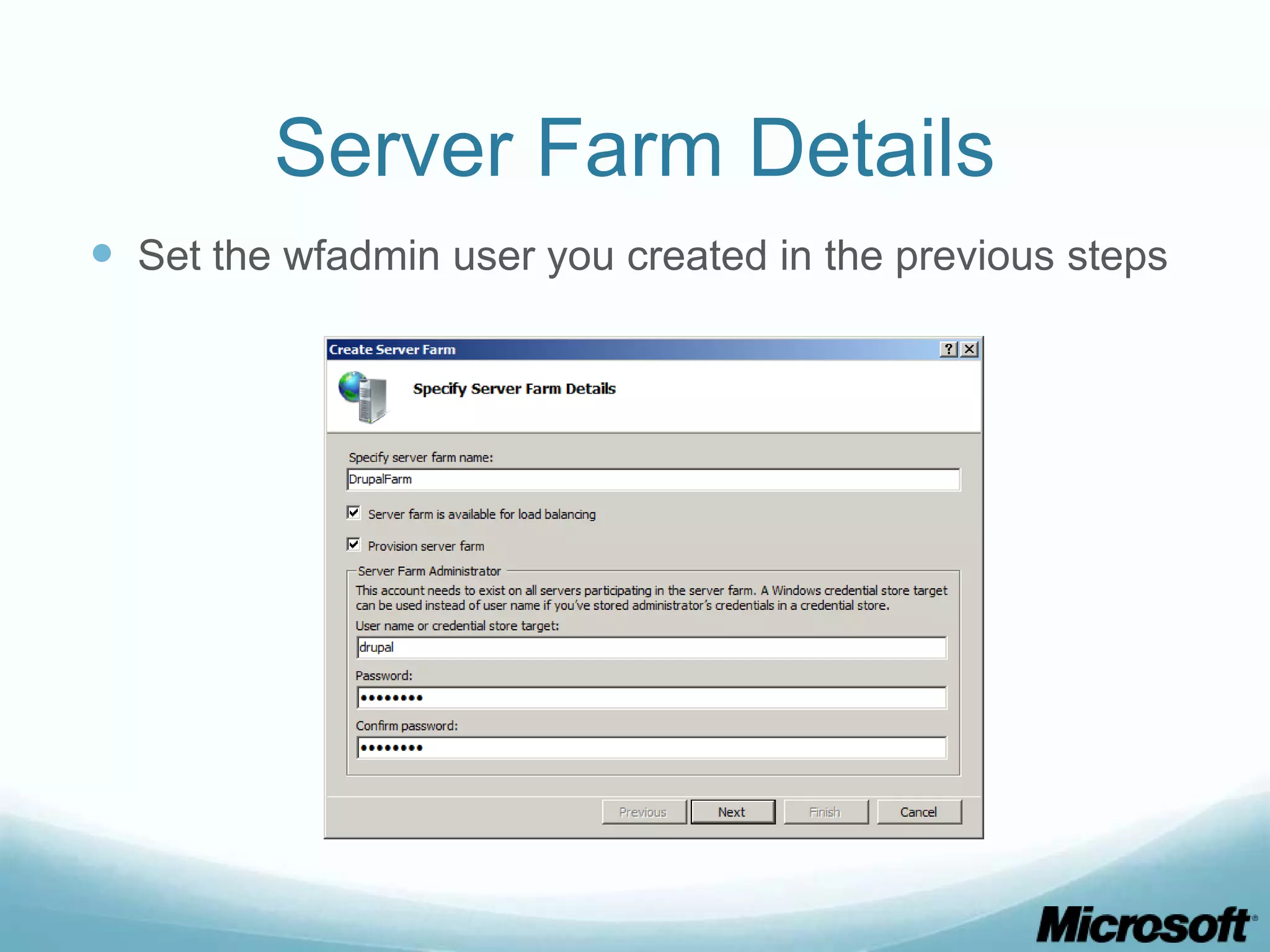
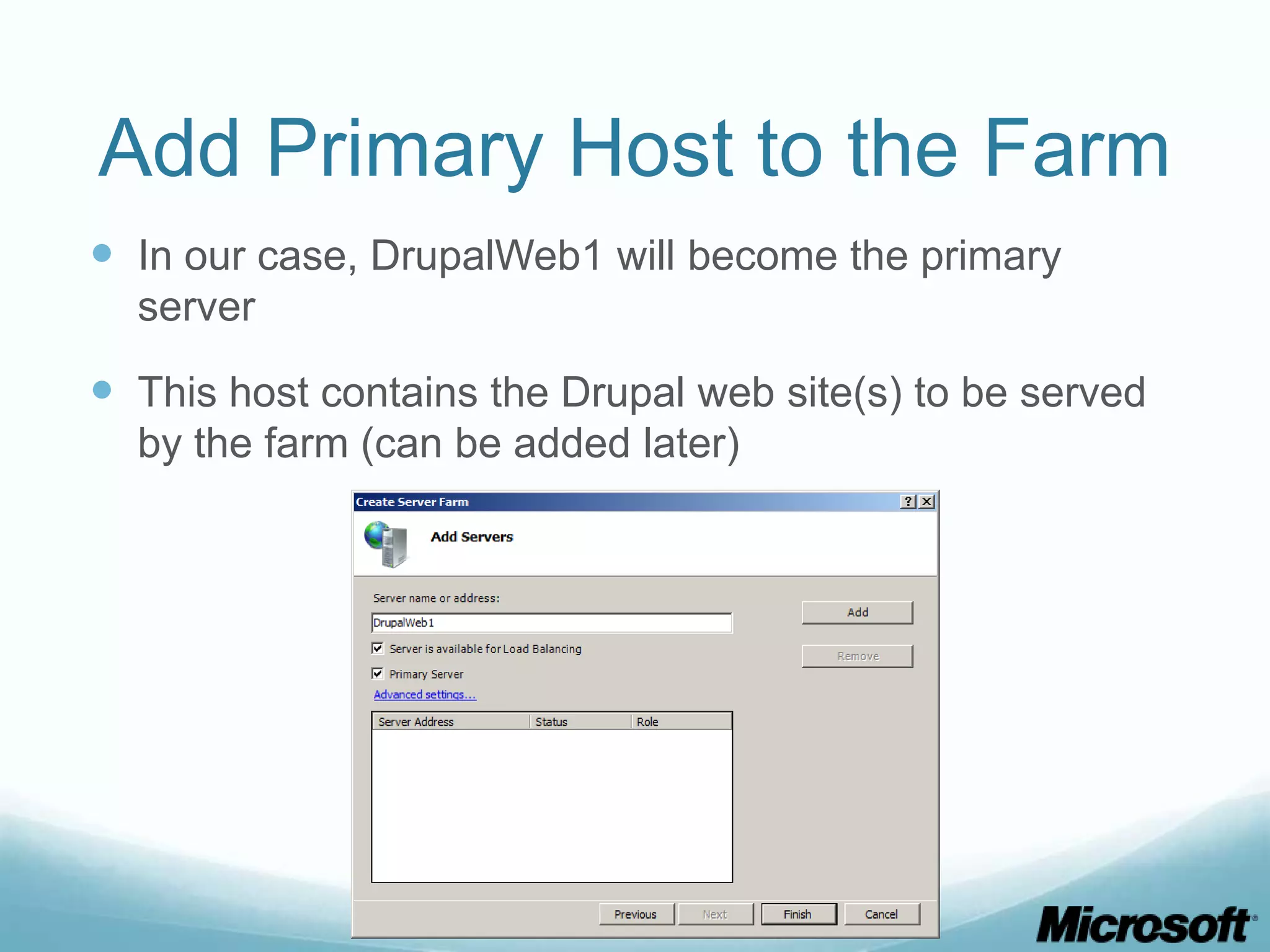
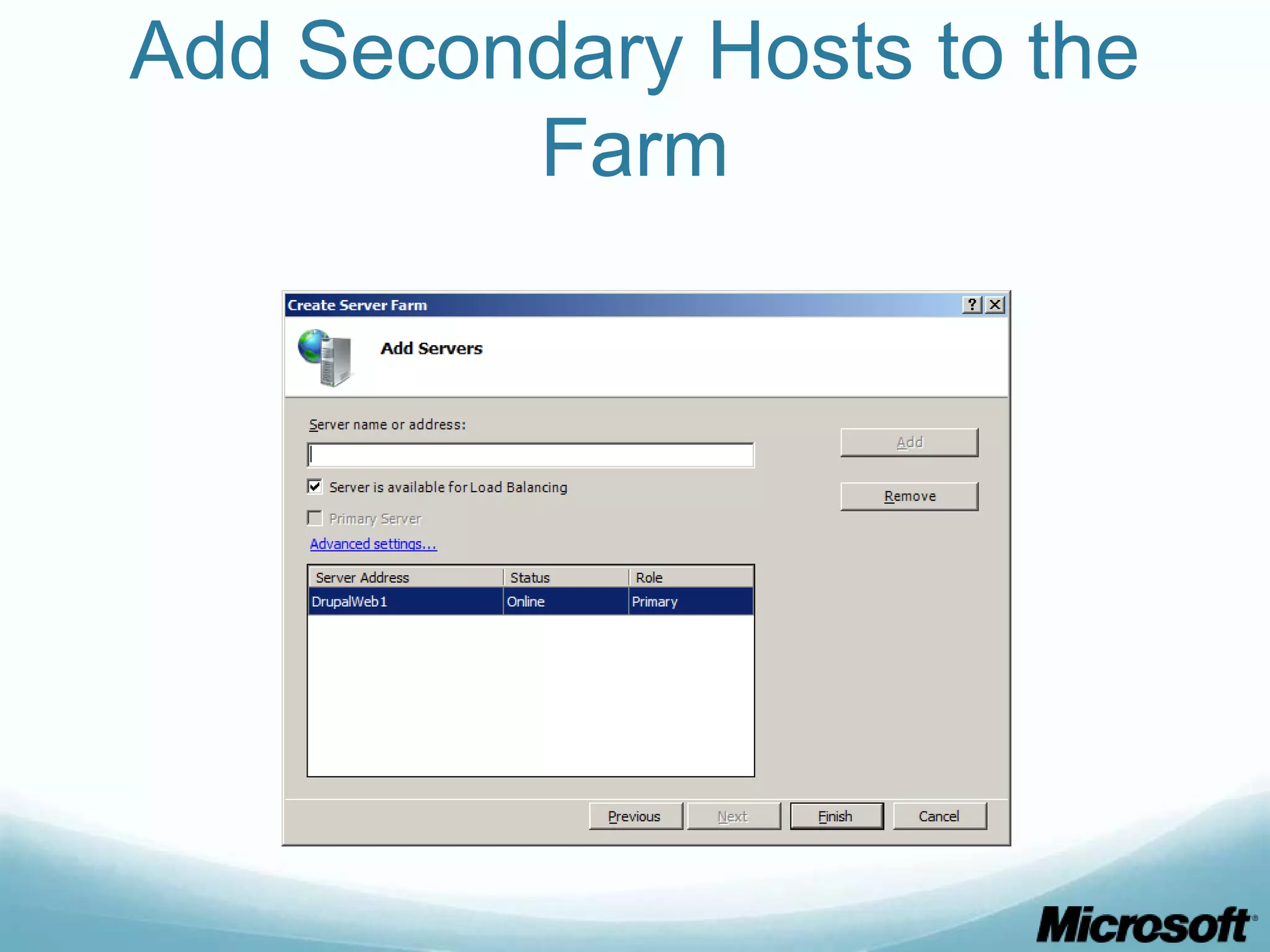
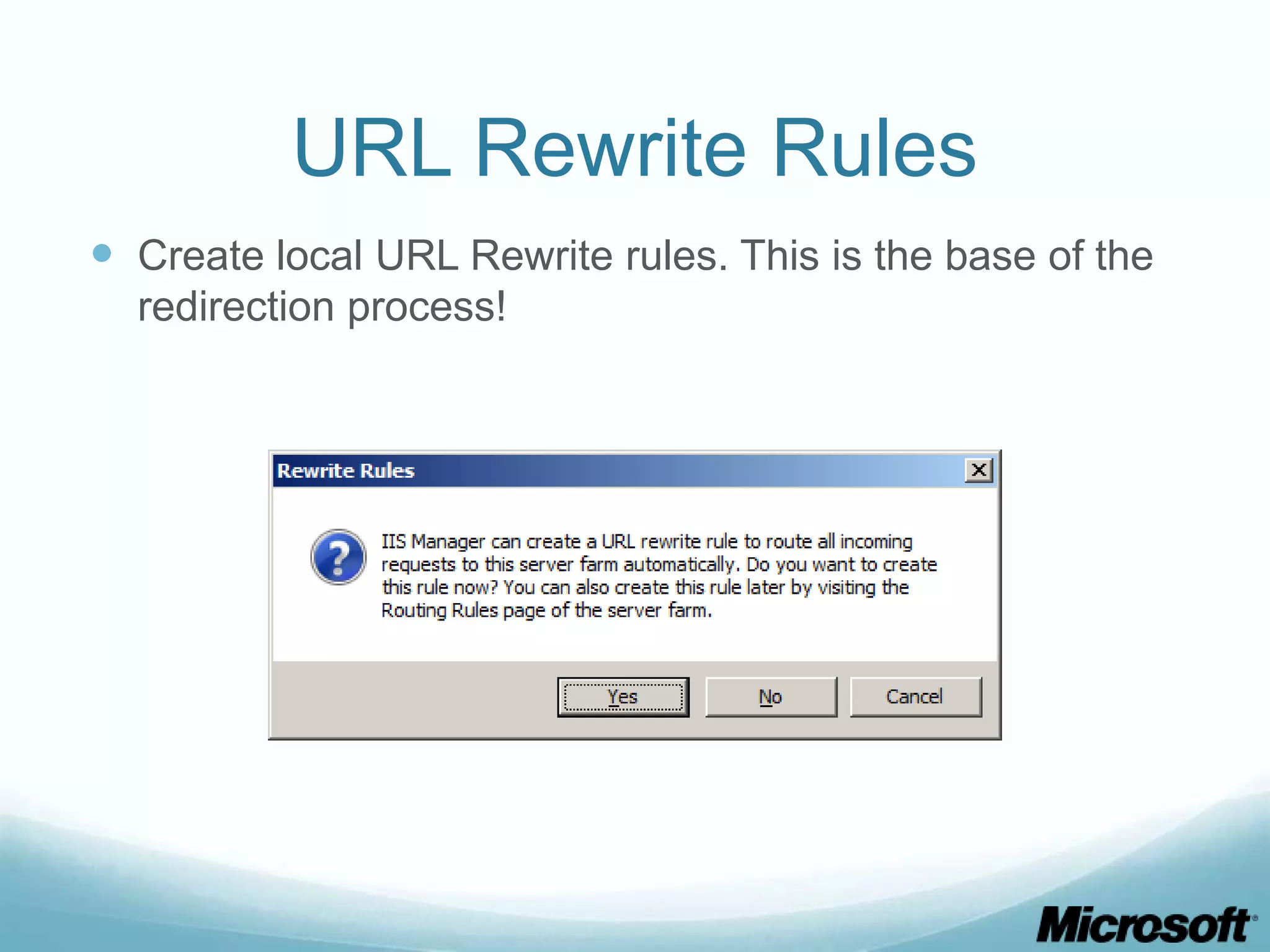
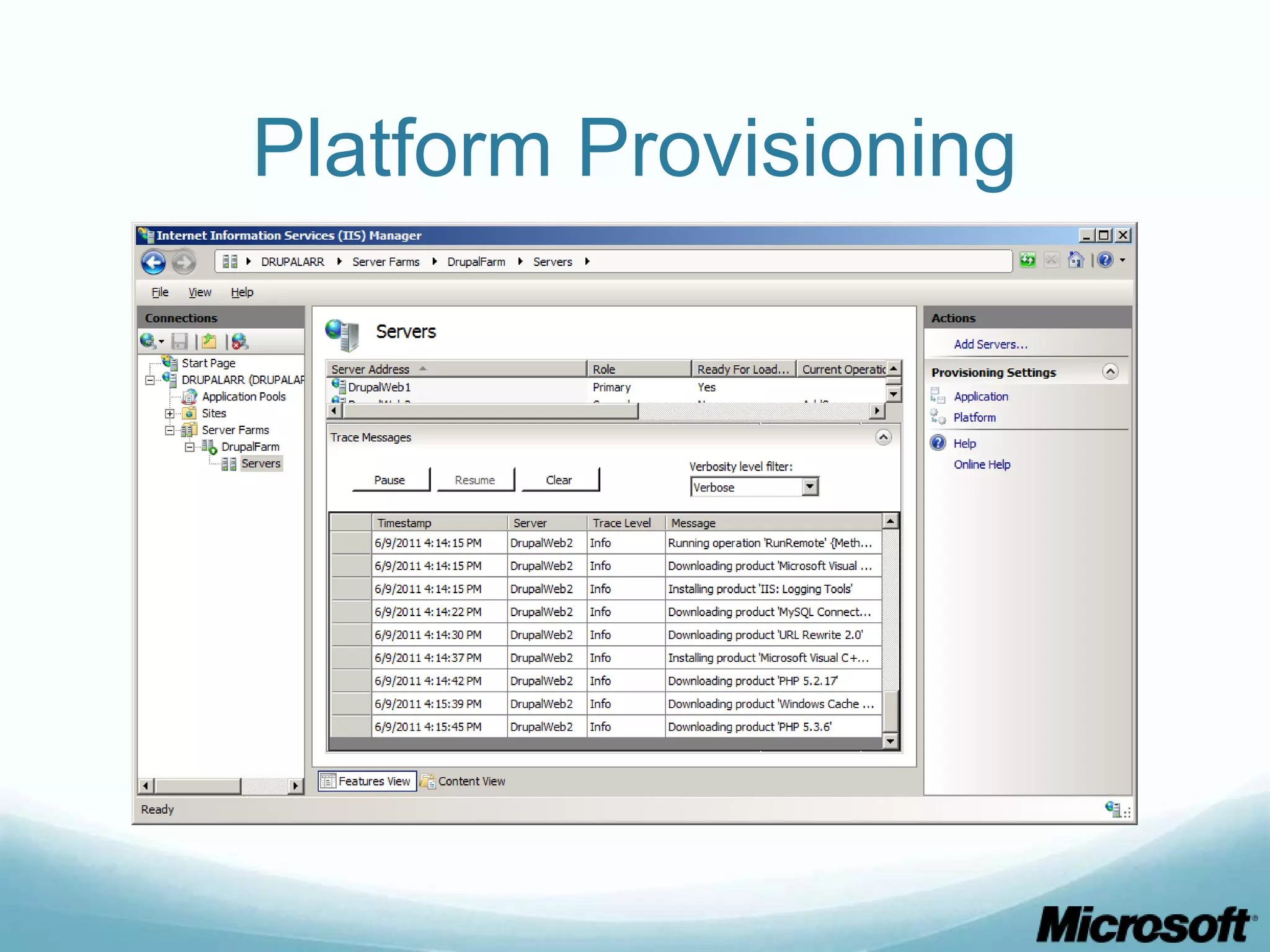
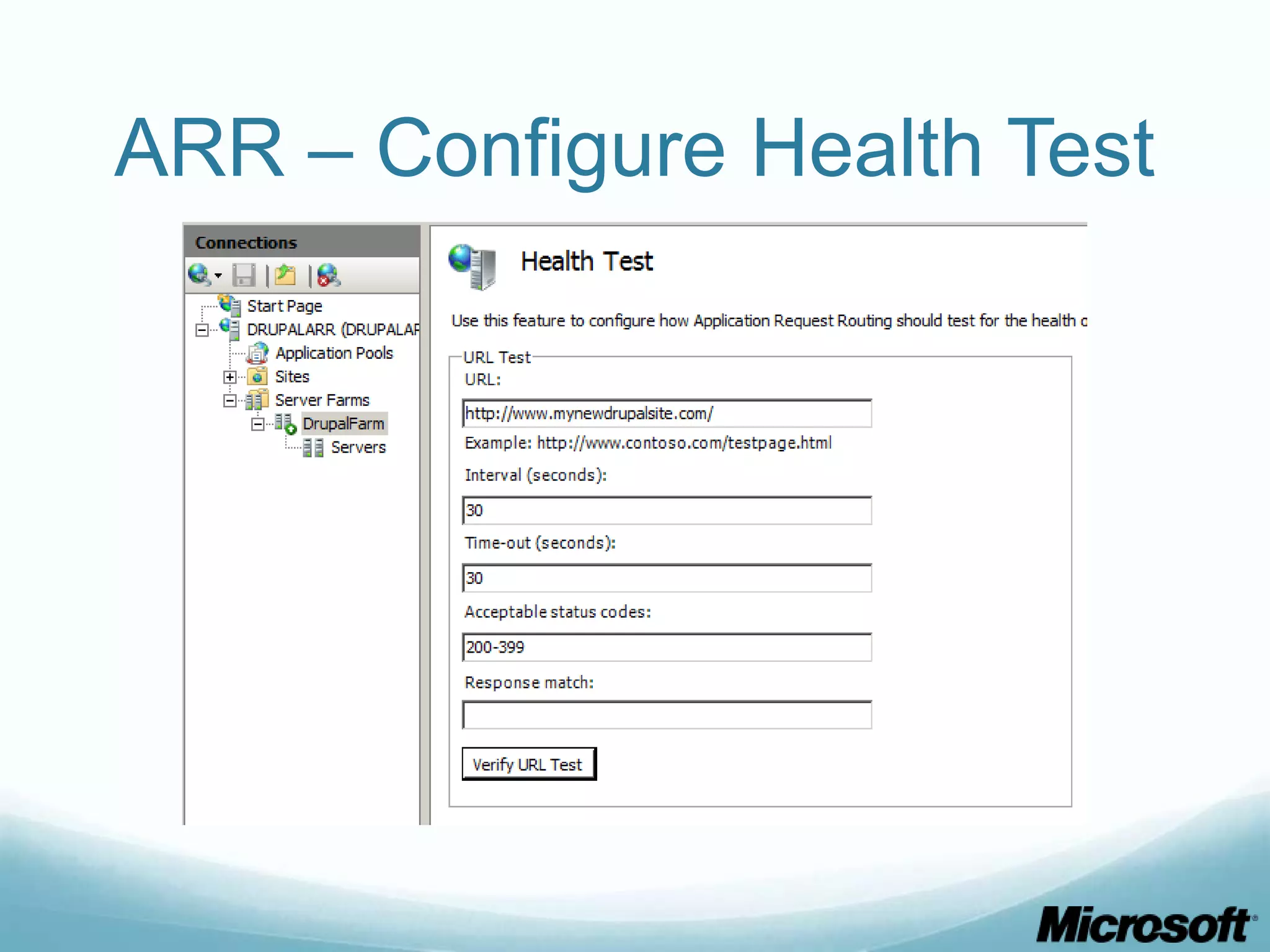
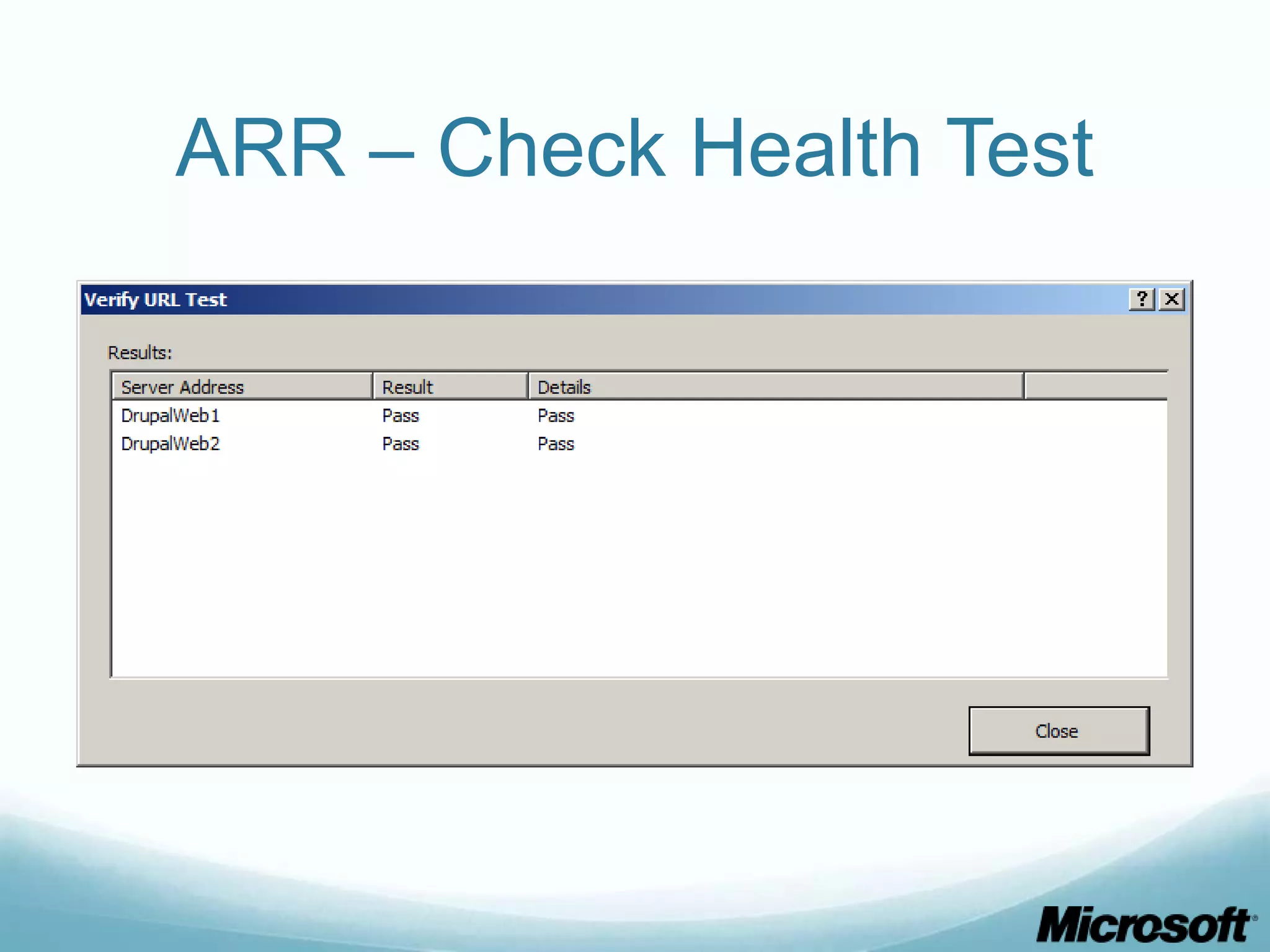
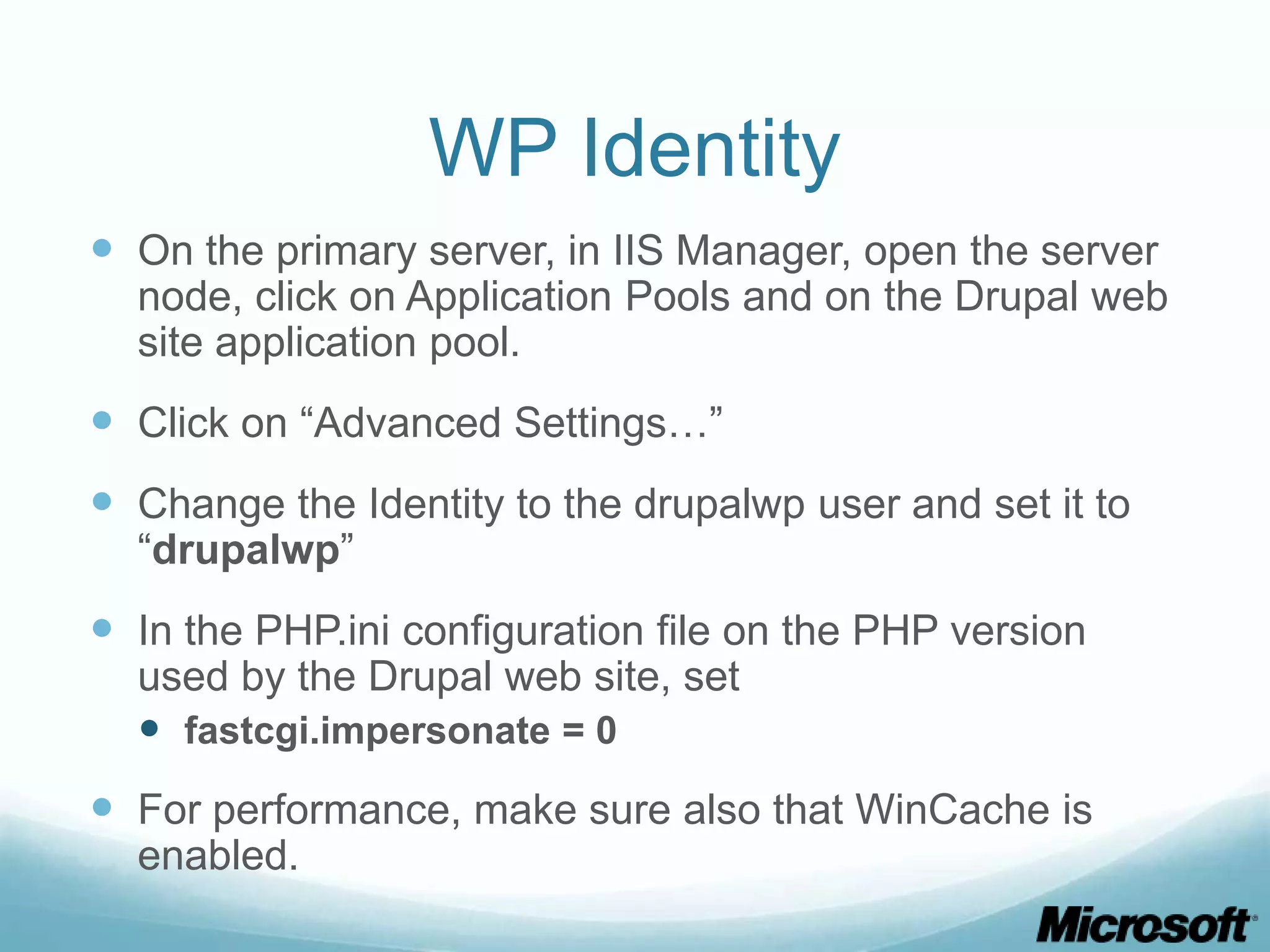
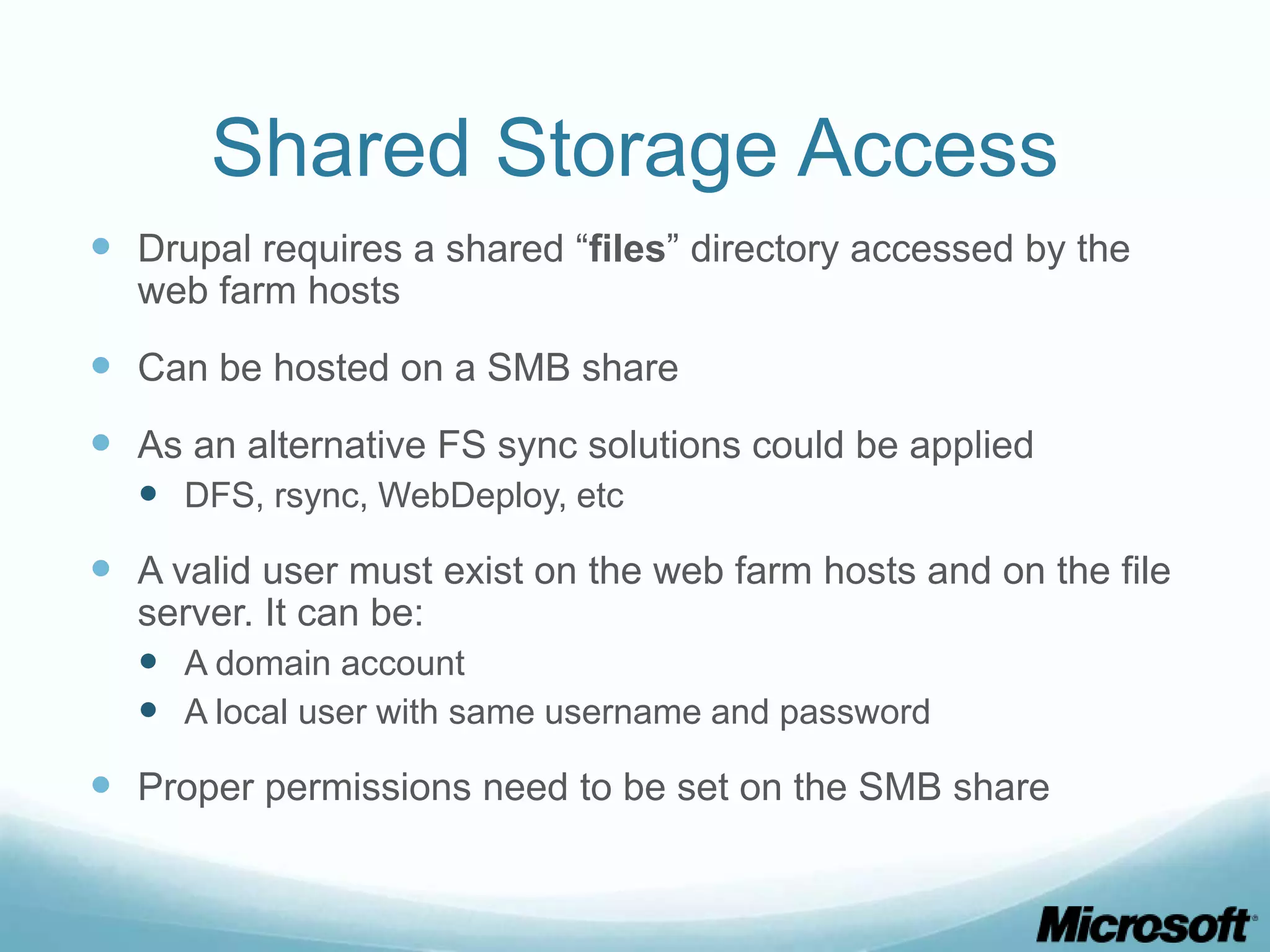
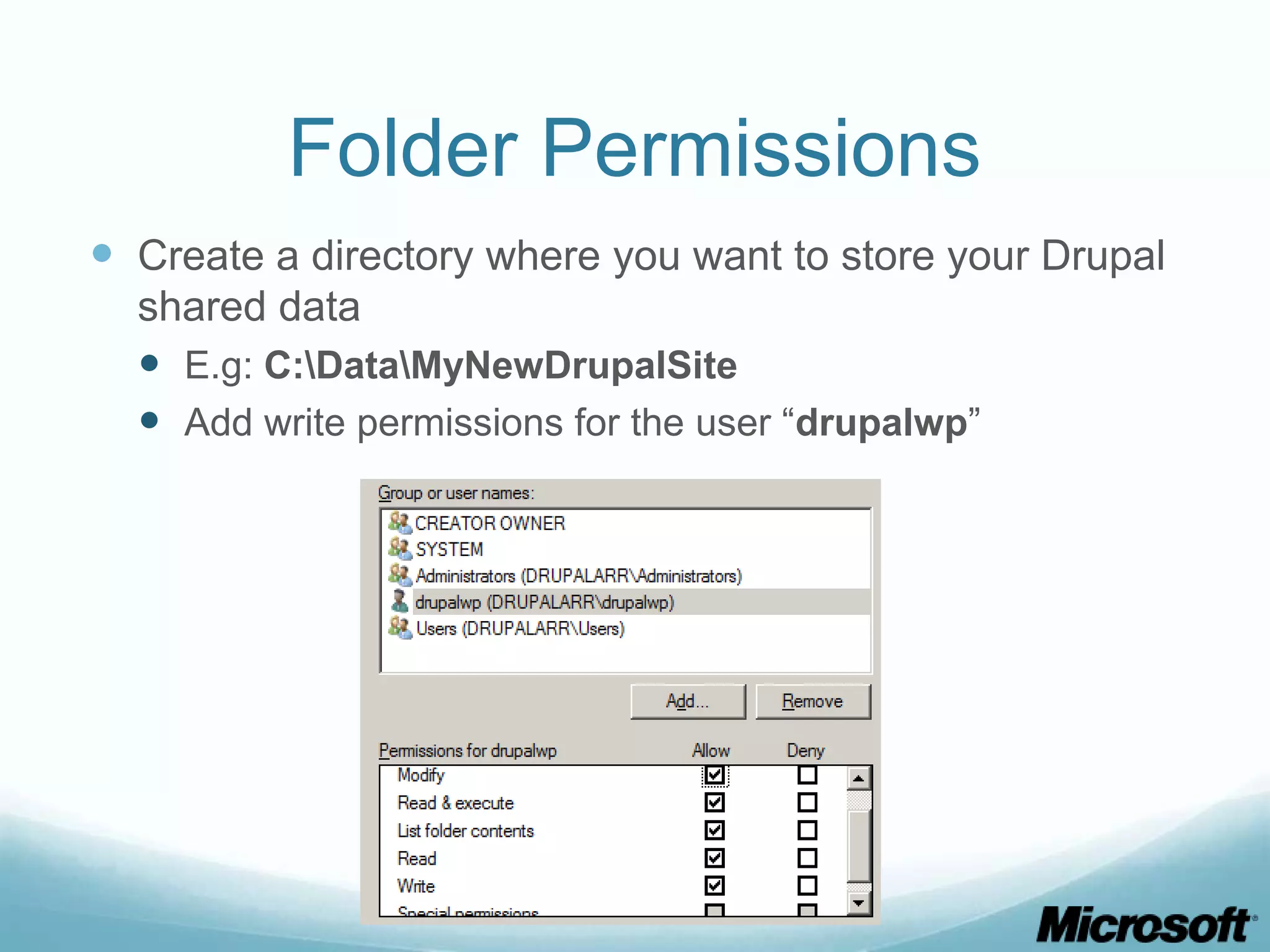
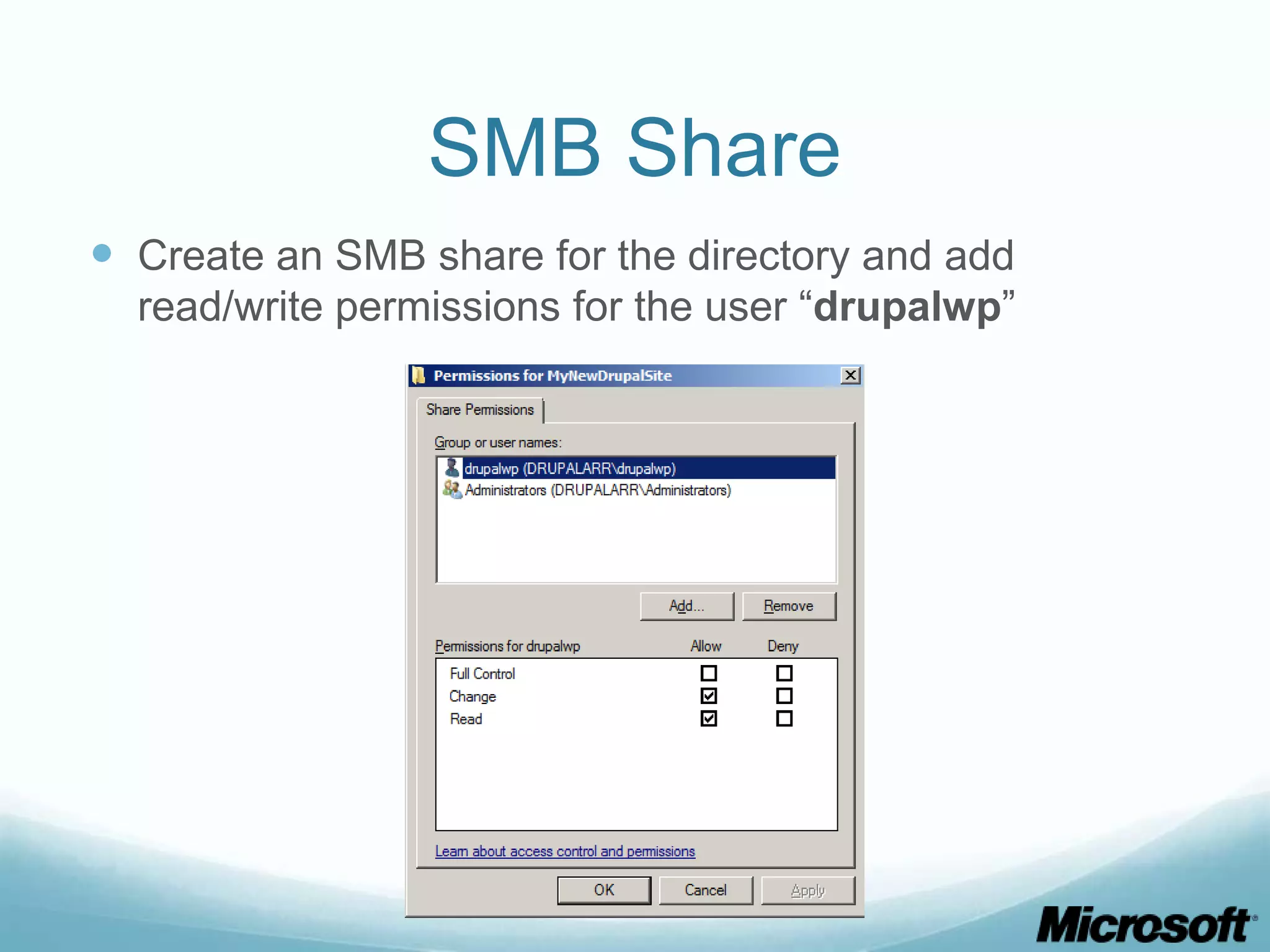
