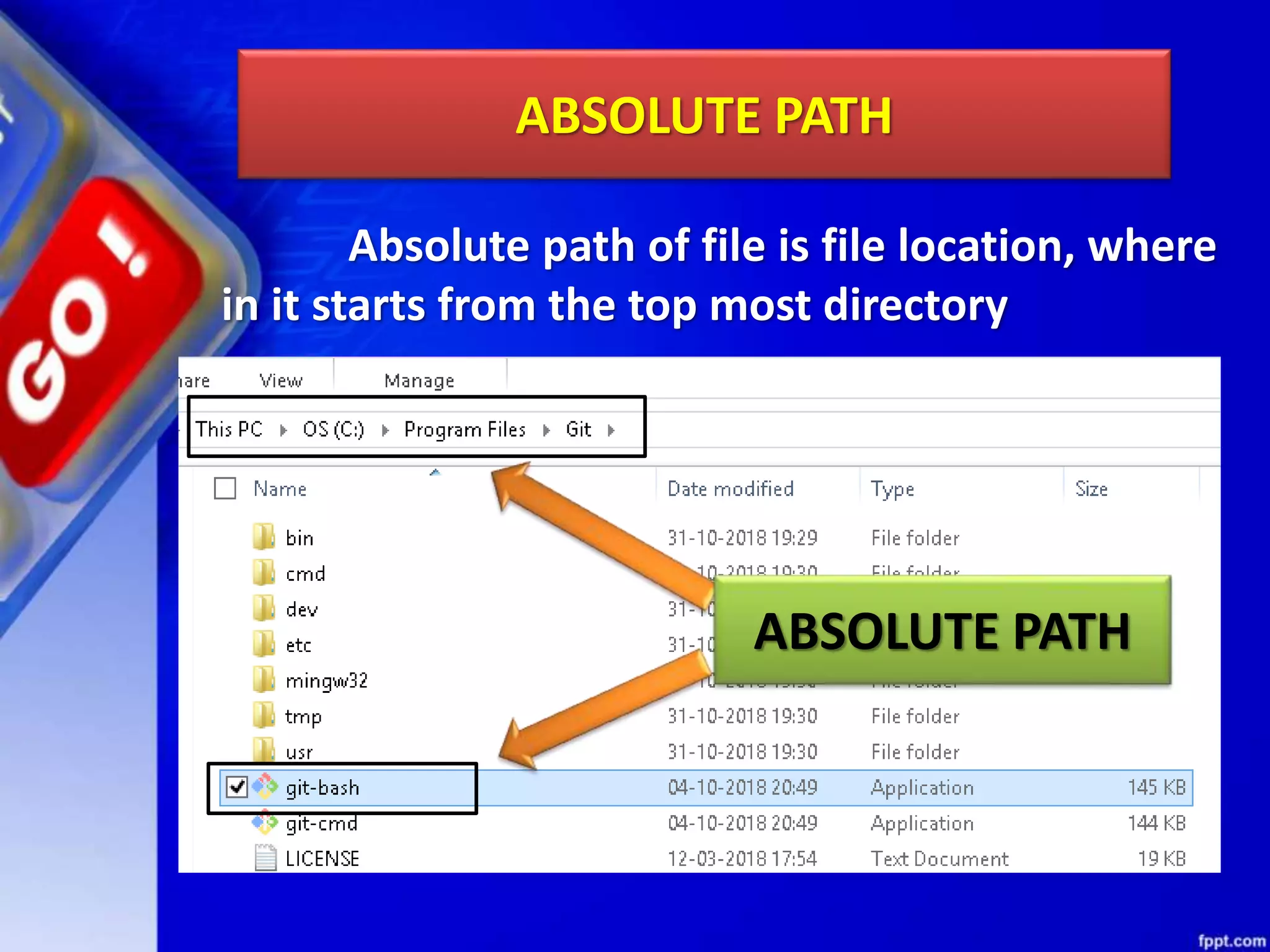
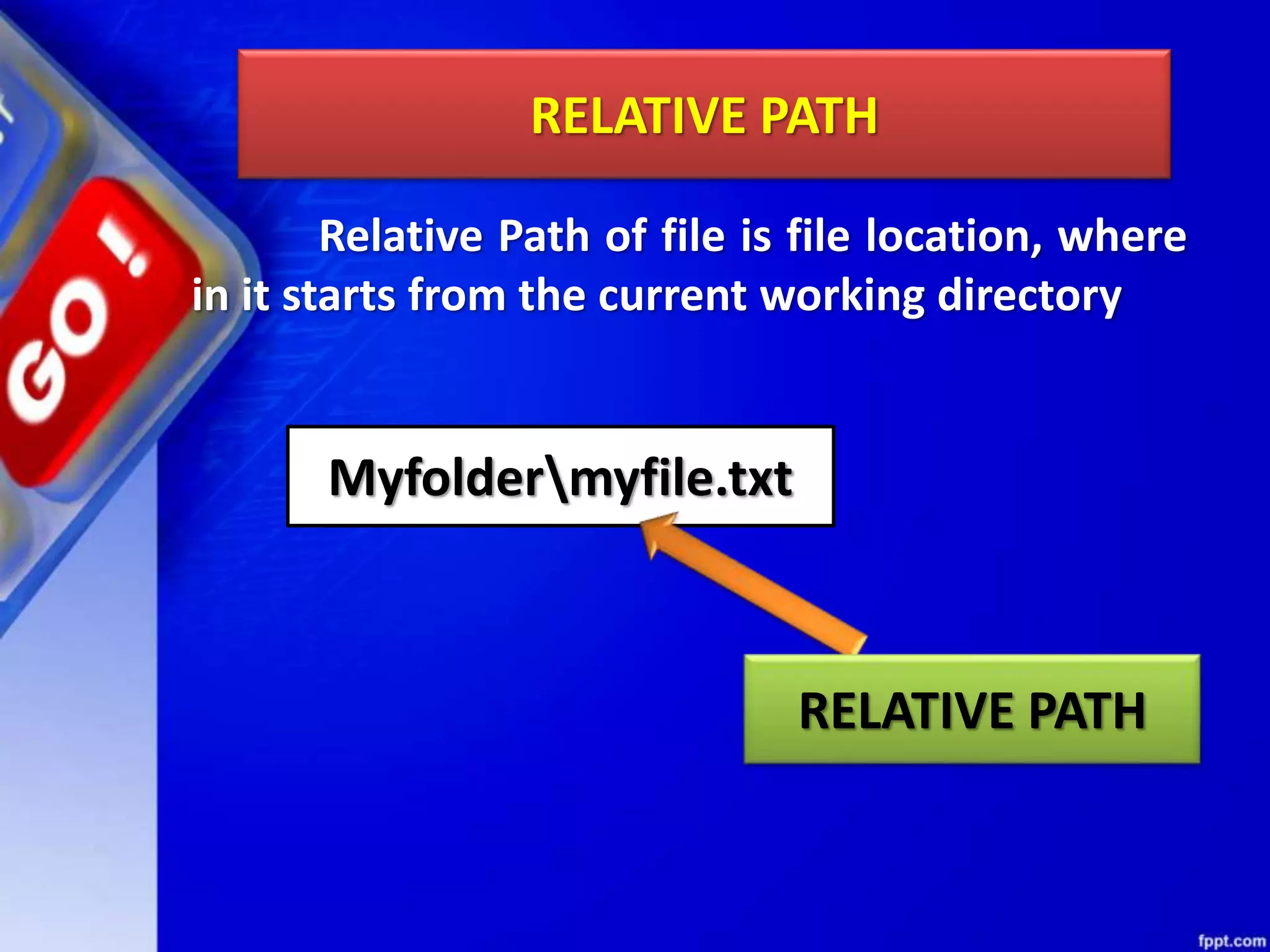
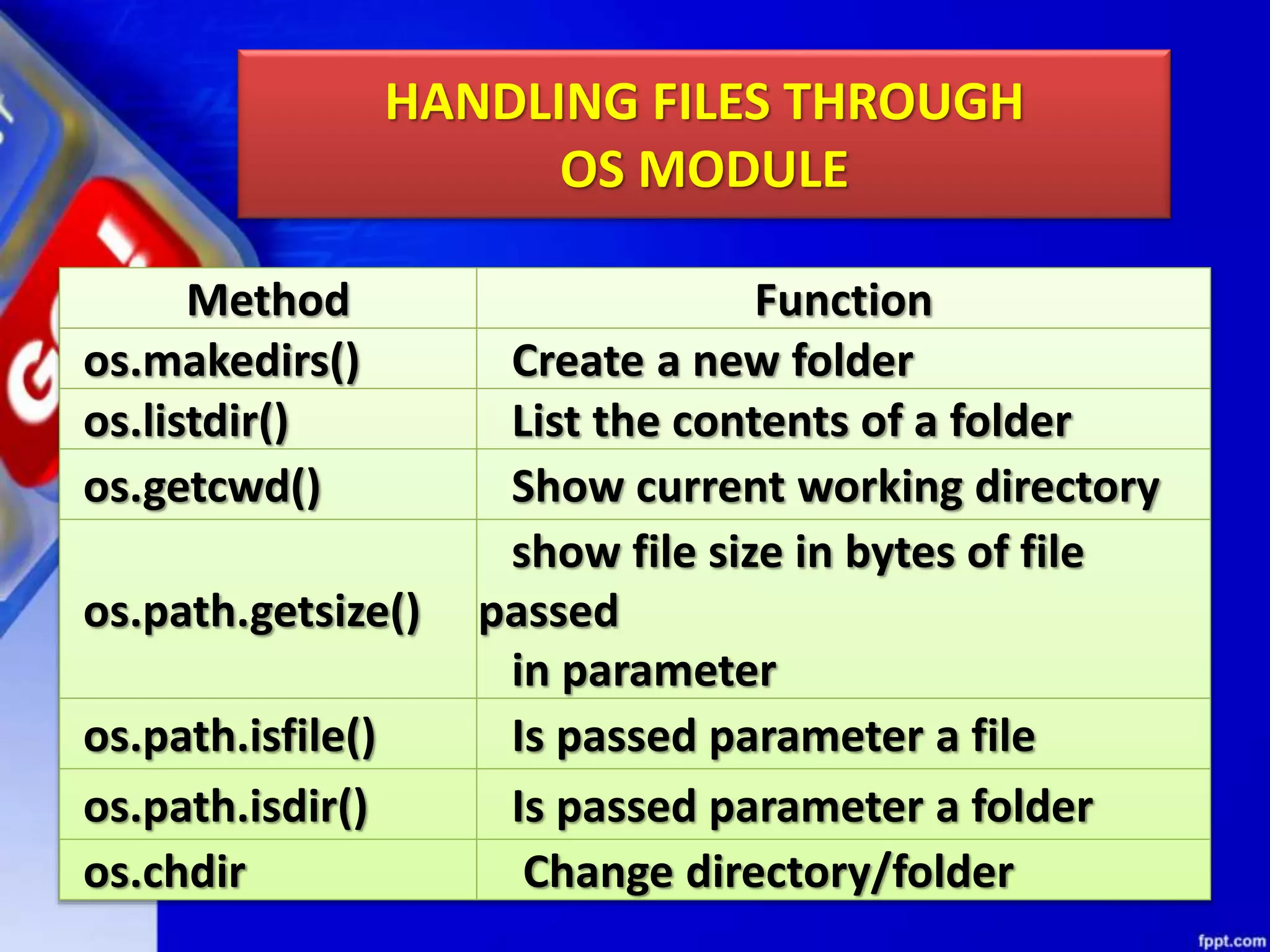
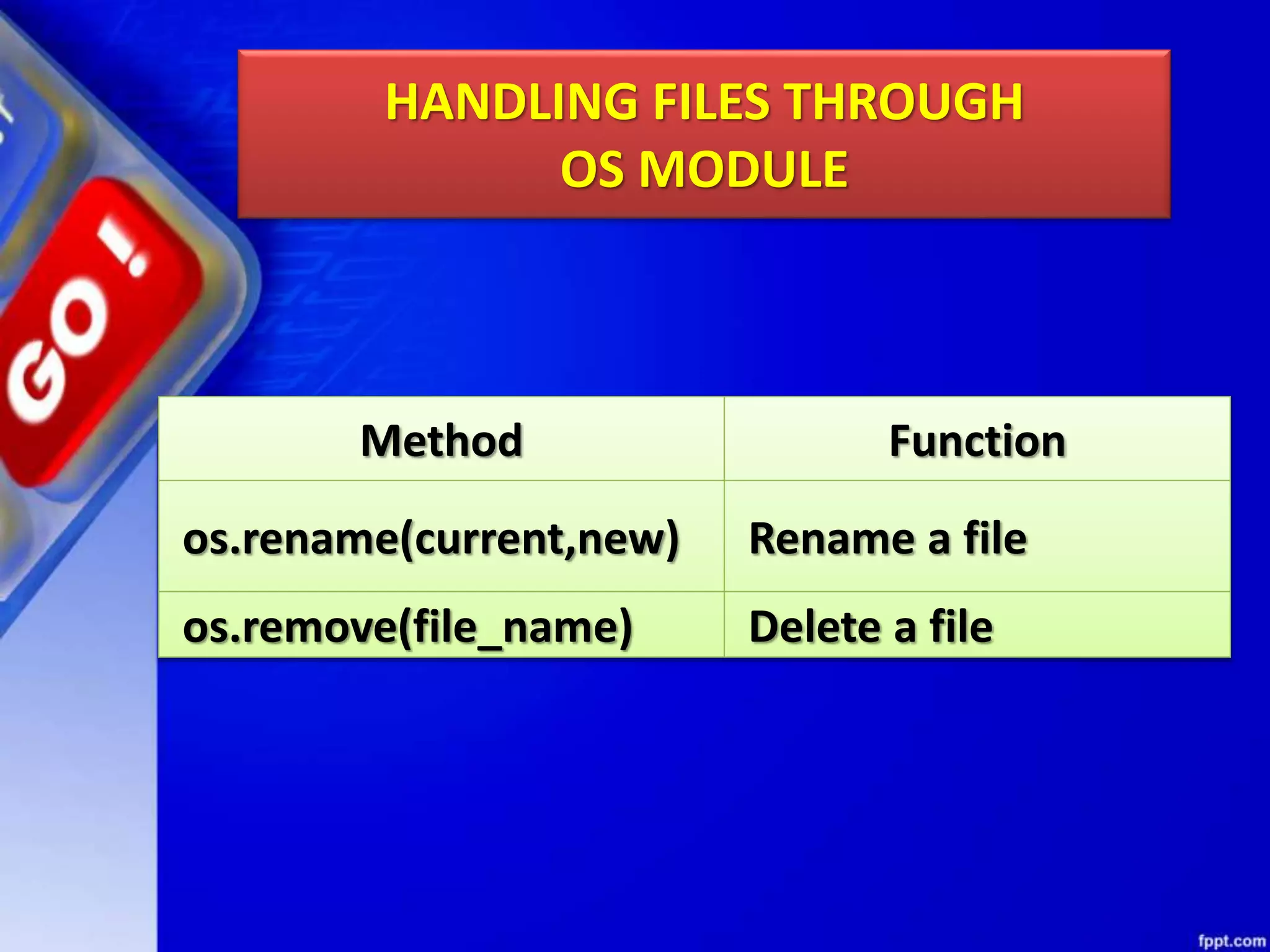
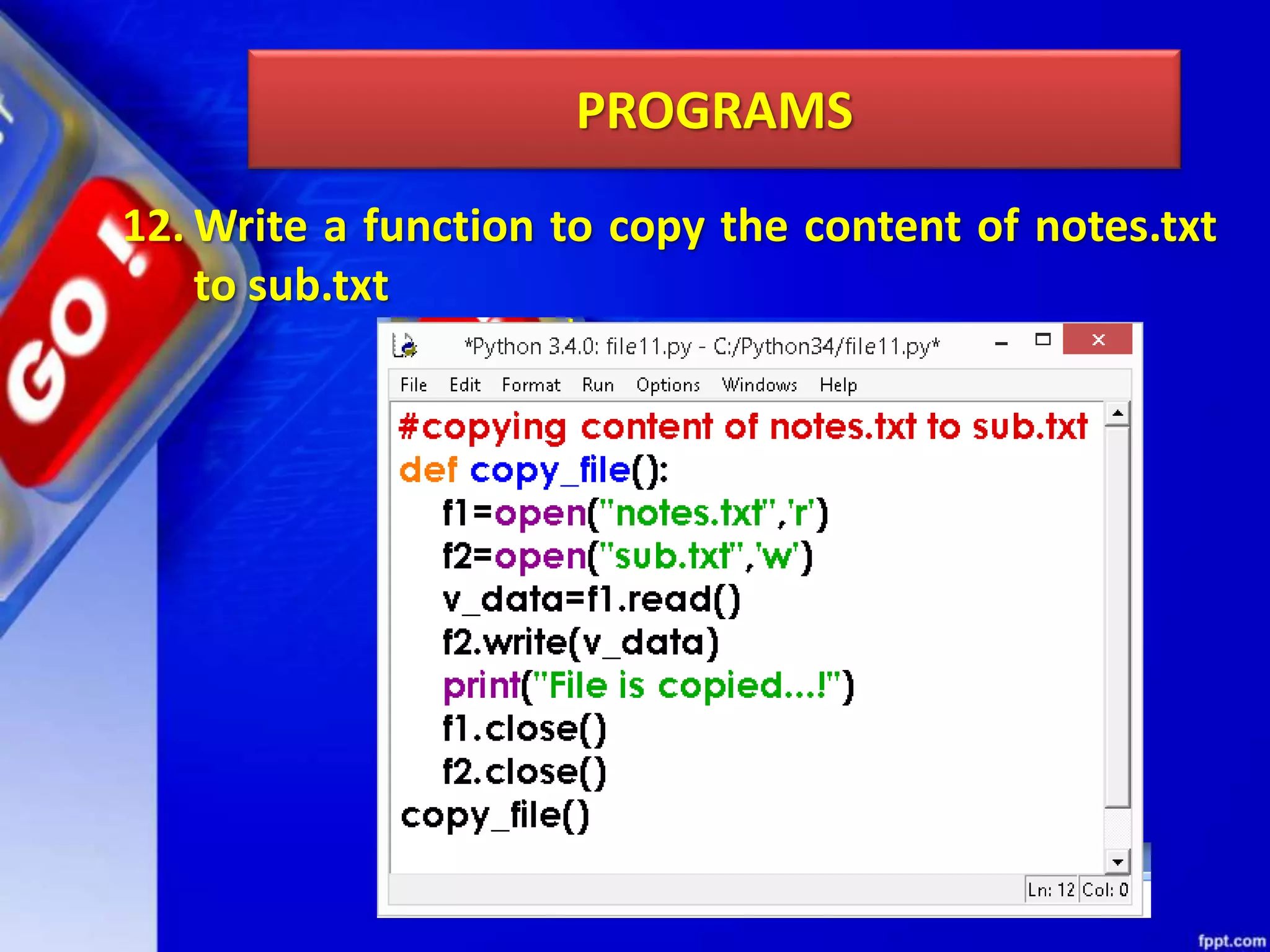
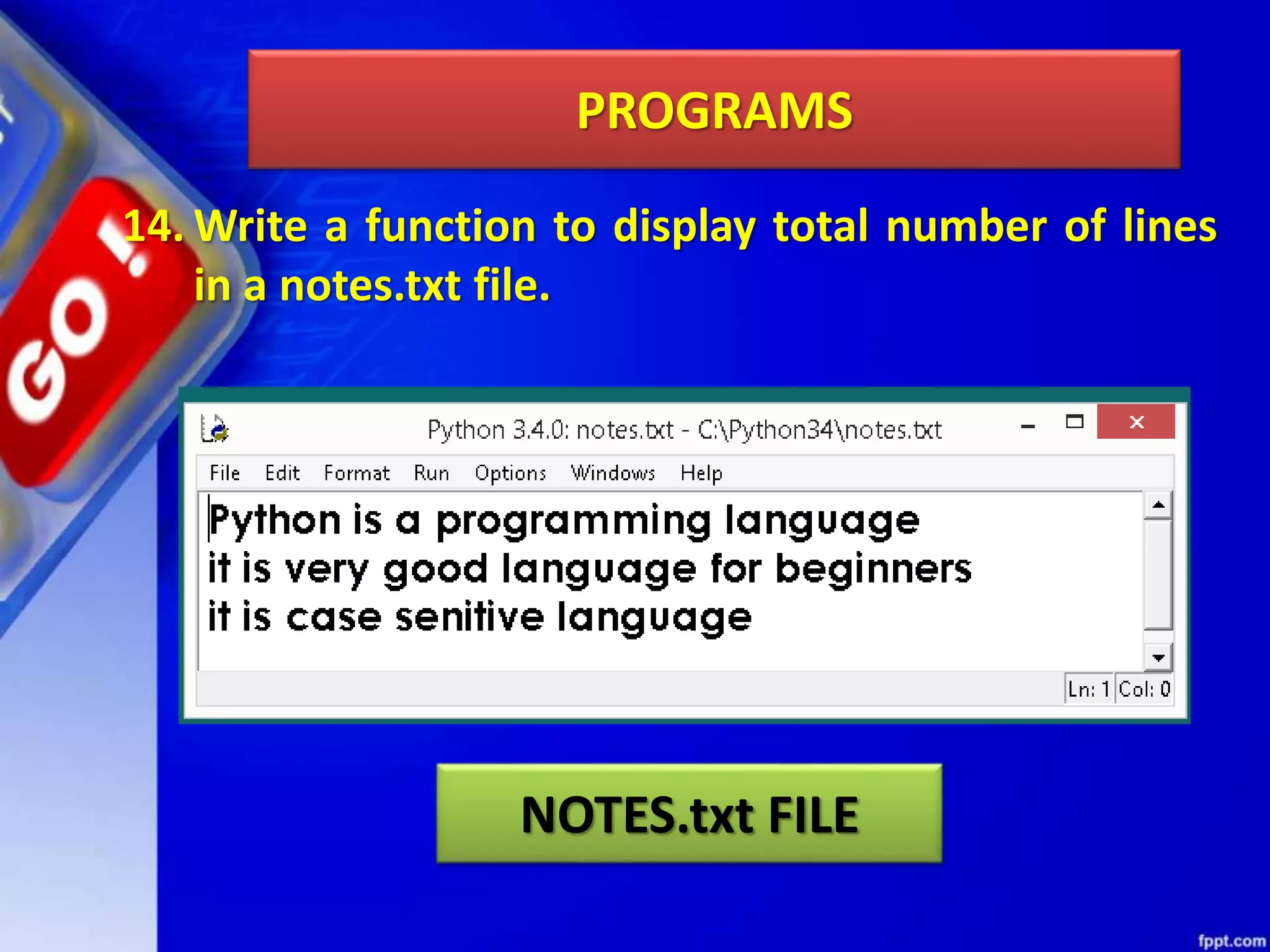
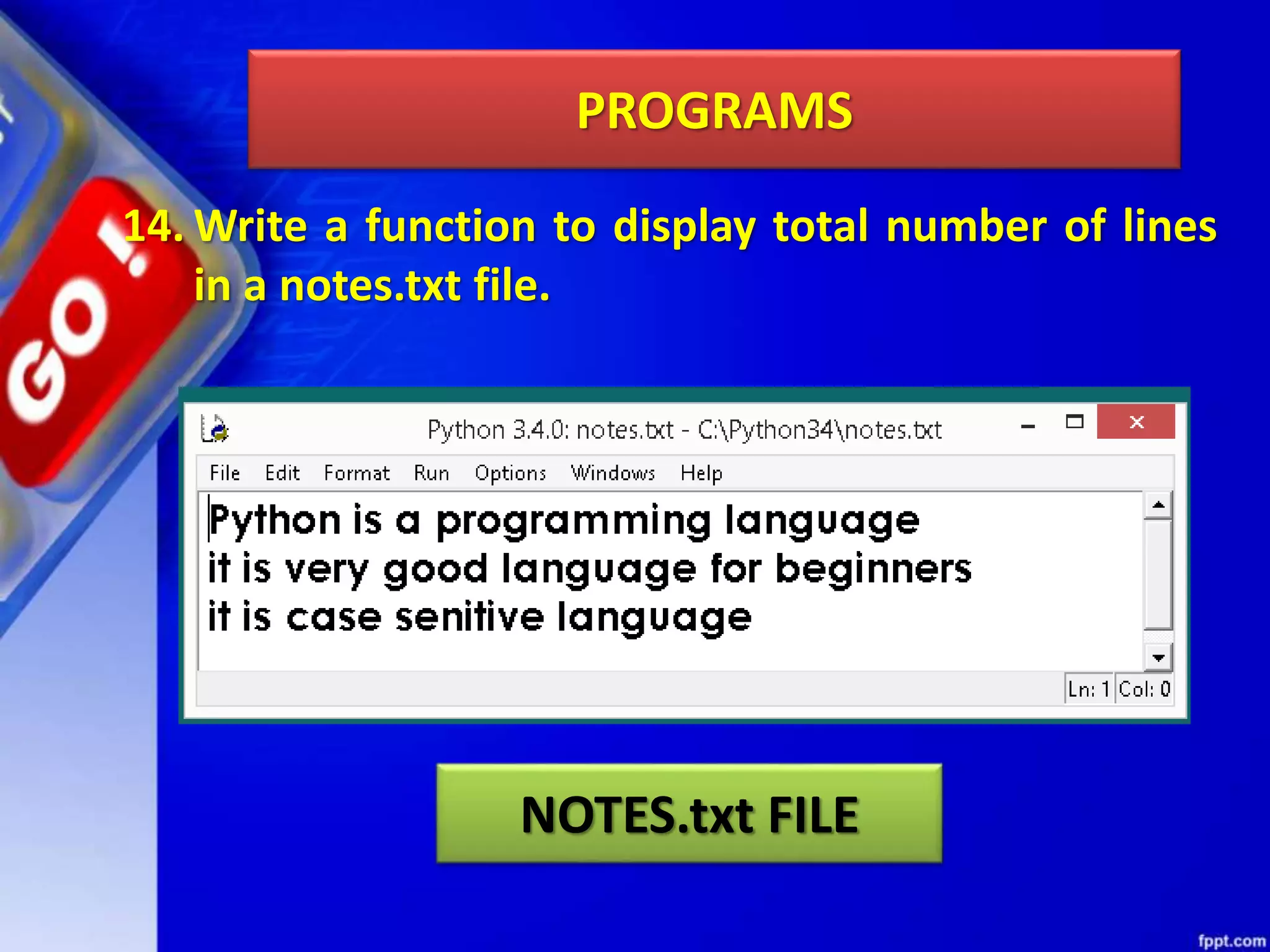
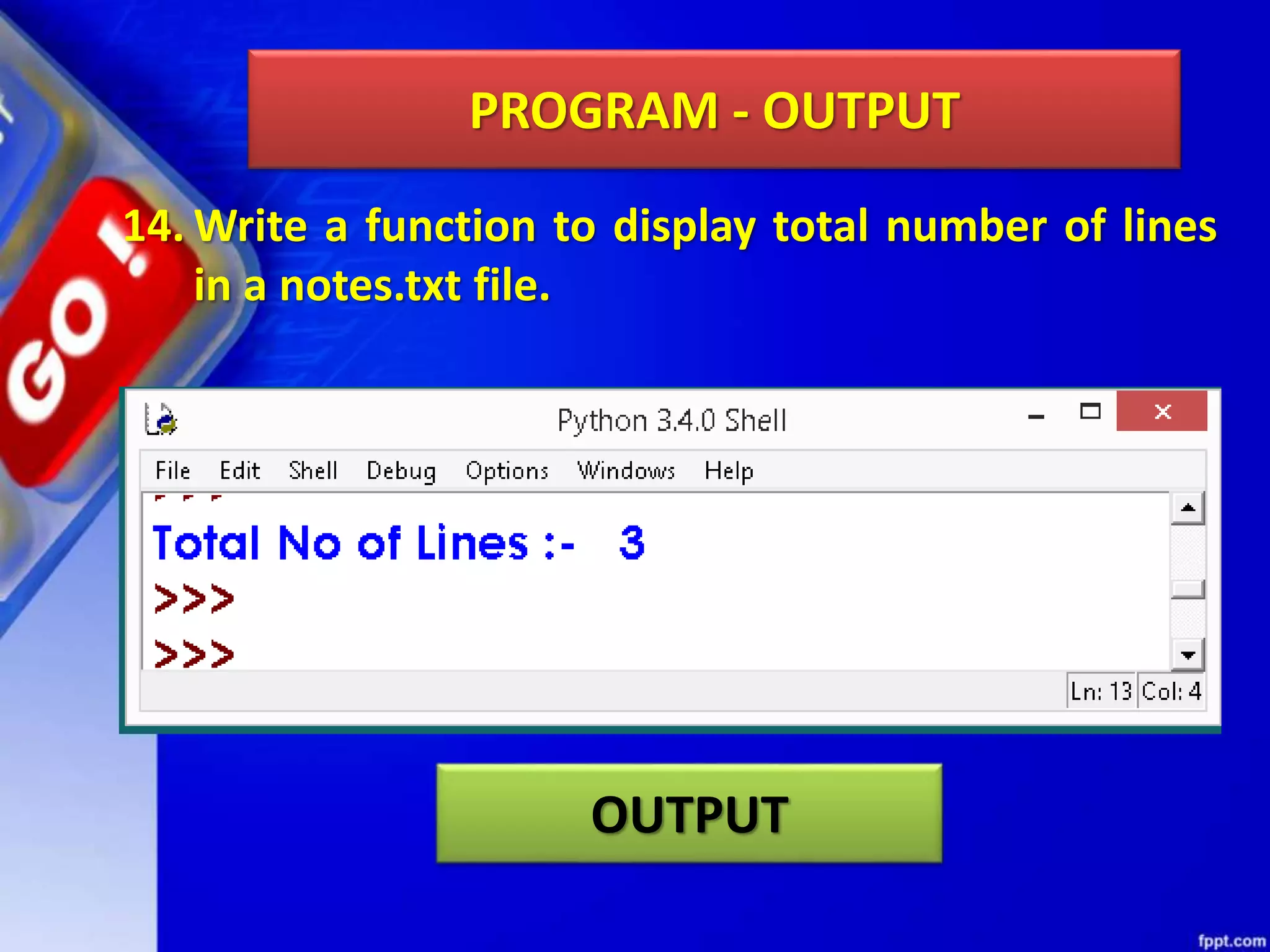
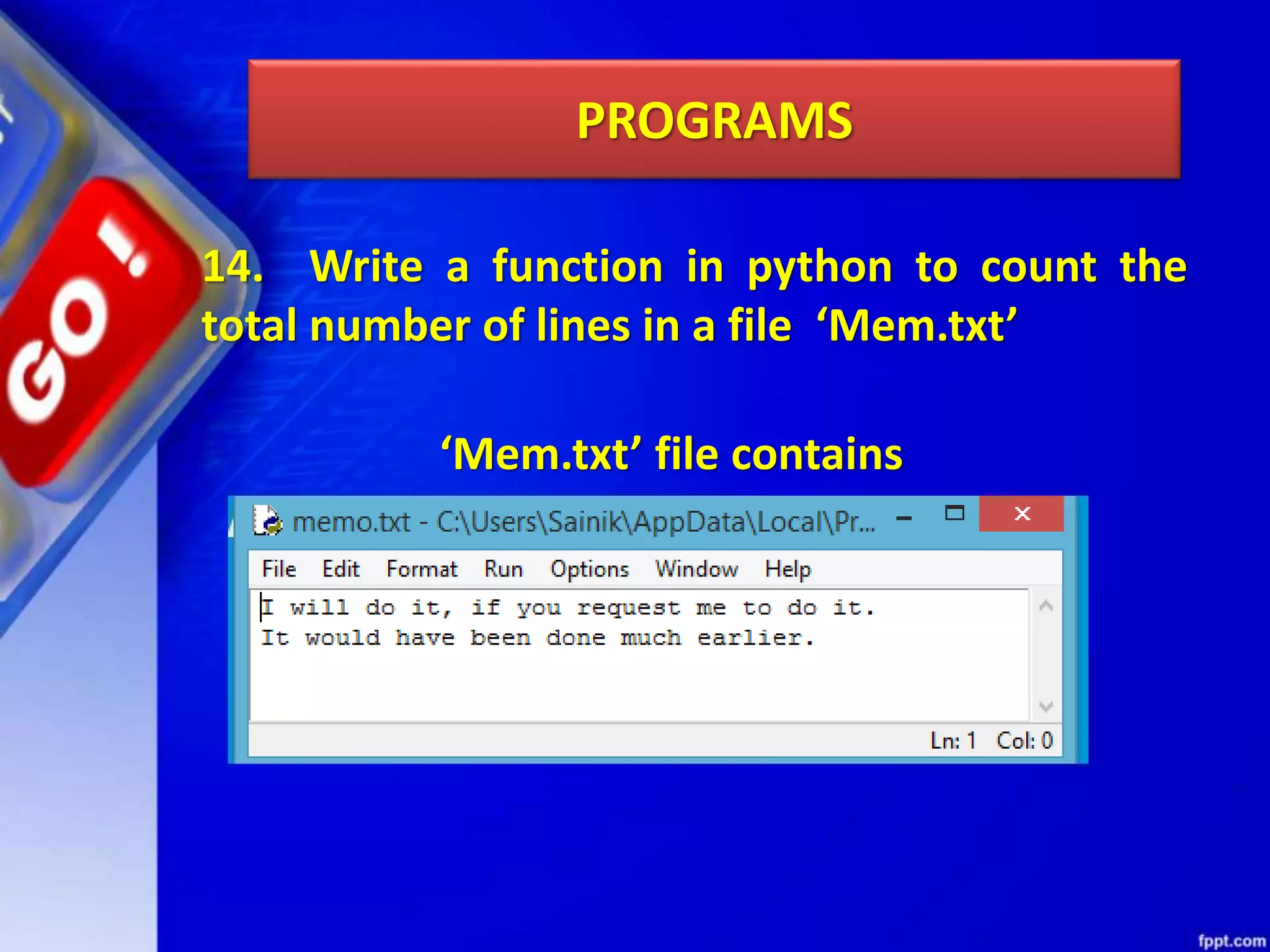
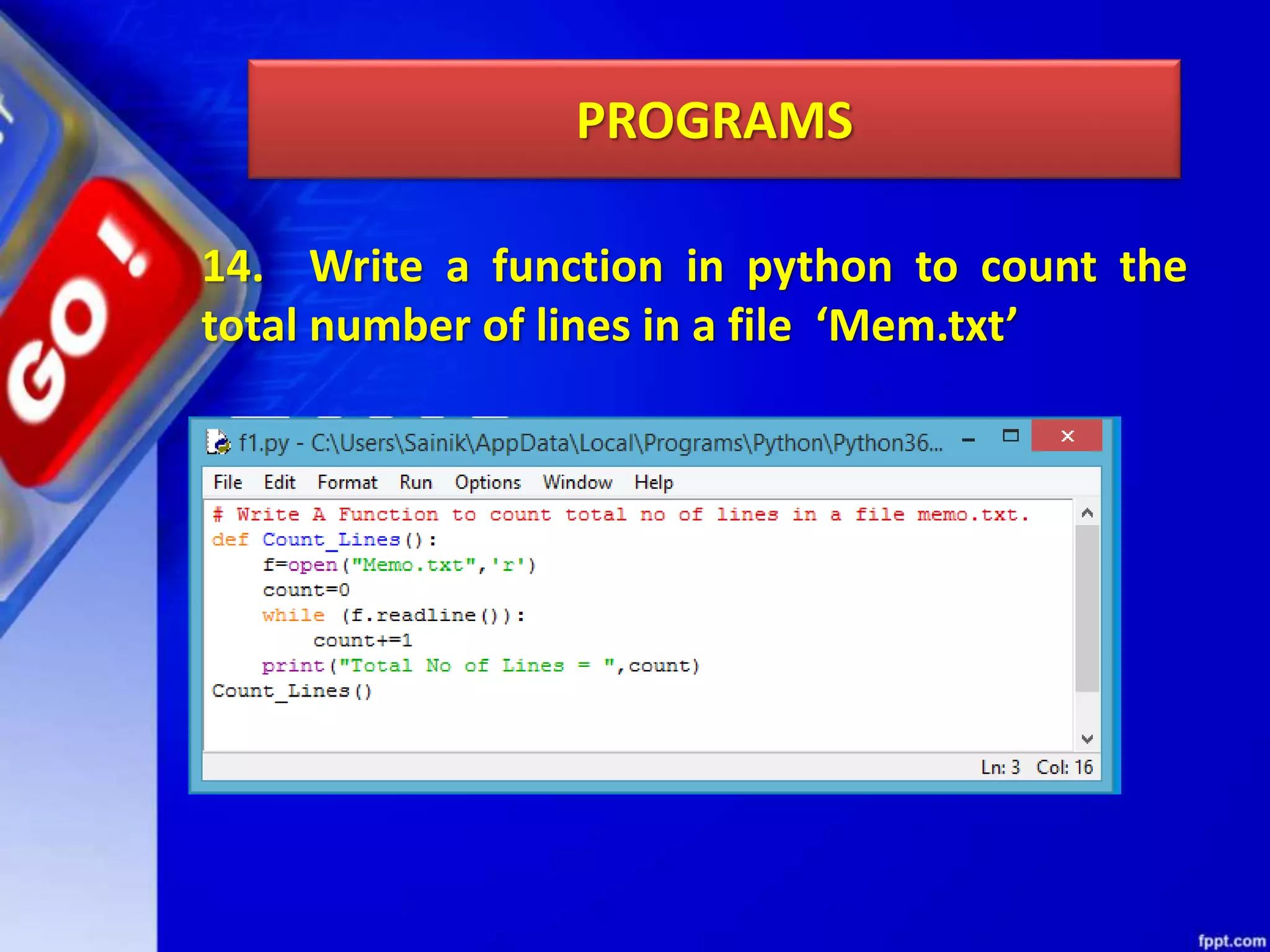
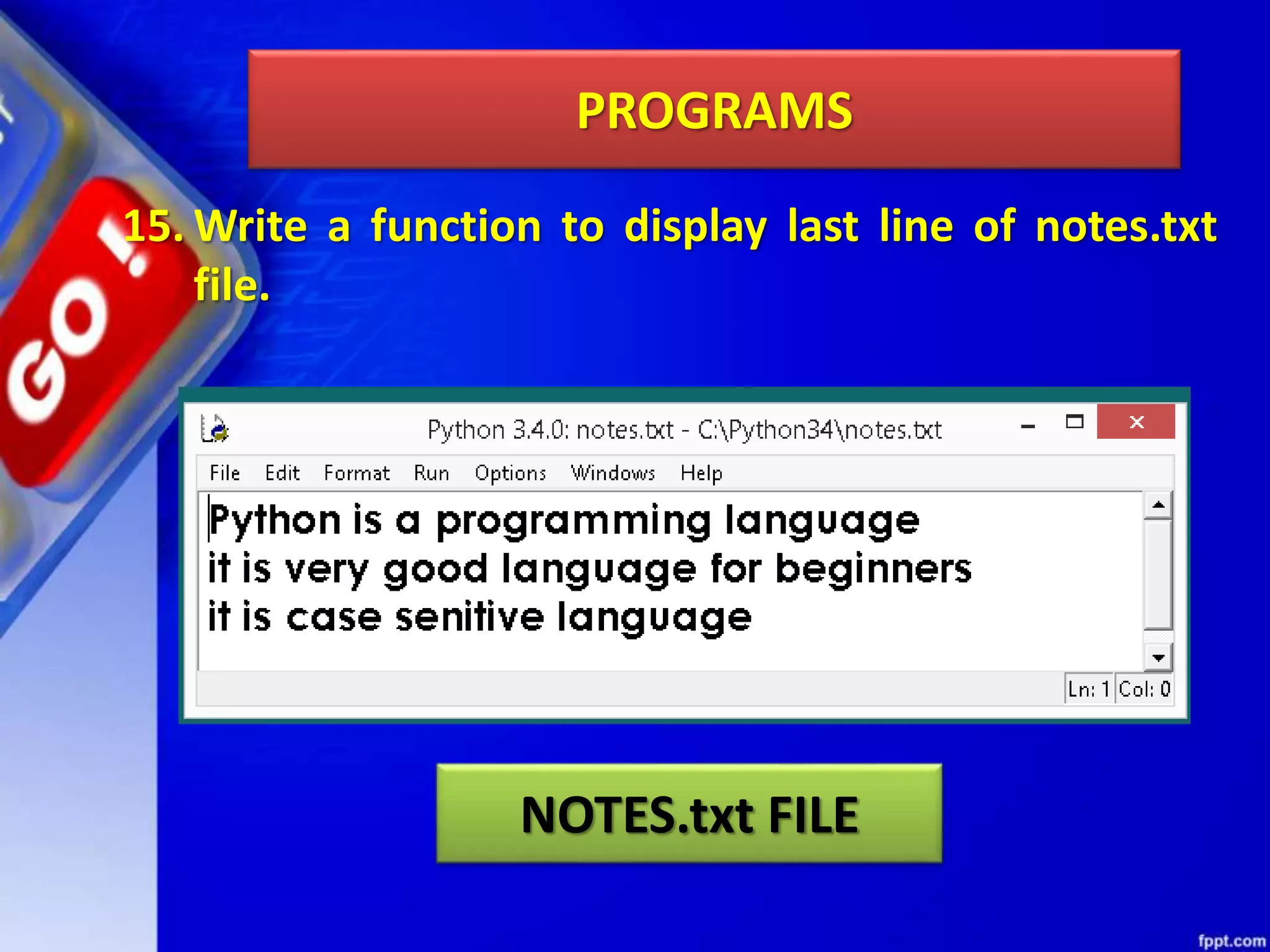
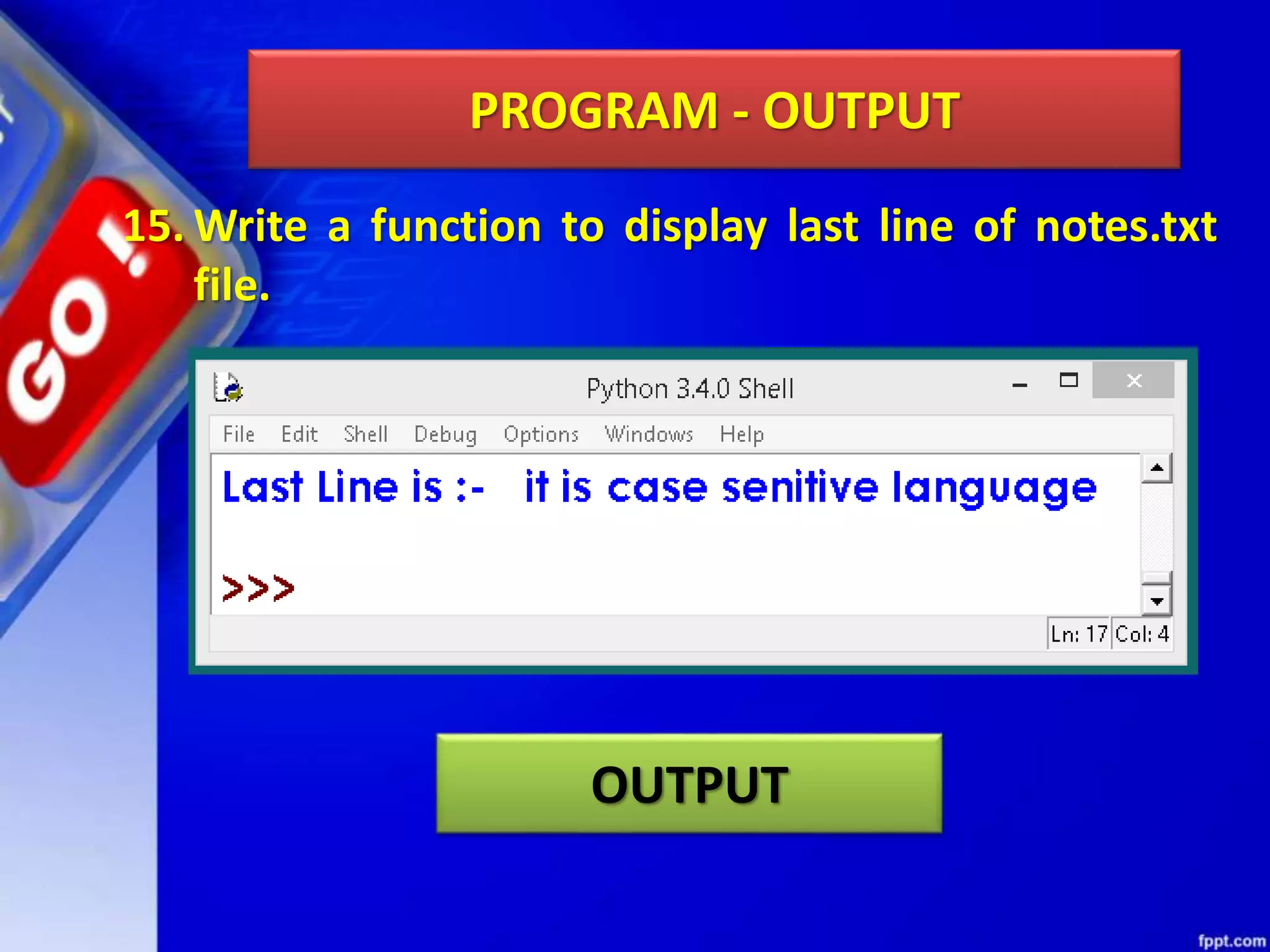
