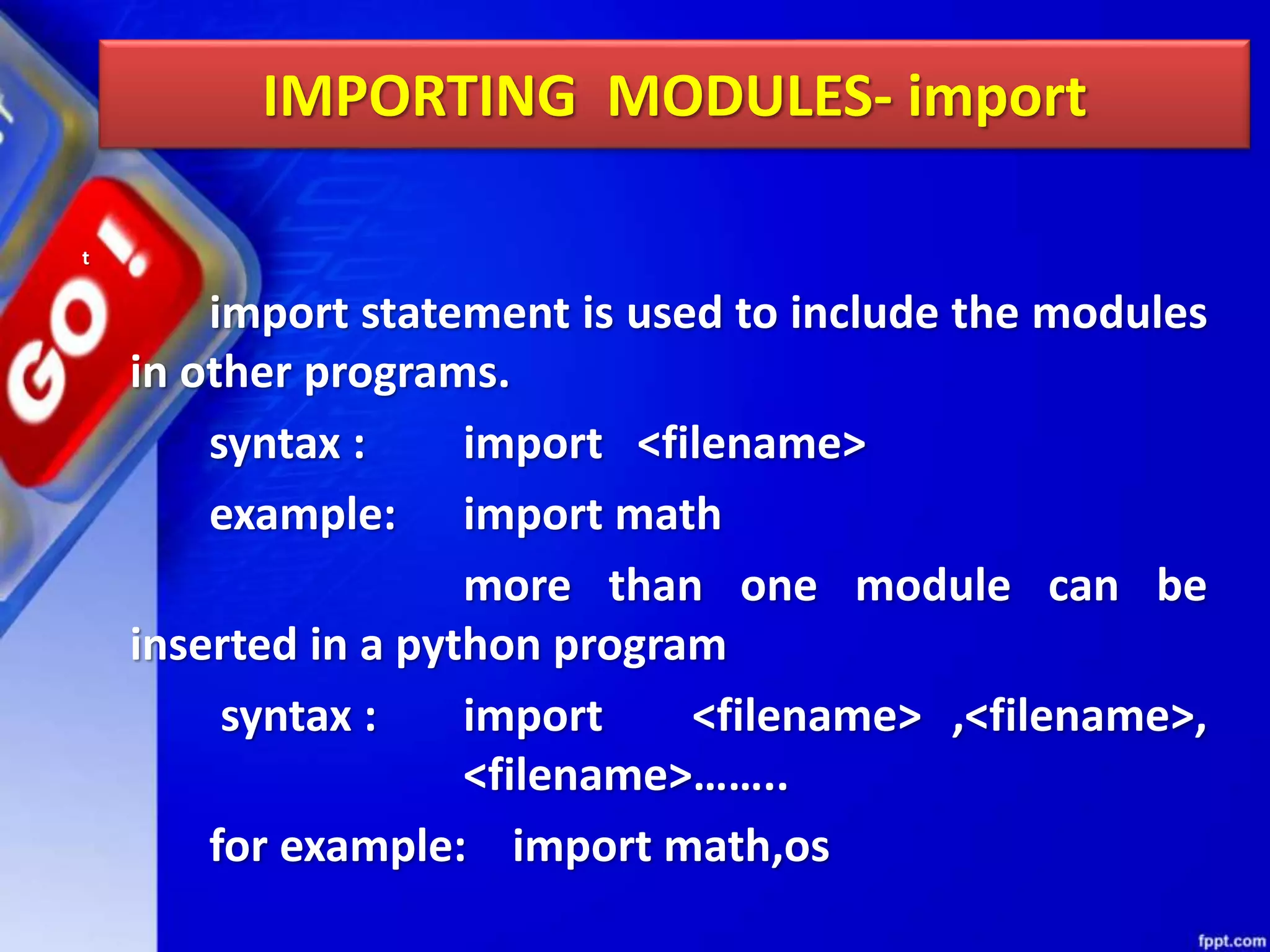
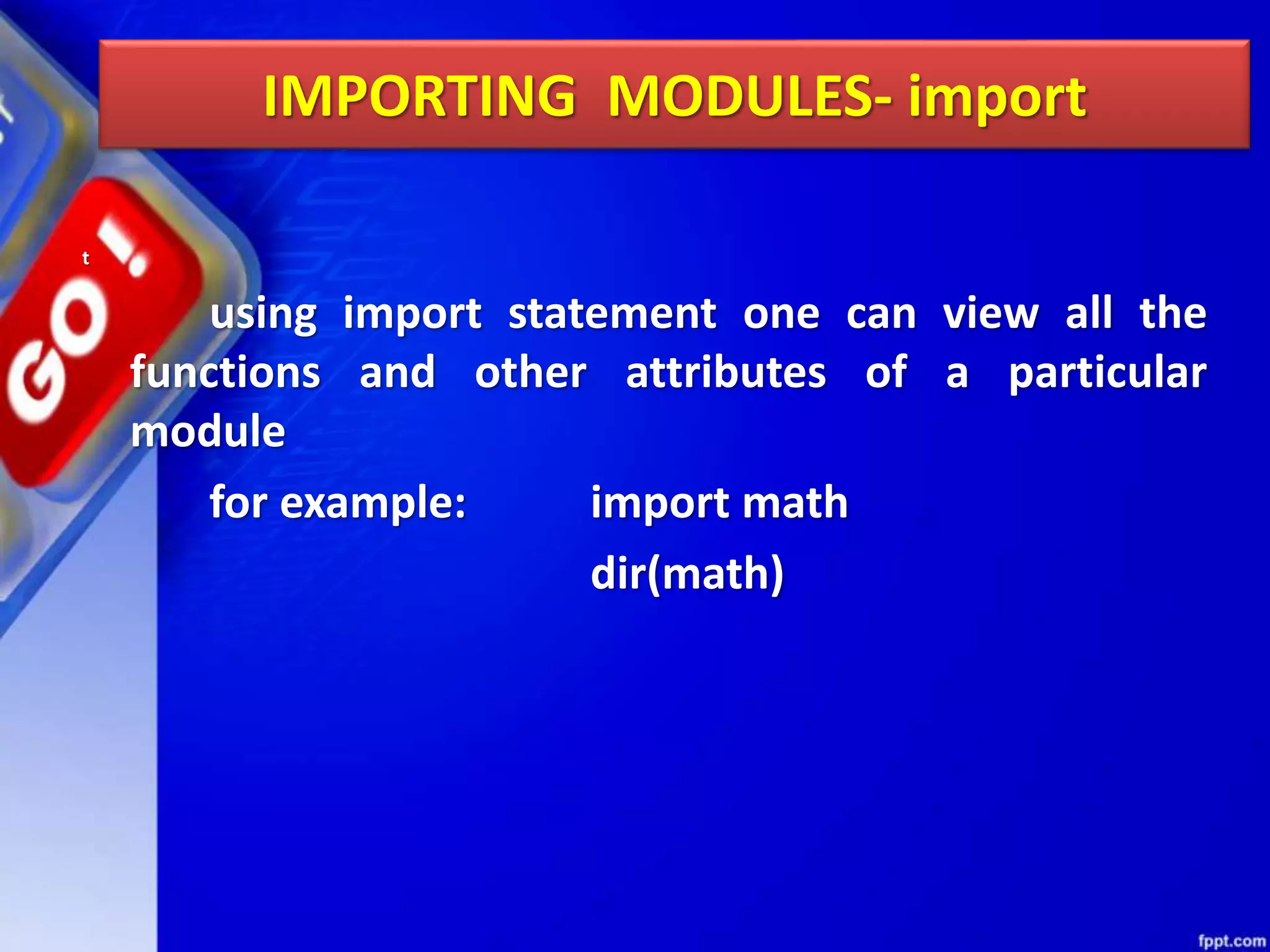
