This document summarizes a research paper that proposes a method for document layout analysis of Hindi newspaper images using inverse support vector machines (I-SVM). The method extracts blocks of text and graphics from newspaper images using bounding boxes. Feature vectors are extracted from each block and classified using an I-SVM classifier to determine the block type and analyze the newspaper layout. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm for newspaper layout analysis and article extraction.

![International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395 -0056 Volume: 04 Issue: 01 | Jan -2017 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2017, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 5.181 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 58 III. Data for work Data in a newspaper document analysis are usually captured by optical scanning and stored in a file of picture elements, called pixels that are sampled in a grid pattern throughout the document. These pixels may have values: OFF (0) or ON (1) for binary images, 0–255 for gray-scale images and 3 channels of 0–255 colour values for colour images. At a typical sampling resolution of 120 pixels per centimeter, a 20 x 30 cm page would yield an image of 2400x3600 pixels. When the document is on a different medium such as microfilm, palm leaves, or fabric, photographic methods are often used to capture images. In any case, it is important to understand that the image of the document contains only raw data that must be further analyzed to collect the information. IV. PROPOSED IMPLEMENTATION We have used scanned images of Hindi newspapers for our experimentation. Each document provides for a number of blocks, typically an average of multiple blocks exists in a single newspaper image. We use Bounding box to obtain these blocks. This is the most important stage of document layout OCR system. Relevant information from the selected data has been extracted for classification. Different shapes of the character parts have been selected from feature selection algorithm. They might be curves or points or linear shapes. But most of them are open curve shaped. In feature extraction, two techniques are proposed here. One is support vector based sub line direction and the other one is bounding box based shape detection. Here, directions are extracted by sub line direction and bounding box procedures from selected portion of character image. A. Preprocessing Of newspaper data The gray scale image is first binaries using the method described in our earlier work [2]. Horizontal and vertical lines are then removed on the basis of aspect ratio of connected components. B. Inverse-SVM classification The classification strategy we have adopted combines both deterministic and probabilistic decision making. First, using training samples, we try to learn the various conflicts among classes and equivalent representations for every class. . From here, we use probabilistic classification to assign a label to the test pattern. The important point to observe here is, the switch to conflict resolution can happen at any level (from 1 to 4), since conflicts can be defined at various levels. Usually this will be dictated by certain trade-offs between accuracy and precision-recall, as we show later. The classifier we use to resolve conflicts is the Inverse Support Vector Machine (I-SVM). Though it is not mandatory to use SVMs, their utility in character recognition has been well documented. We have chosen RBF kernel, and the SVM formulation “support vector classification” for multi-class classification. C. SOBEL OPERATOR The most popular approximation of equation (1) but using a 33 mask is the following. )2()2()2()2( 741963321987 zzzzzzzzzzzzf (1) This approximation is known as the Sobel operator. If we consider the left of mask the Sobel operator, this causes differentiation along the y direction. If we isolate the following part of the mask and treat it as a one dimensional mask, we are interested in finding the effects of that mask. We will therefore, treat this mask as a one dimensional impulse response ][nh of the form Sobel operator - 1 00 2 - 2 1 0 - 1 1 -1 0-2 0 0 1 2 1 -1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irjet-v4i109-171031071353/75/Document-Layout-analysis-using-Inverse-Support-Vector-Machine-I-SVM-for-Hindi-News-Paper-in-Image-Processing-2-2048.jpg)