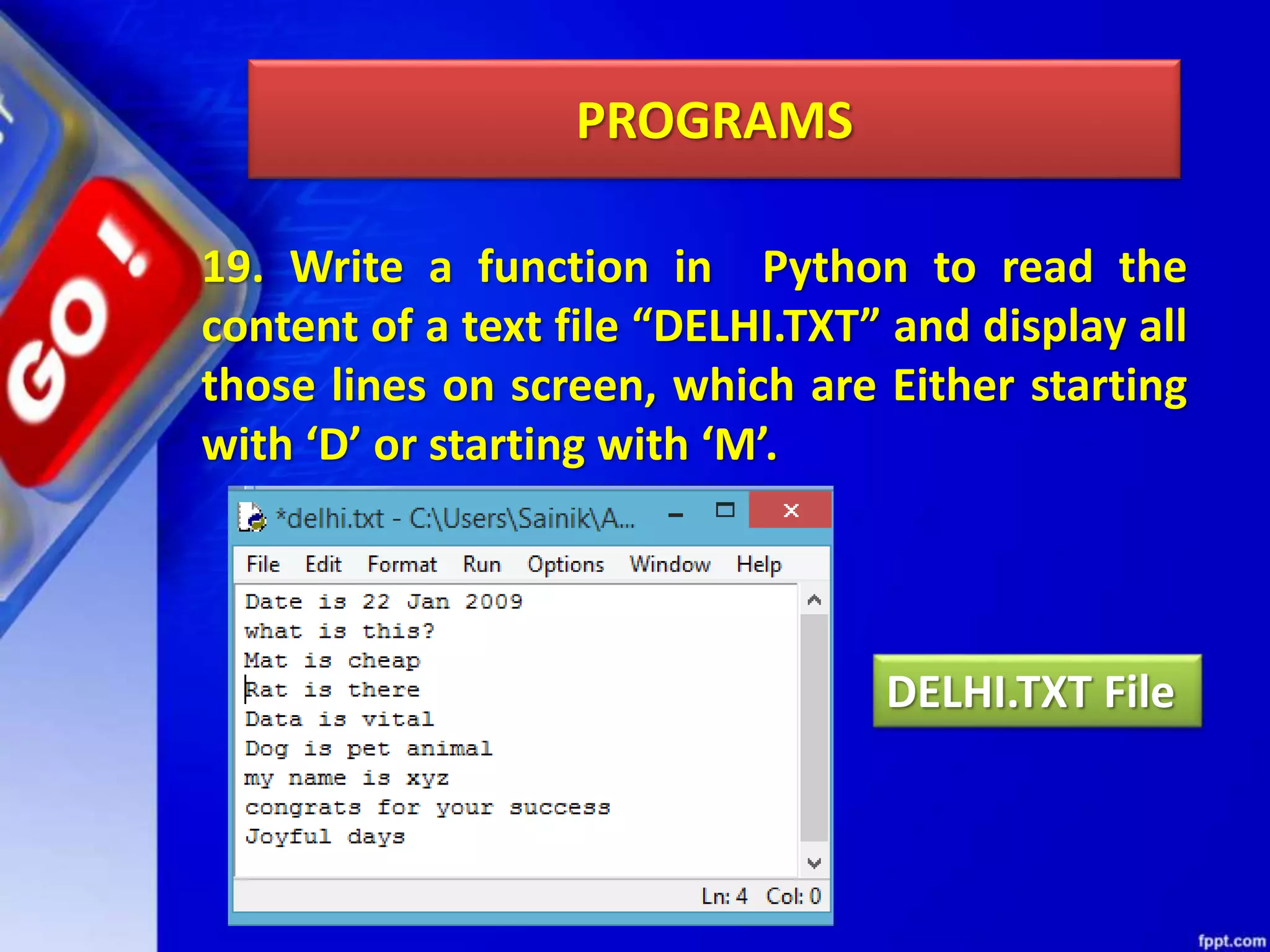
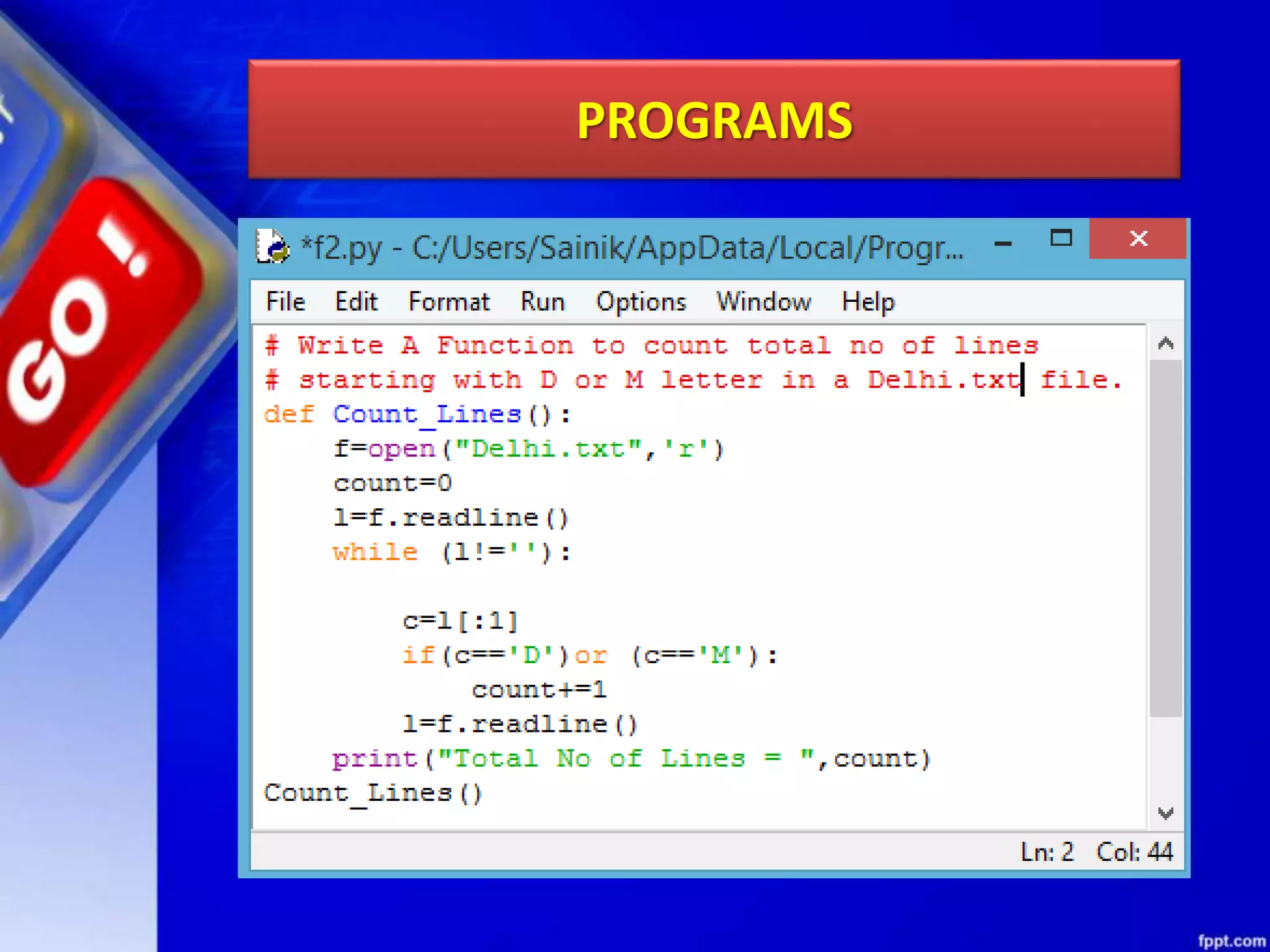
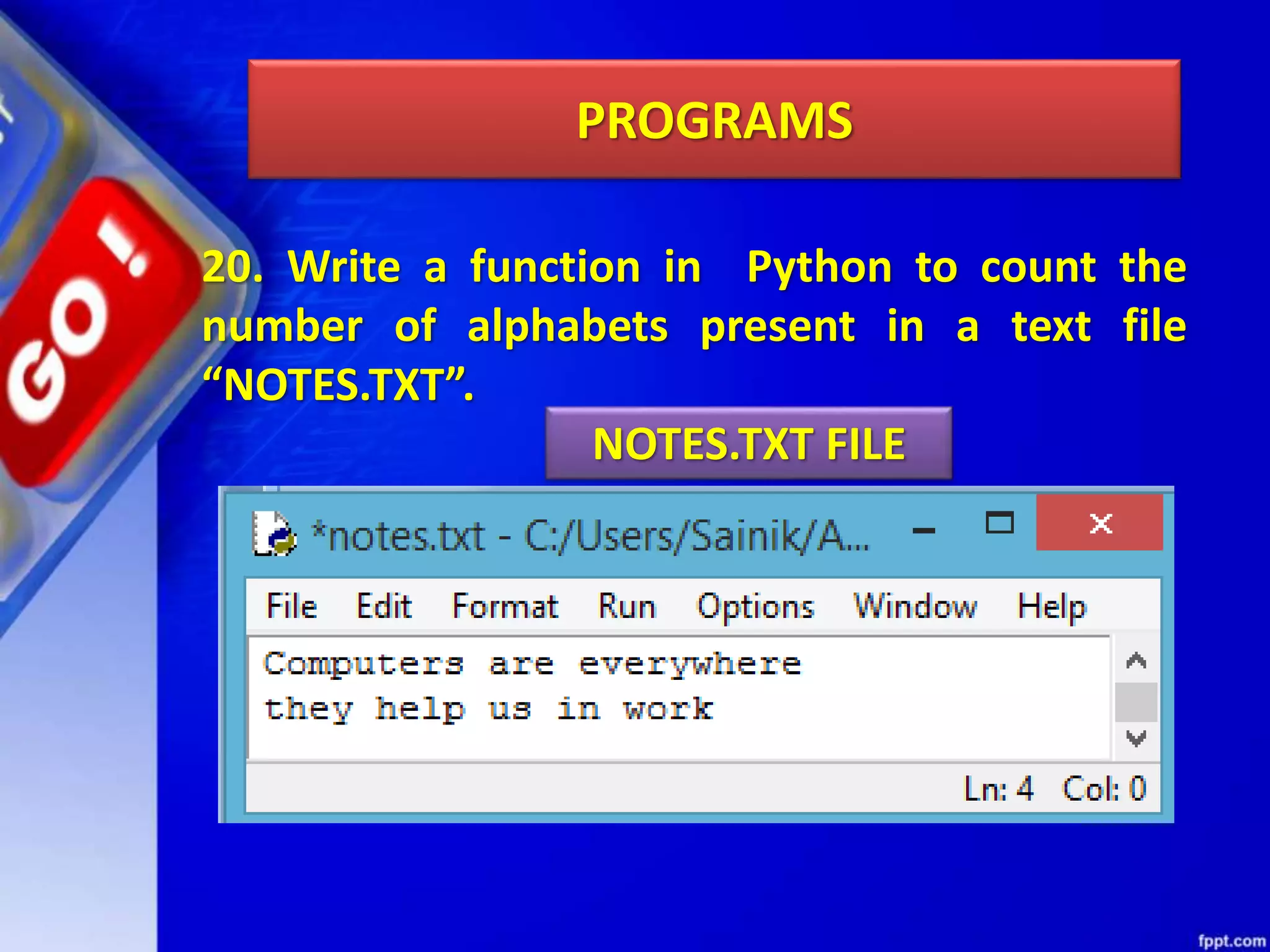
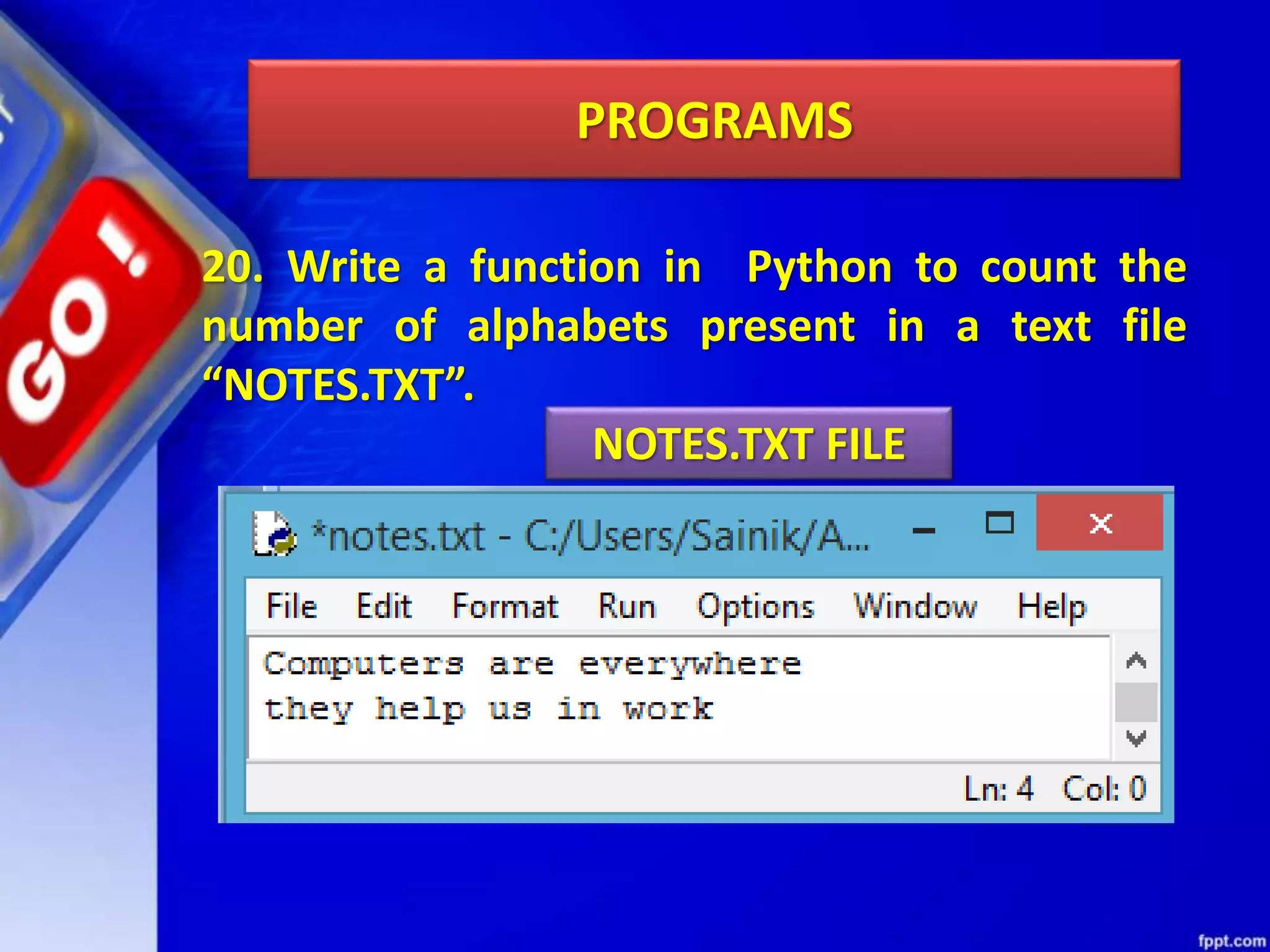
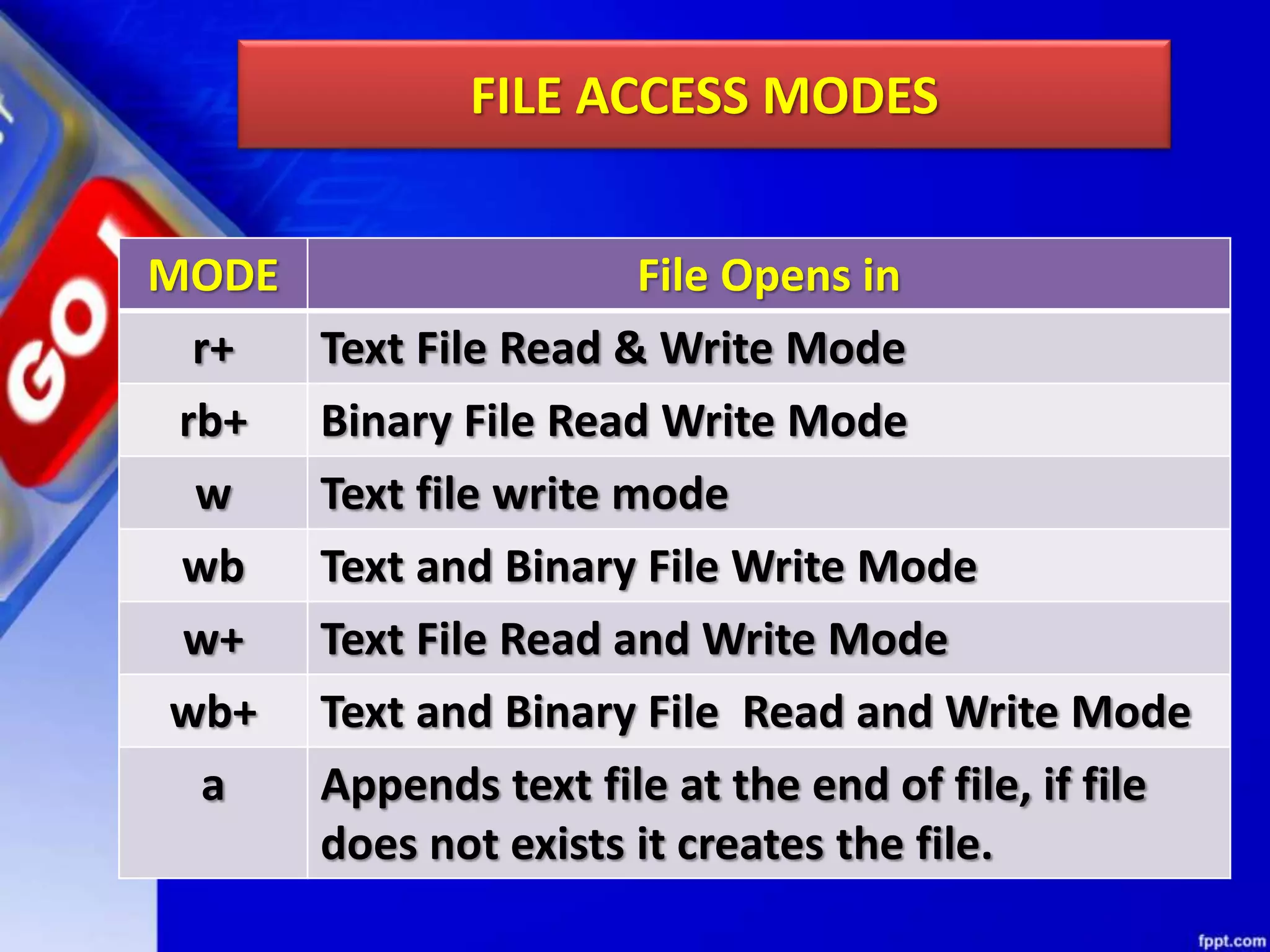
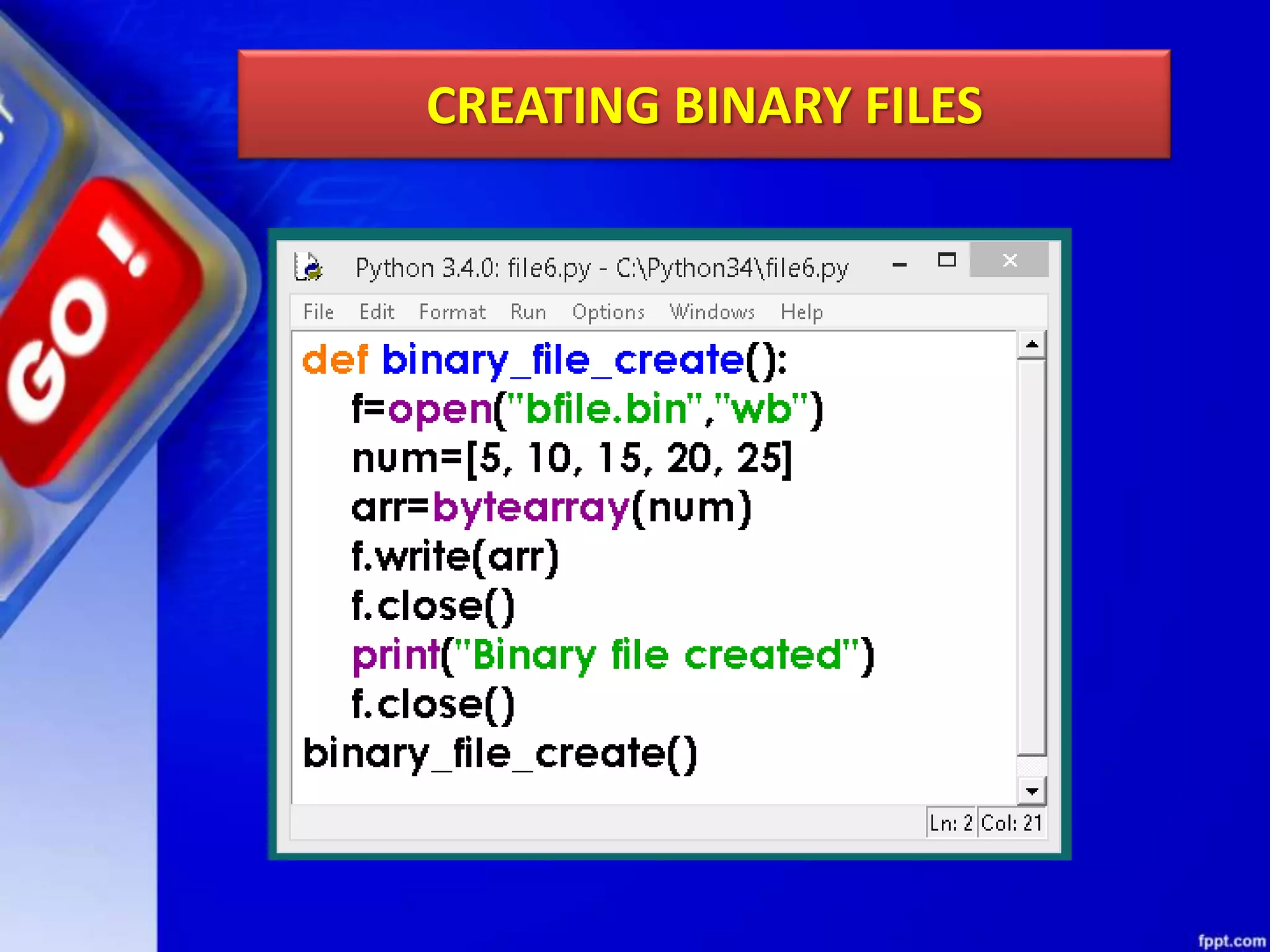
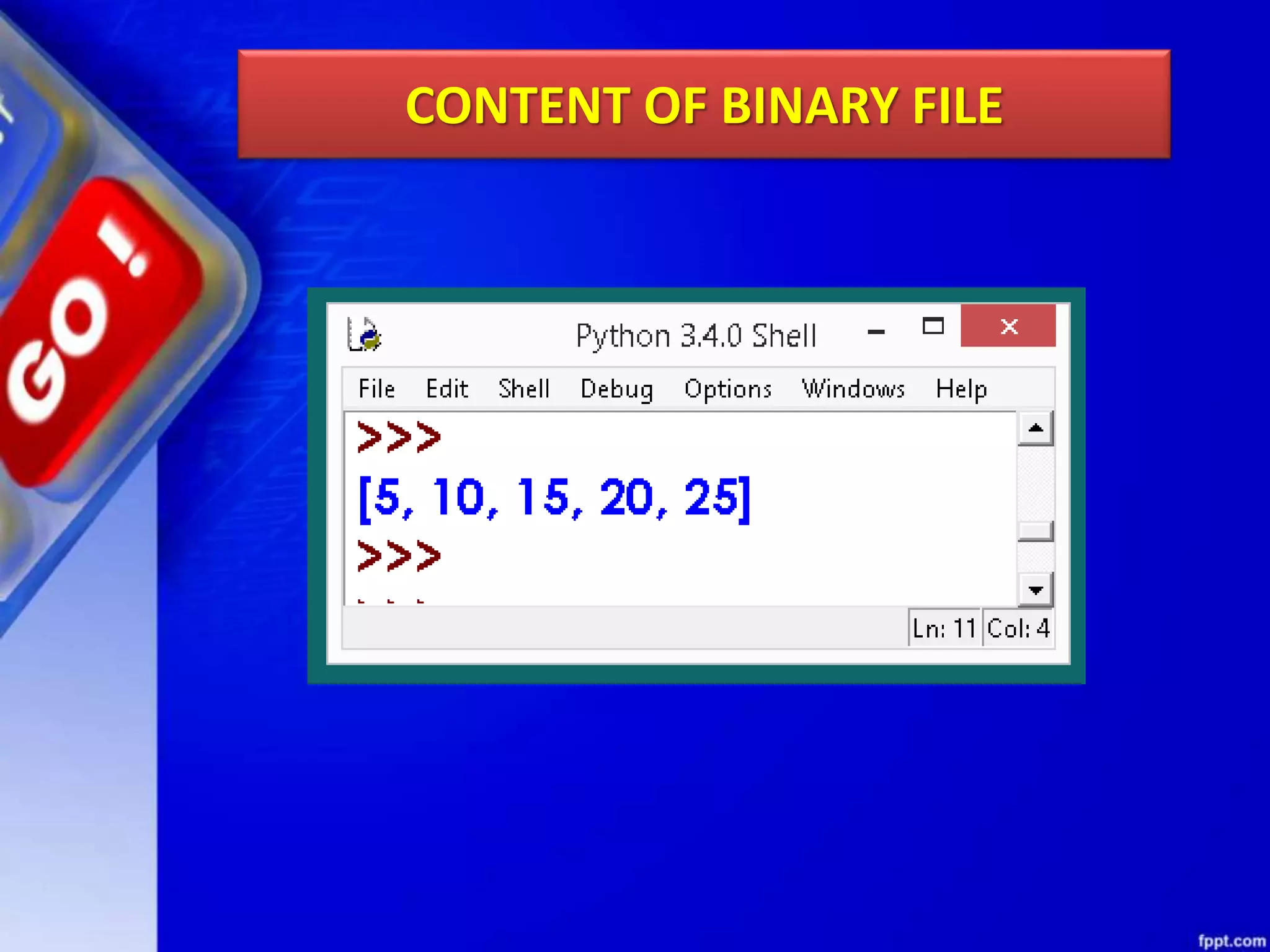
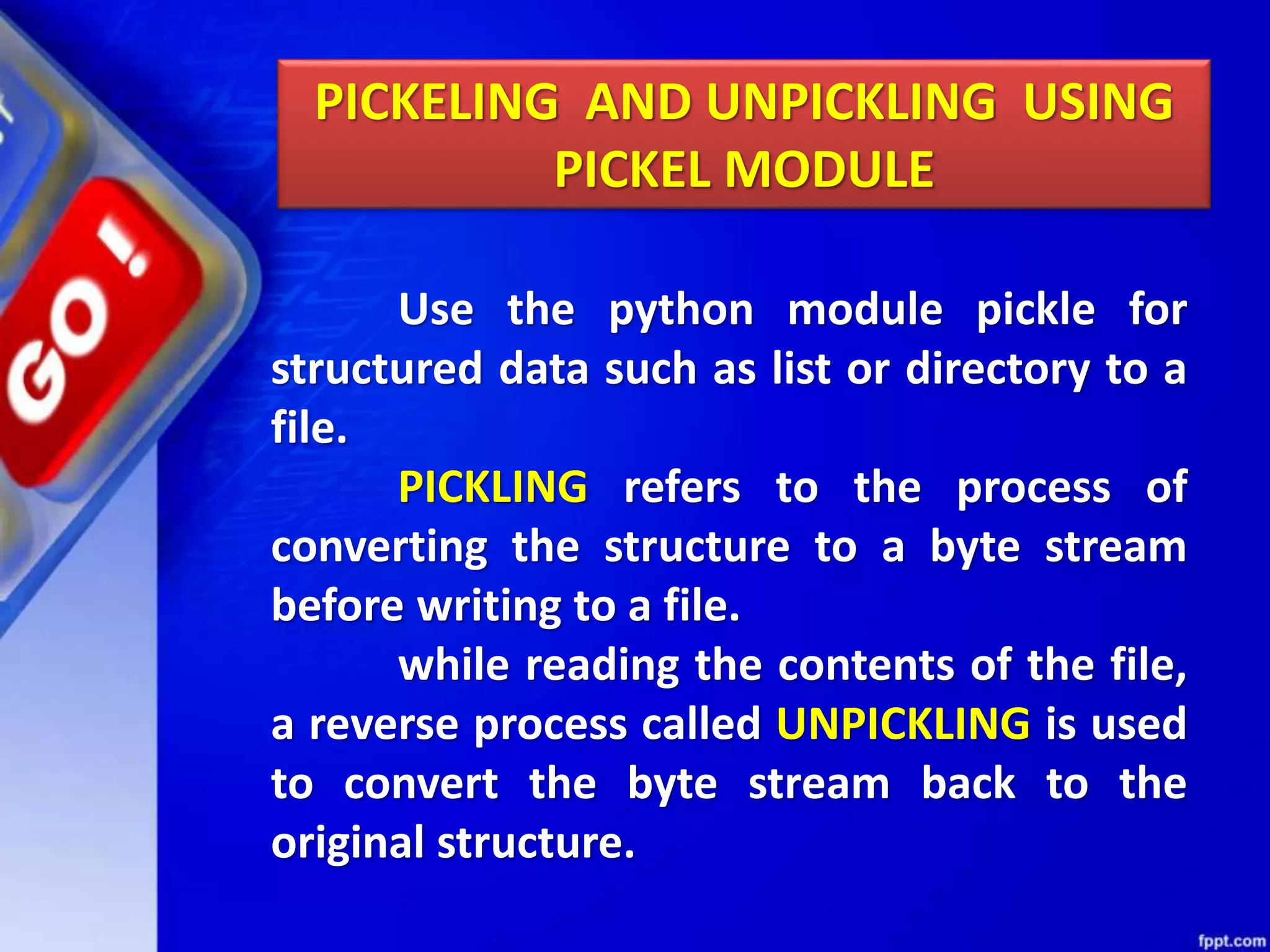
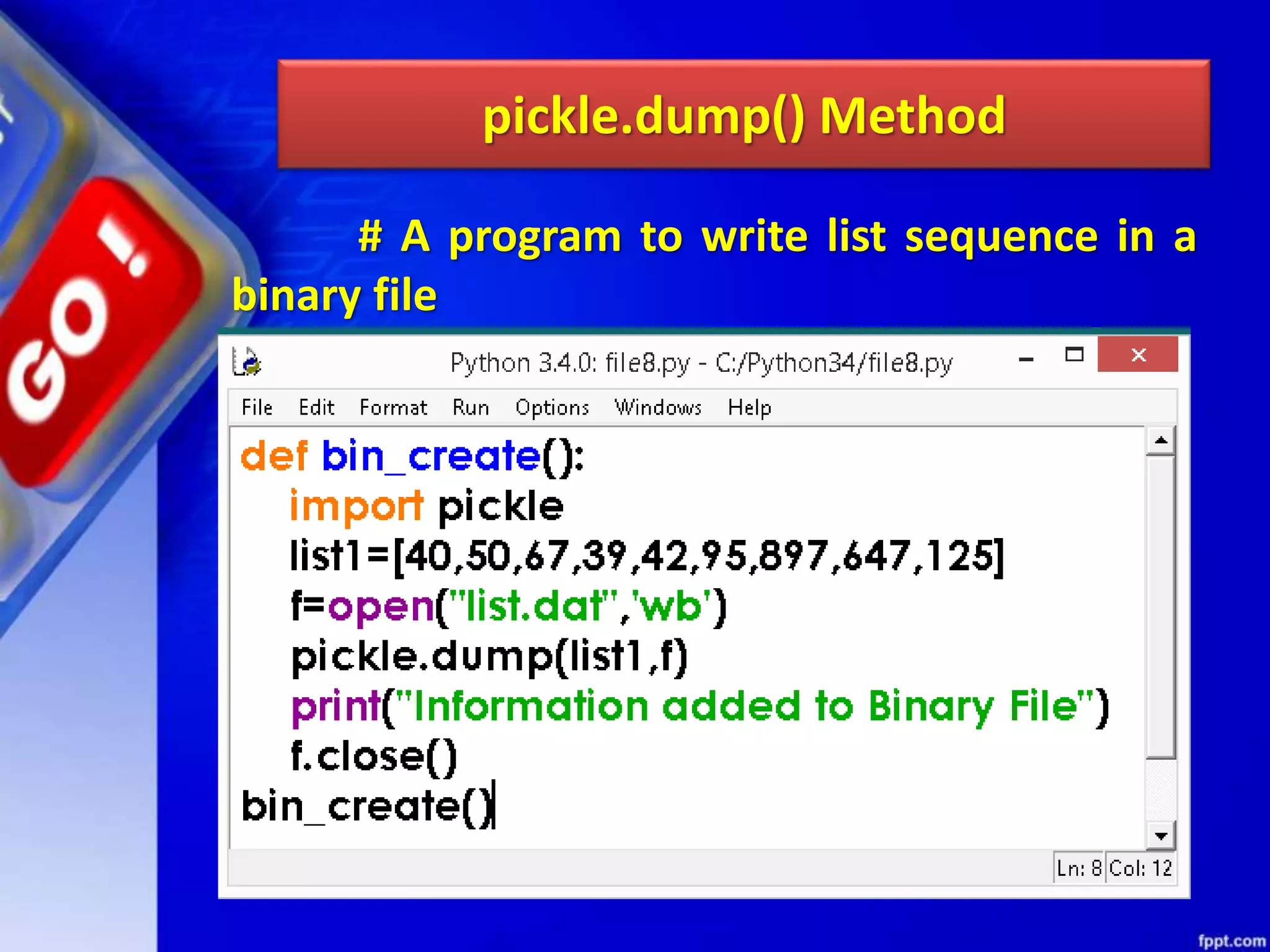
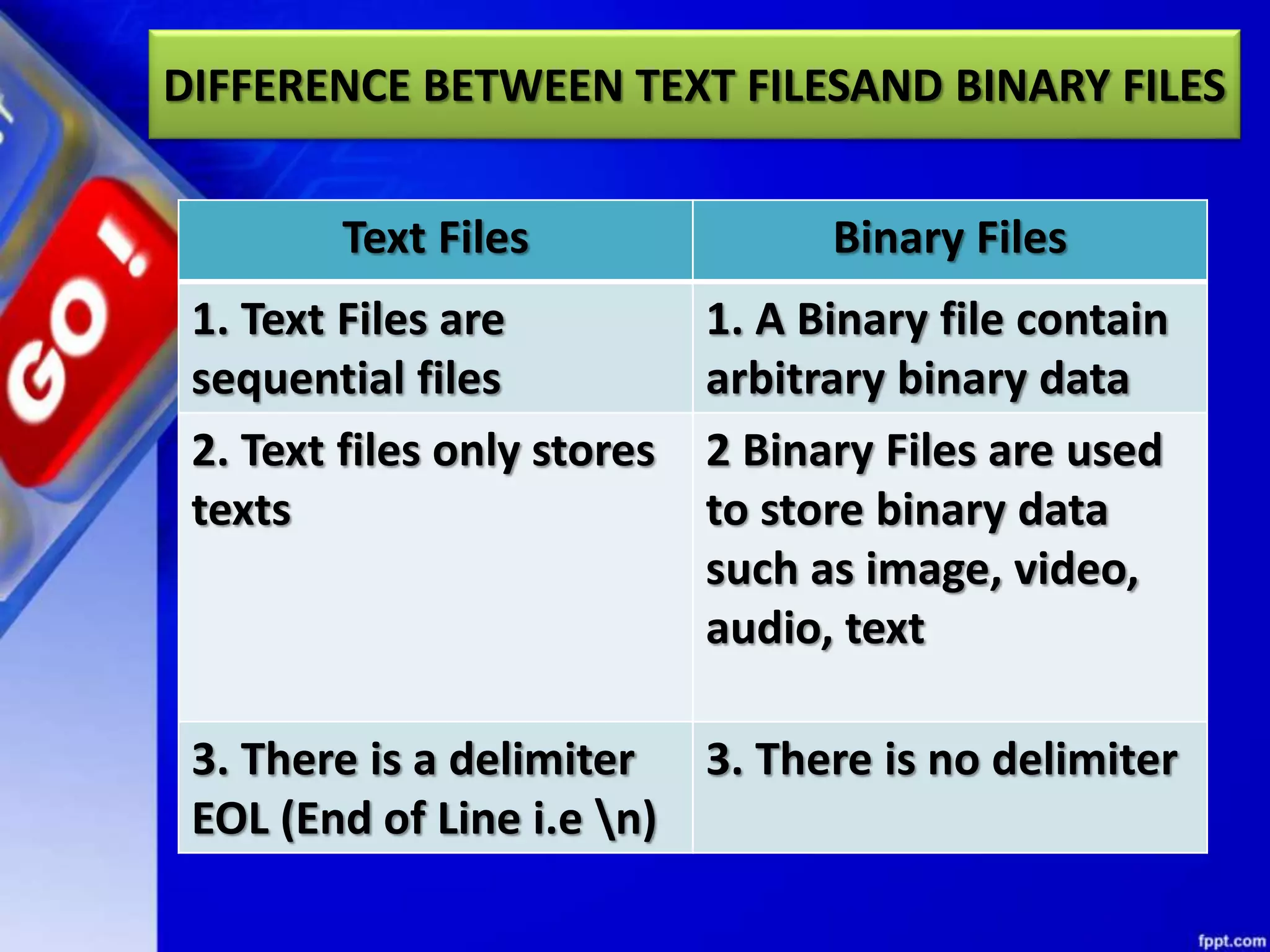
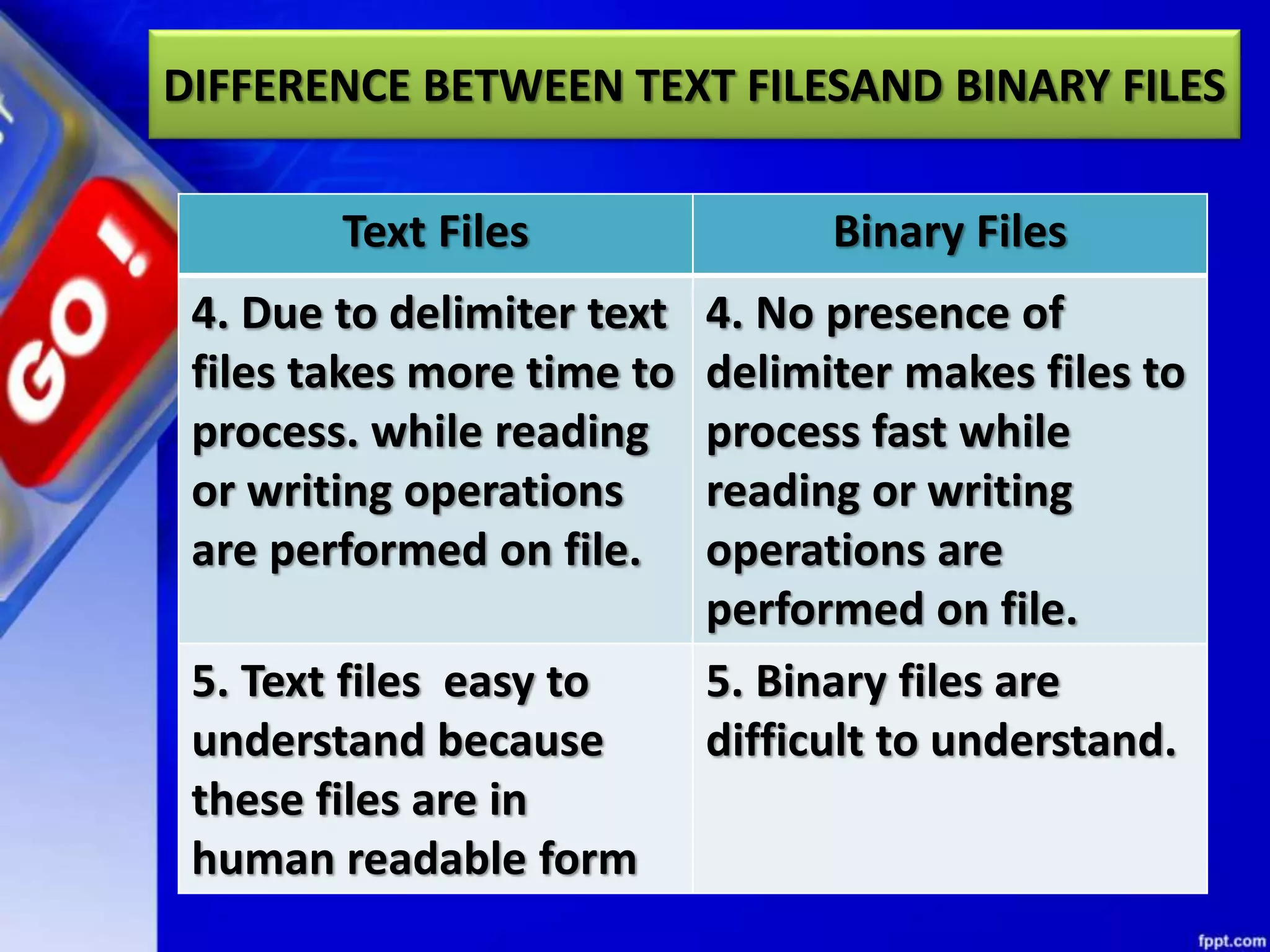