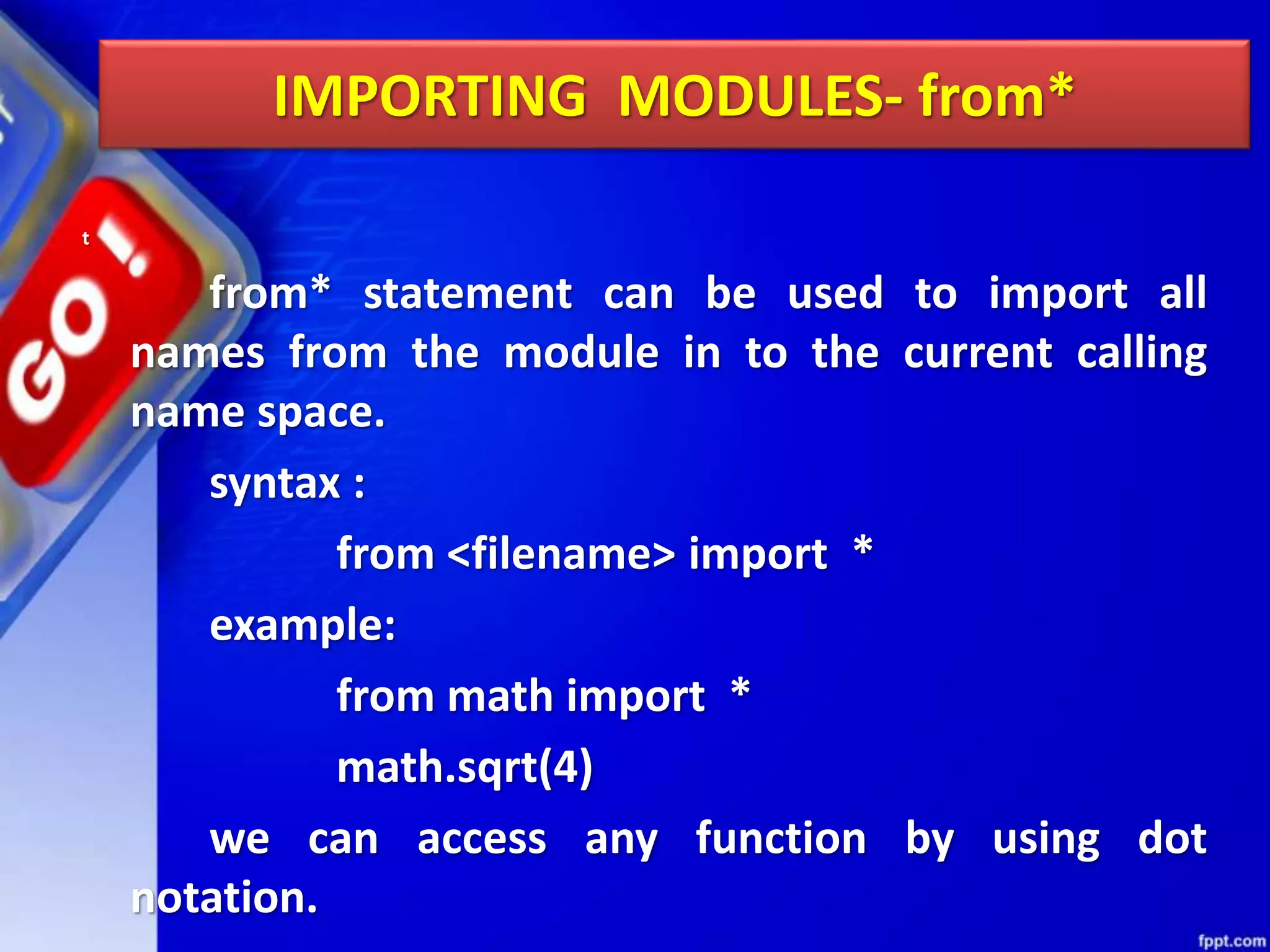
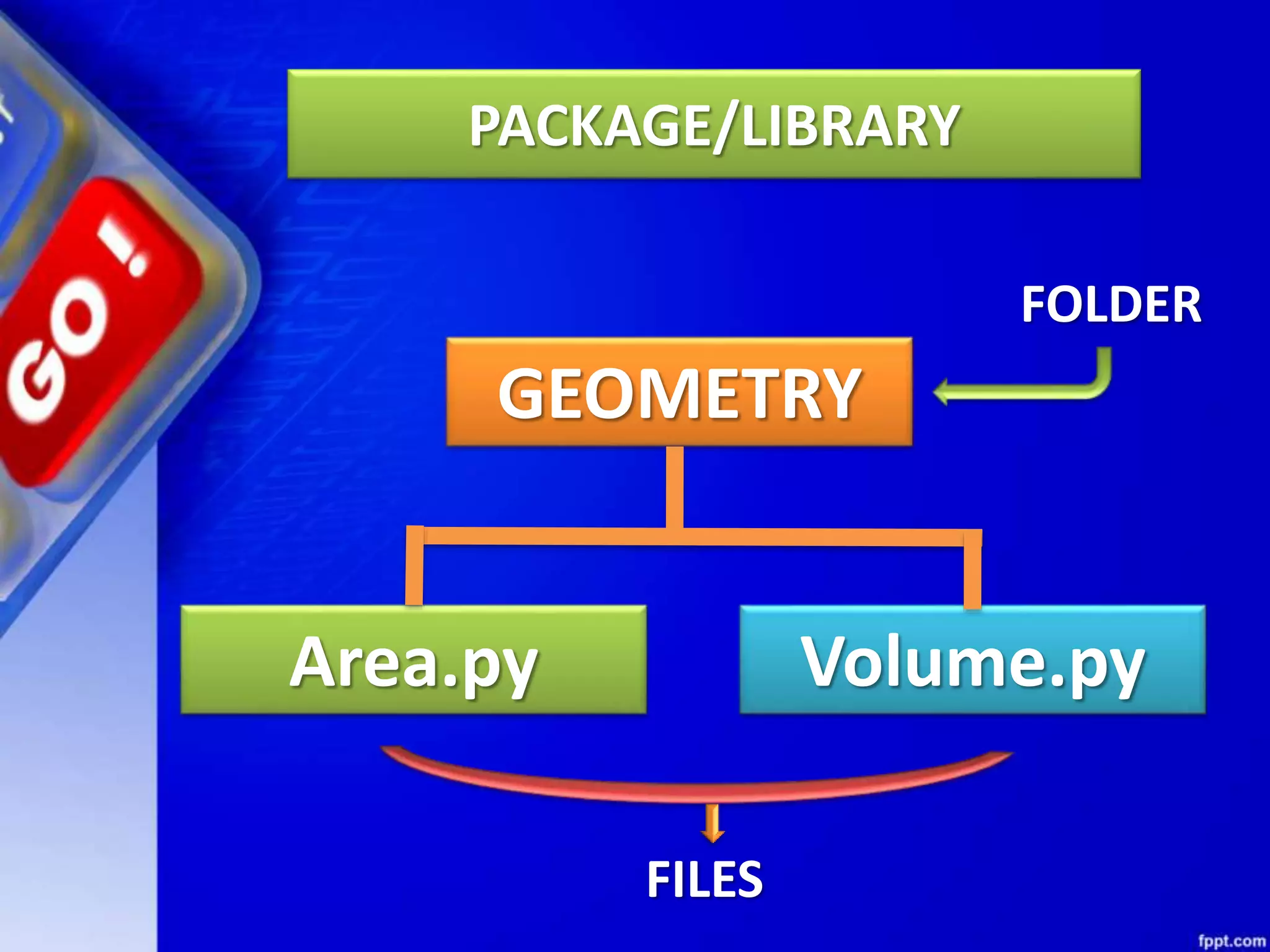
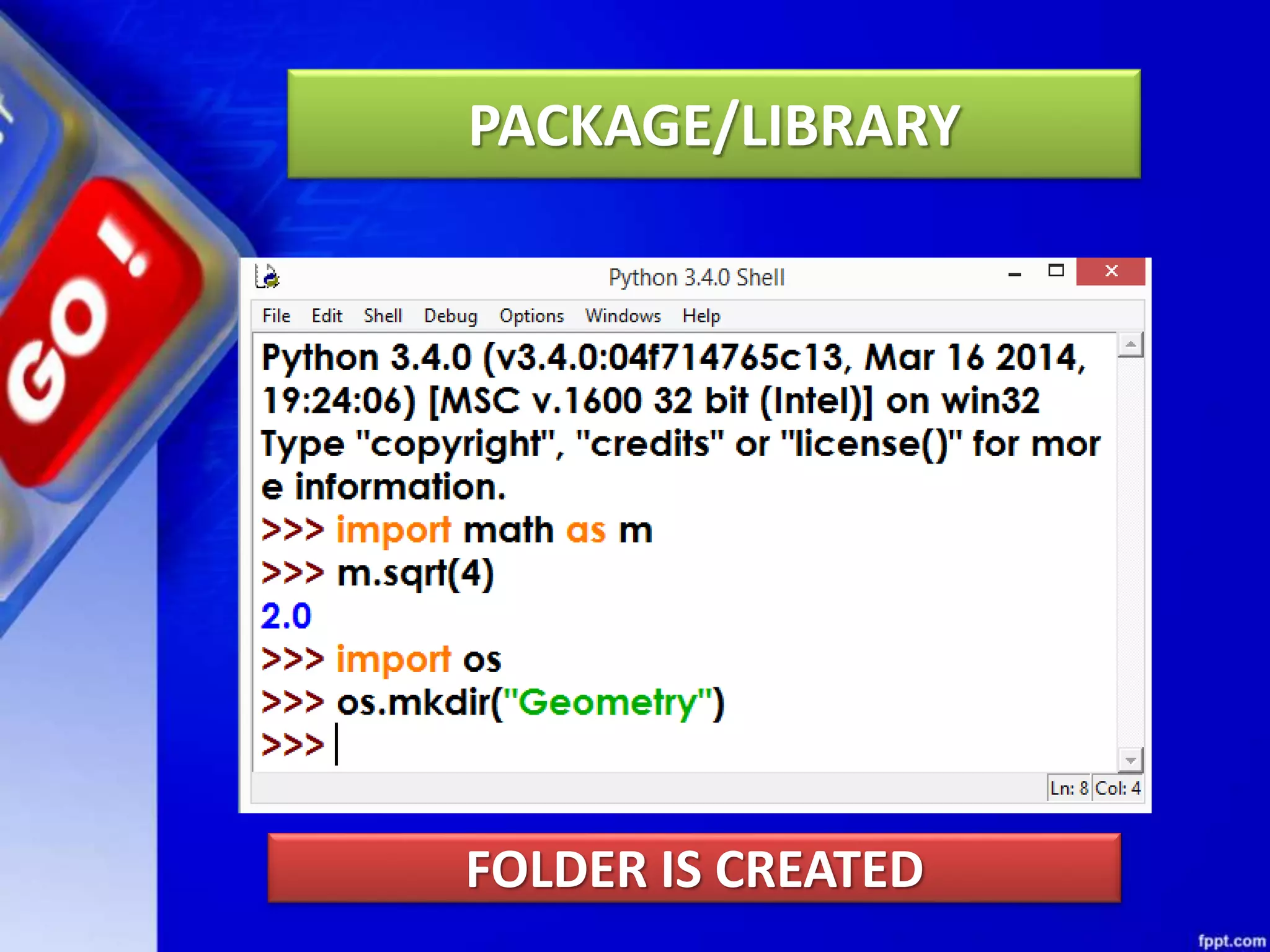
