Embed presentation
Download to read offline







Programmable Logic Array (PLA) is a programmable logic device that implements Boolean functions using programmable AND gates and OR gates. It allows any Boolean function in Sum of Products form to be realized. A PLA has three main components: input buffers, a programmable AND gate matrix, and a programmable OR gate matrix. The input buffers reduce loading on input sources. The AND matrix generates product terms from inputs. The number of AND gates equals the number of minterms. The OR matrix performs addition to produce the output functions. The number of OR gates equals the number of functions. PLAs are easier to design and modify than logic gate networks but are slower and use more chip area.















Introduction of PLA as a programmable logic device in Module 4.
Explanation of PLA as a device for implementing Boolean functions using programmable AND and OR gates.
Description of the main components of PLAs: Input buffer, Programmable AND gate matrix, and OR gate matrix.
Function of input buffers in PLAs, including output generation and their relation to Boolean expression variables.
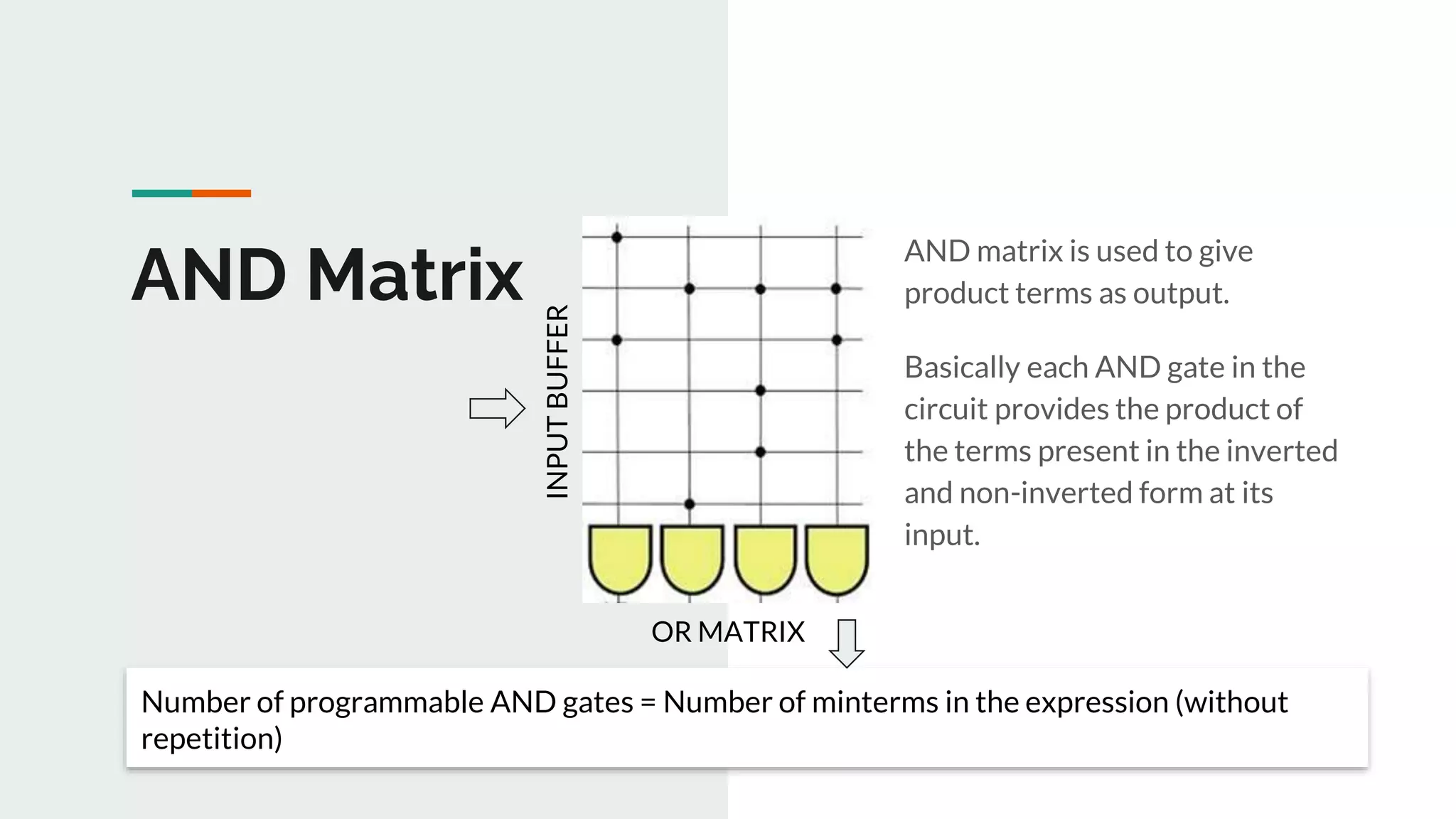
Role of the AND matrix in generating product terms from inputs, with focus on the number of programmable gates.