The document discusses data file handling in Python. It covers the basics of opening, reading from, and writing to both text and binary files. The key points covered include: opening and closing files, different file access modes, reading methods like readline(), readlines(), and read(), writing methods like write() and writelines(), random access methods like seek() and tell(), pickling and unpickling using the pickle module, and the differences between text and binary files.













![OPENING AND CLOSING FILES To handle data files in python, we need to have a file object. Object can be created by using open() function or file() function. To work on file, first thing we do is open it. This is done by using built in function open(). Syntax of open() function is file_object = open(filename [, access_mode] [,buffering])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter08datafilehandling-190528091659/75/Chapter-08-data-file-handling-16-2048.jpg)

















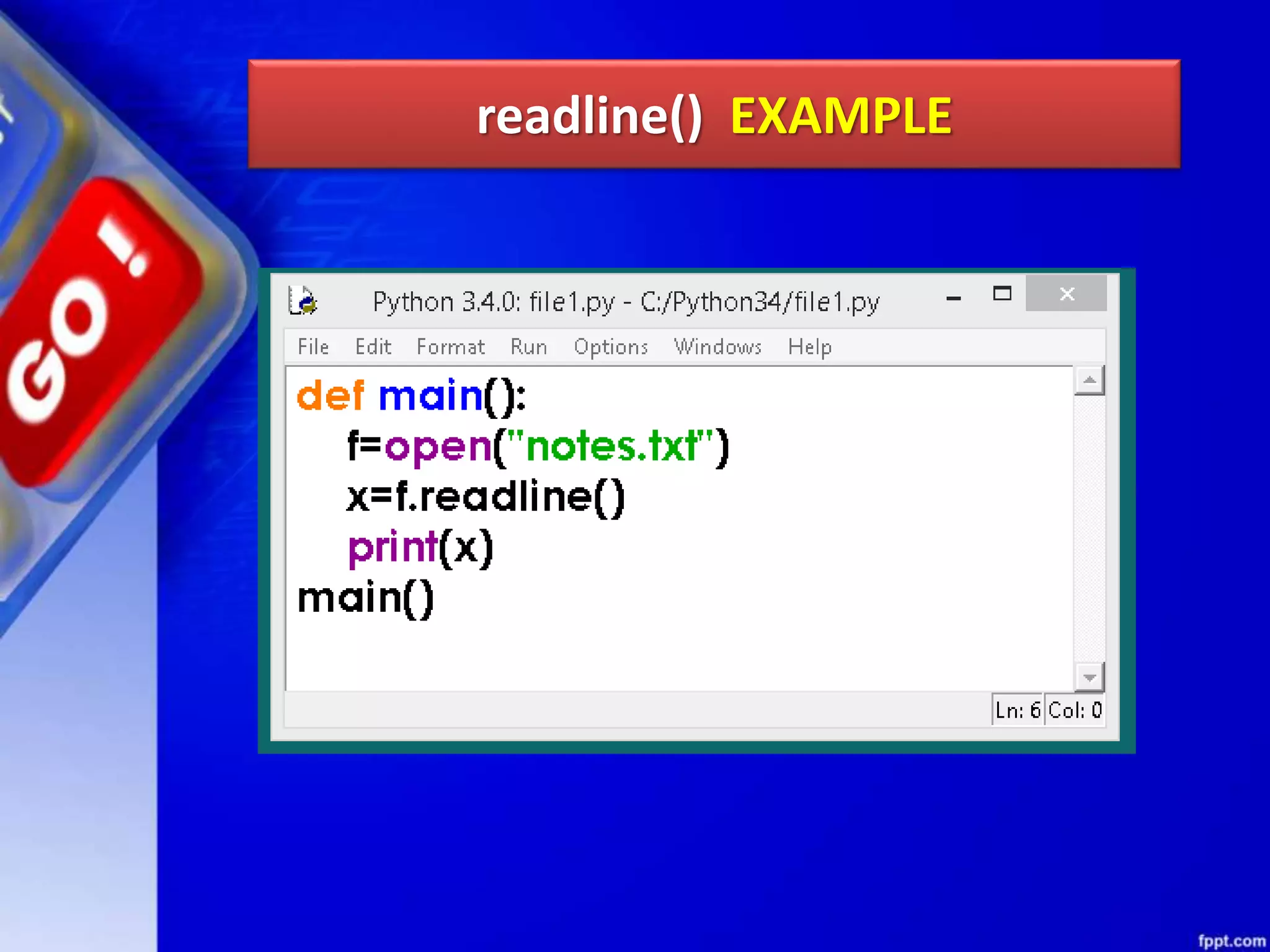