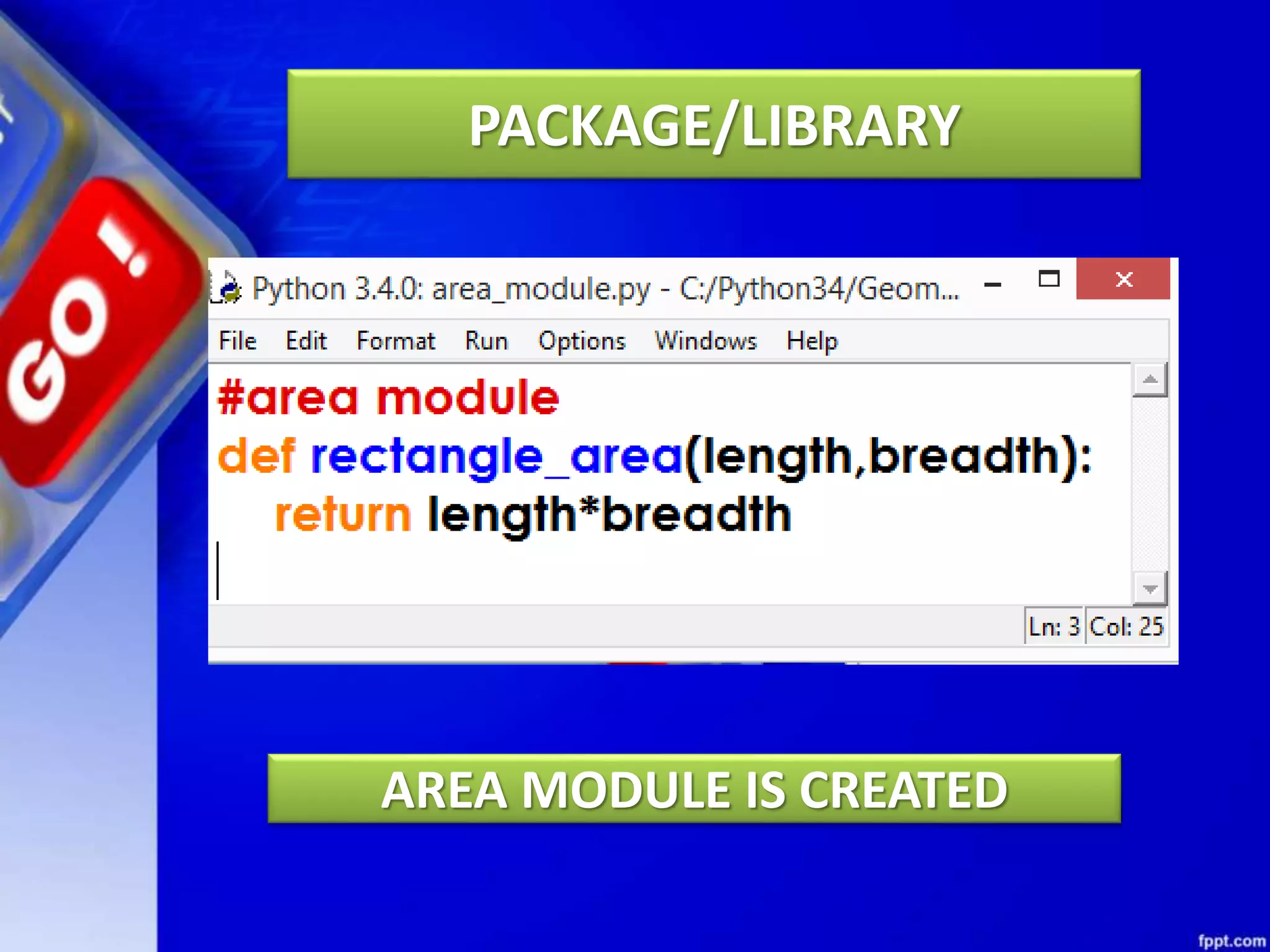
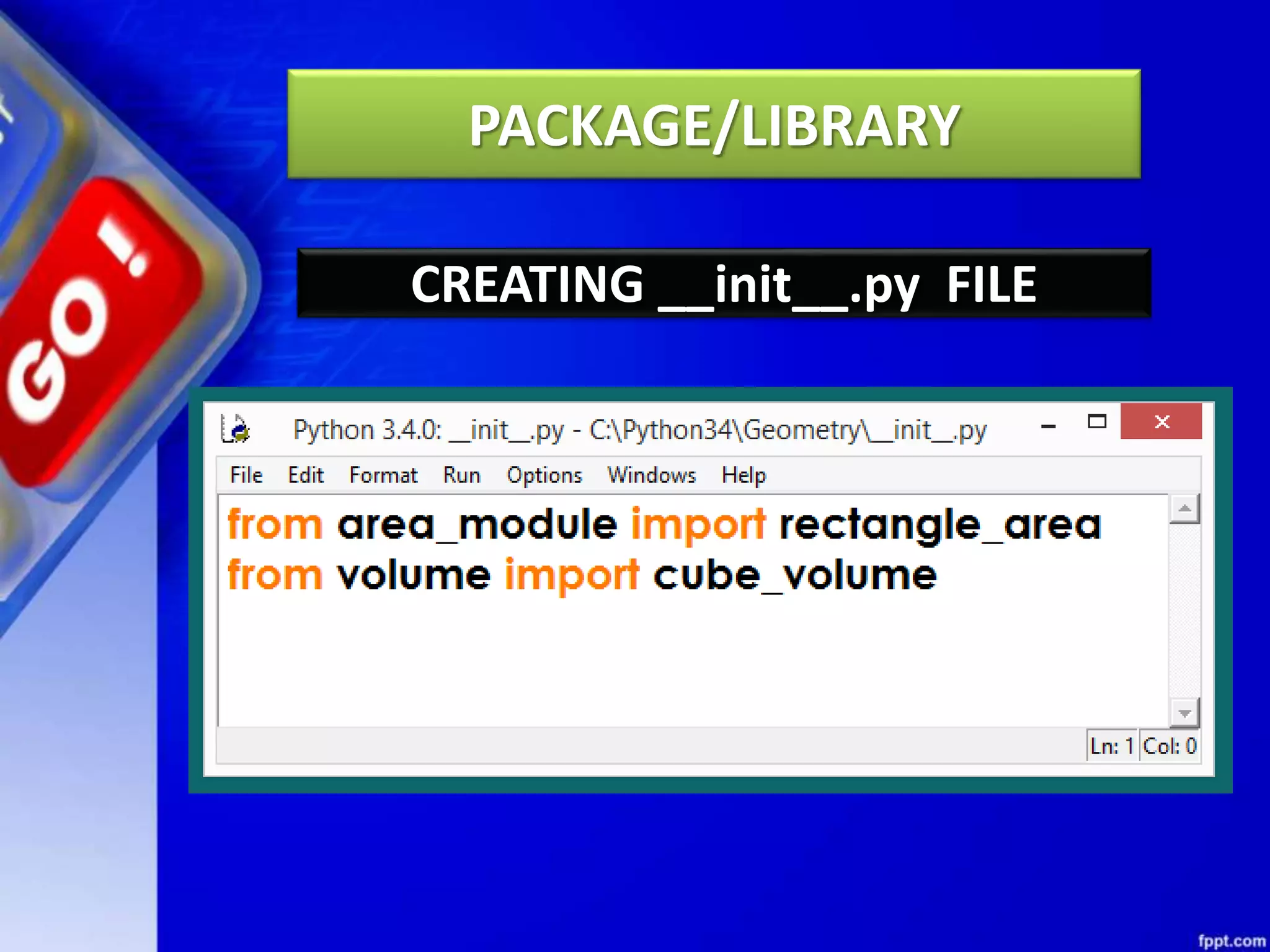
