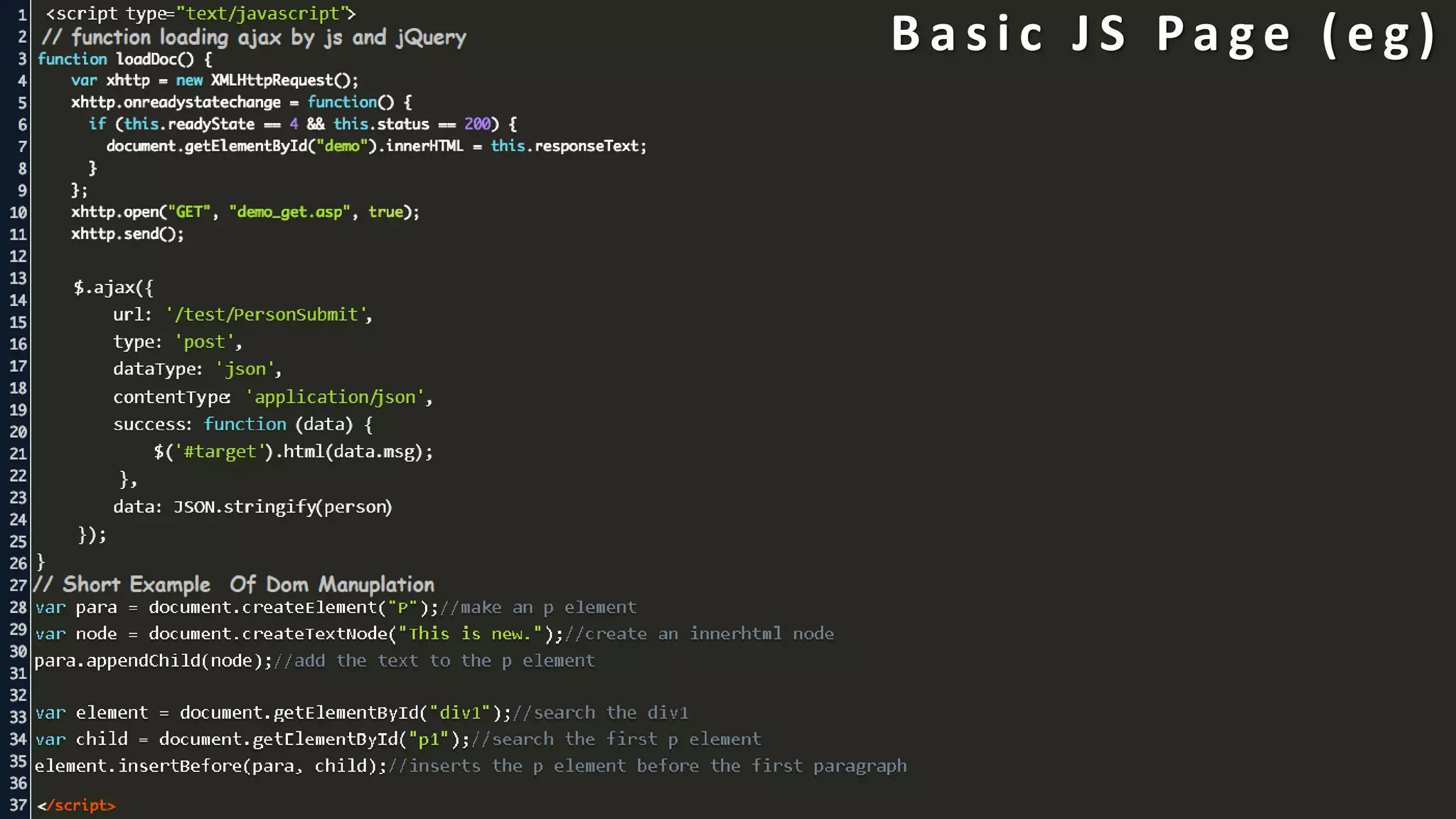
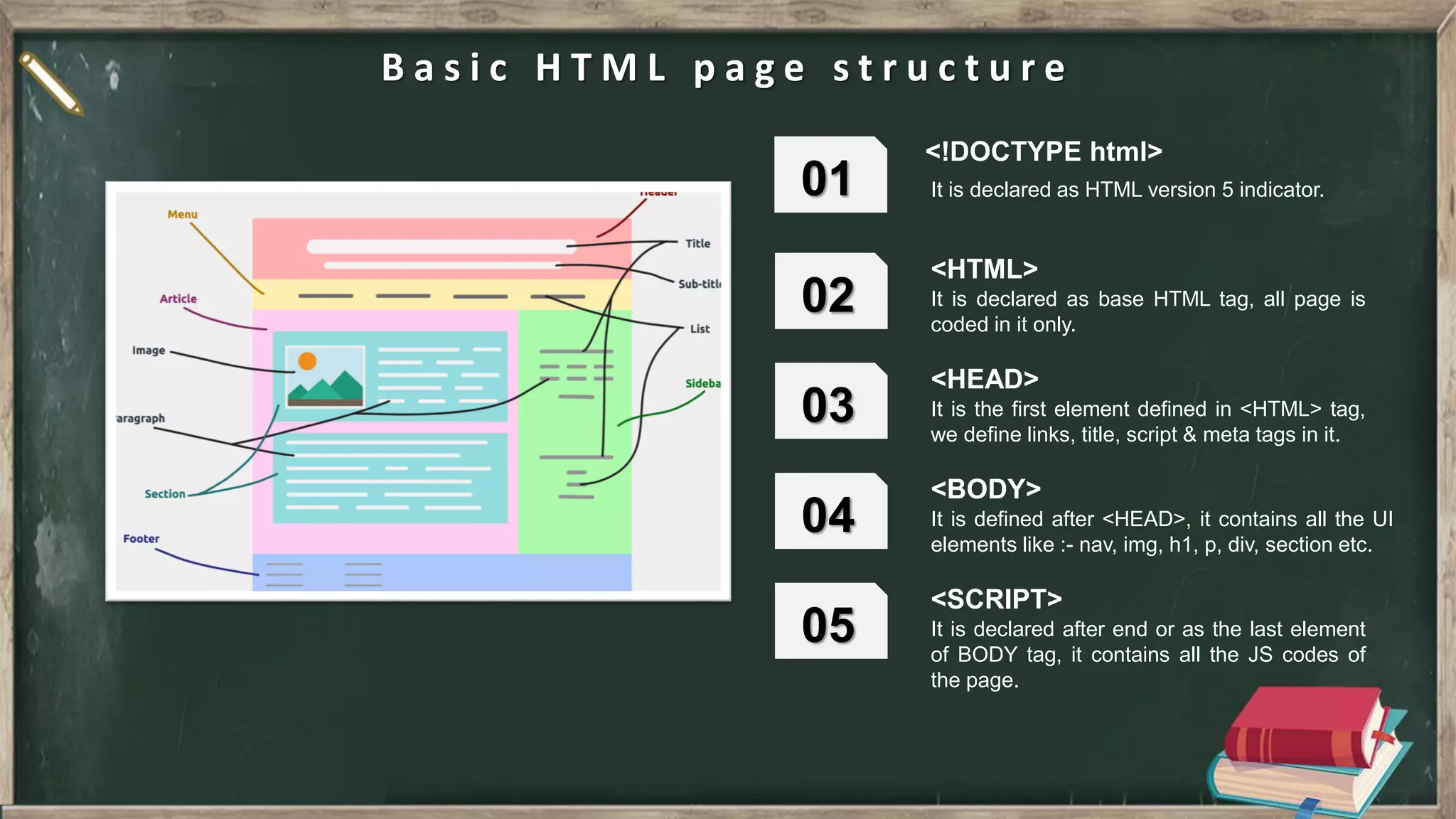
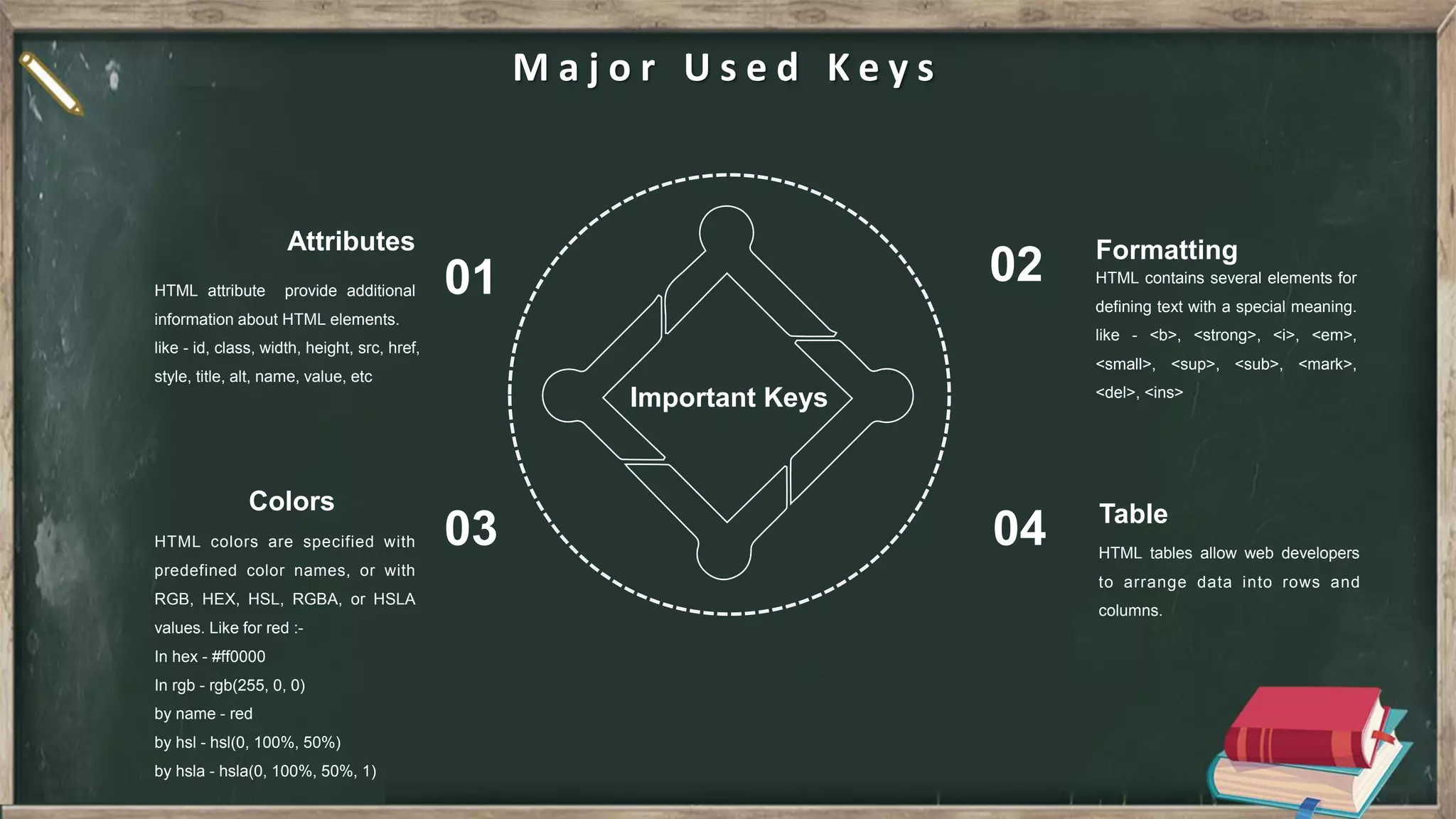
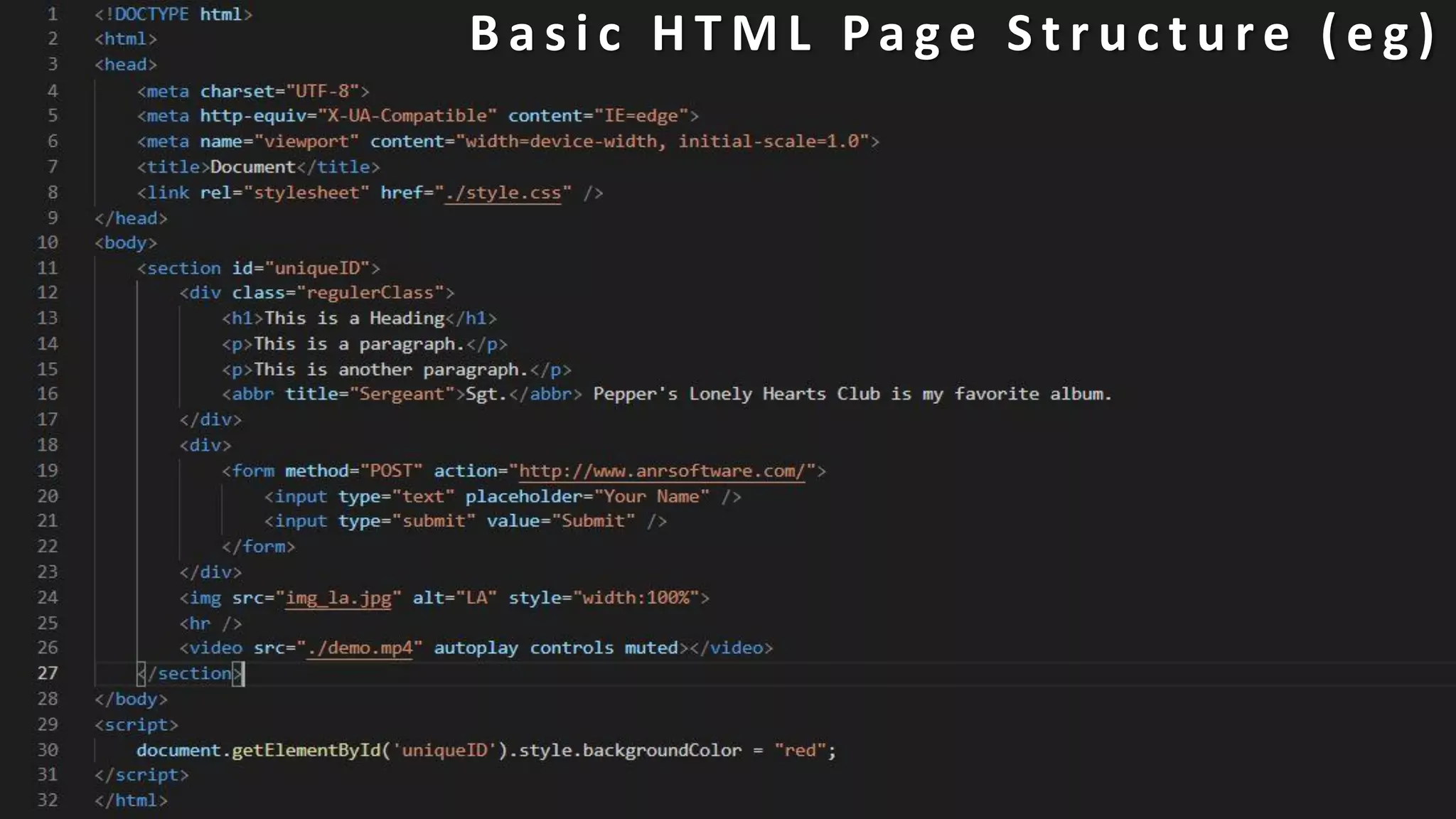
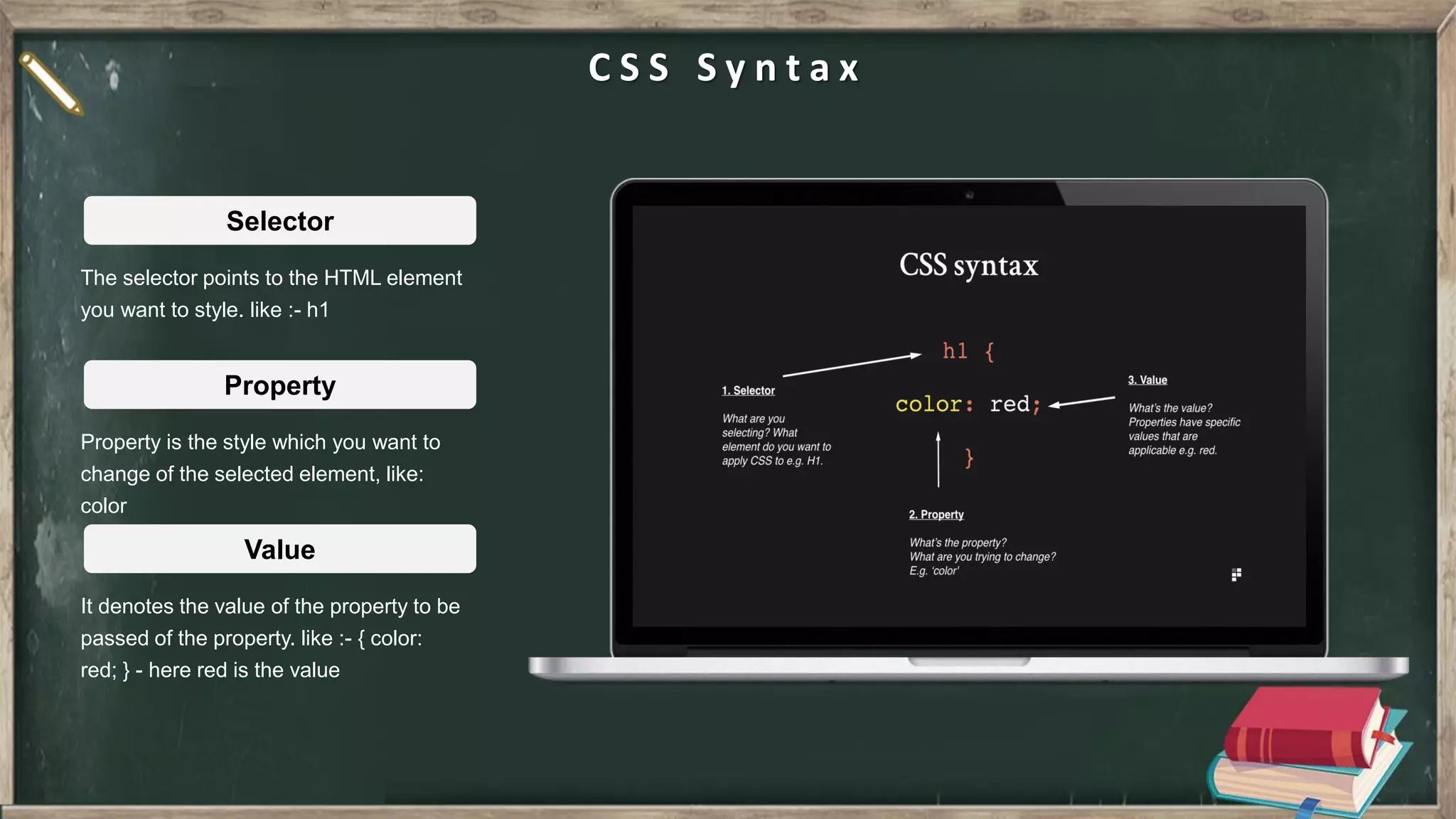
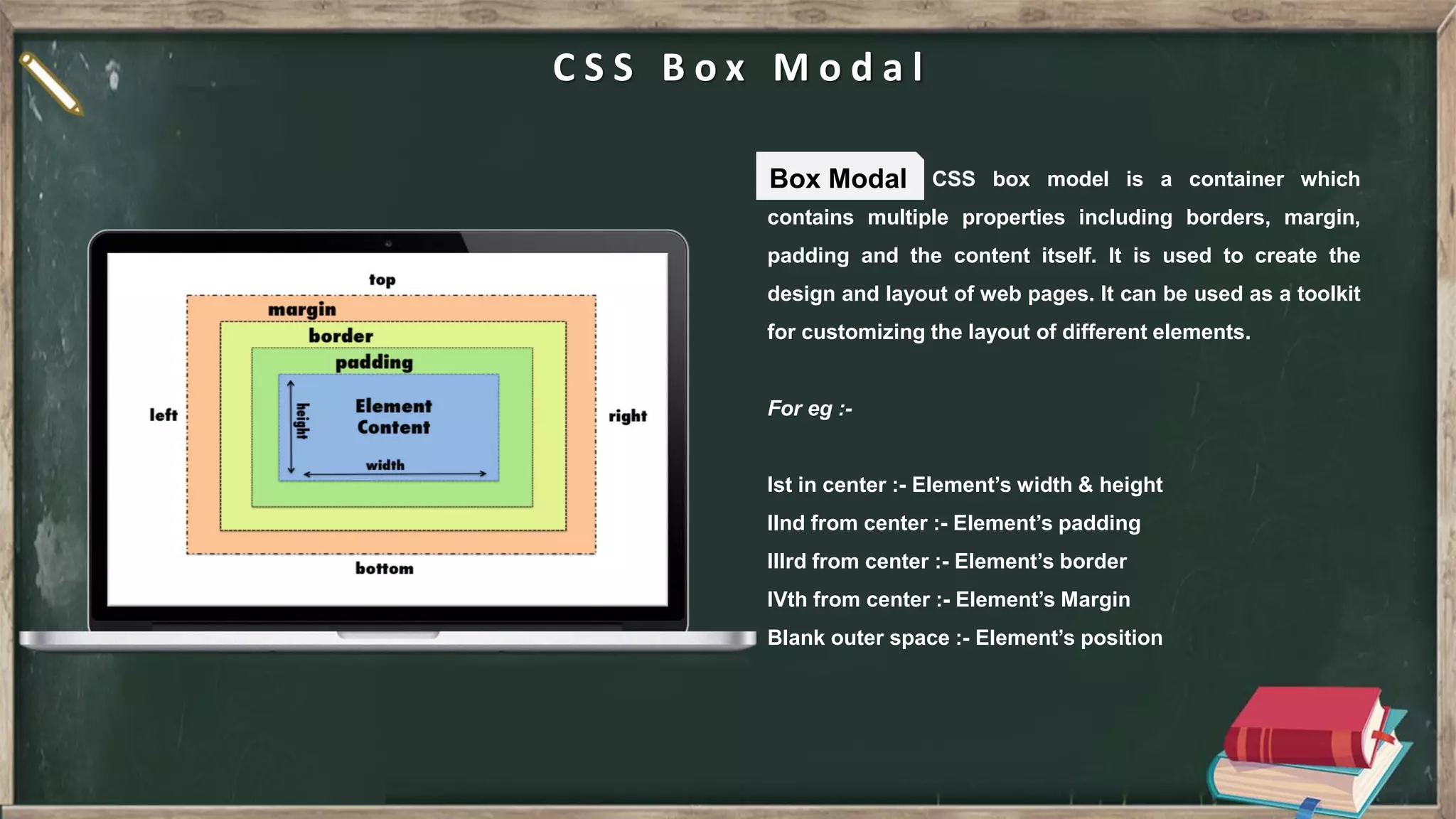
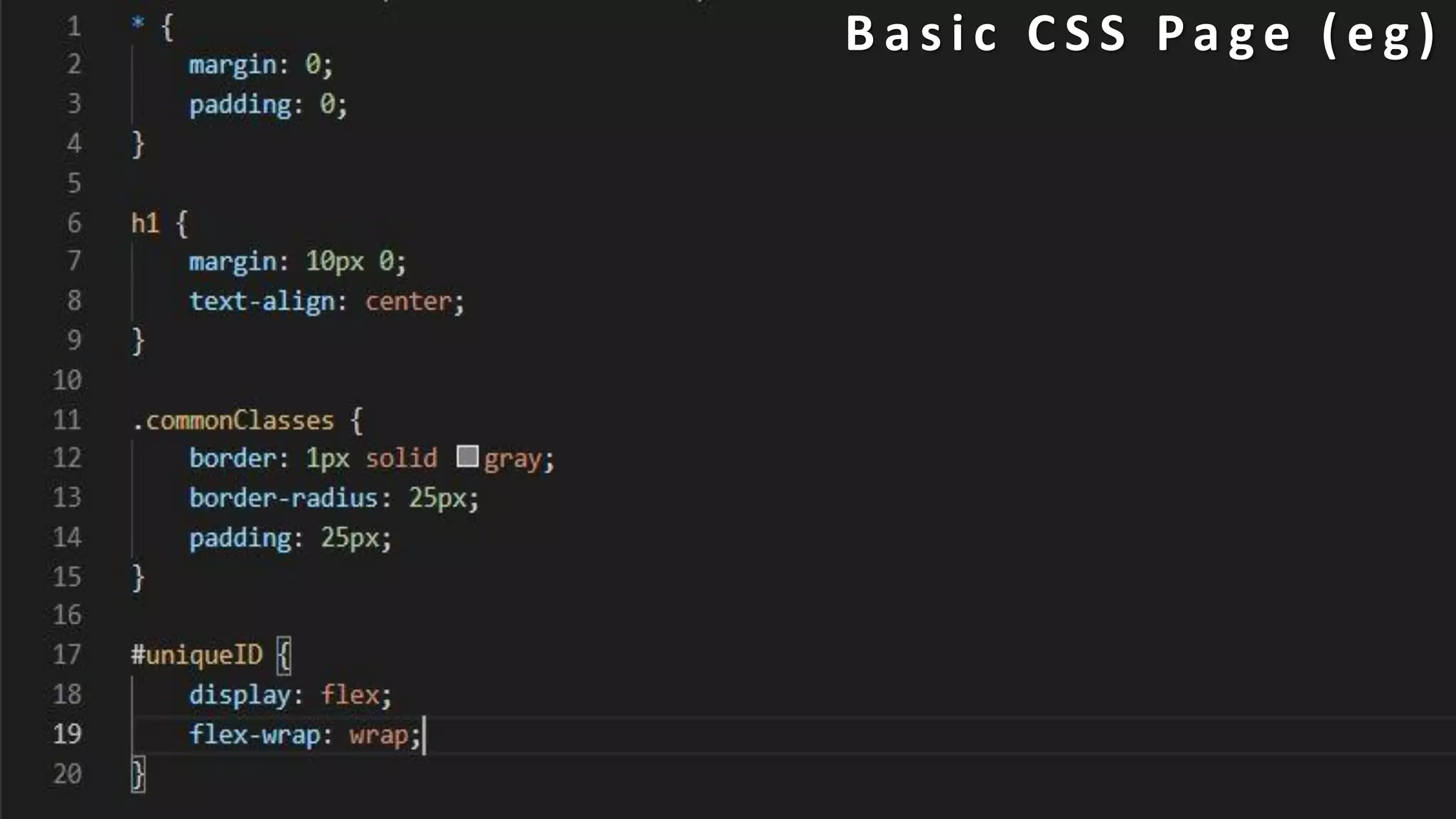
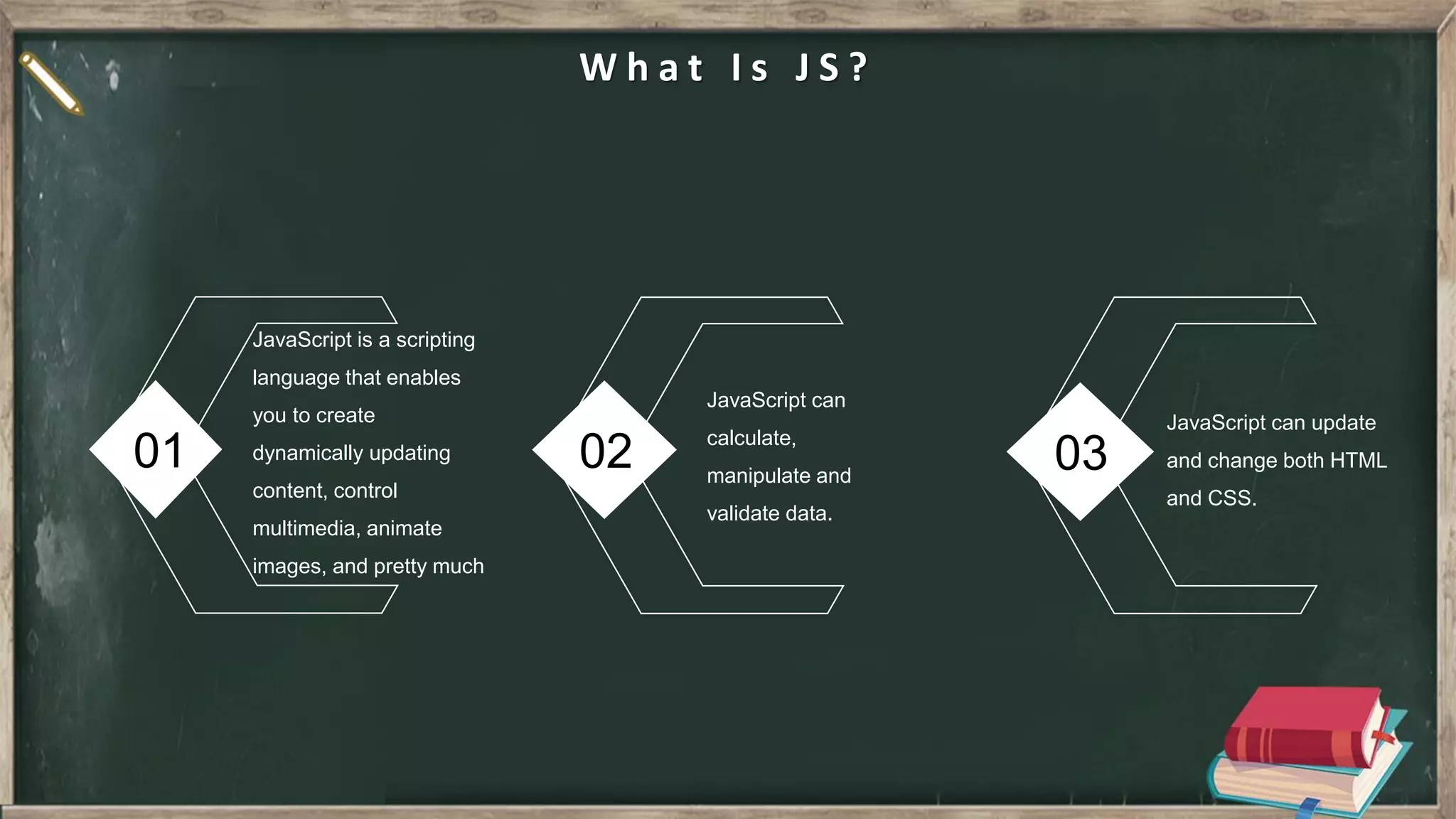