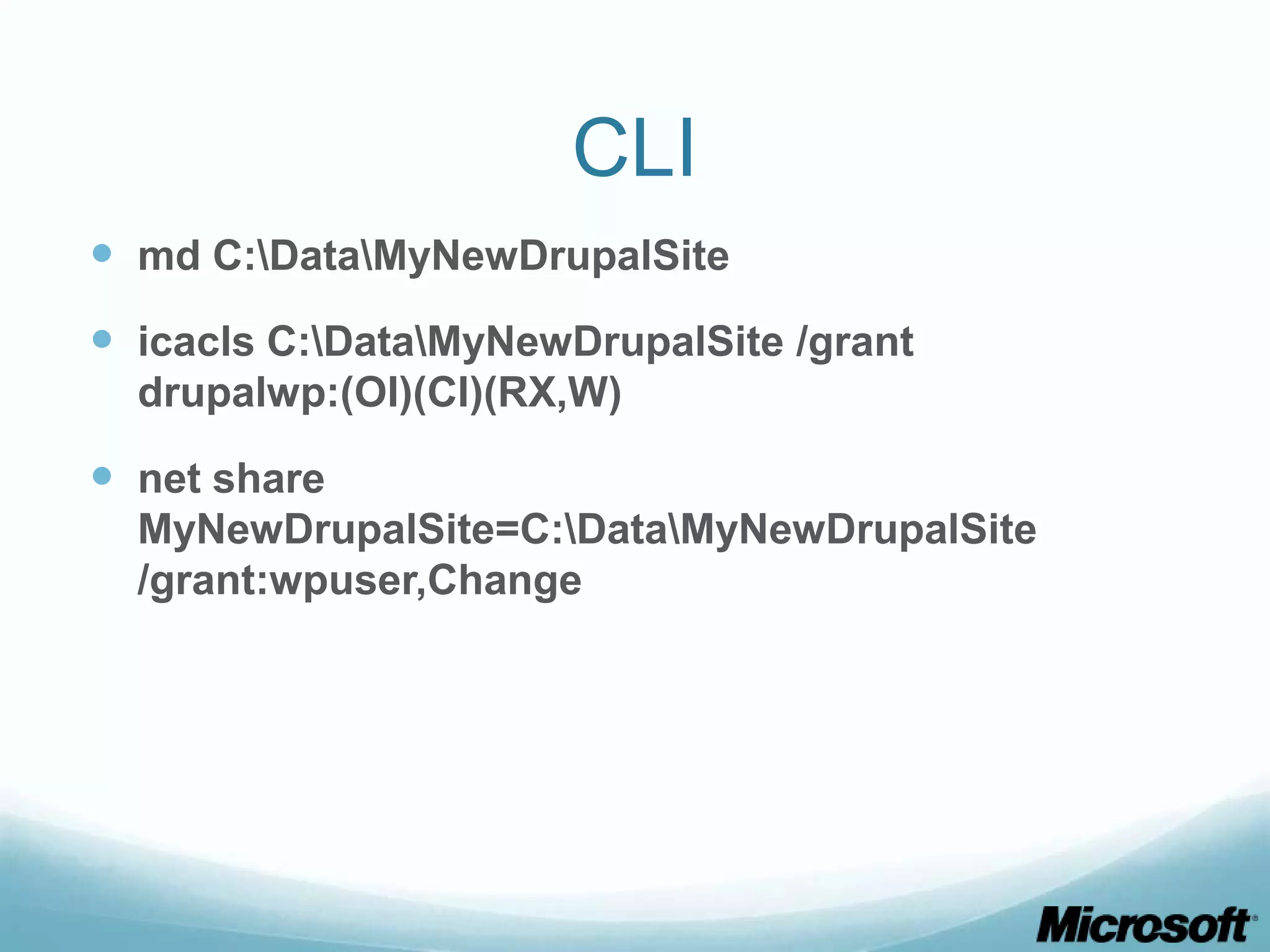
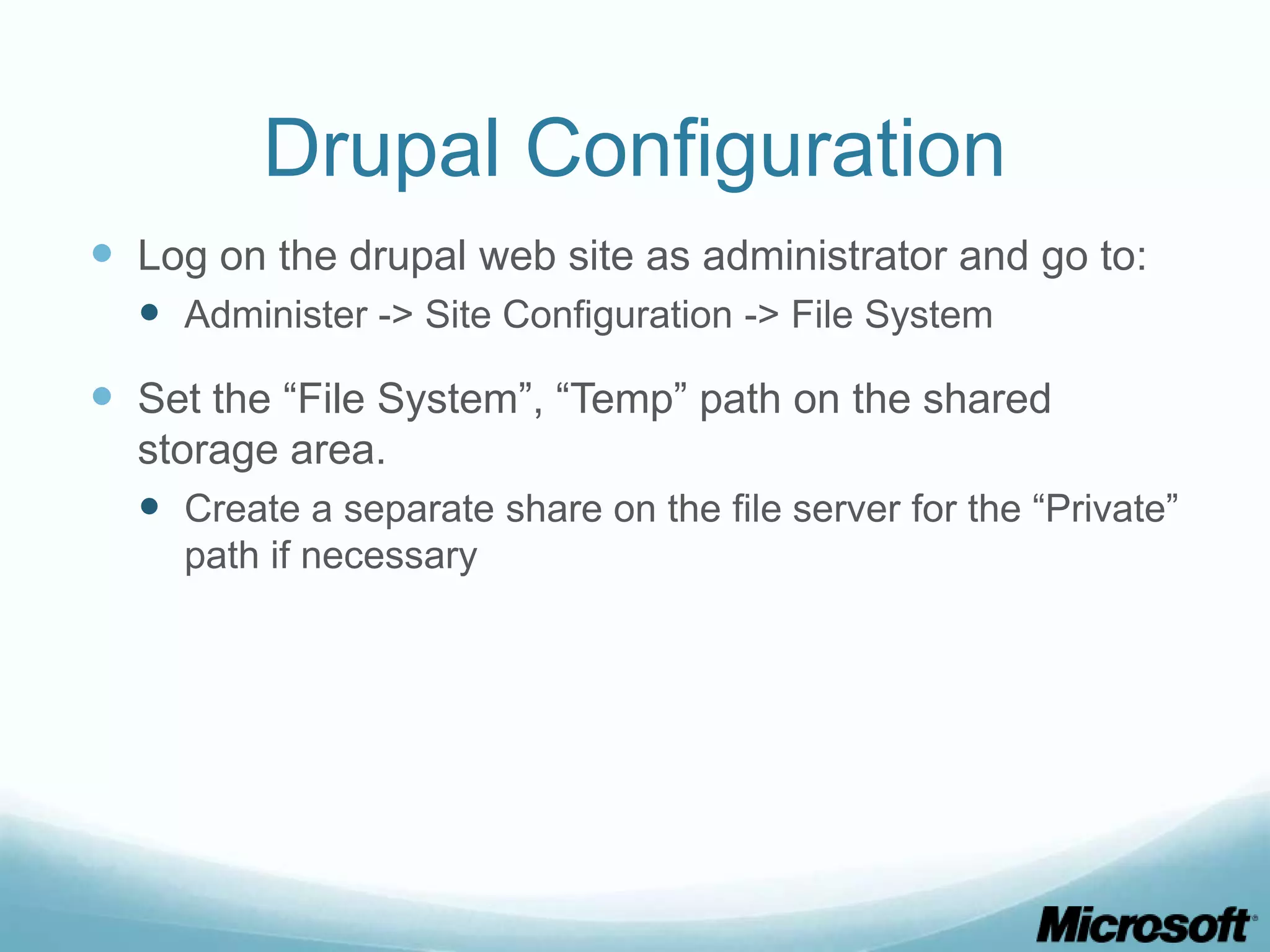
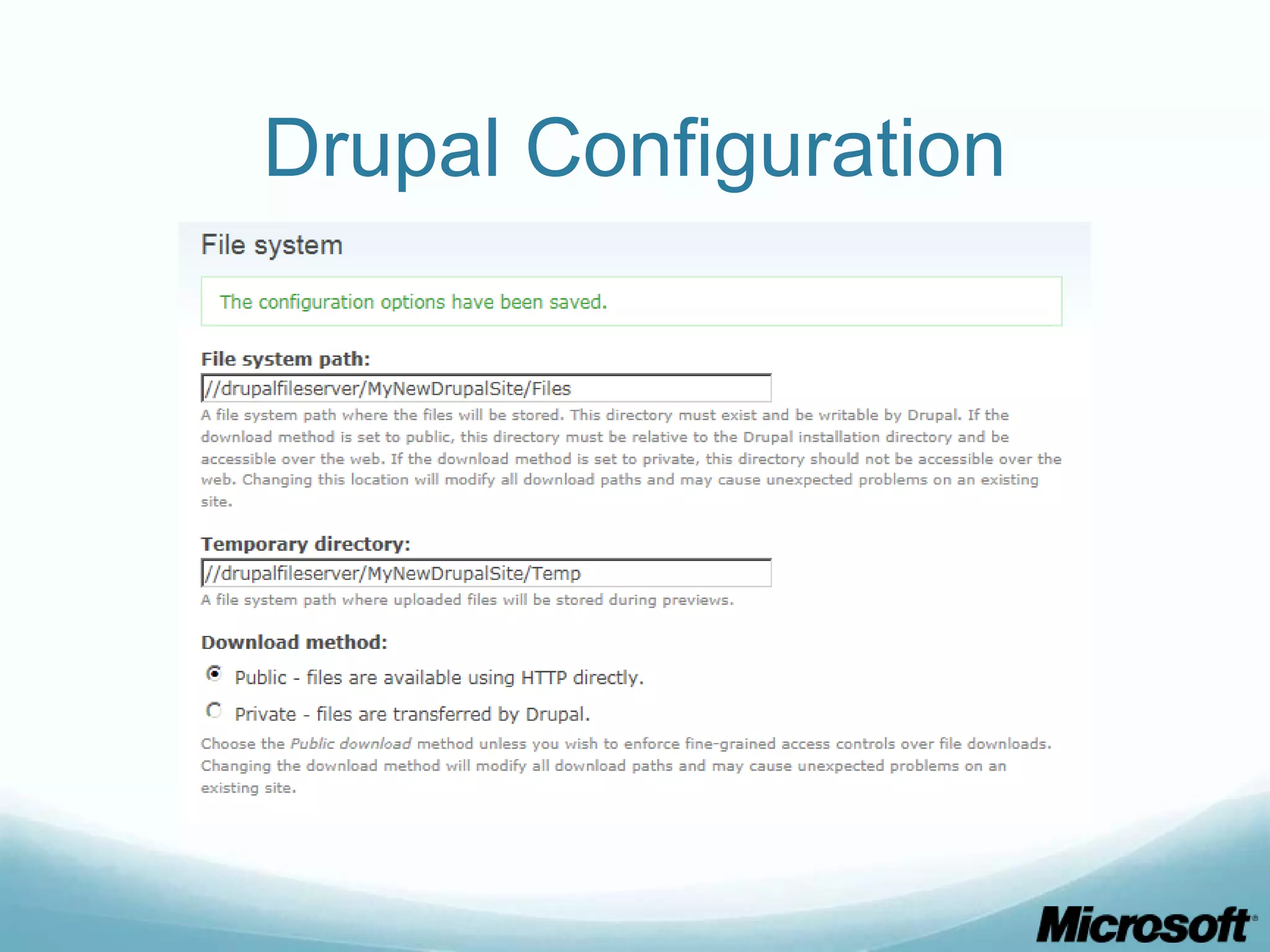
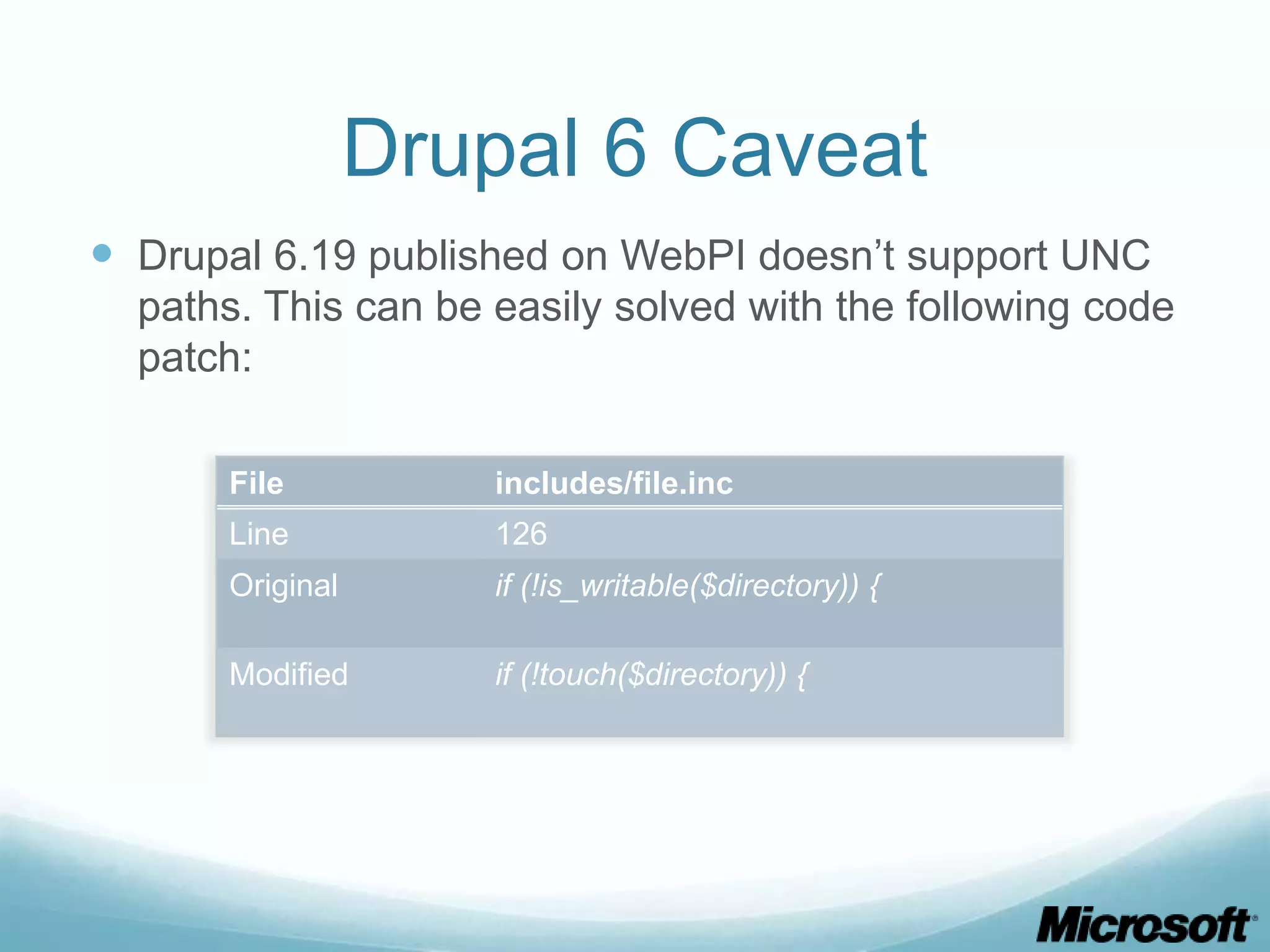
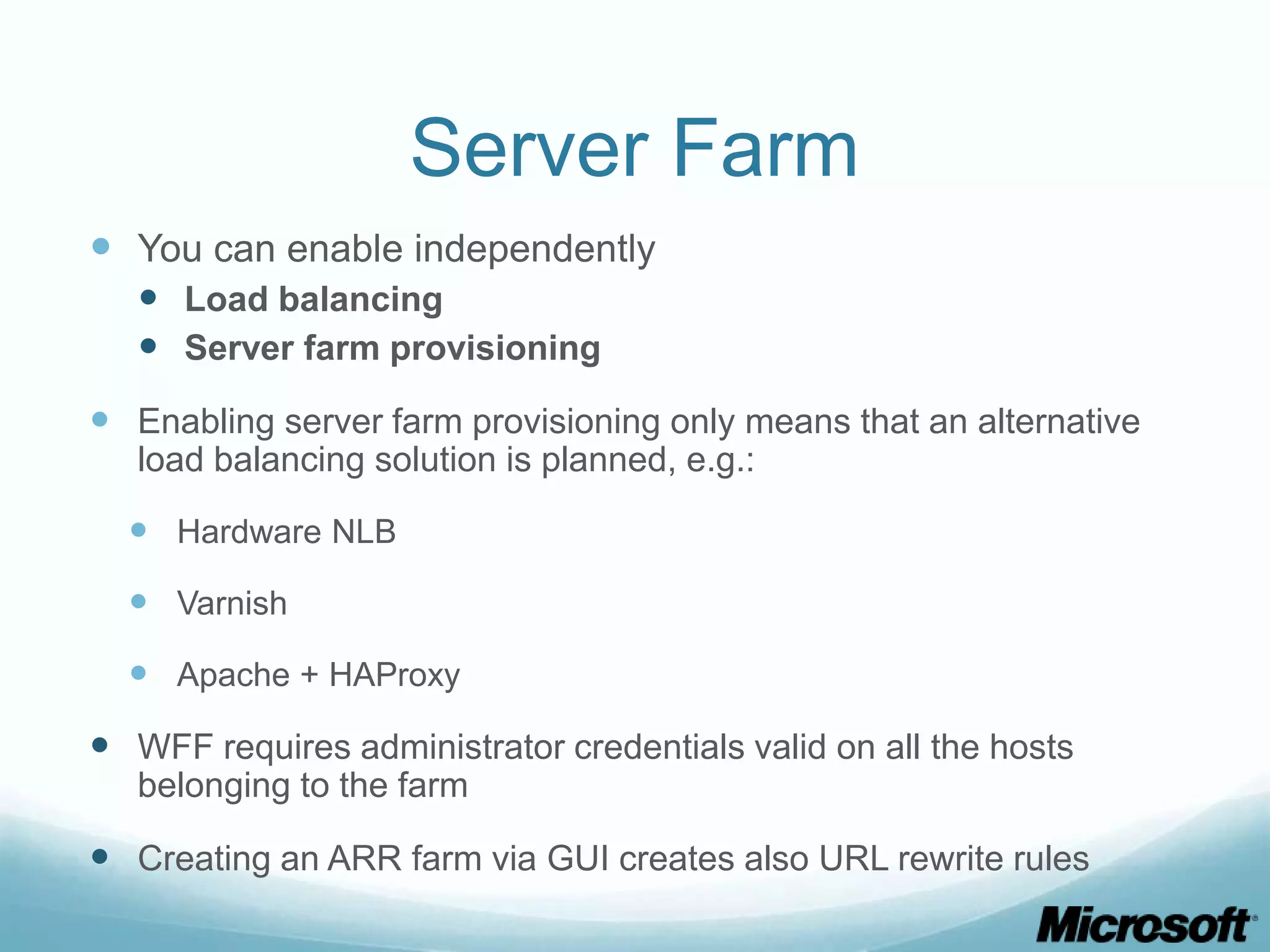
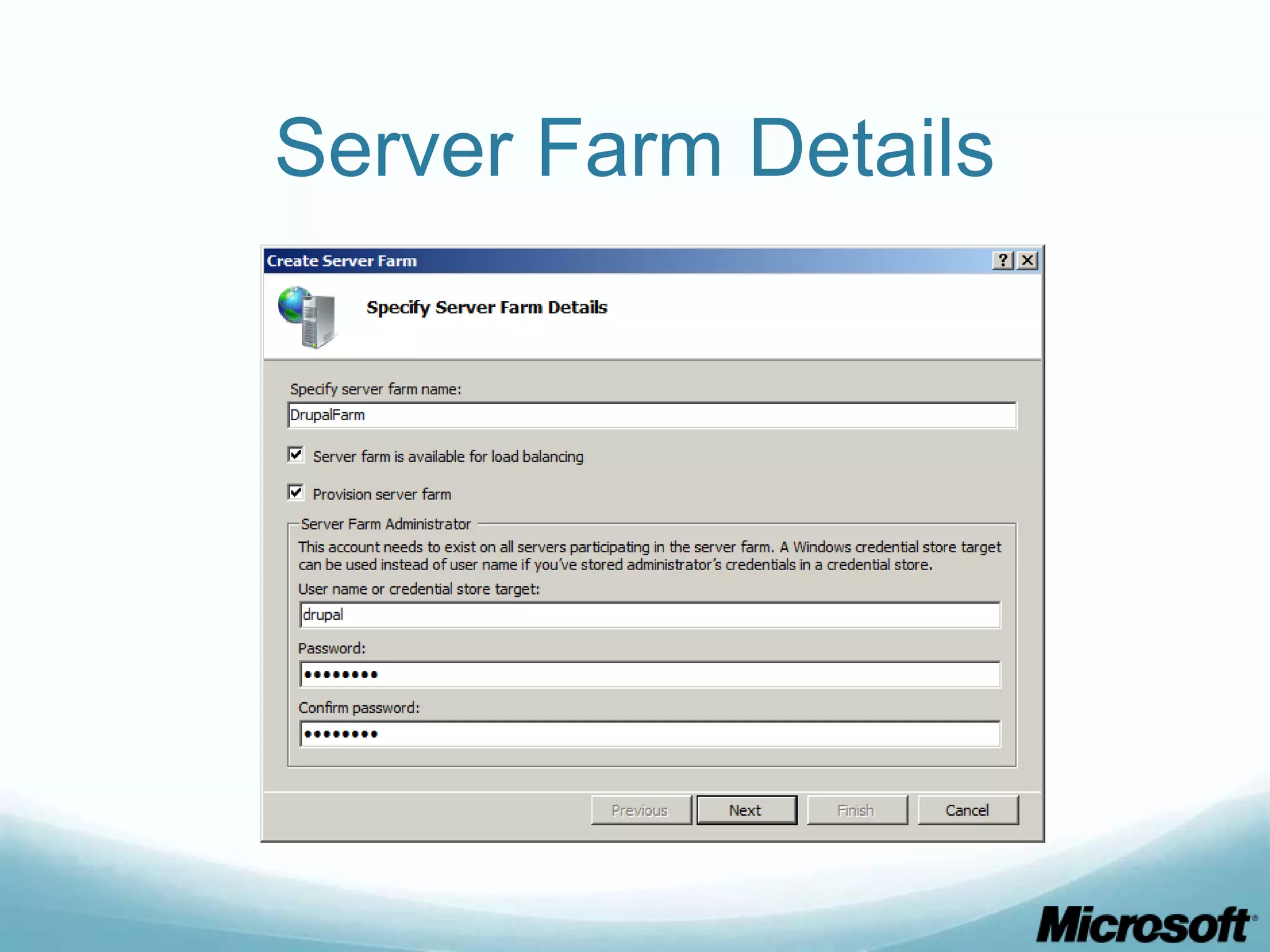
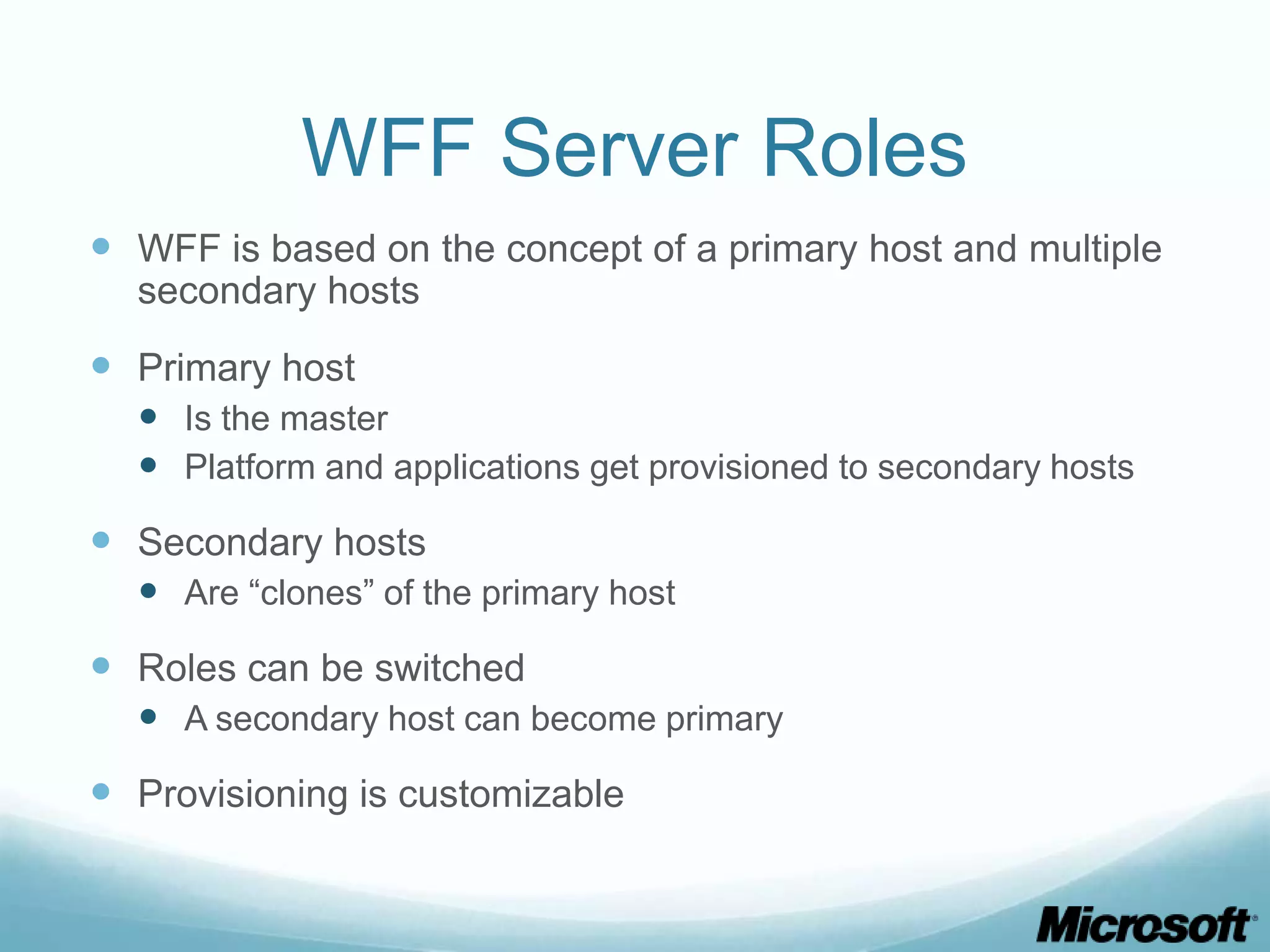
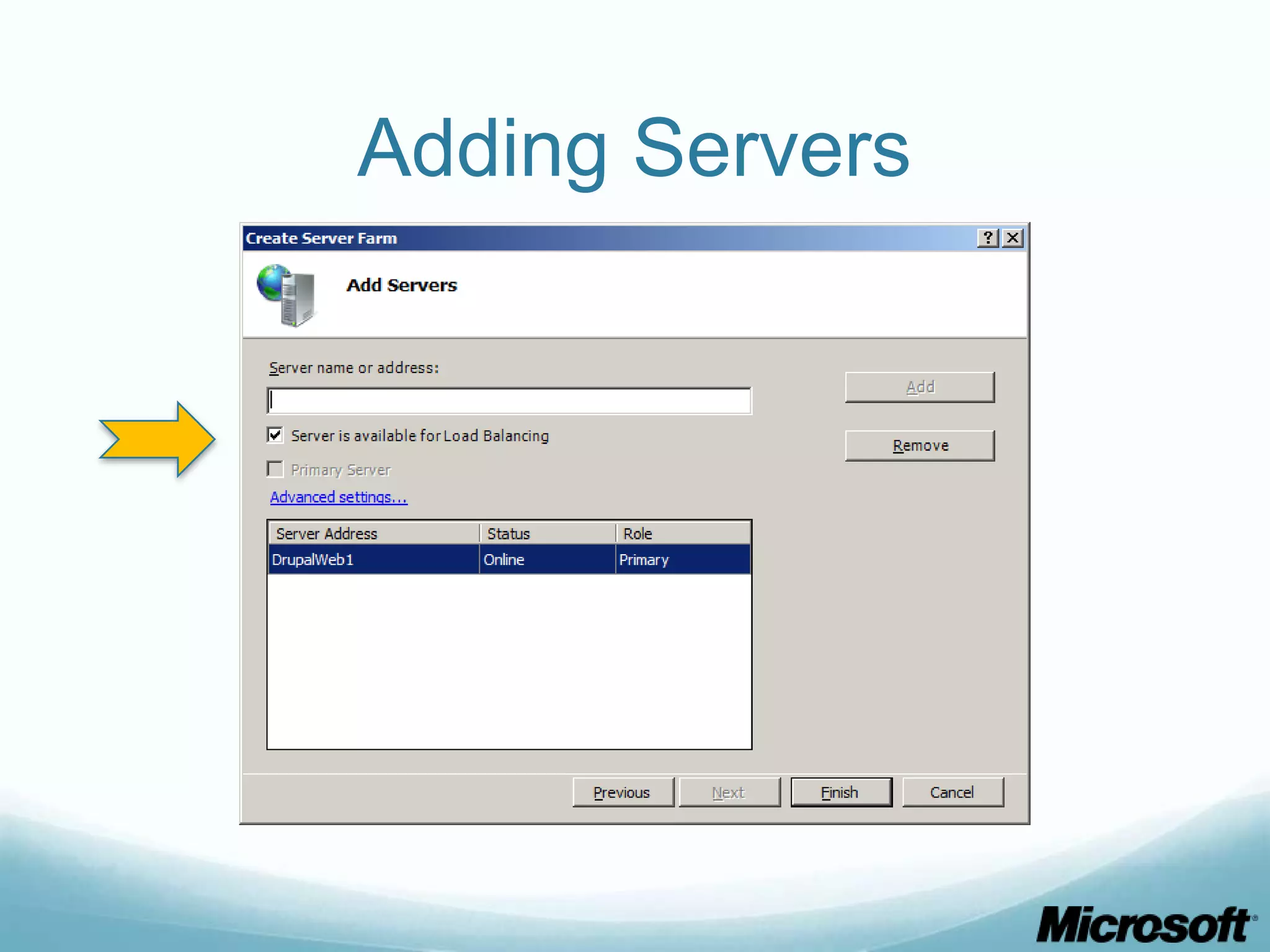
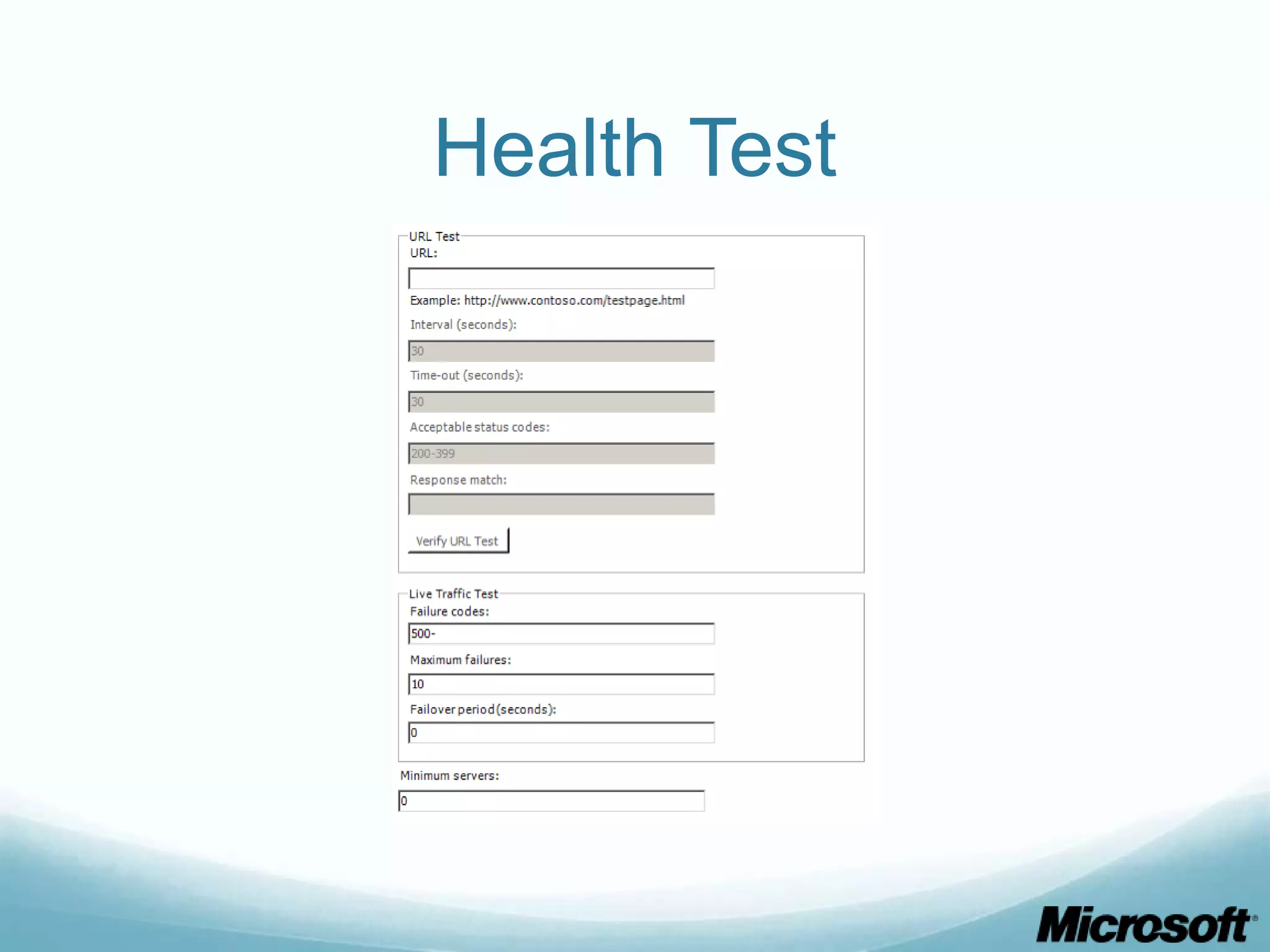
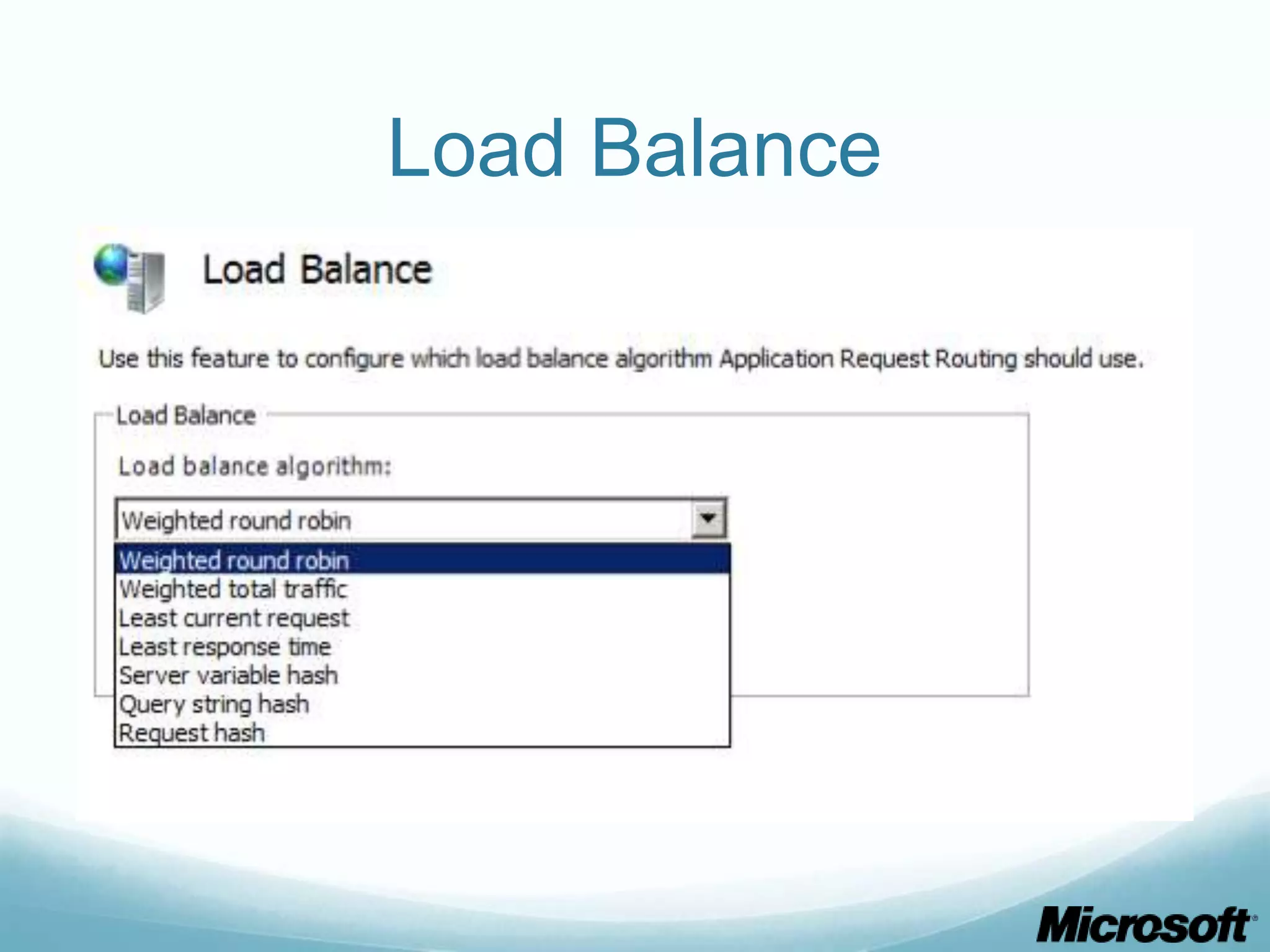
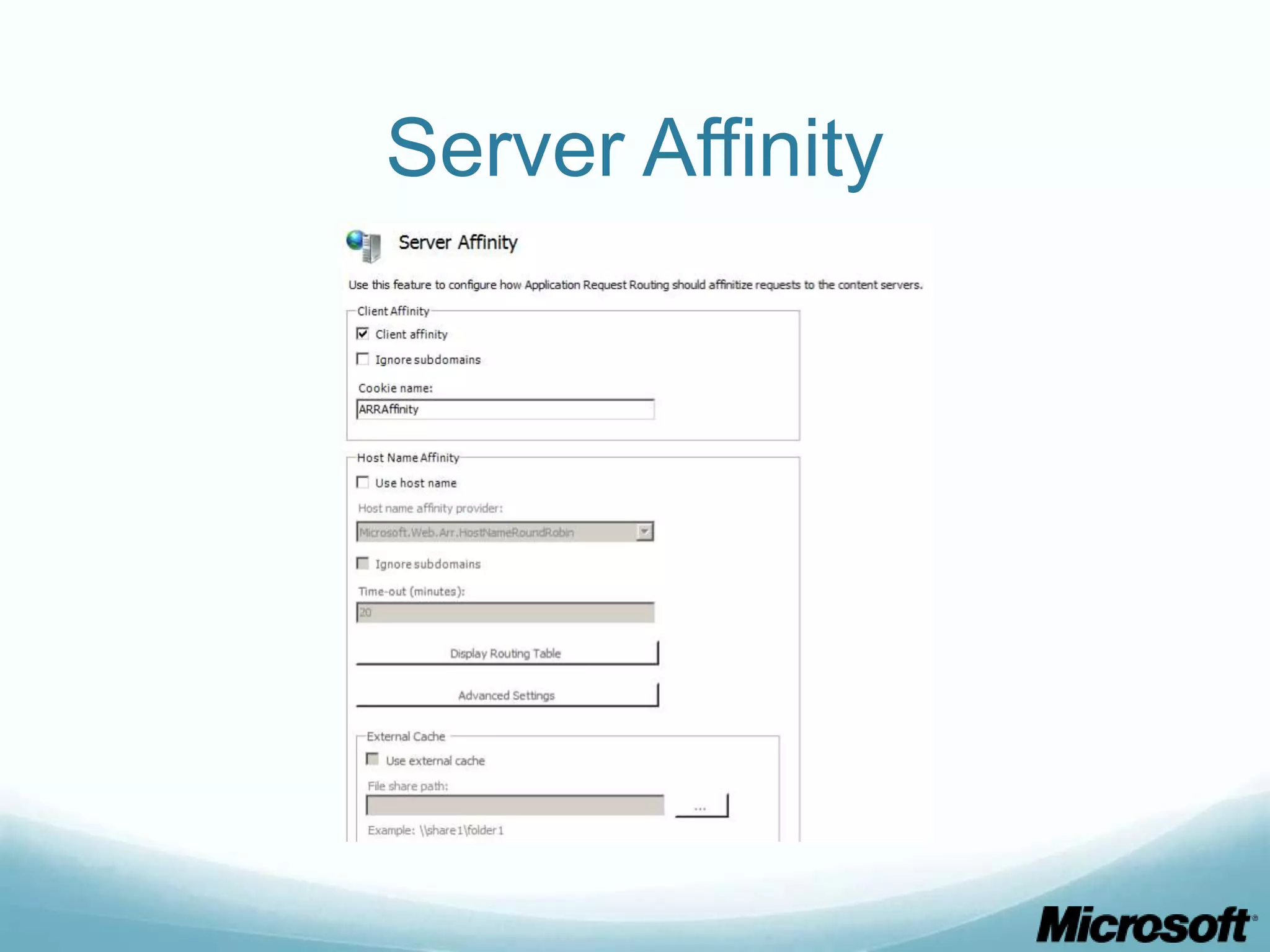
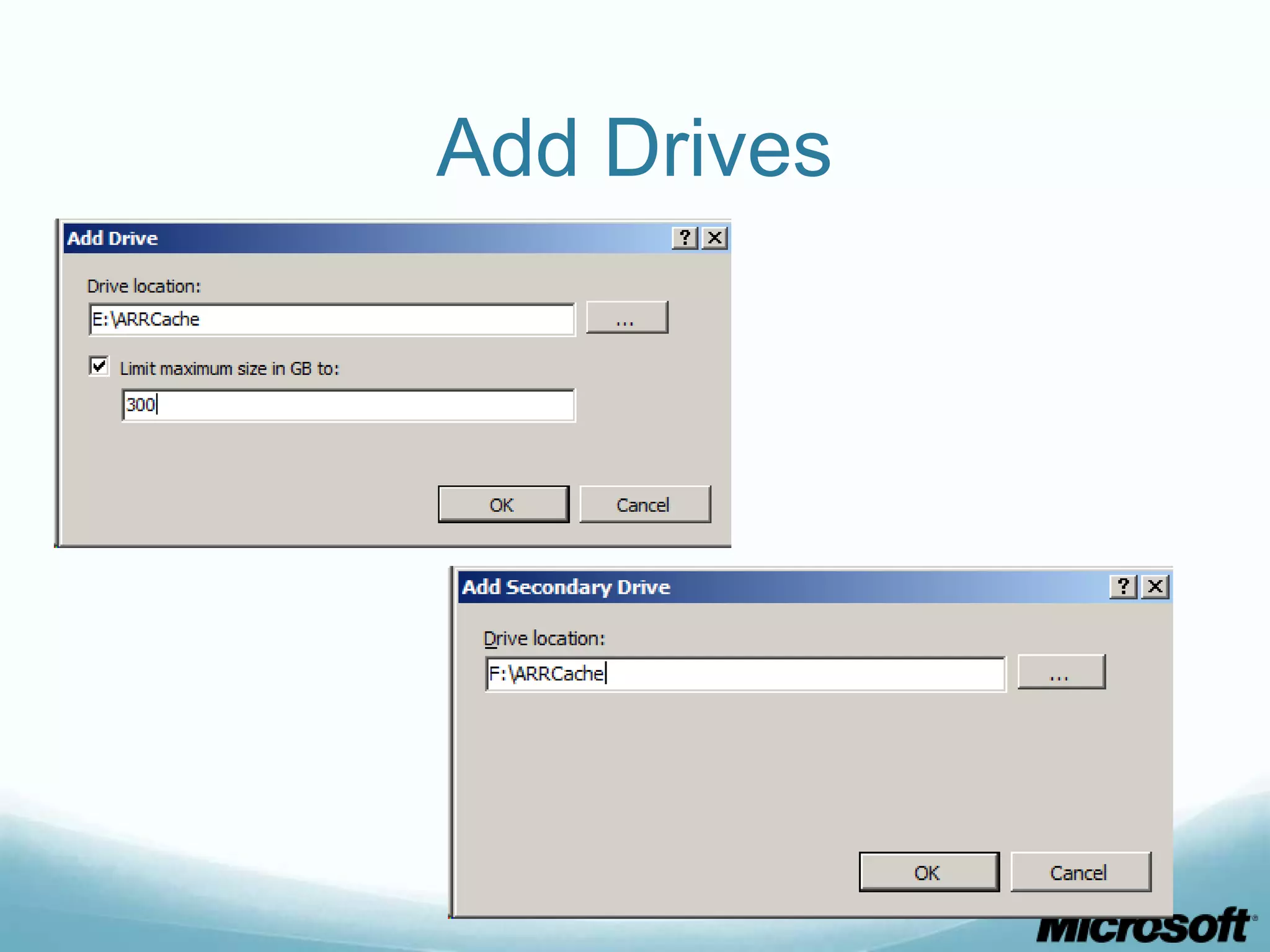
