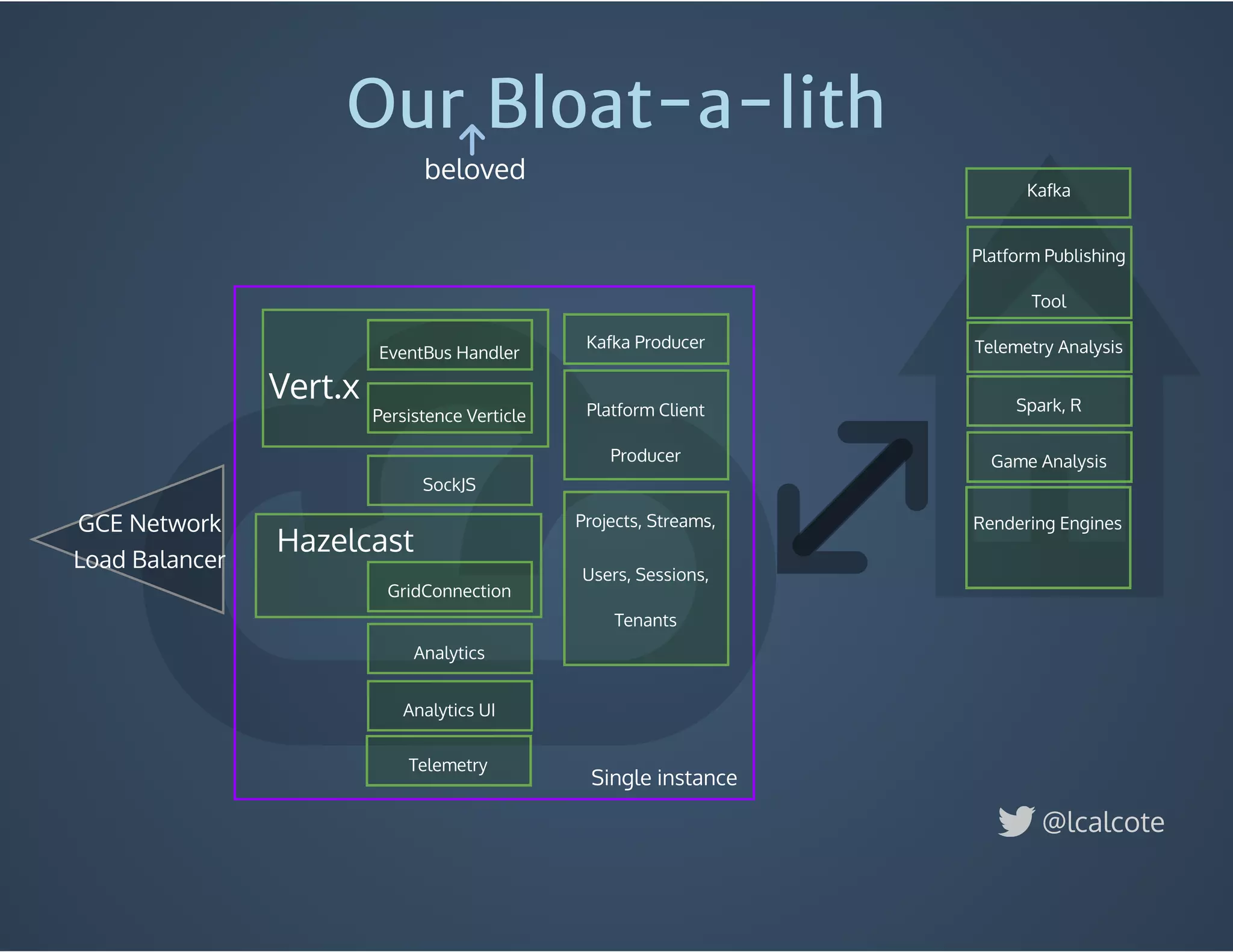