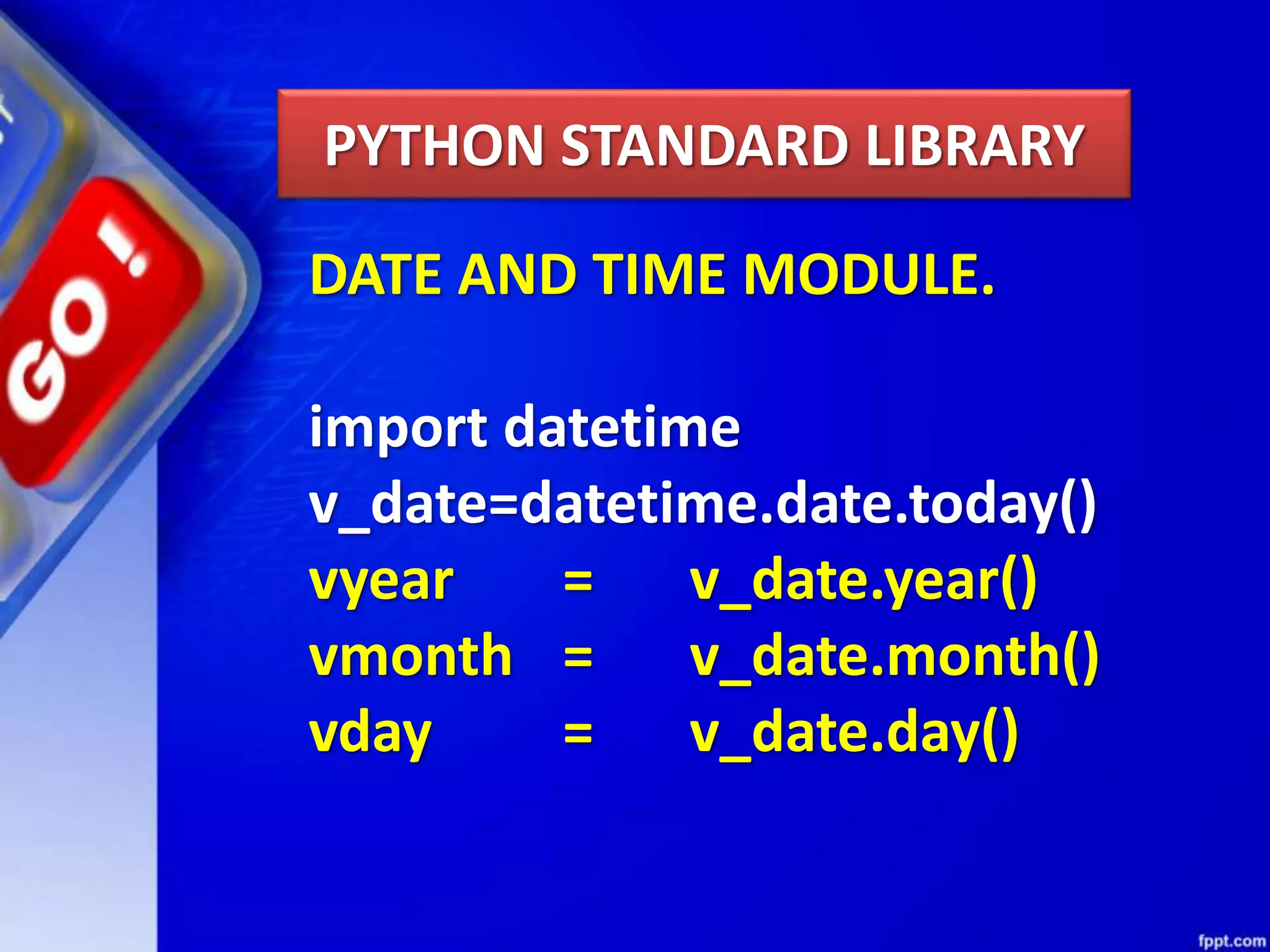
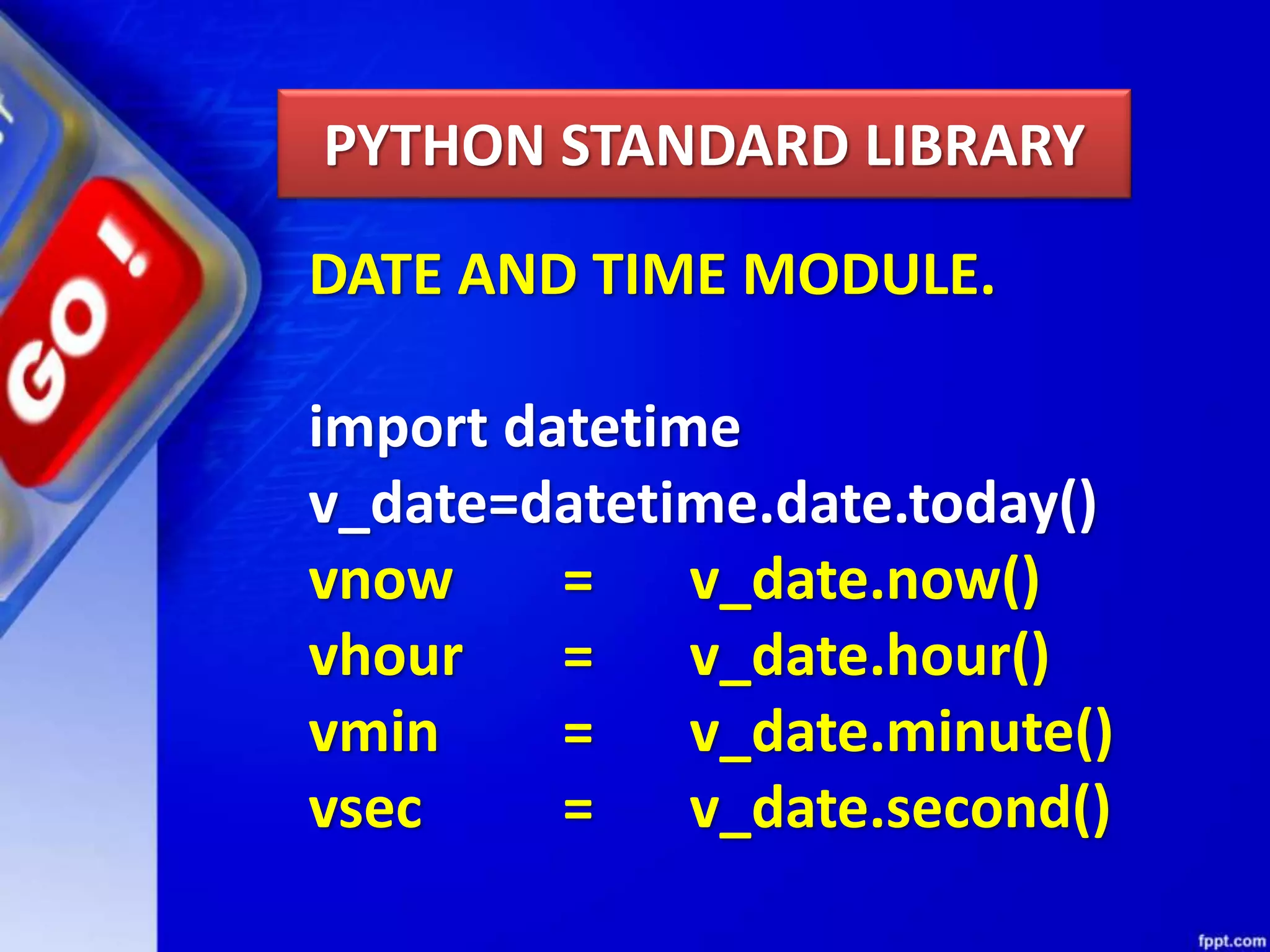
Python modules allow for code reusability and organization. There are three main components of a Python program: libraries/packages, modules, and functions/sub-modules. Modules can be imported using import, from, or from * statements. Namespaces and name resolution determine how names are looked up and associated with objects. Packages are collections of related modules and use an __init__.py file to be recognized as packages by Python.