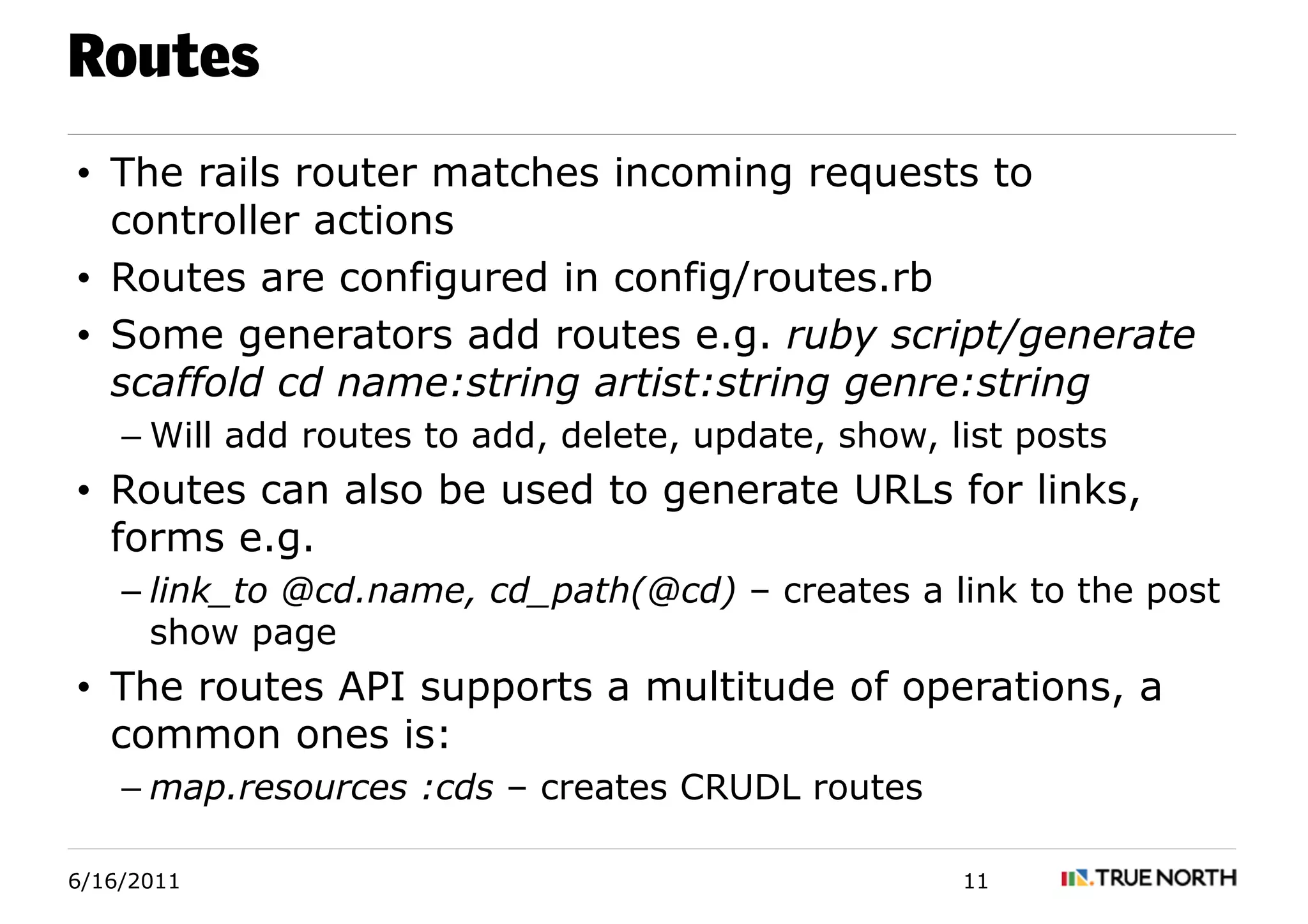
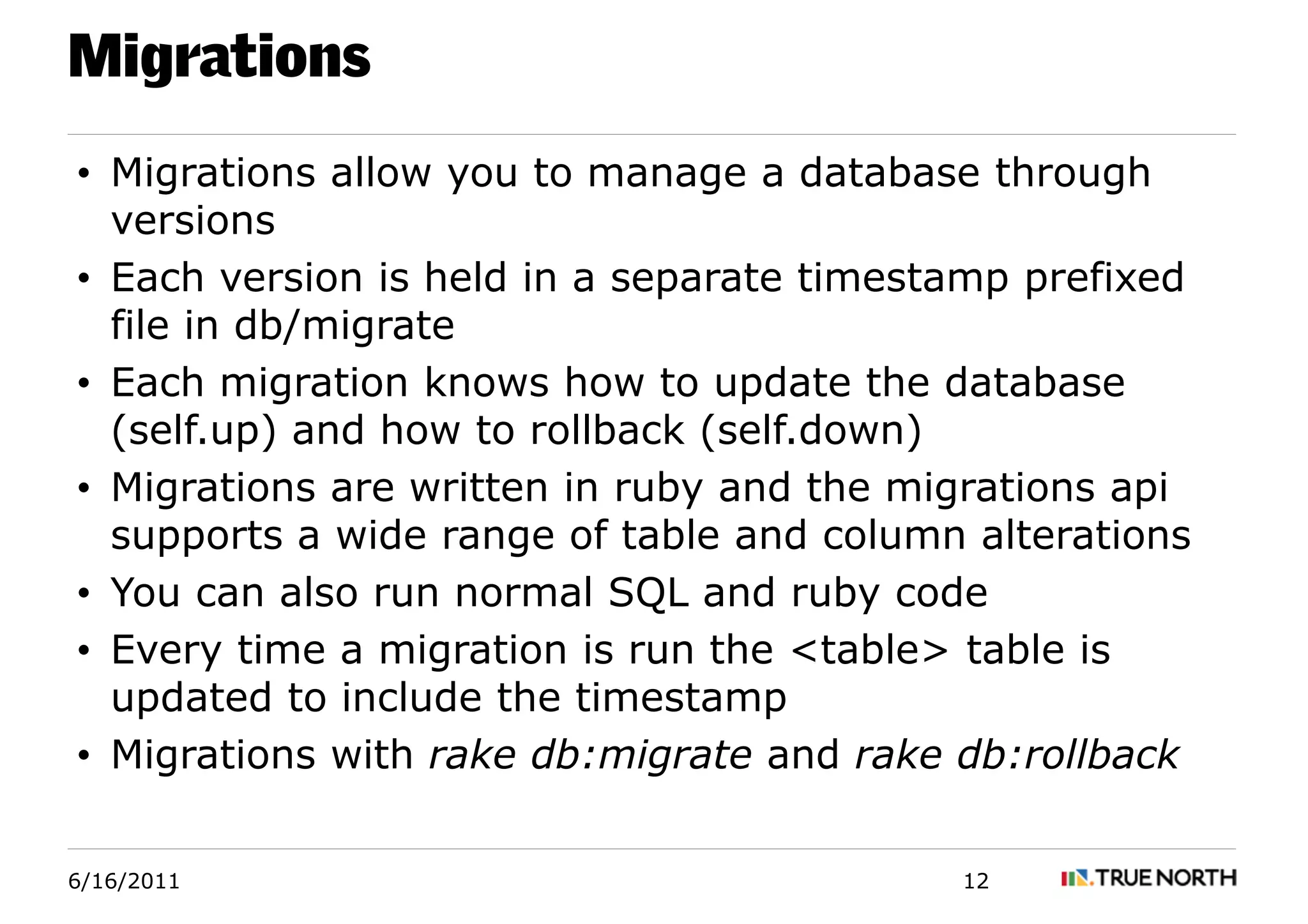
Rails is a web application framework written in Ruby that uses the MVC architecture. It aims to reduce coding burden through its APIs and generators. Rails makes use of conventions like naming and placement of files to reduce configuration. The large Rails community provides support through documentation and libraries called gems that extend the framework's functionality. Key Rails concepts include routes, migrations, generators, object relationships and validations. Migrations allow managing the database schema through versions. Generators produce common code artifacts to speed development. Relationships define how objects connect to each other in the database. Validations ensure data integrity.













![Create relationships between models • ruby script/generate scaffold track name:string cd_id:integer • rake db:migrate • Create associations in the model classes – track.rb - belongs_to :cd – cd.rb - has_many :track • Allow tracks to select an album in track/edit.html.erb – <%= select( “track", “cd_id", Cd.all.map {|cd| [cd.name, cd.id]}, { :include_blank => "No part of an album" }, {:class => "fieldSelect"}) %> 6/16/2011 19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rails-gettingstarted-110616072428-phpapp01/75/Rails-getting-started-19-2048.jpg)