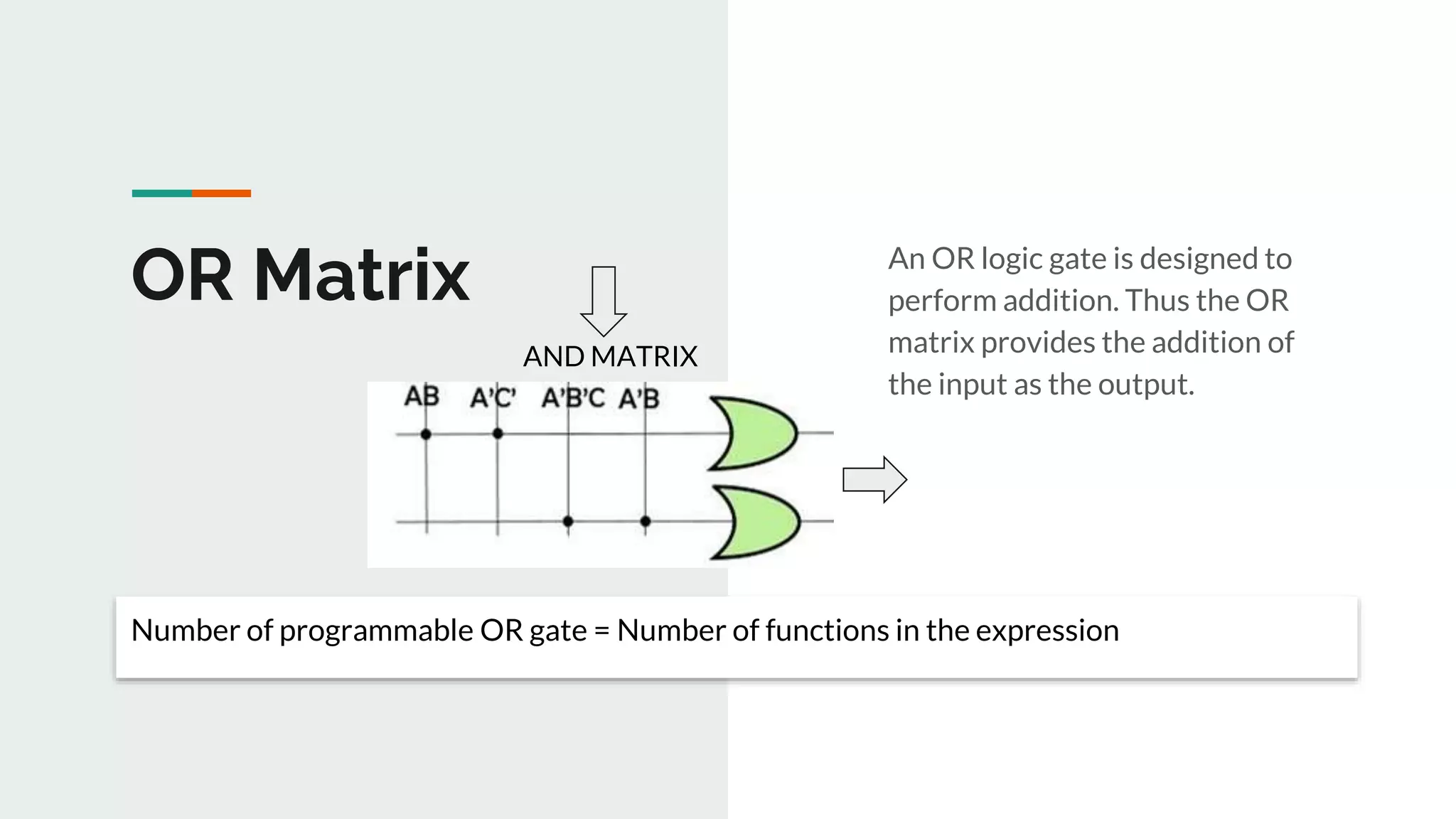
Explanation of the OR matrix and its role in providing output by adding inputs, with relevance to the number of OR gates.