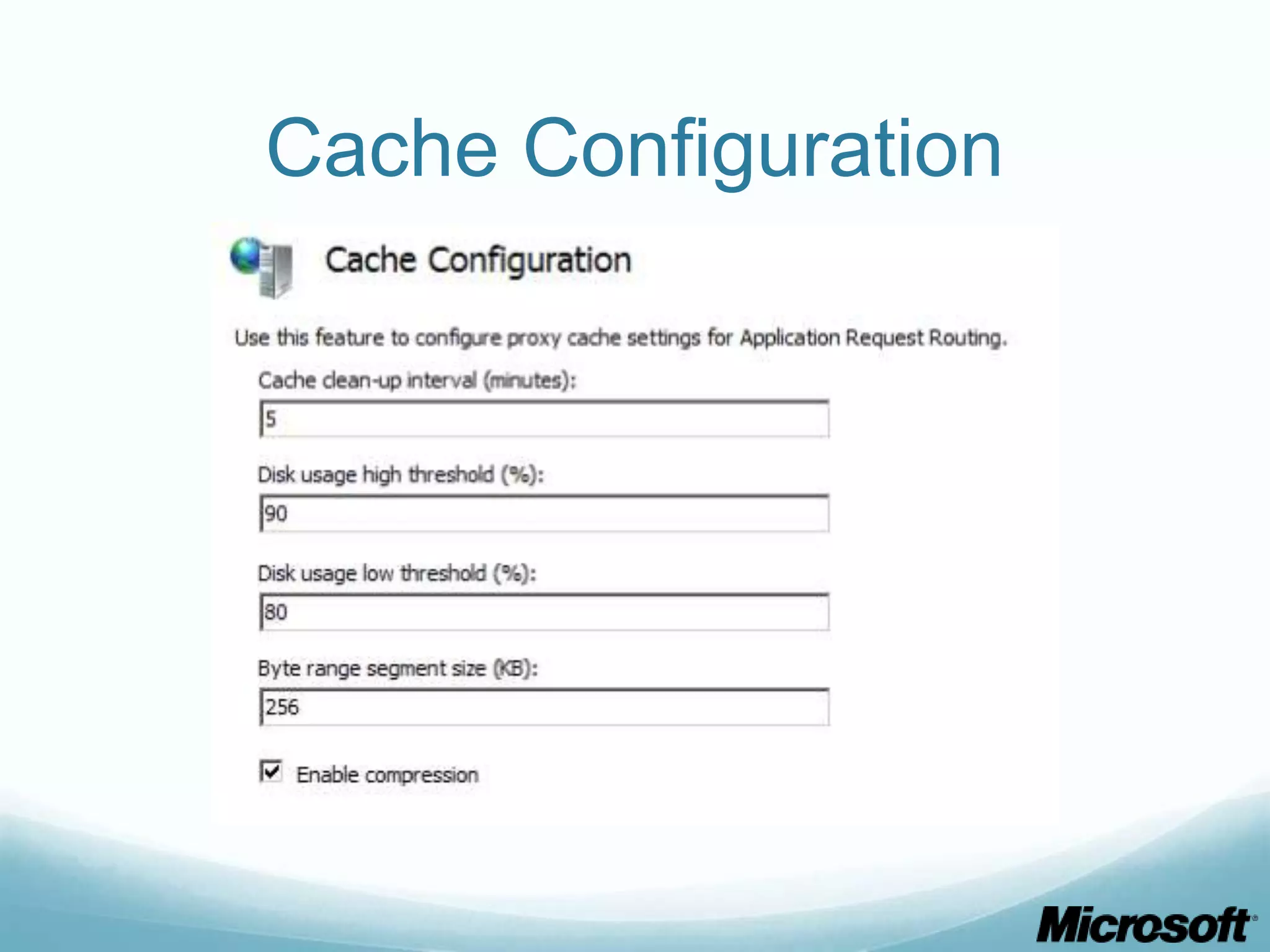
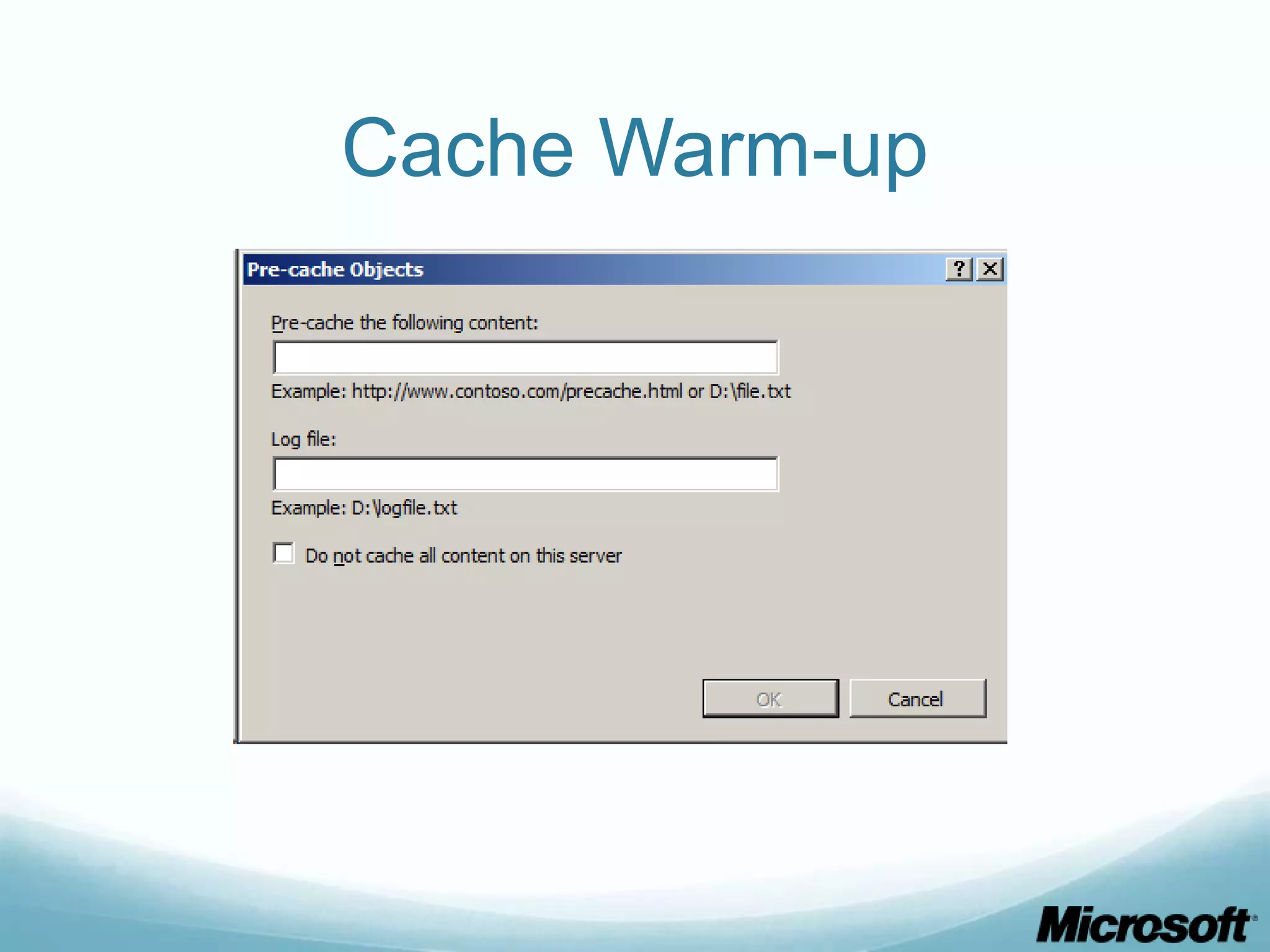
The document discusses building Drupal web farms using IIS, covering Application Request Routing (ARR) and Web Farm Framework (WFF) features, including load balancing, health monitoring, and application provisioning. It details the architecture for creating server farms, roles of primary and secondary hosts, and configurations needed for provisioning, caching, and health