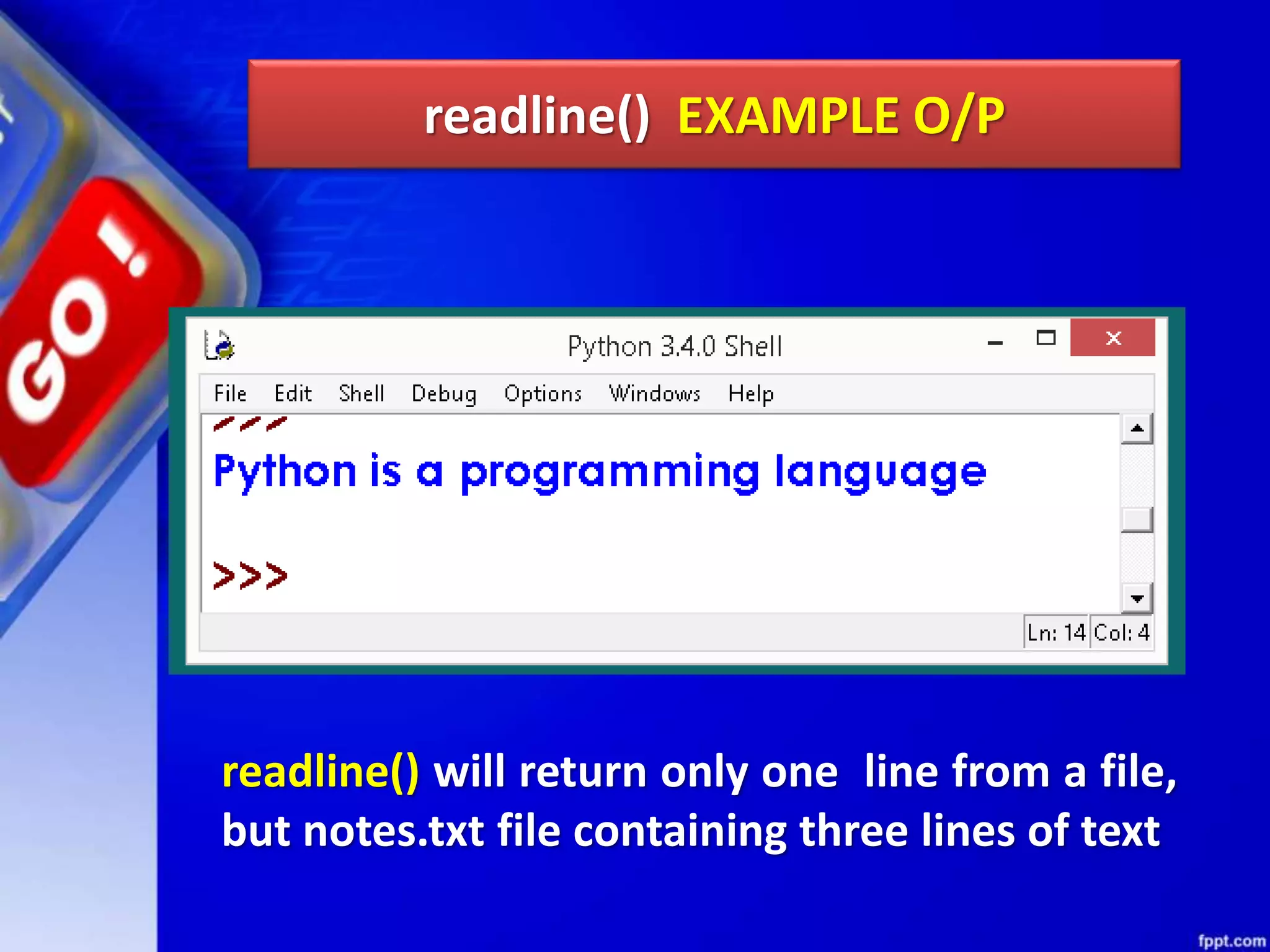

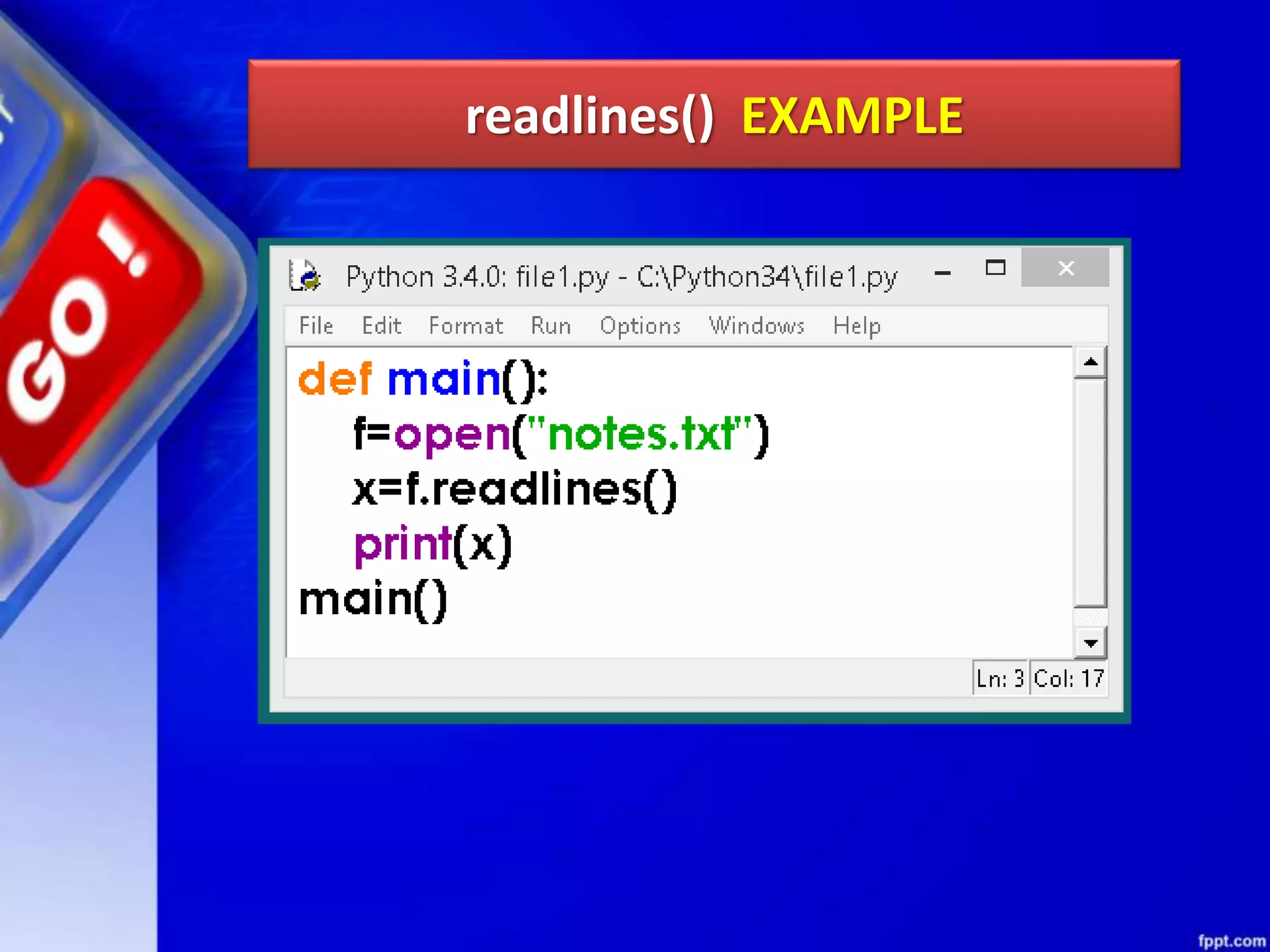


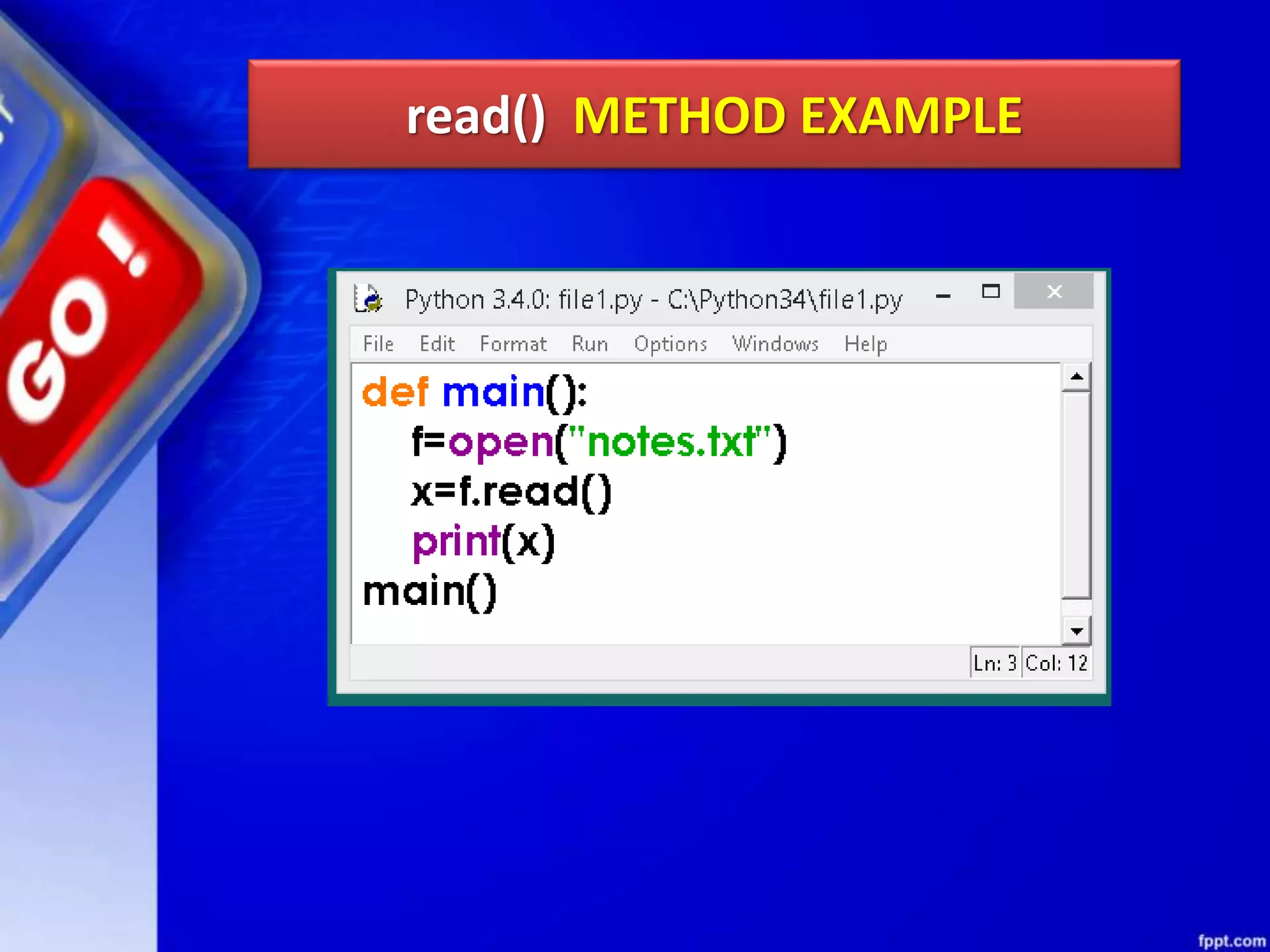


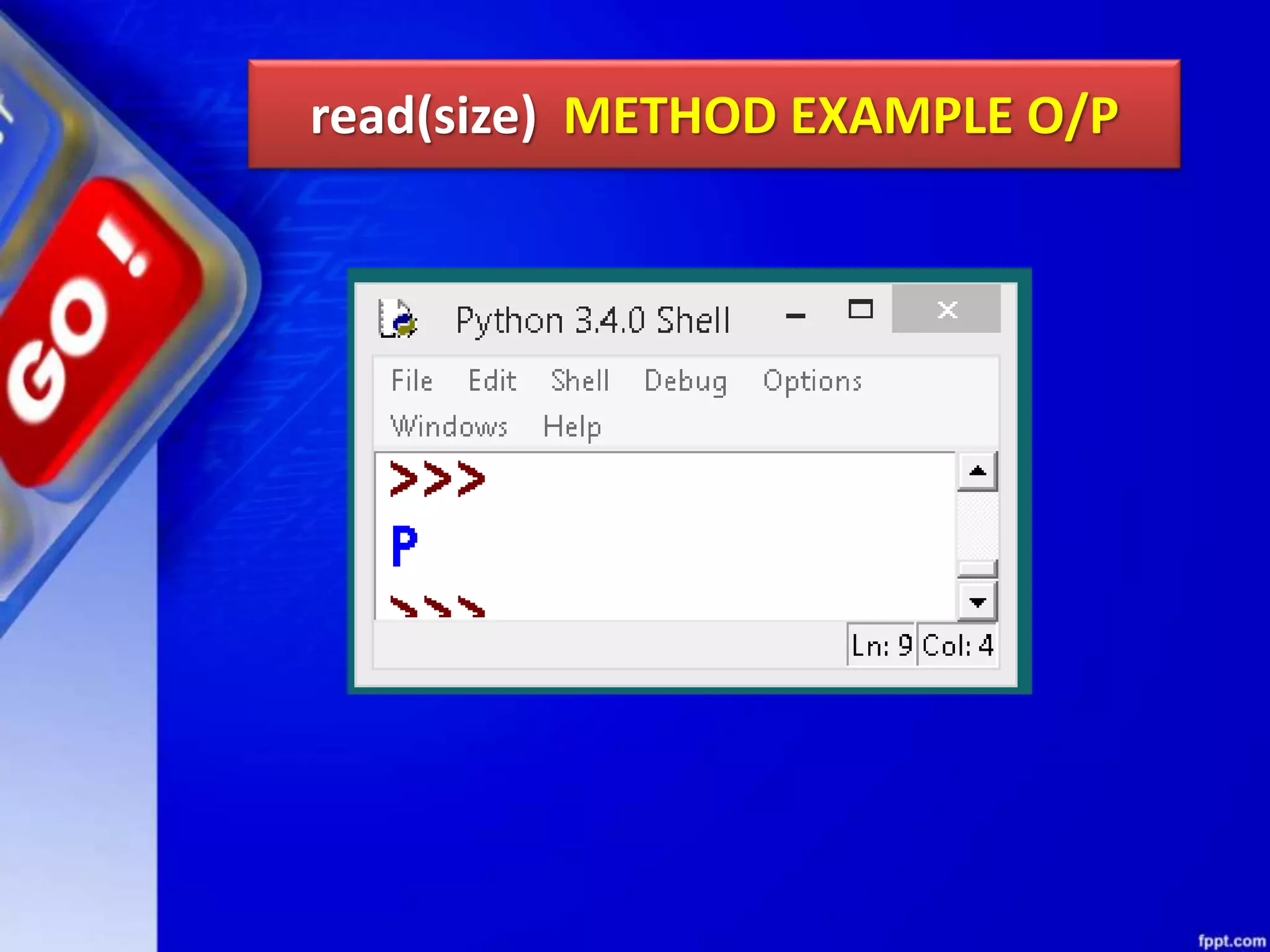
![read(size) METHOD read() can be used to read specific size string from file. This function also returns a string read from the file. Syntax of read() function is: fileobject.read([size]) For Example: f.read(1) will read single byte or character from a file.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter08datafilehandling-190528091659/75/Chapter-08-data-file-handling-45-2048.jpg)