Outline of steps to implement a Boolean expression in a PLA, including connections for buffers, AND, and OR matrices.
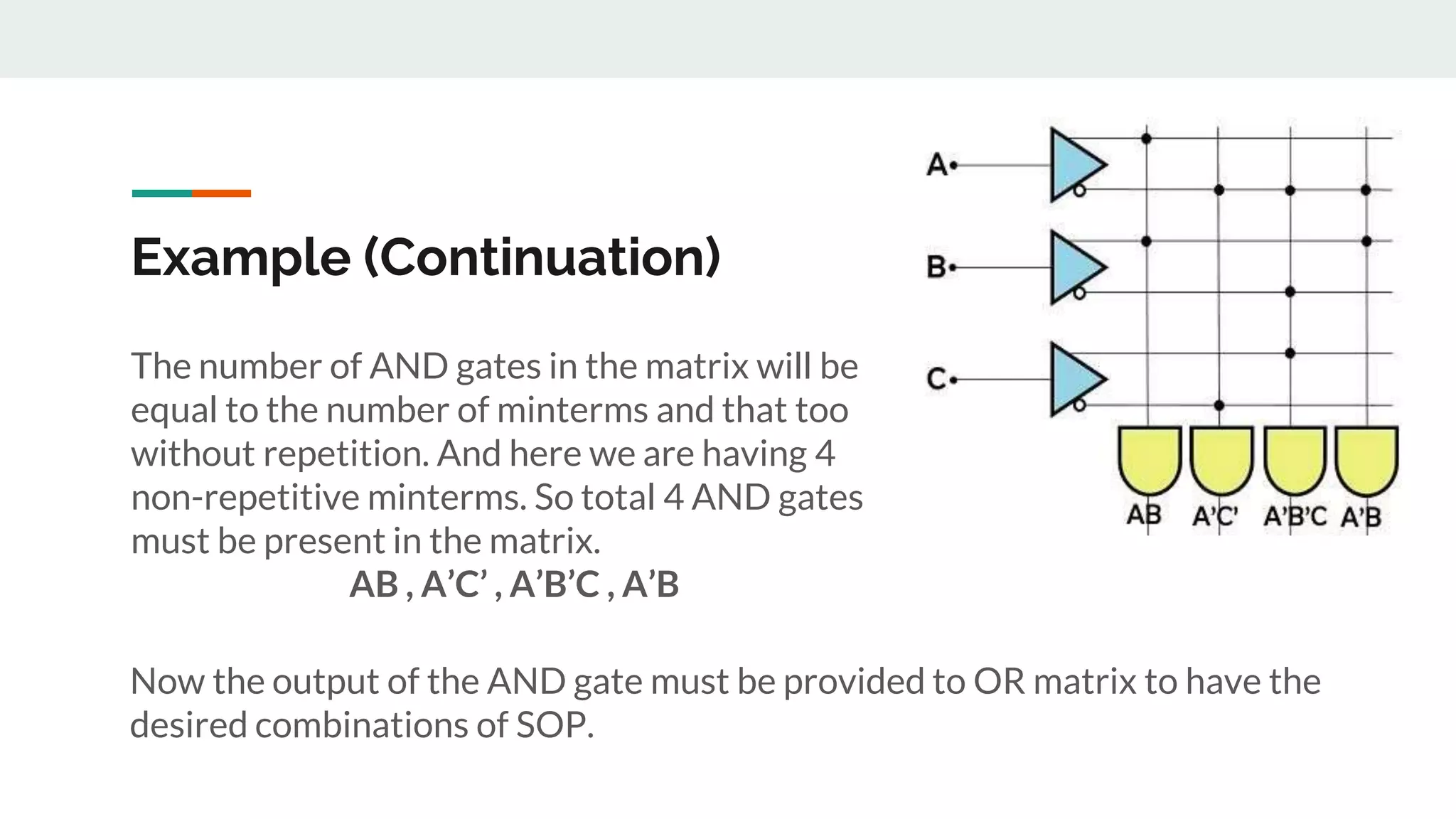
Realization of specific Boolean expressions, showing output connections between input buffers and the AND matrix.