checks. Additionally, it addresses shared storage access for Drupal, providing step-by-step instructions for setup and troubleshooting, alongside considerations for user account management and database configuration.

![CLI To achieve the same result as seen before: appcmd.exe set config -section:webFarms /+"[name='myServerFarm']" /commit:apphost appcmd.exe set config -section:webFarms /+"[name='myServerFarm'].[address=’DrupalWeb1']" /commit:apphost URL Rewrite rules: appcmd.exe set config -section:system.webServer/rewrite/globalRules /+"[name='ARR_myServerFarm_loadbalance', patternSyntax='Wildcard',stopProces sing='True']" /commit:apphost appcmd.exe set config -section:system.webServer/rewrite/globalRules /[name='ARR_myServerFarm_loadbalance',patternSyntax='Wildcard',stopProcessin g='True'].match.url:"*" /commit:apphost appcmd.exe set config -section:system.webServer/rewrite/globalRules /[name='ARR_myServerFarm_loadbalance',patternSyntax='Wildcard',stopProcessin g='True'].action.type:"Rewrite" /[name='ARR_myServerFarm_loadbalance',patternSyntax='Wildcard',stopProcessin g='True'].action.url:"http://myServerFarm/{R:0}" /commit:apphost](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingdrupalwebfarmswithiis-part1-120717105223-phpapp01/75/Building-drupal-web-farms-with-IIS-part-1-10-2048.jpg)

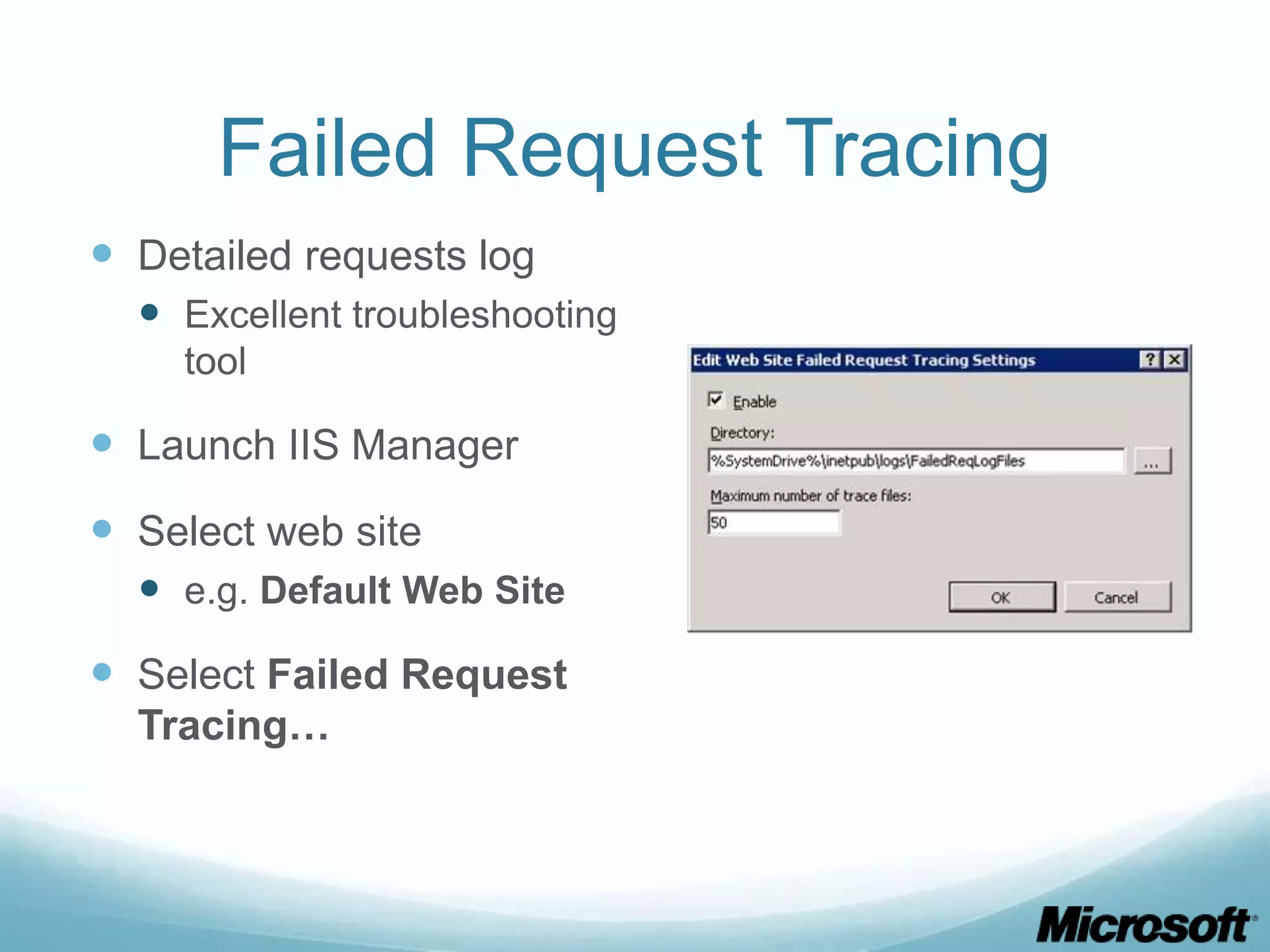
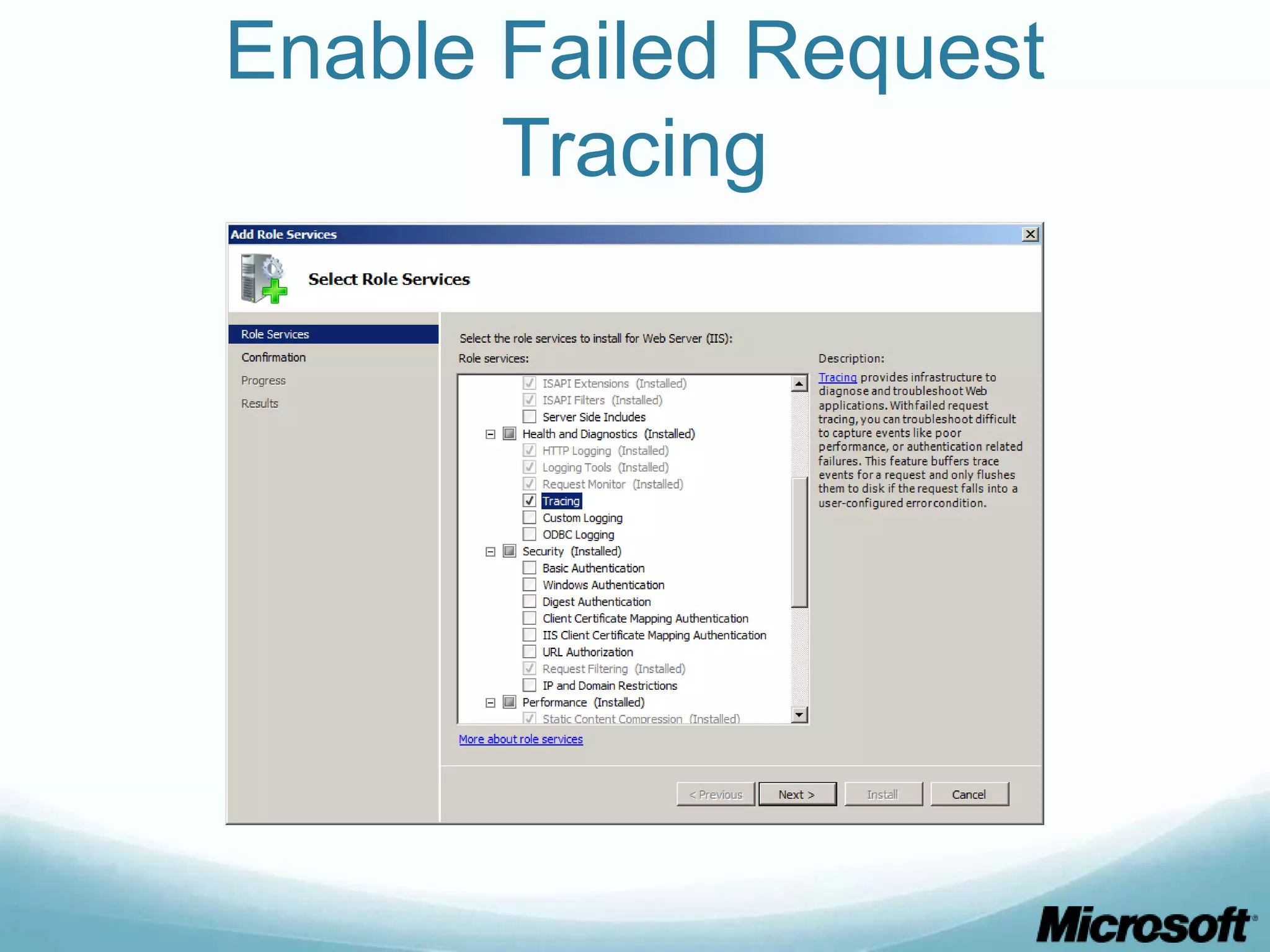