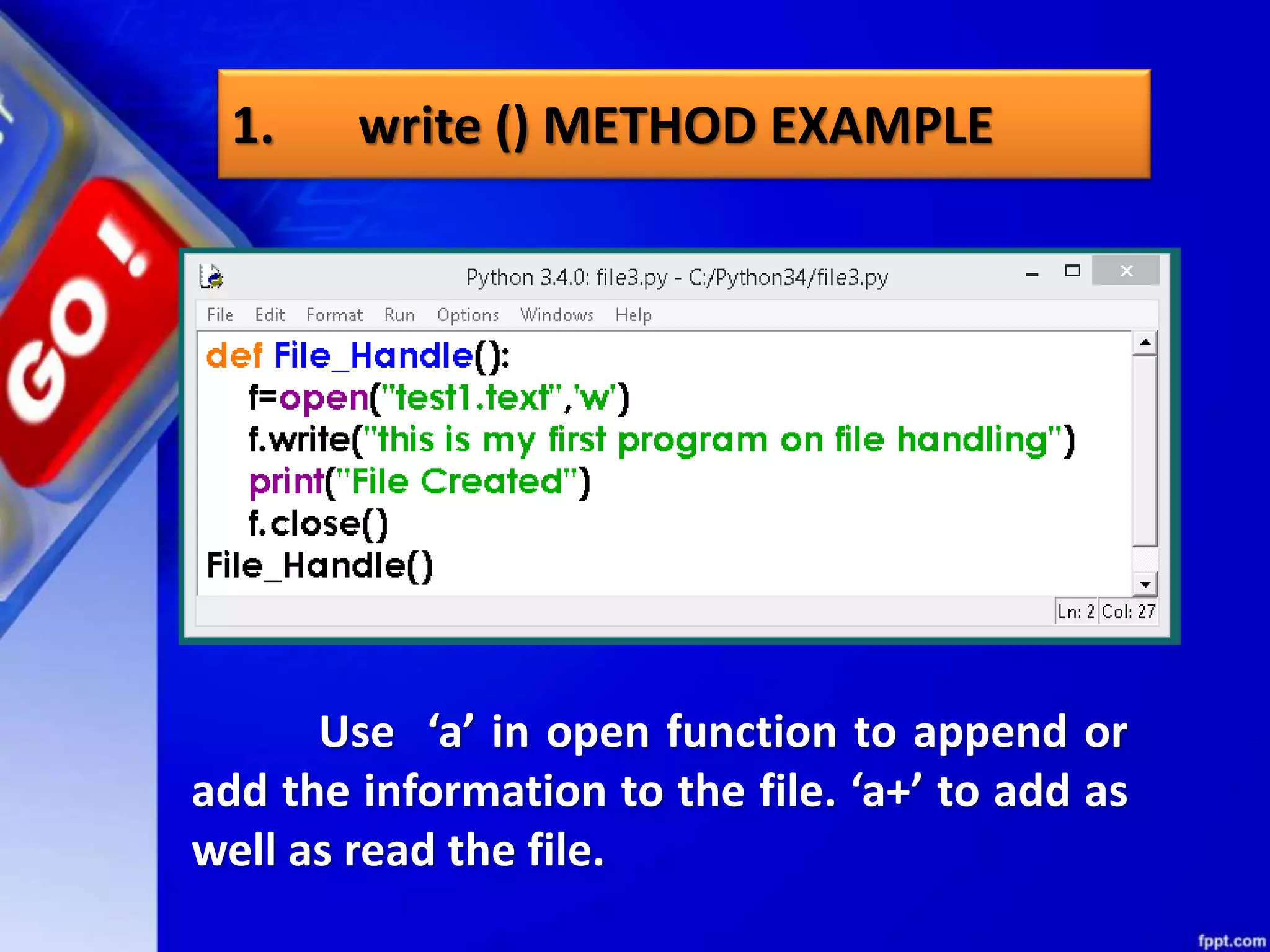
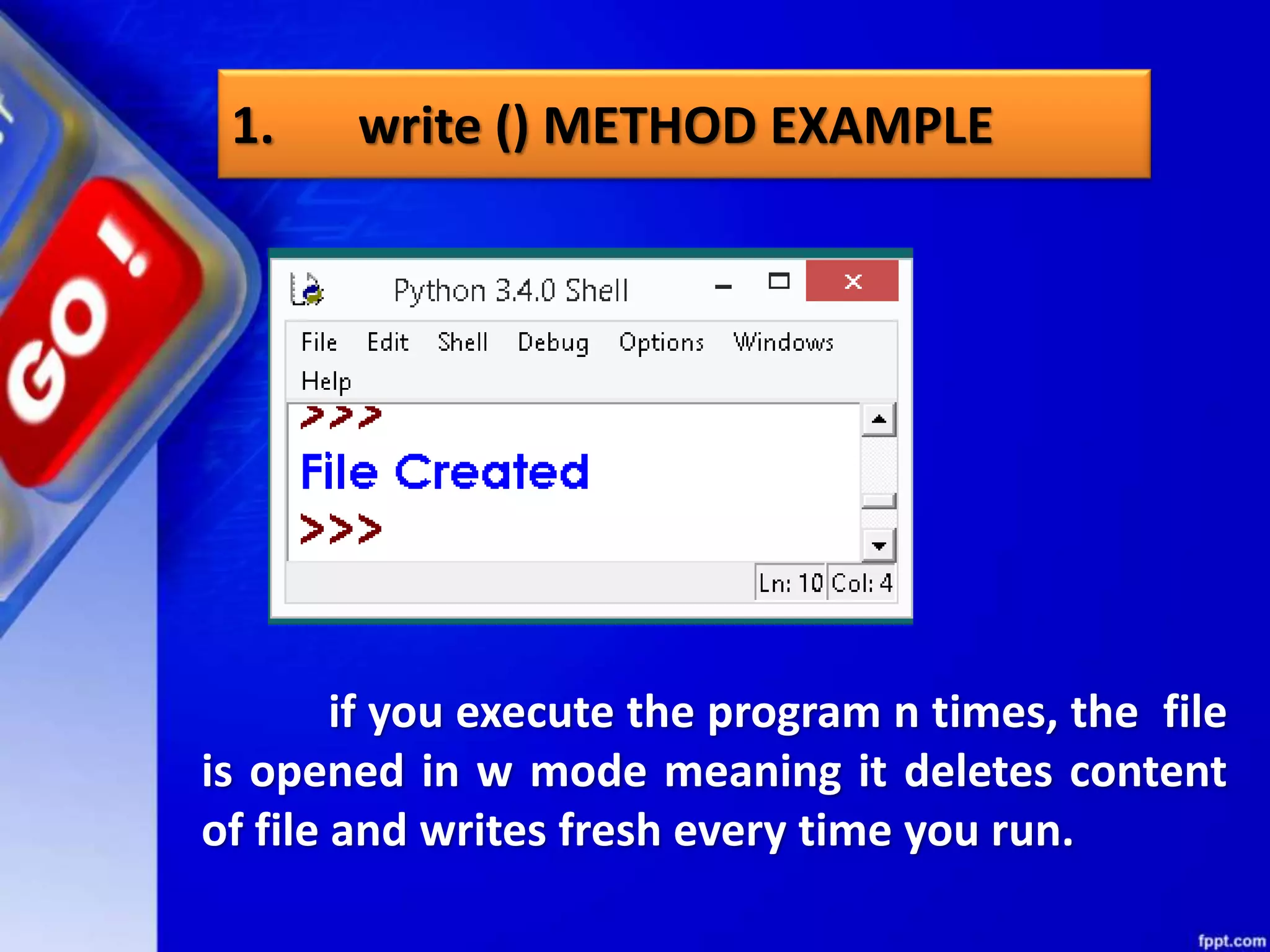


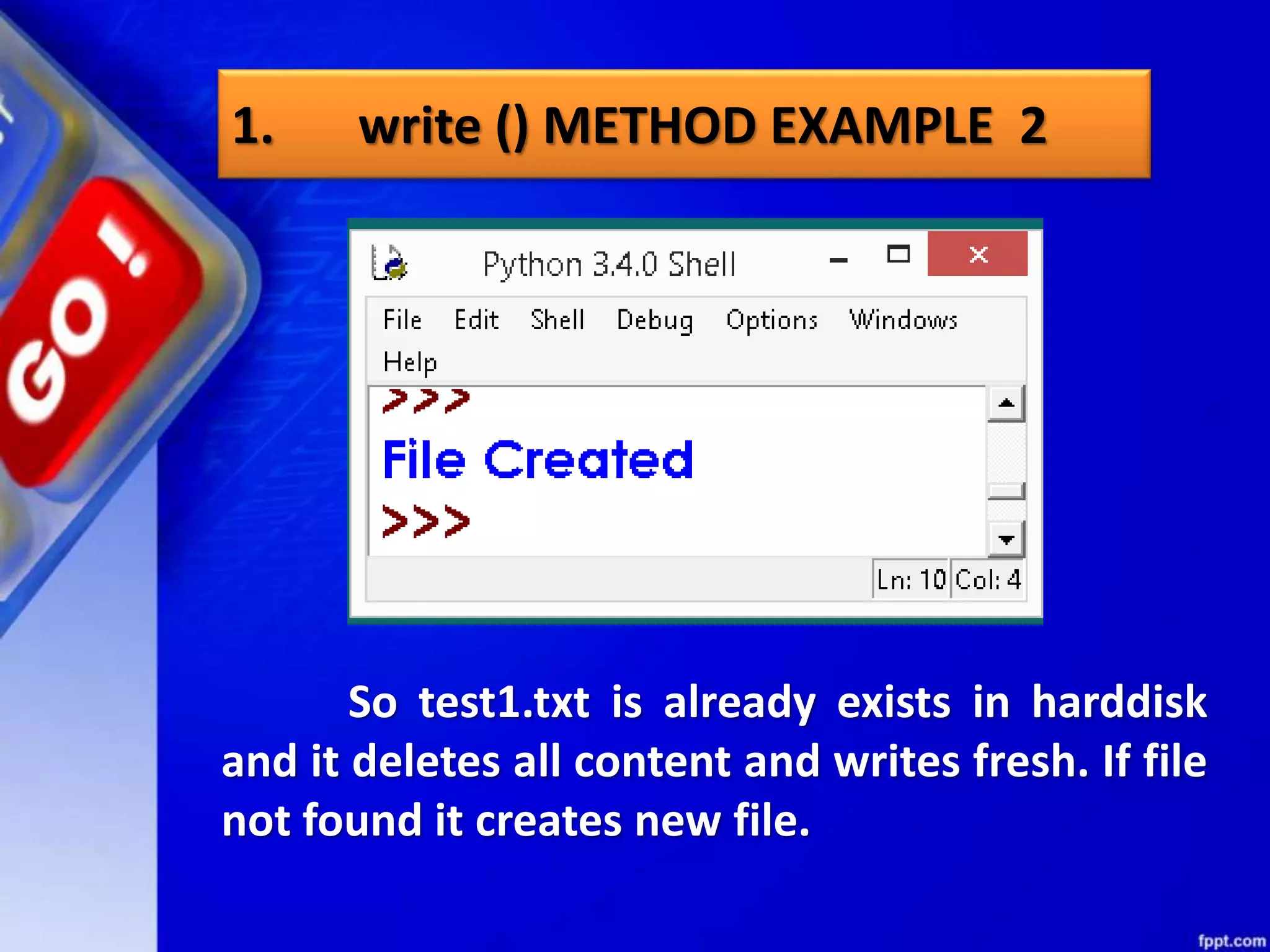





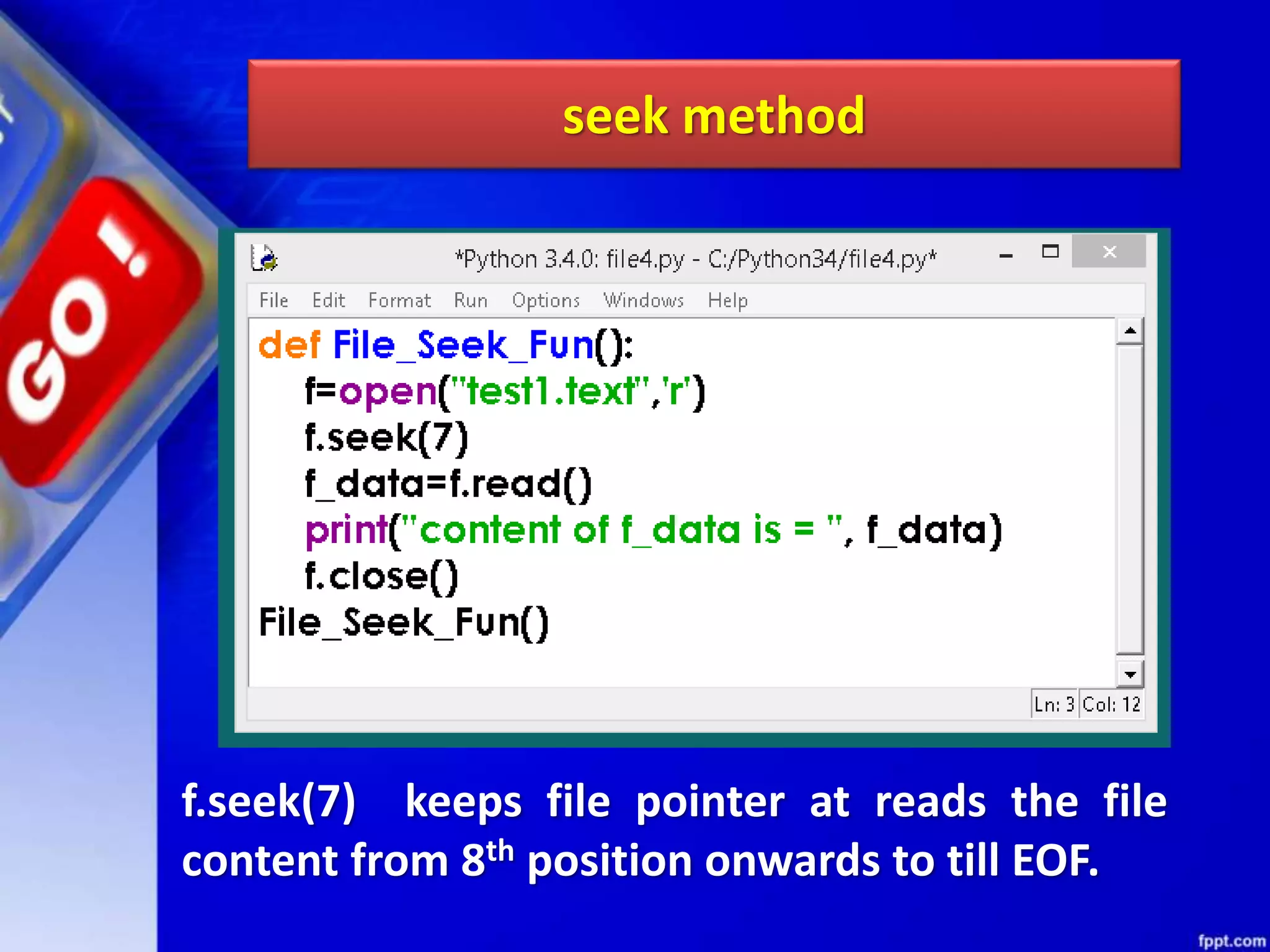
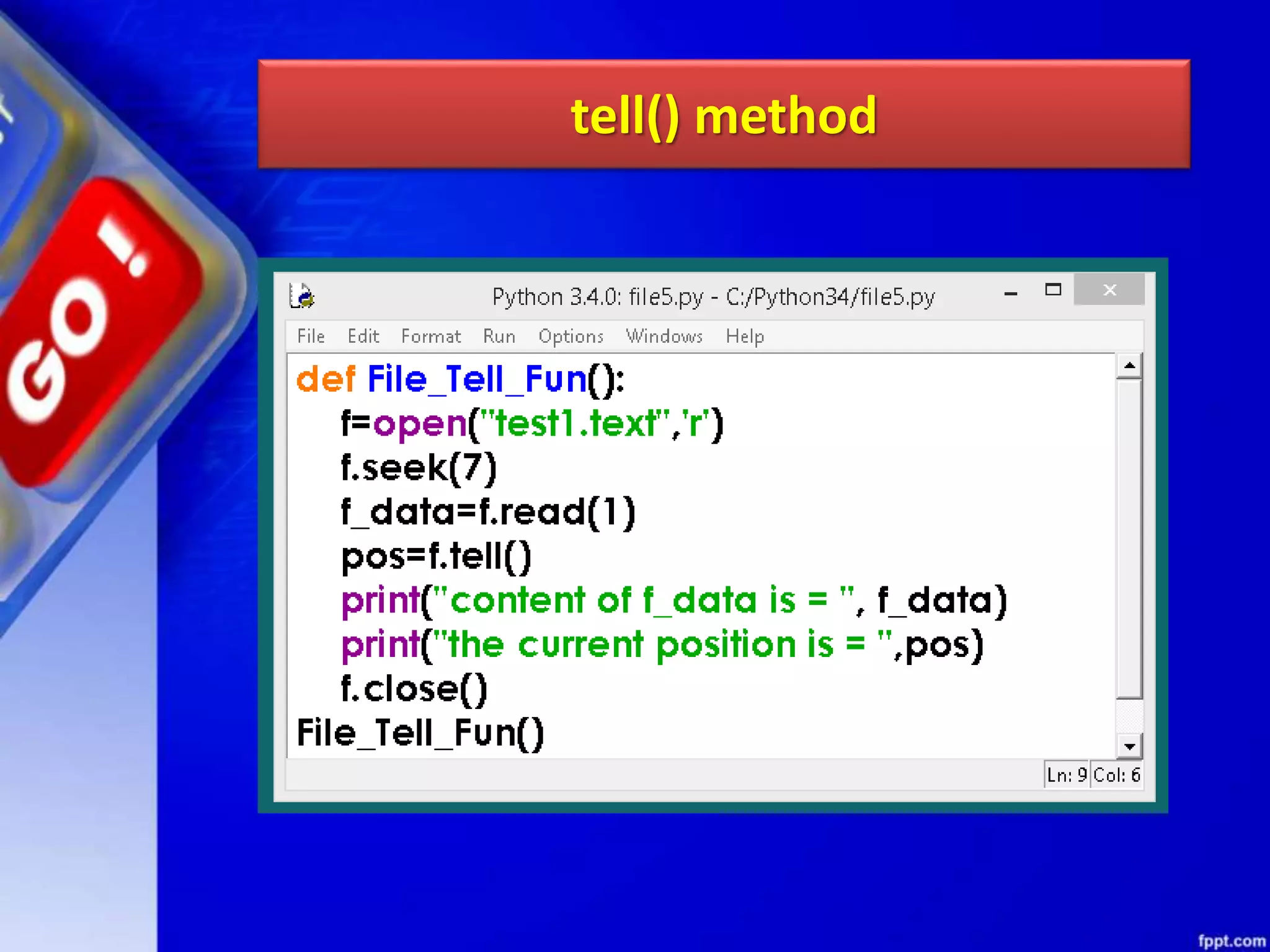
![seek()method can be used to position the file object at particular place in the file. It's syntax is : fileobject.seek(offset [, from_what]) here offset is used to calculate the position of fileobject in the file in bytes. Offset is