![International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395 -0056 Volume: 04 Issue: 01 | Jan -2017 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2017, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 5.181 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 59 otherwise0 11 02 11 ][ n n n nh The above response applied to a signal ][nx yields a signal ]1[][2]1[][ nxnxnxny or in z-transform domain )()1(cos2)()()2()( 1 jXjYzXzzzY . (2) Therefore, ][nh is the impulse response of a system with transfer function )()1(cos2)( jHjH Shown in the figure below for ],0[ . This is a low pass filter type of response. Therefore, we can claim that the Sobel operator has a differentiation effect along one of the two directions and a smoothing effect along the other direction. D. Finding text lines Precise identification of text lines is an important part for most OCR systems. It is also very useful for document layout analysis. Numerous methods have been proposed for text line and baseline finding. Some methods attempt to find just text lines, e.g. by using Hough transforms, projection profiles, and Radon transforms. Others find text lines as part of more general document layout analysis tasks, e.g. XY cuts, whitespace segmentation, Voronoi diagrams, and distance-based grouping. Usually, such methods start by performing a rough analysis of the layout, often based on the proximity of bounding boxes of connected components or connected components themselves. More precise base- and text-line models are employed in subsequent steps, as required. The text line fitting algorithm correctly identified all lines present in the documents when the extracted bounding boxes allowed it to do so. No spurious text lines were detected, and some short one-word lines were ignored. One particularly interesting property of this algorithm is that it allows variations in text line orientations. This permits the algorithm to be applied to document images captured by photo or video cameras rather than by scanners. E. MORPHOLOGICAL OPERATION A morphological operation is used to remove the noise and smooth the shape of the candidate text areas. The element used here is also cross-shaped with size 11x45. The size of the elements for the morphological operations and the geometrical constraints give to the algorithm the ability to detect text in a specific range of character sizes (12-48 pixels). F. Canny edge detection We use canny edge detector applied in grey scale images. Canny uses Sobel masks in order to find the edge magnitude of the image, in gray scale, and then uses non- Maxima suppression and hysteresis thresholding. With these two post-processing operations canny edge detector manage to remove no maxima pixels, preserving the connectivity of the contours. After computing the Canny edge map, dilation by an element 5x21 is performed to connect the character contours of every text line. Dilation by a cross-shaped element 5x21 is performed to connect the character contours of every text line. G. Pseudo code of proposed method 1. Initialize input image from dataset 2. If input image in RGB format then convert in gray image 3. If no then go to next step 4. Now do the preprocessing step using Bounding box 5. Also apply the morphology operation 6. Then extract the feature 7. Testing and classification using Inverse support vector machine 8. Find the F-measure, Accuracy and Precision Recall value. 9. Finally get the output result 10. End 2 1 -1 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irjet-v4i109-171031071353/75/Document-Layout-analysis-using-Inverse-Support-Vector-Machine-I-SVM-for-Hindi-News-Paper-in-Image-Processing-3-2048.jpg)

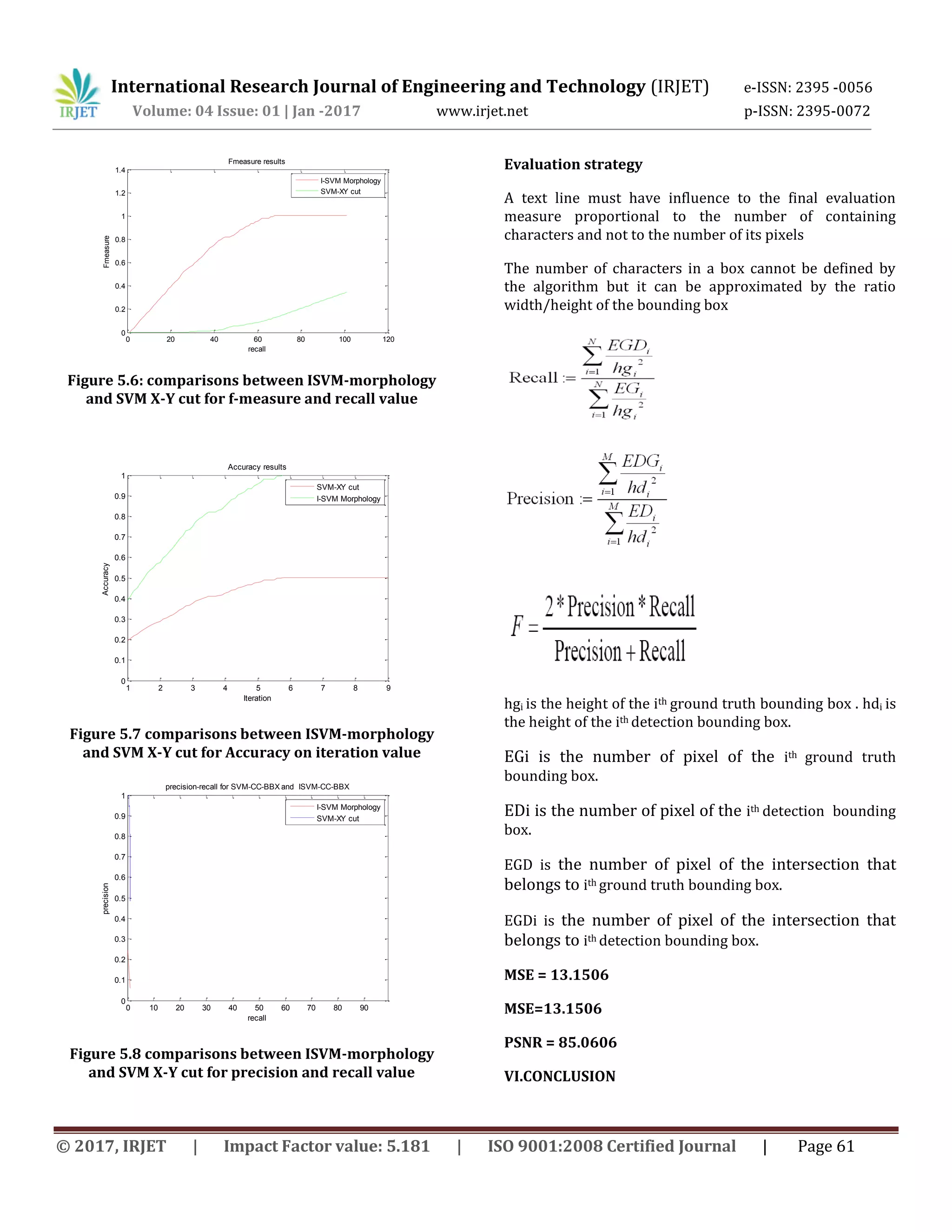