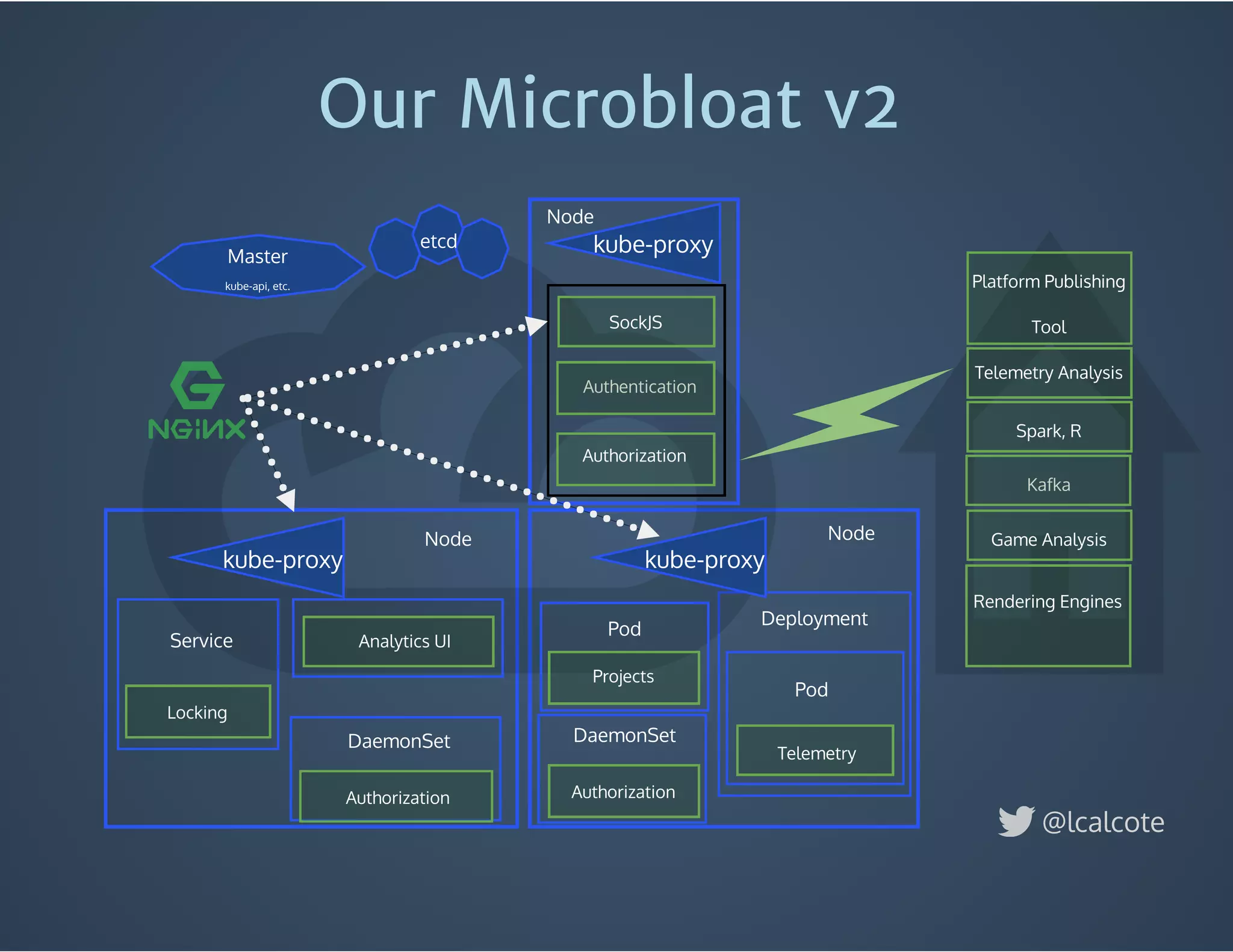