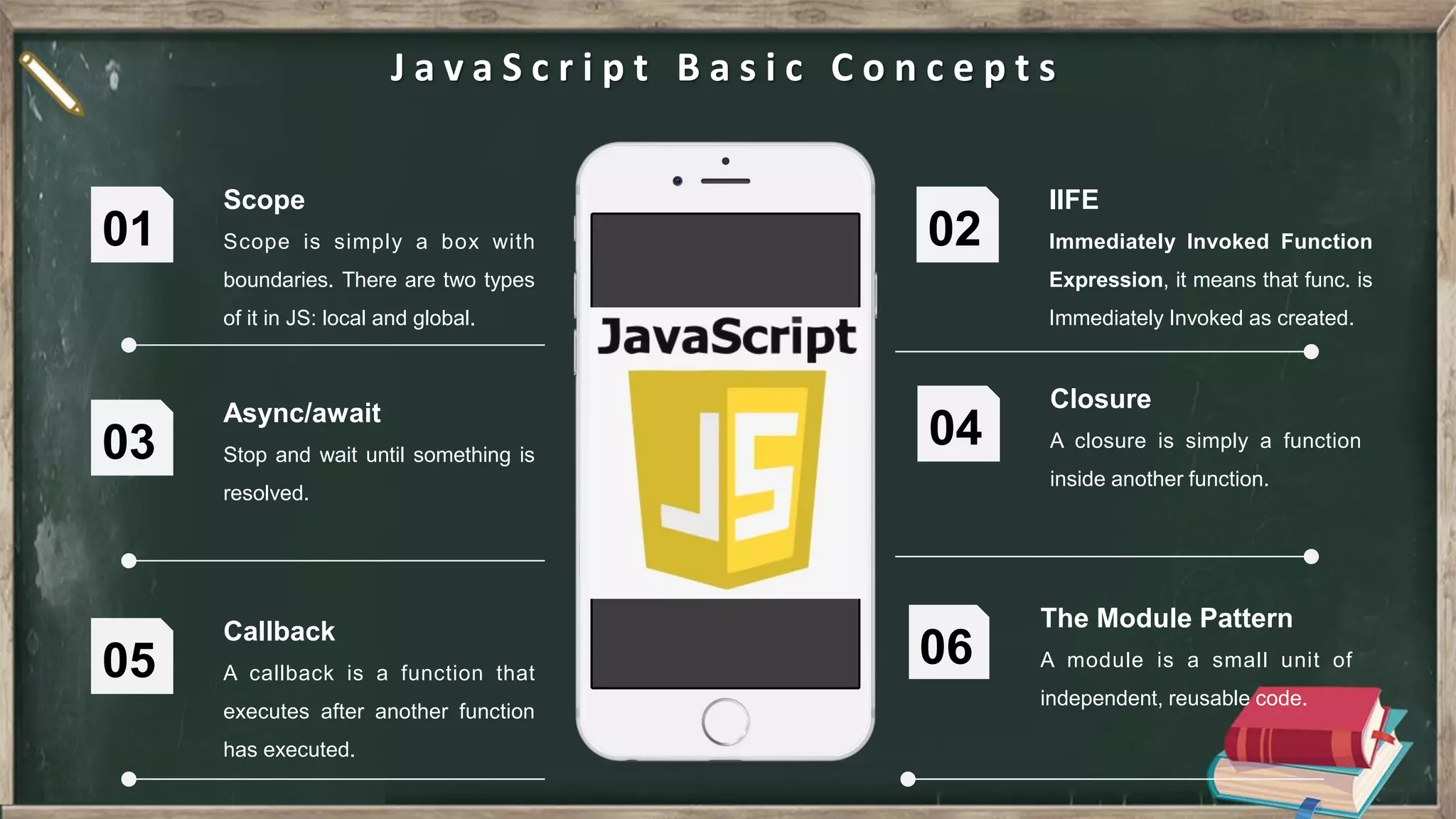
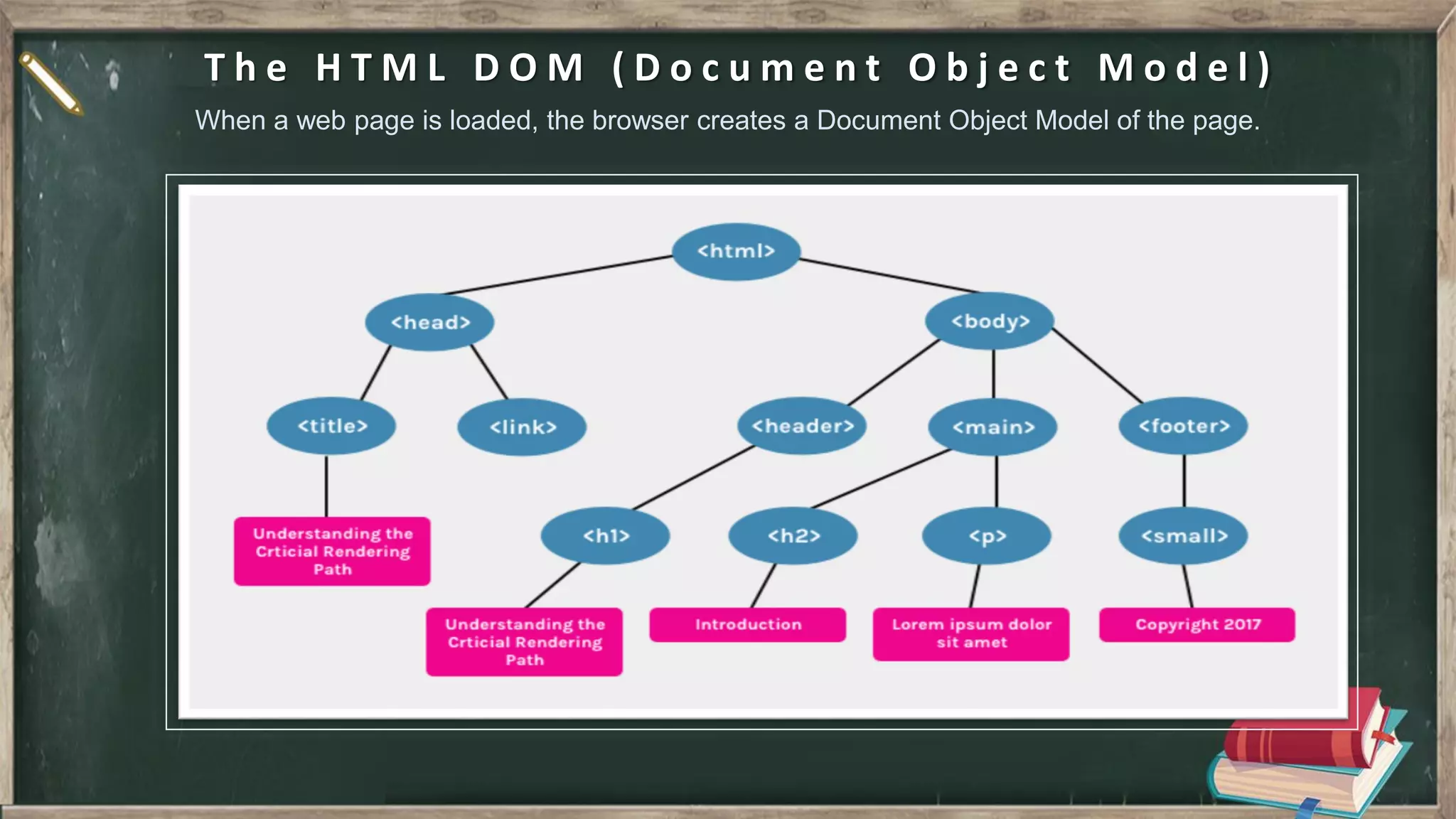
The document provides an introduction to HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. It includes sections on: - What HTML, CSS, and JavaScript are and their purposes. HTML is for describing web pages, CSS is for styling elements, and JavaScript