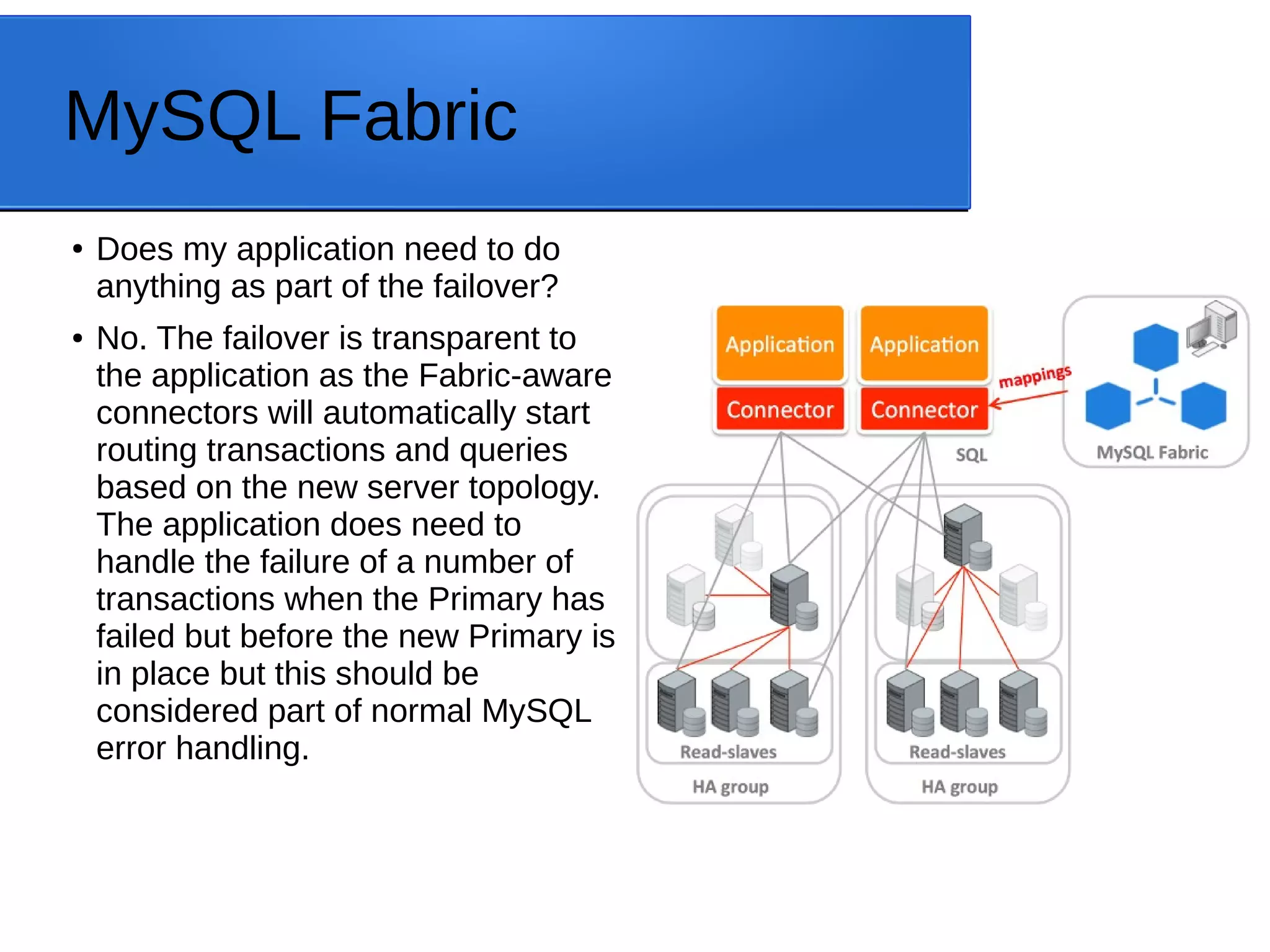
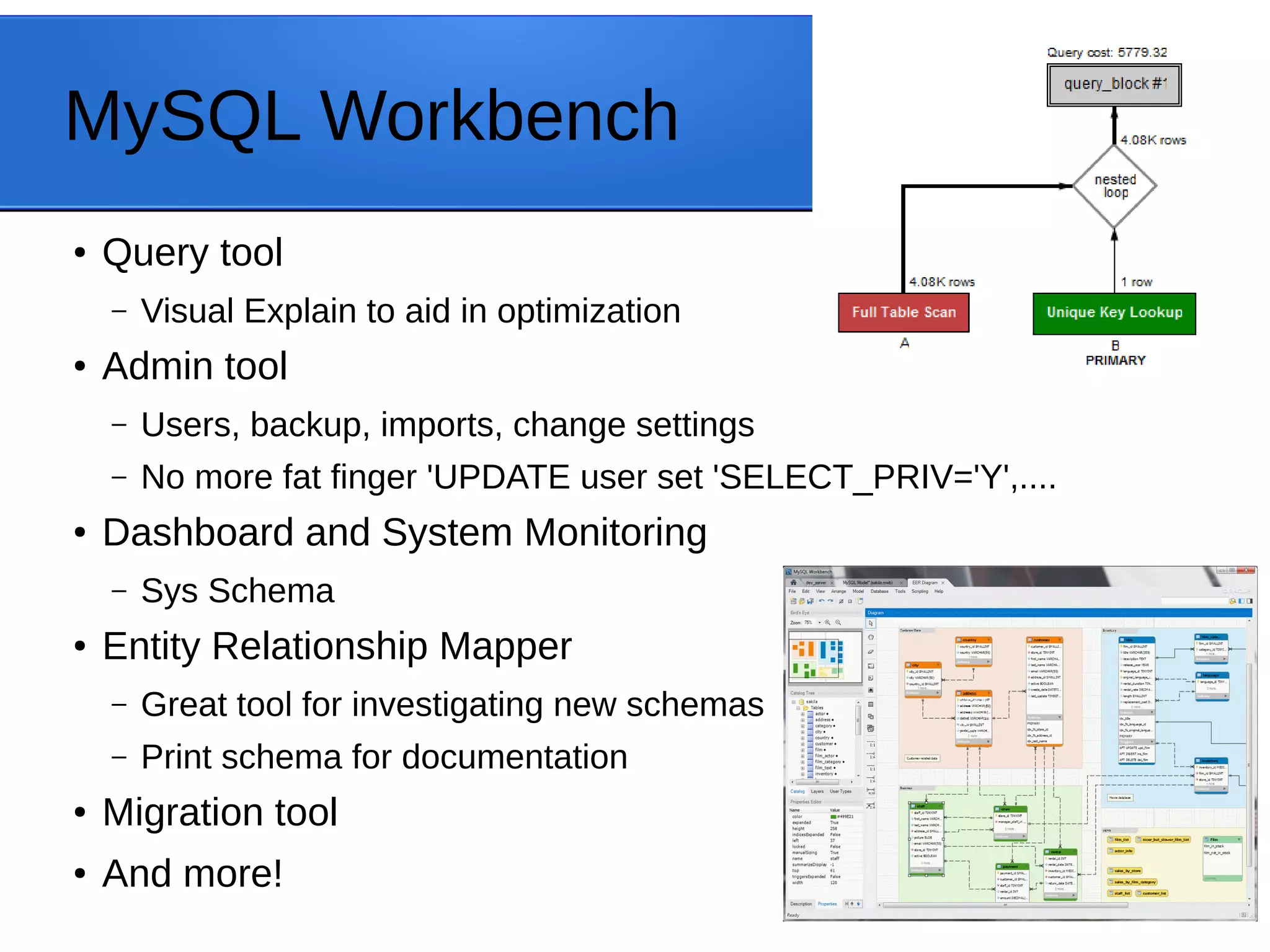
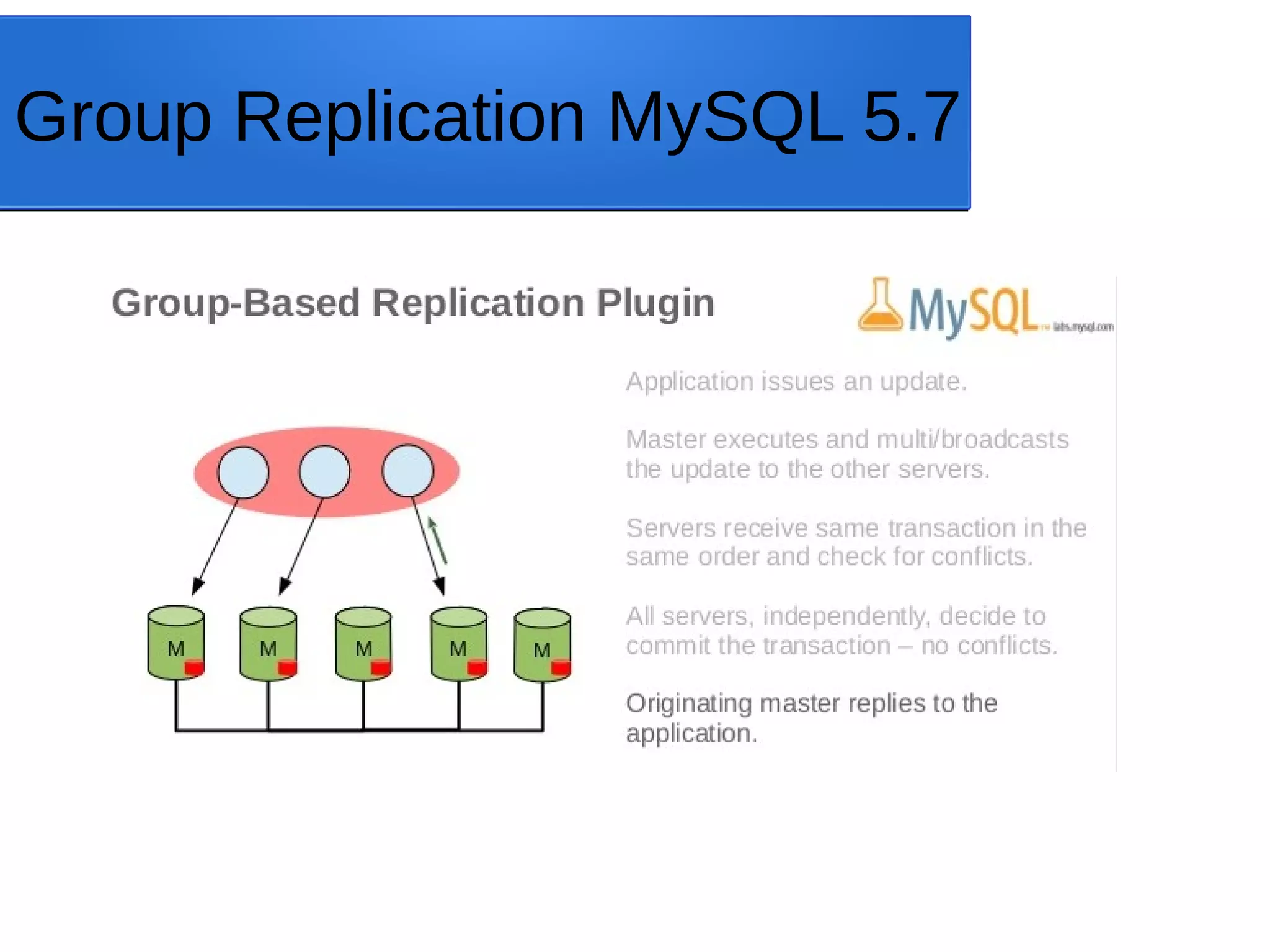
The document outlines MySQL Utilities, a Python-based package for managing MySQL servers, and highlights the features and installation processes across different operating systems. It provides details on various database operations, general operations, high availability operations, and specialized operations for auditing. Additionally, it discusses tools such as MySQL Fabric and MySQL Router for enhancing server management and availability.




