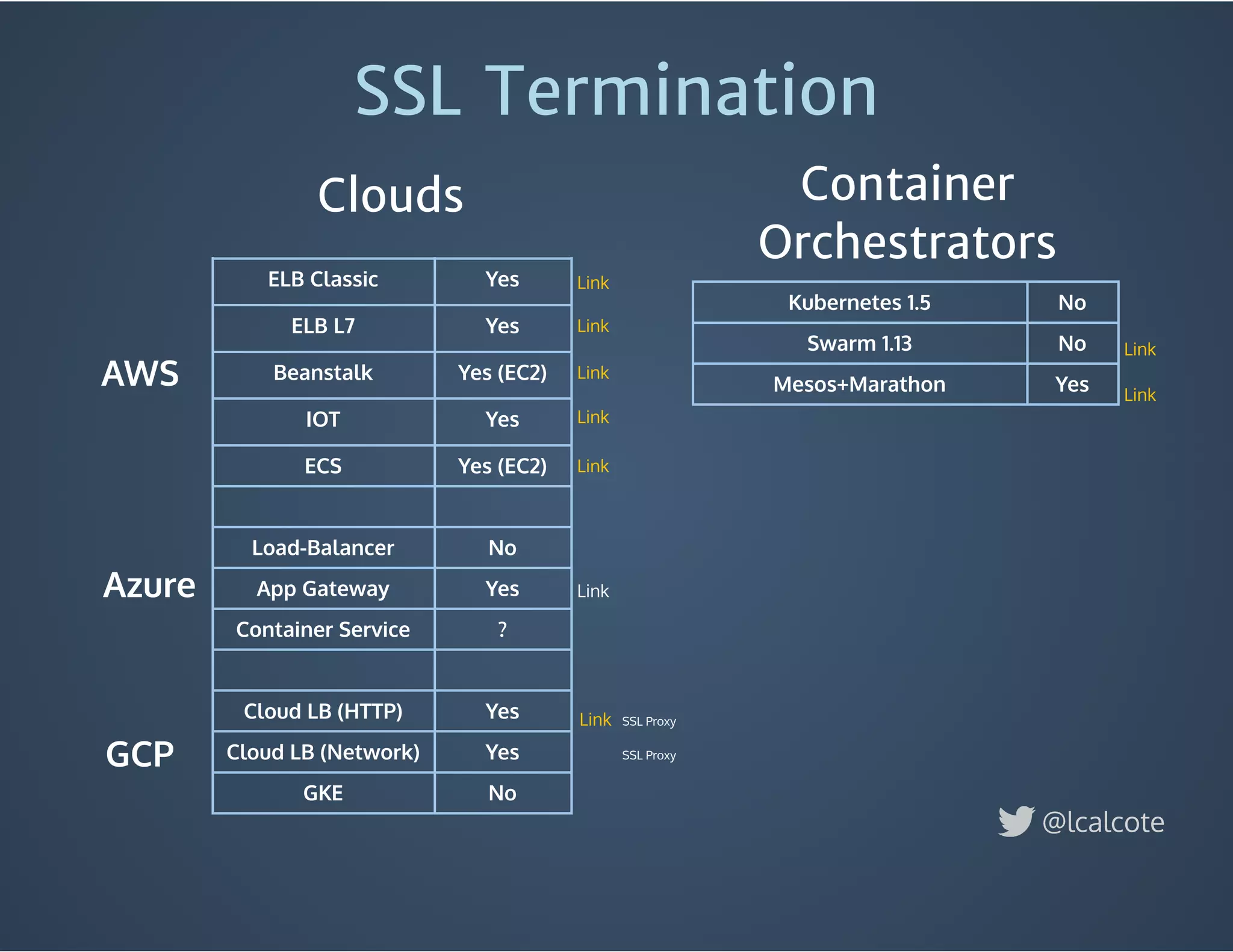
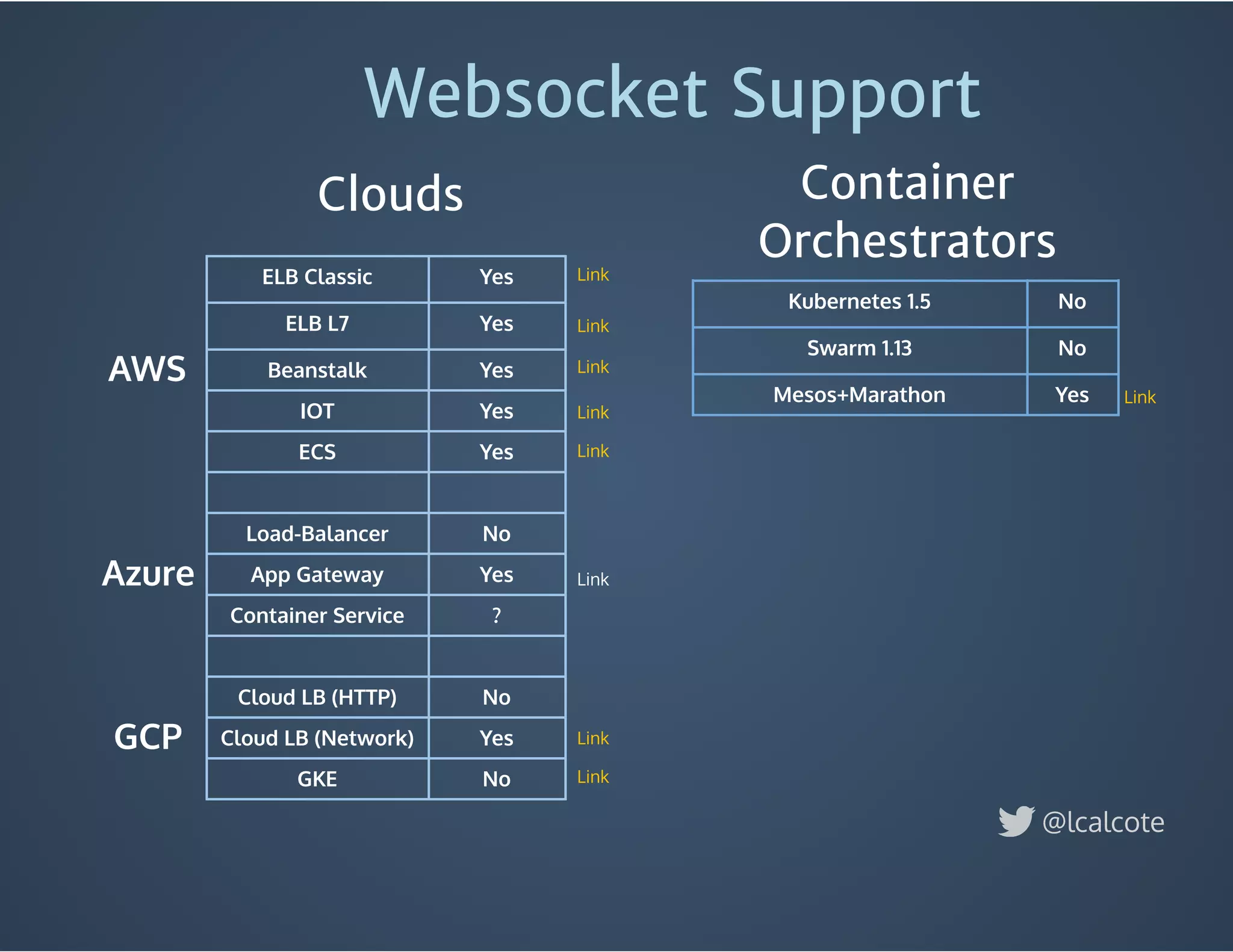