![International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395 -0056 Volume: 04 Issue: 01 | Jan -2017 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2017, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 5.181 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 62 In this paper, document layout analysis text extraction techniques such as I-SVM, bounding box, sobel operator, morphological method etc. have been discussed. The performance comparison of these methods for document text extraction on the basis of accuracy, precision rate, recall rate, processing time has been done. It is observed that better accuracy is best for document texture Analysis) approach and edge based text extraction techniques. Precision and recall rate is best in case of I-SVM algorithm and segmentation method. Future work We plan to exploit the colour homogeneity of text temporal, text detection from frame to frame.Multi-frame integration for image enhancement REFERENCES [1] Vijay Singh and Bhupendra Kumar “Document layout analysis for Indian newspapers using contour based symbiotic approach” 2014 International Conference on Computer Communication and Informatics (ICCCI -2014), Jan. 03 – 05, 2014, Coimbatore, INDIA. [2] S. Malakar, S. Halder, R. Sarker, N. Das, S. Basu, M. Nasipuri, Text line Extraction from Handwritten Document pages using spiral run length smearing algorithm, International Conference on communications, Devices and Intelligent Systems, Kolkata, Dec. 28-29 (2012) 616-619. [3] S.J. Ha, B. Jin, N.I. Cho, Fast Text Line Extraction in Document Images, 19th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Orlando, Sept. 30-Oct 3 (2012) 797-800. [4] S.V. Seeri, S. Giraddi, Prashant B.M, A Novel Approach for Kannada Text Extraction, Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Informatics and Medical Engineering, Tamil Naidu, Mar. 21-23 (2012) 444-448. [5] Z. Li, J. Luo, Resolution Enhancement from Document Images for Text Extraction, 5th International Conference on Multimedia and Ubiquitous Engineering, Loutraki, June 28- 30 (2011) 251-256. [6] D. Zaravi, H. Rostami, A. Malahzaheh, S.S Mortazavi, Journals Subheadlines Text Extraction Using Wavelet Thresholding and New Projection Profile, World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology, 49 (2011) 686-689. [7] T.V. Hoang, S. Tabbone, Text Extraction From Graphical Document Images Using Sparse Representation, International Workshop on Document Analysis Systems, June 9-11 (2010) 143-150. [8] P. Nagabhushan, S. Nirmala, Text Extraction in Complex Color Document Images for Enhanced Readability, Intelligent Information Management, 2 (2010) 120-133. [9] D. Dunn, W. E. Higgins, and J. Wakeley, “Texture segmentation using 2-D Gabor elementary functions,” IEEE transaction on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 130-149, 1994. [l0] W. Chan and G. Coghill, “Text analysis using local energy,” Pattern Recognition, vol. 34, pp. 2523-2532,2001. [l1] U. Pal and B. B. Chaudhuri, “Script line separation from Indian muliti-script document,” in Proceedings of the International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, pp. 406-409, 1999. [I21 D. Dhanya, A. G. Ramakrishnan, and P. B. Pati, “Script identification in printed bilingual docuements,” Sadhana, vol. 27, pp. 73-82,2002. [13] Chih-Wei Hsu, Chih-len Lin. A comparison of methods for multiclass support vector machines. IEEE Trans Neural Networks. 13: 415-425, March (2002). [14] Vijay singh and Bhupendra kumar “document layout analysis for Indian newspapers using contour based symbiotic approach”, 2014 International Conference on Computer Communication and Informatics (ICCCI - 2014),IEEE. [15] Chih-Chung Chang and Chih-Jen Lin, LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines, Software available at http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/ cjlin/libsvm. [16] F. Liu, Y. Luo, D. Hu, and M. Yoshikawa. A new component based algorithm for newspaper layout analysis. pages 1176 1180. IEEE Computer Society, 2001. [17] S. Mao, A. Rosenfeld, and T. Kanungo. Document structure analysis algorithms: a literature survey. volume 5010 of SPIE Proceedings, pages 197–207. SPIE, 2003.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irjet-v4i109-171031071353/75/Document-Layout-analysis-using-Inverse-Support-Vector-Machine-I-SVM-for-Hindi-News-Paper-in-Image-Processing-6-2048.jpg)