added to from_what (reference point) to get the position. Following is the list of from_what values: seek method](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter08datafilehandling-190528091659/75/Chapter-08-data-file-handling-62-2048.jpg)
















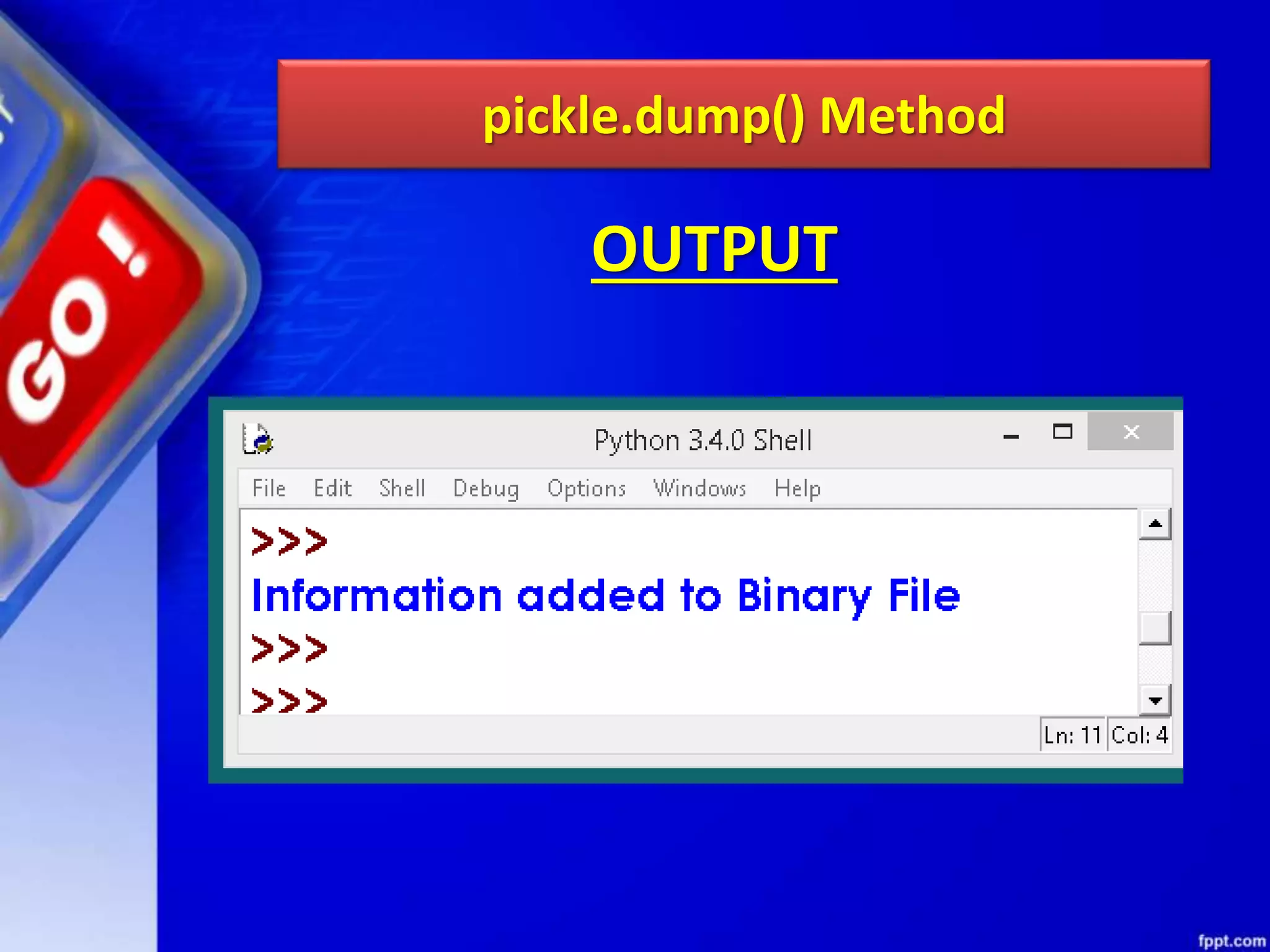
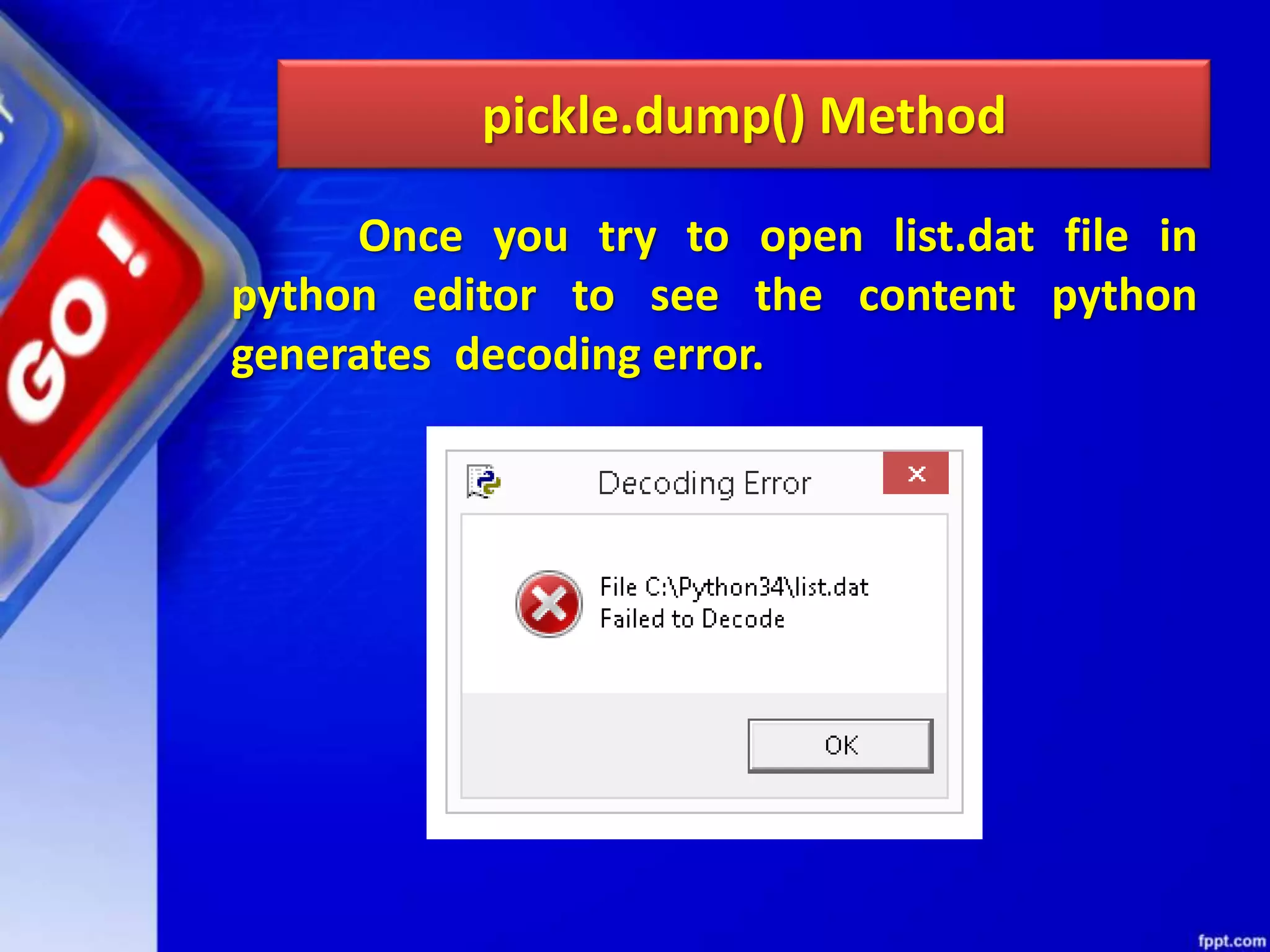

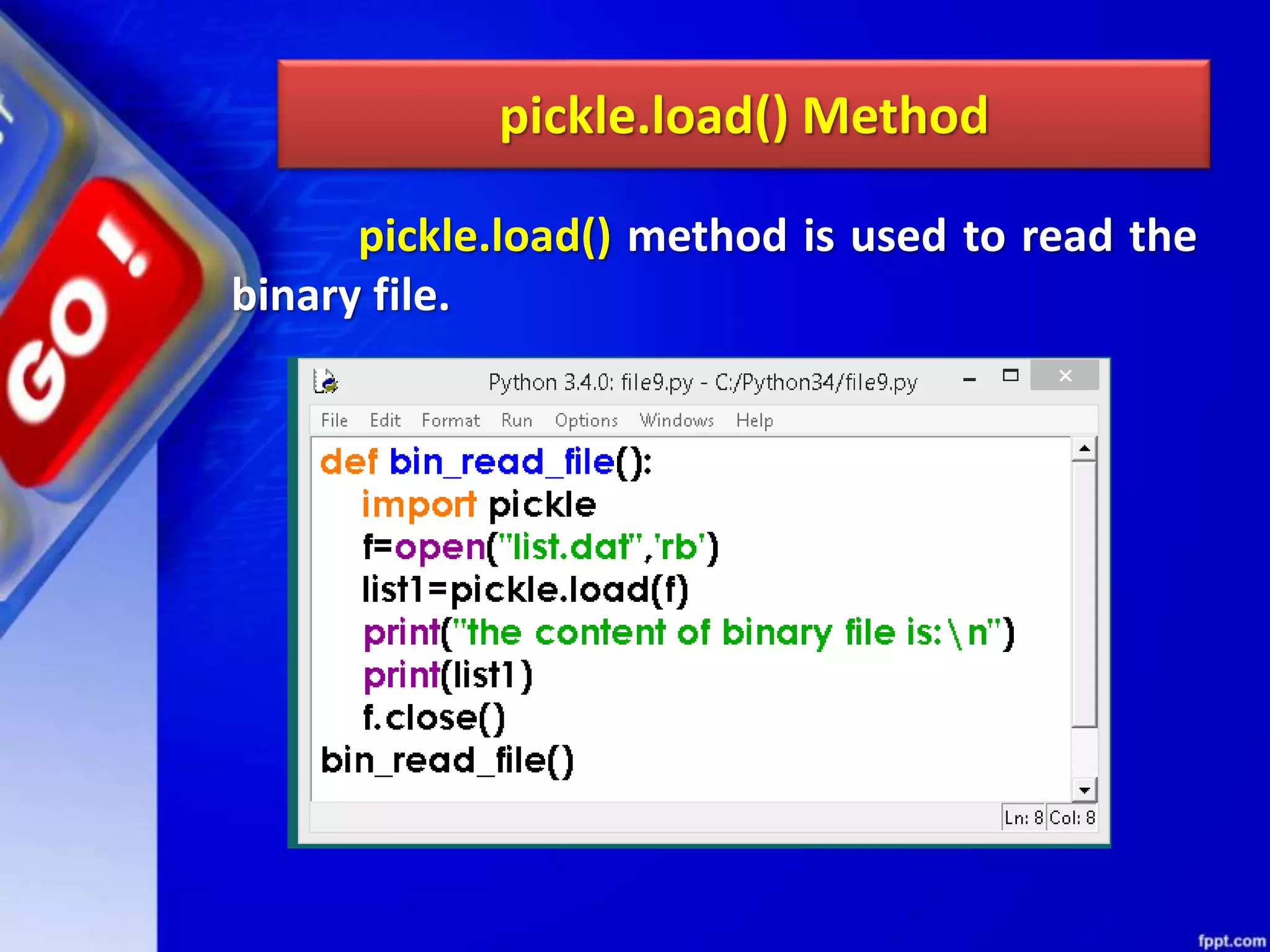
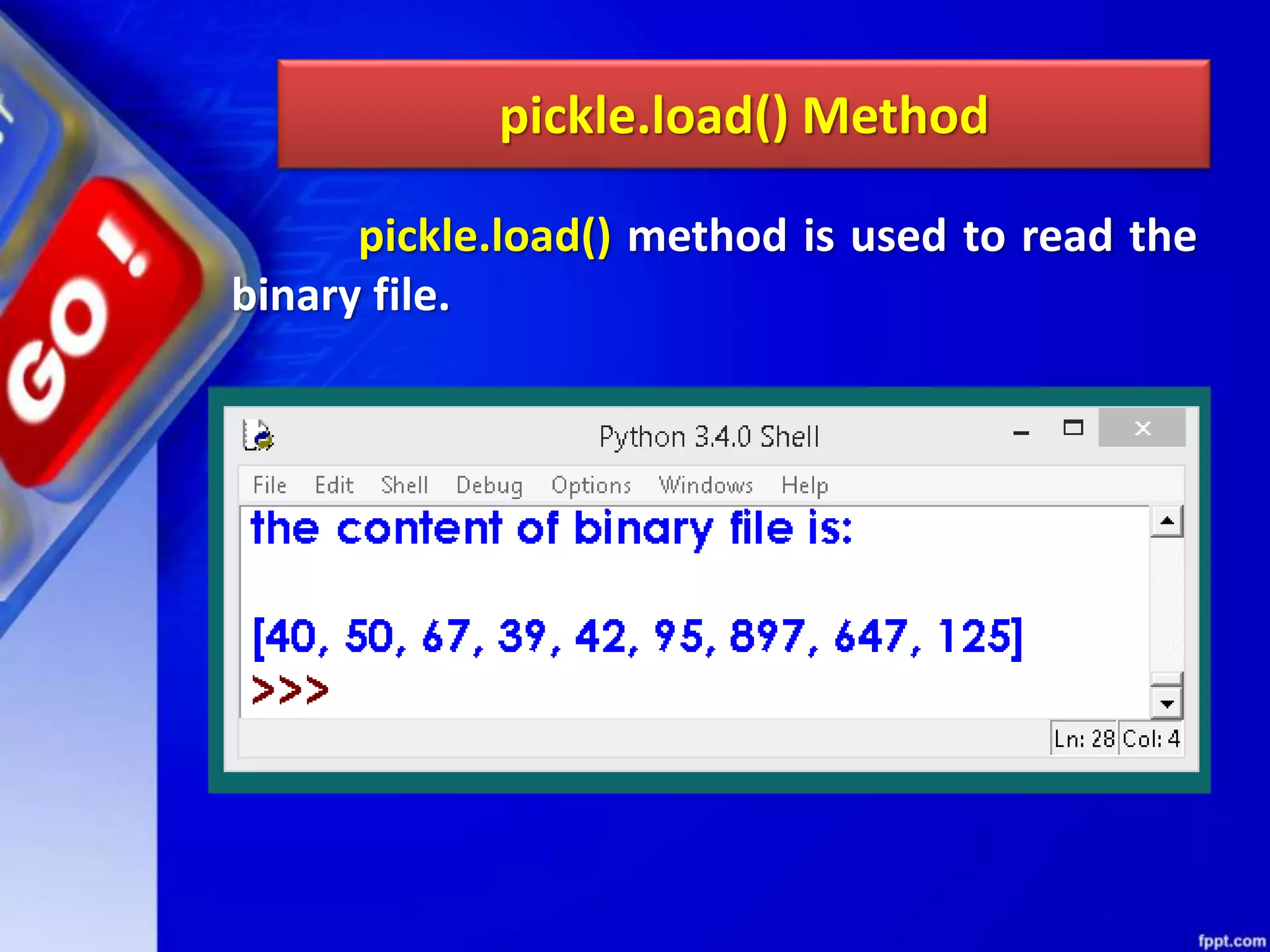






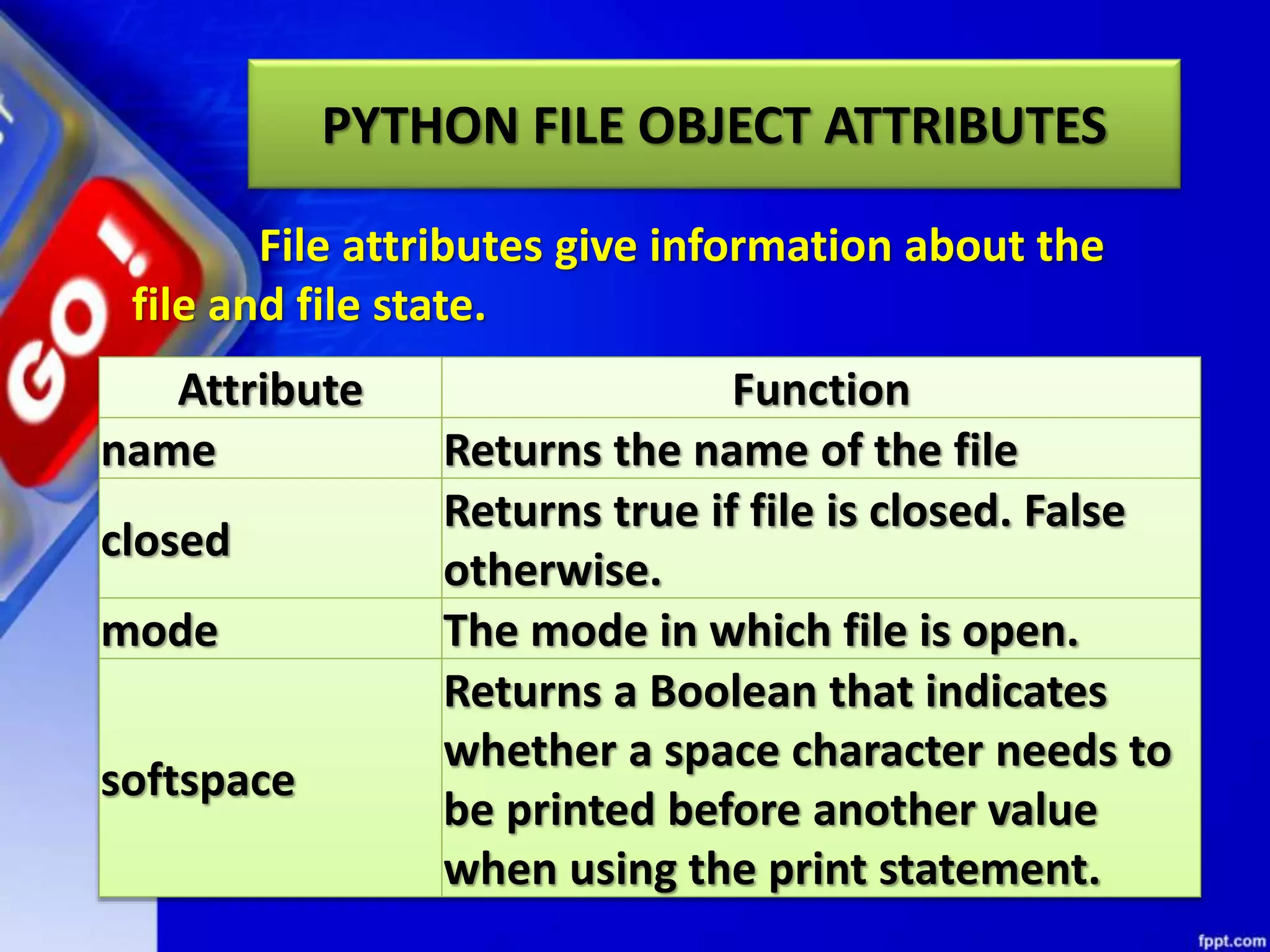