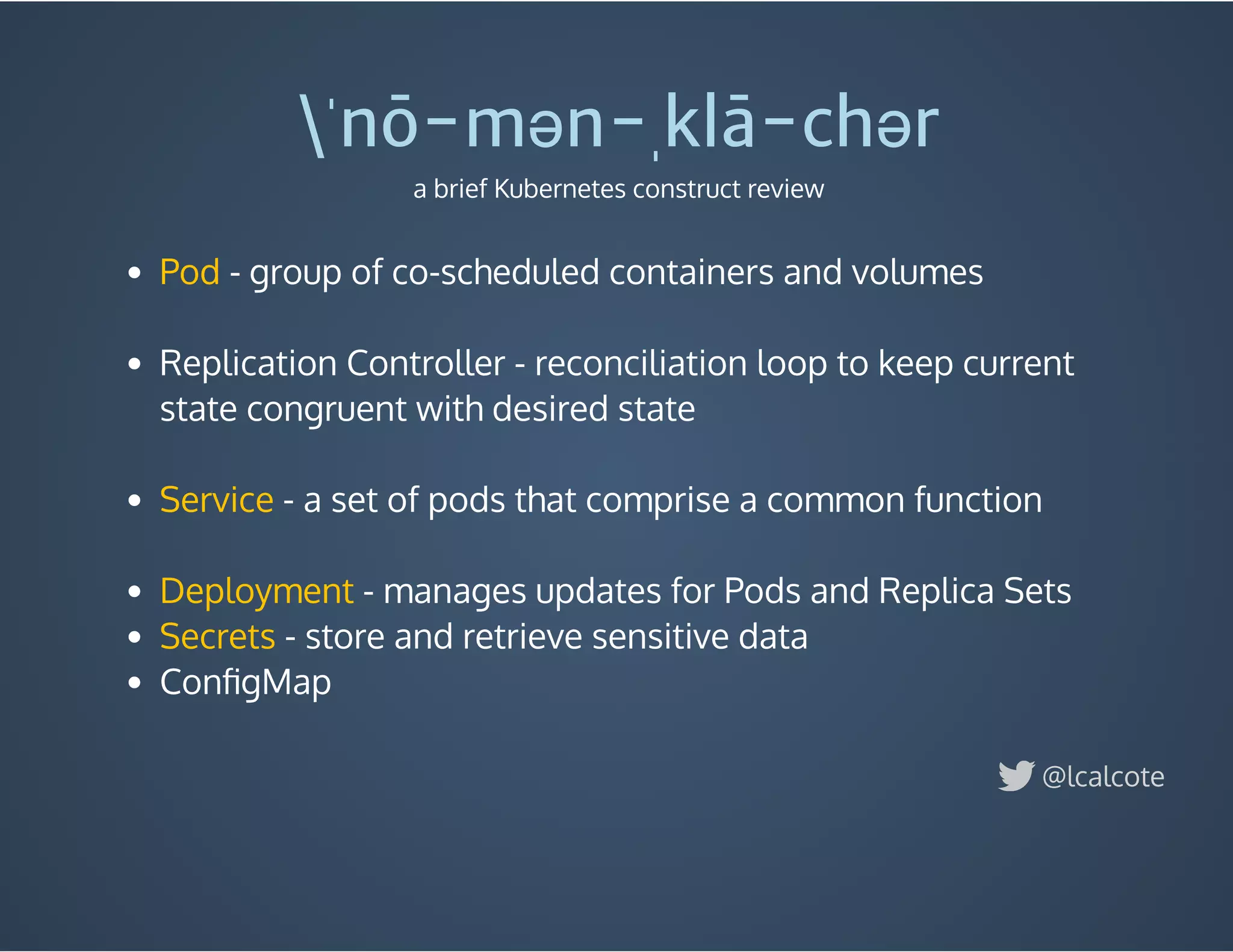