is for creating dynamic content. - Basic HTML page structure including common tags like <html>, <head>, <body>. - Key CSS concepts like selectors, properties, values, and the box model. - Core JavaScript concepts including the DOM, jQuery, AJAX, and the differences between JavaScript and jQuery. - Examples are provided throughout to demonstrate uses of each technology.




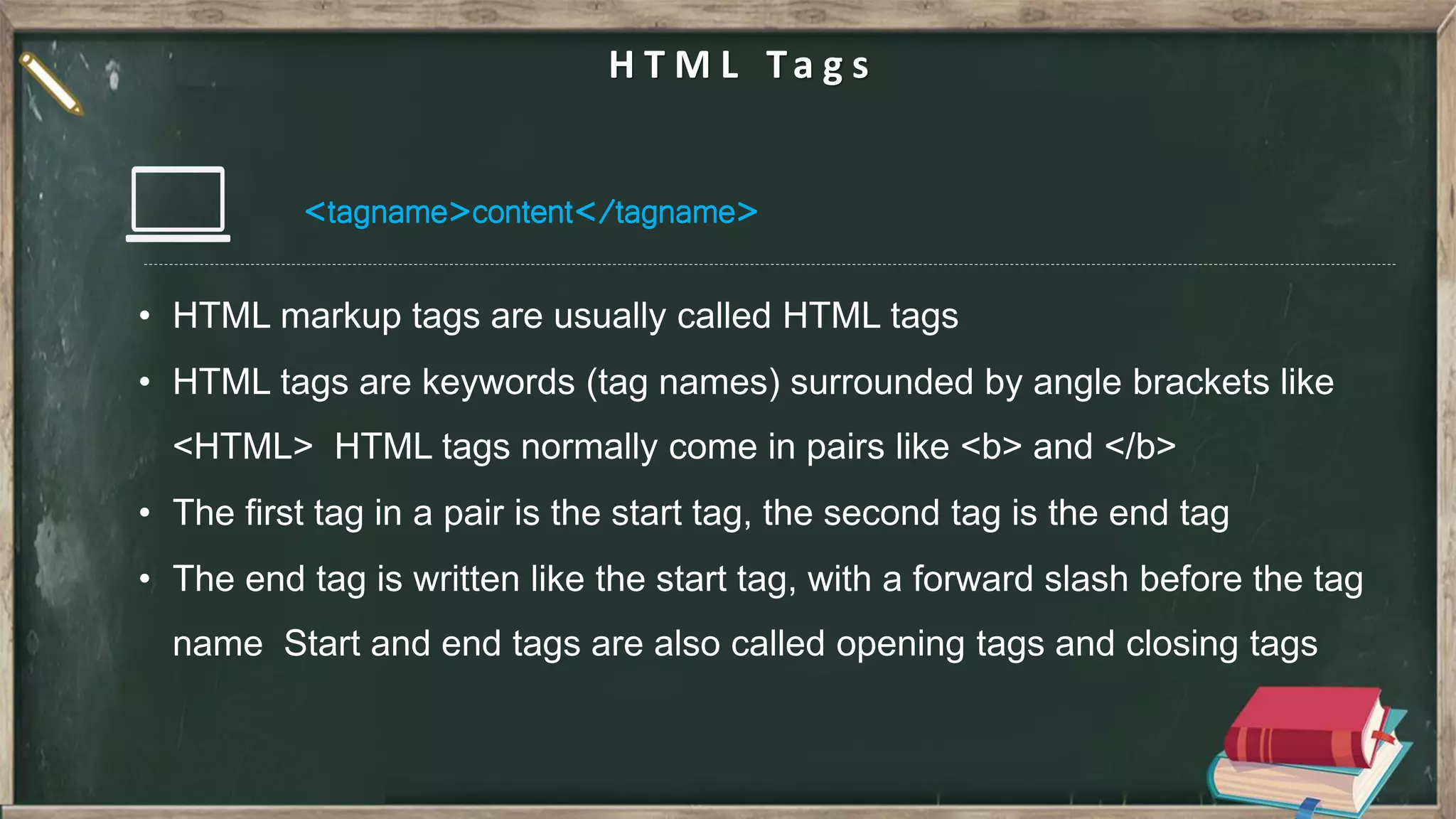





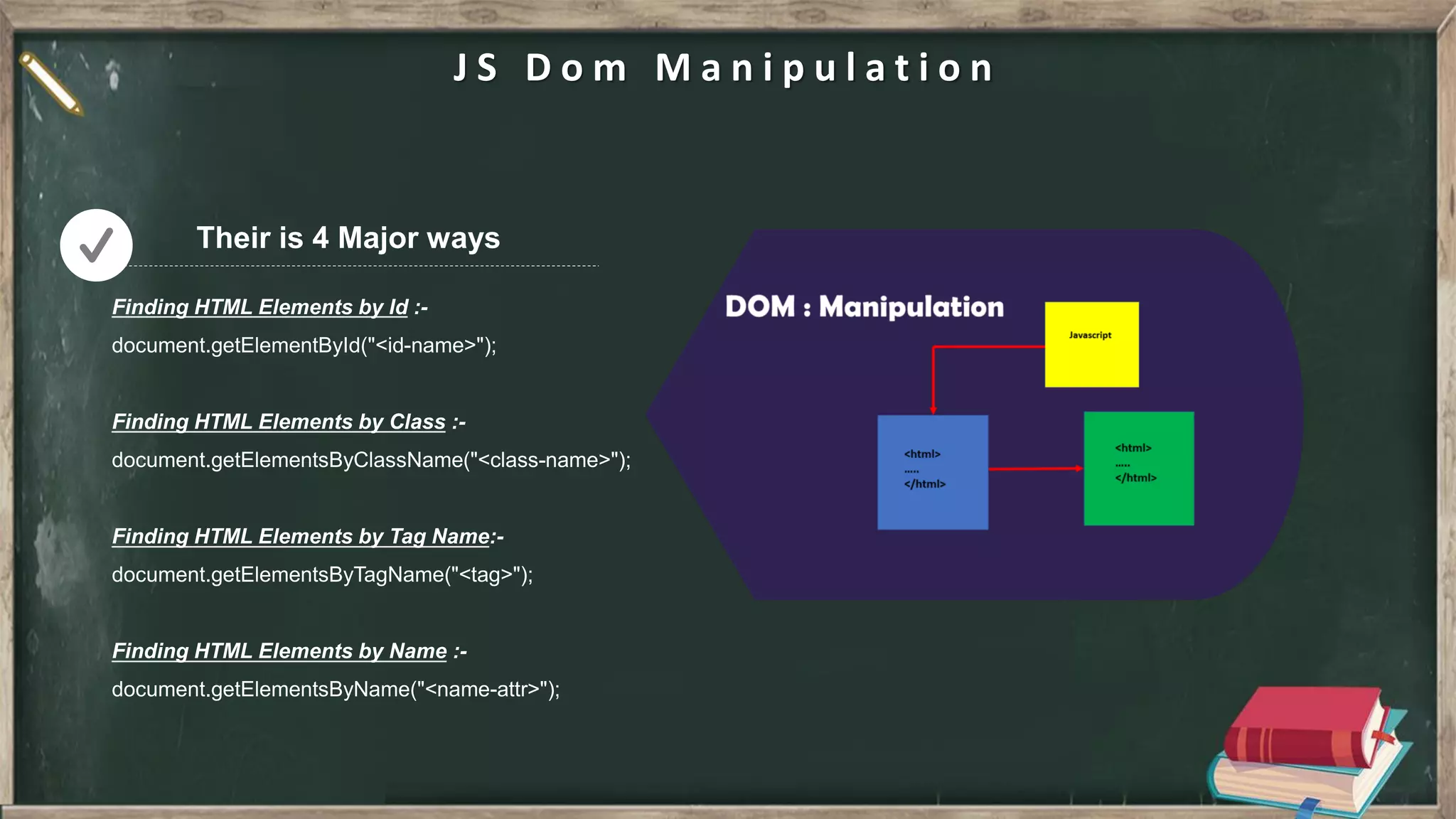
![J Q u e r y j Query is a lightweight, "write less, do more", JavaScript library. The purpose of JQuery is to make it much easier to use JavaScript on your website. JQuery takes a lot of common tasks that require many lines of JavaScript code to accomplish, and wraps them into methods that you can call with a single line of code. For eg :- Finding HTML Element by ID - $(“#uniqueID”) Finding HTML Element by Class - $(“#commonClass”) Finding HTML Element by Tag Name - $(“h1”) Finding HTML Element by Attr Name - $(“[data-attr=value]”) JQuery](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/htmlcssjs-introduction-211130195939/75/HTML-CSS-JS-in-Nut-shell-21-2048.jpg)
![JavaScript JavaScript uses JIT[Just in Time Compiler] which is combination of interpreter and Compile and is written in C. It’s a combination of ECMA script and DOM (Document Object Model). JavaScript is an independent language and can exist on its own. JQuery While JQuery Uses the resources that are provided by JavaScript to make things easier. It is a light-weight JavaScript library. It has only the DOM. JQuery is a JavaScript library. J a v a S c r i p t v s J Q u e r y Conclusion All JQuery code is JavaScript, but JQuery doesn't include all the JavaScript code. The point is that they are not two programming languages. JQuery is just optimized to do the common scripting functions with fewer lines of code](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/htmlcssjs-introduction-211130195939/75/HTML-CSS-JS-in-Nut-shell-22-2048.jpg)