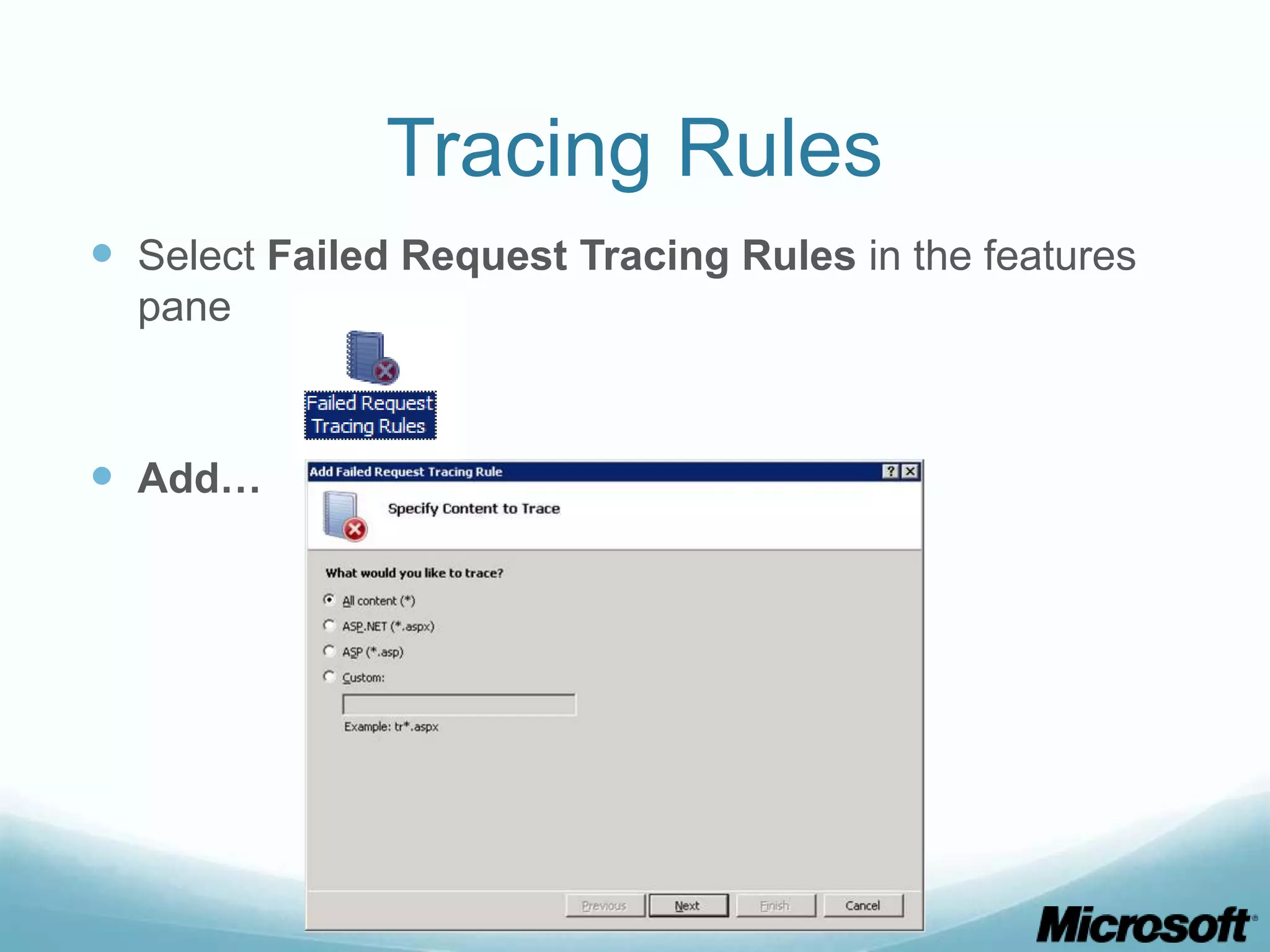
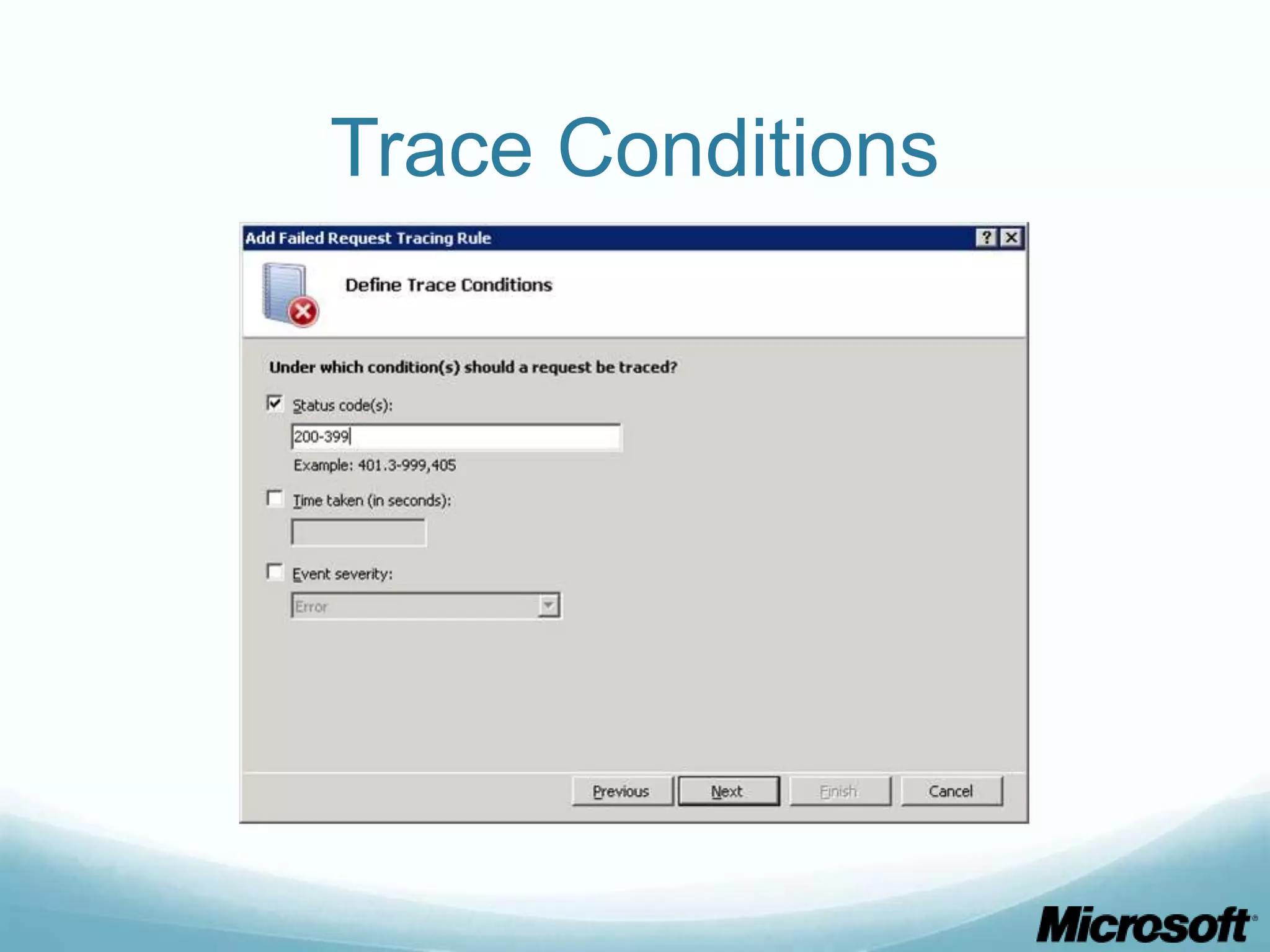
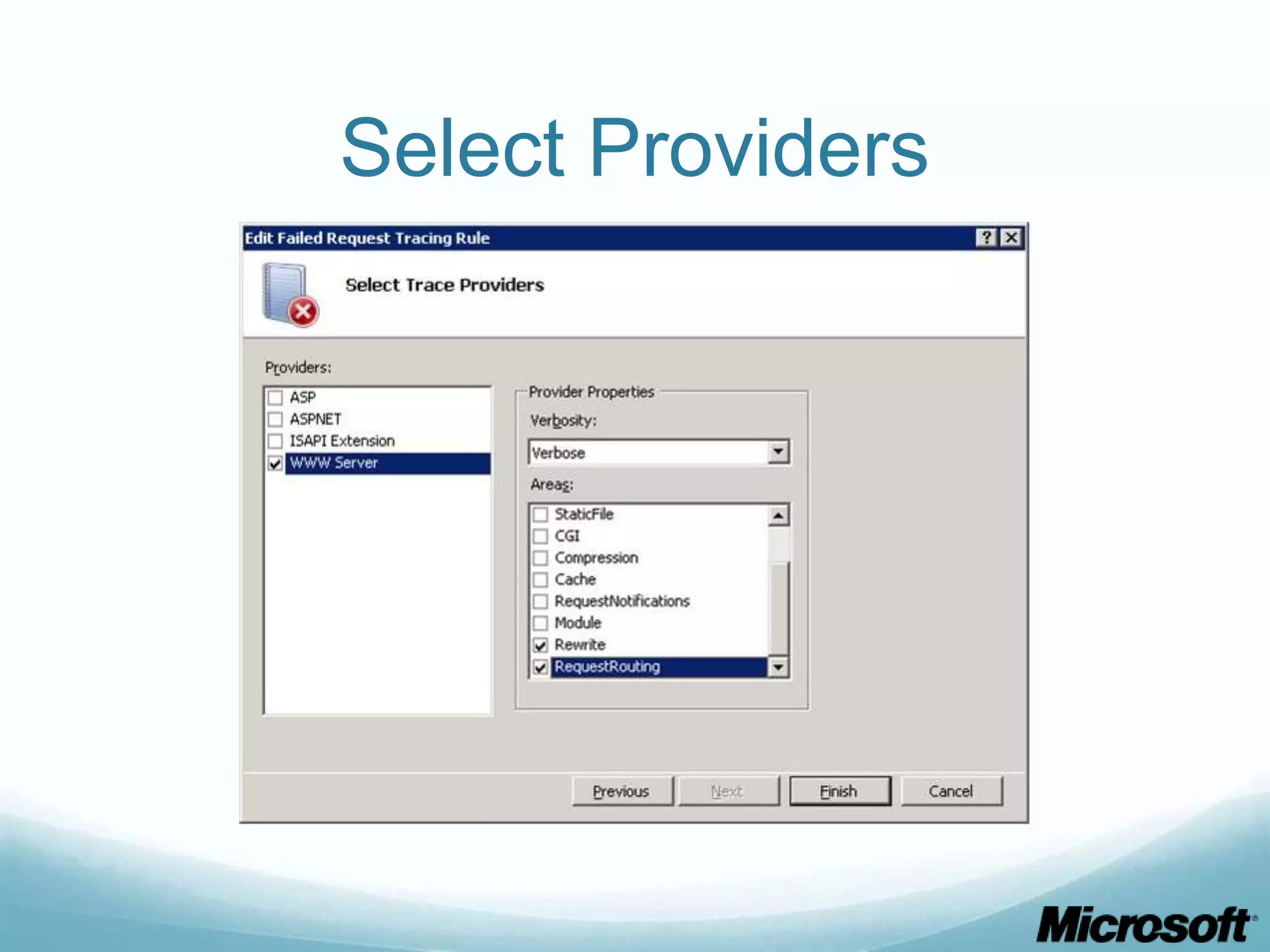
![CLI To obtain what we did via GUI: appcmd set site "Default Web Site" - traceFailedRequestsLogging.enabled:"true" /commit:apphost appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site" - section:system.webServer/tracing/traceFailedRequests /+"[path='*']” appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site" - section:system.webServer/tracing/traceFailedRequests /+"[path='*'].traceAreas.[provider='WWW Server',areas='Rewrite,RequestRouting',verbosity='Verbose']” appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site" - section:system.webServer/tracing/traceFailedRequests /[path='*'].failureDefinitions.statusCodes:"200-399"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingdrupalwebfarmswithiis-part1-120717105223-phpapp01/75/Building-drupal-web-farms-with-IIS-part-1-30-2048.jpg)