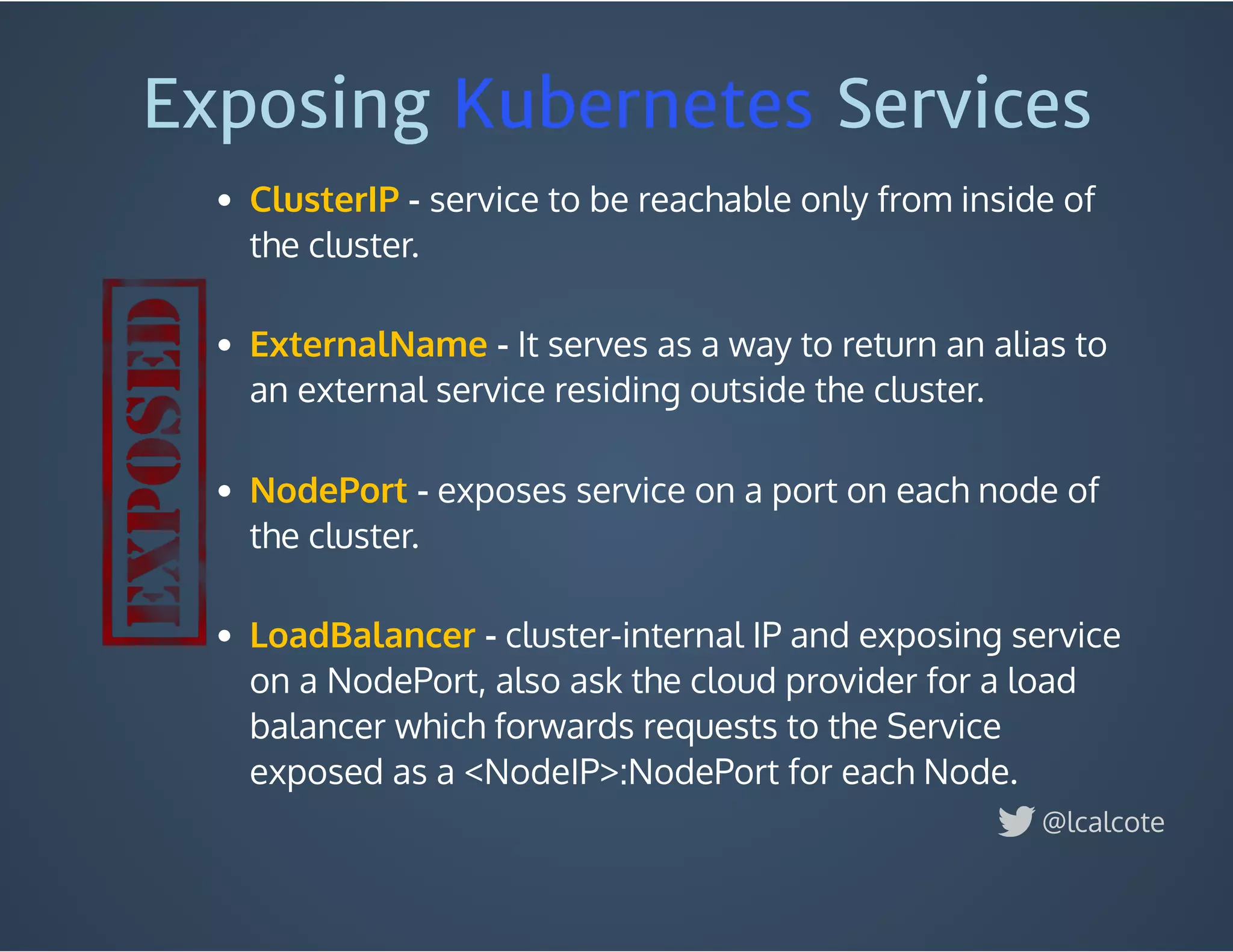