Details on the number of AND gates required in the matrix corresponding to the given Boolean minterms.
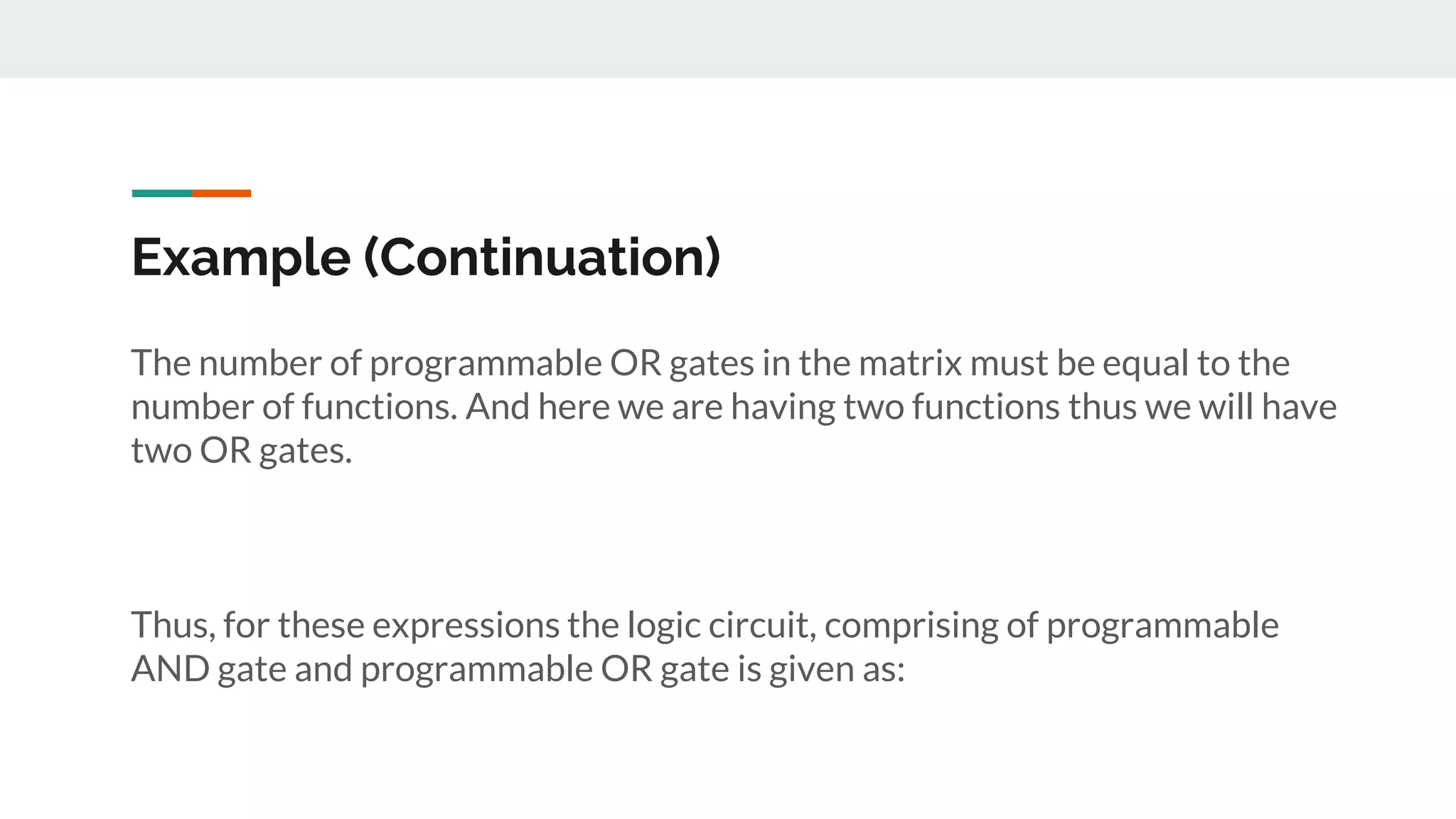
Explanation of the number of programmable OR gates needed in the matrix for the defined functions.