![mysqlrplcheck shell> mysqlrplsync --master=user:pass@localhost:3310 --slaves=rpl:pass@localhost:3311,rpl:pass@localhost:3312 # # GTID differences between Master and Slaves: # - Slave 'localhost@3311' is 15 transactions behind Master. # - Slave 'localhost@3312' is 12 transactions behind Master. # # Checking data consistency. # # Using Master 'localhost@3310' as base server for comparison. # Checking 'test_rplsync_db' database... # - Checking 't0' table data... # [OK] `test_rplsync_db`.`t0` checksum for server 'localhost@3311'. # [OK] `test_rplsync_db`.`t0` checksum for server 'localhost@3312'. # - Checking 't1' table data... # [OK] `test_rplsync_db`.`t1` checksum for server 'localhost@3311'. # [OK] `test_rplsync_db`.`t1` checksum for server 'localhost@3312'. # Checking 'test_db' database... # - Checking 't0' table data... # [OK] `test_db`.`t0` checksum for server 'localhost@3311'. # [OK] `test_db`.`t0` checksum for server 'localhost@3312'. # - Checking 't1' table data... # [OK] `test_db`.`t1` checksum for server 'localhost@3311'. # [OK] `test_db`.`t1` checksum for server 'localhost@3312'. # #...done. # # SUMMARY: No data consistency issue found.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mysqlutilities-150926223542-lva1-app6891/75/MySQL-Utilities-PyTexas-2015-23-2048.jpg)