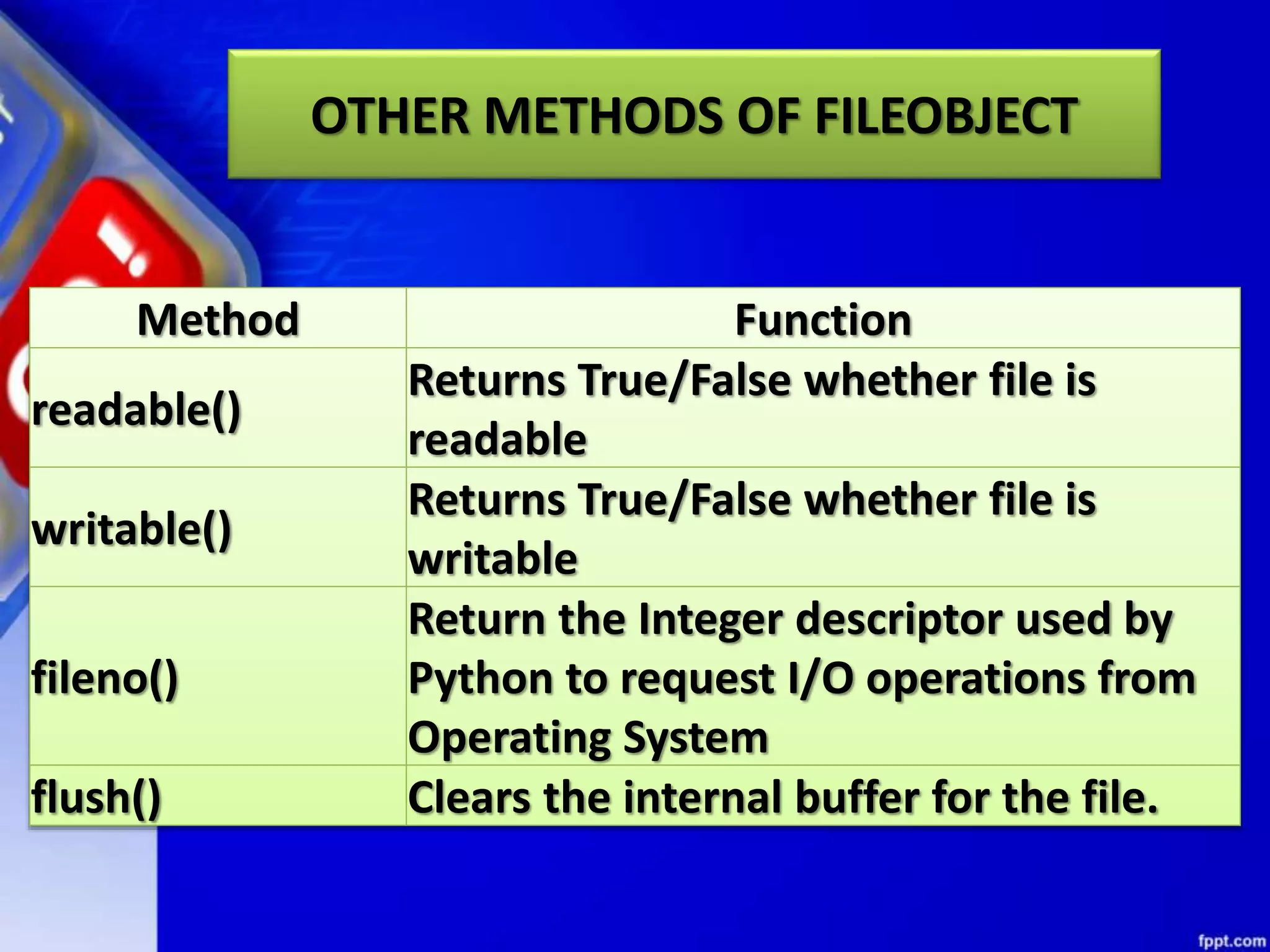
![OTHER METHODS OF FILEOBJECT Method Function isatty() Returns True if file is connected to a Tele-TYpewriter (TTY) device or something similar. truncate([size) Truncate the file, up to specified bytes. next(iterator,[def ault]) Iterate over a file when file is used as an iterator, stops iteration when reaches end-of-file (EOF) for reading.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter08datafilehandling-190528091659/75/Chapter-08-data-file-handling-104-2048.jpg)