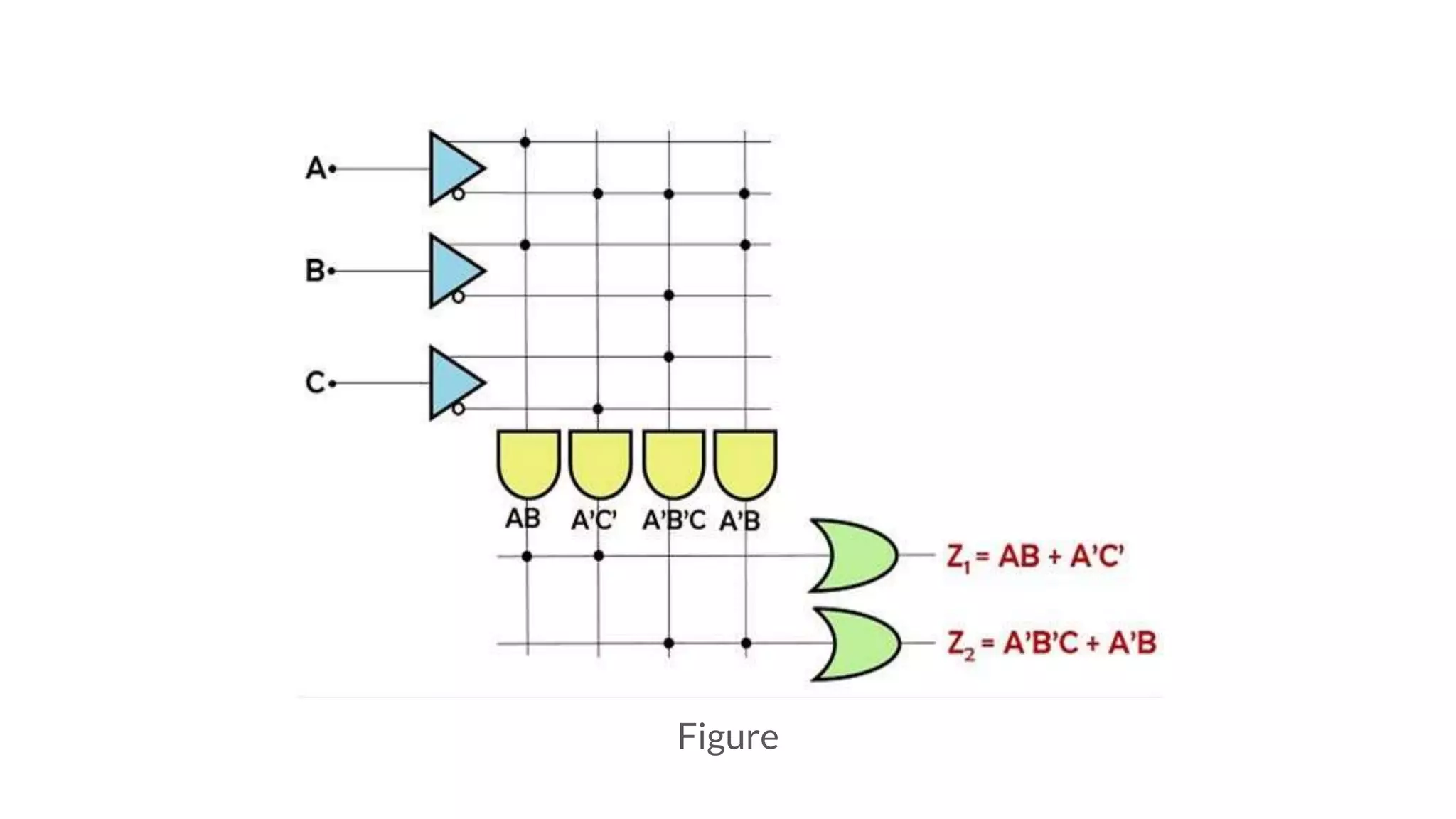
A visual representation of the logic circuit combining programmable AND and OR gates.
Overview of PLA advantages, such as ease of design changes, simpler layouts, and adaptable design for new technologies.
Discussion on disadvantages of PLAs, including slower speed, larger chip areas, and higher costs compared to random-logic networks.
Examples of PLA applications in microprocessors, control logic, code conversions, and more.
Conclusion of the presentation with a Thank You.