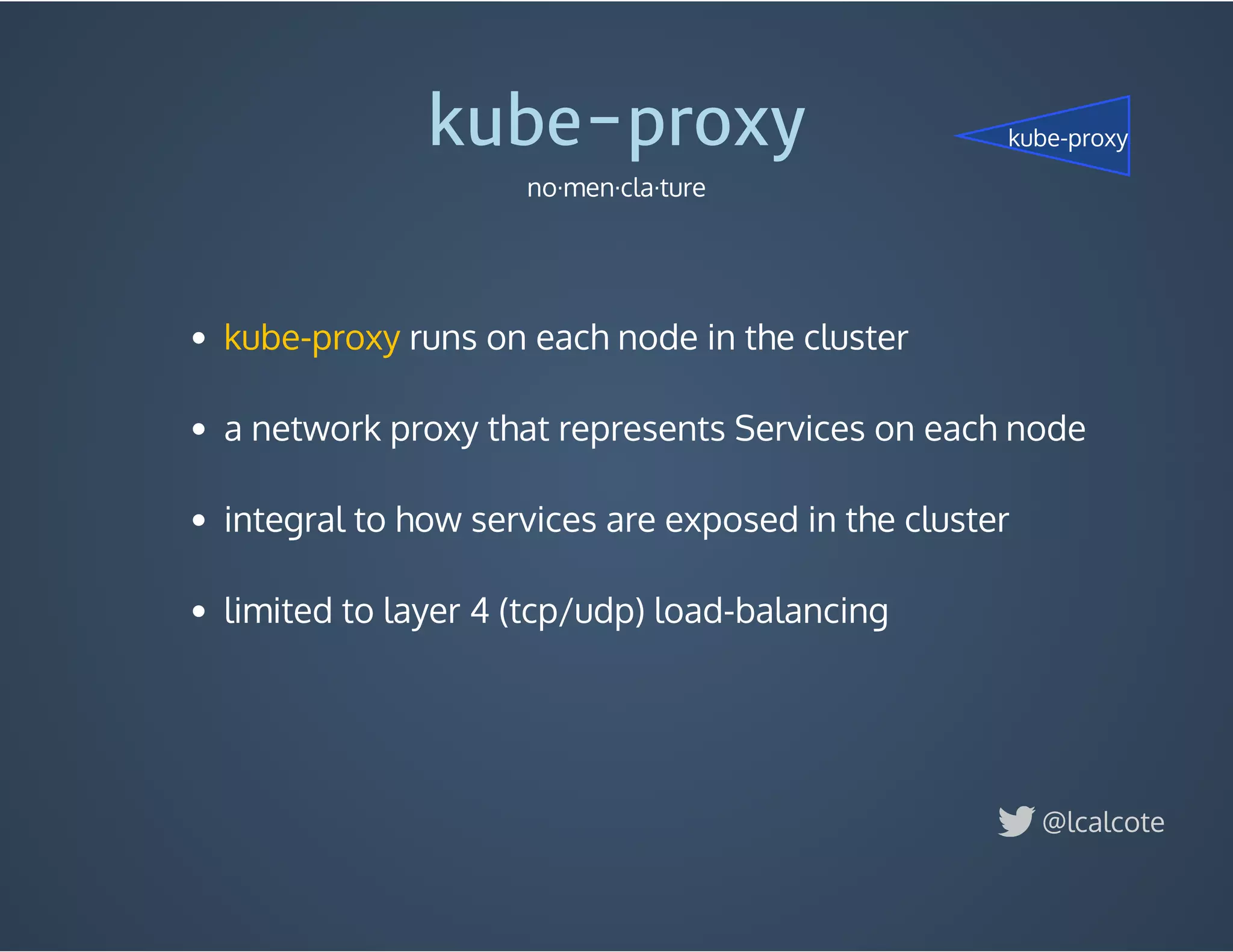
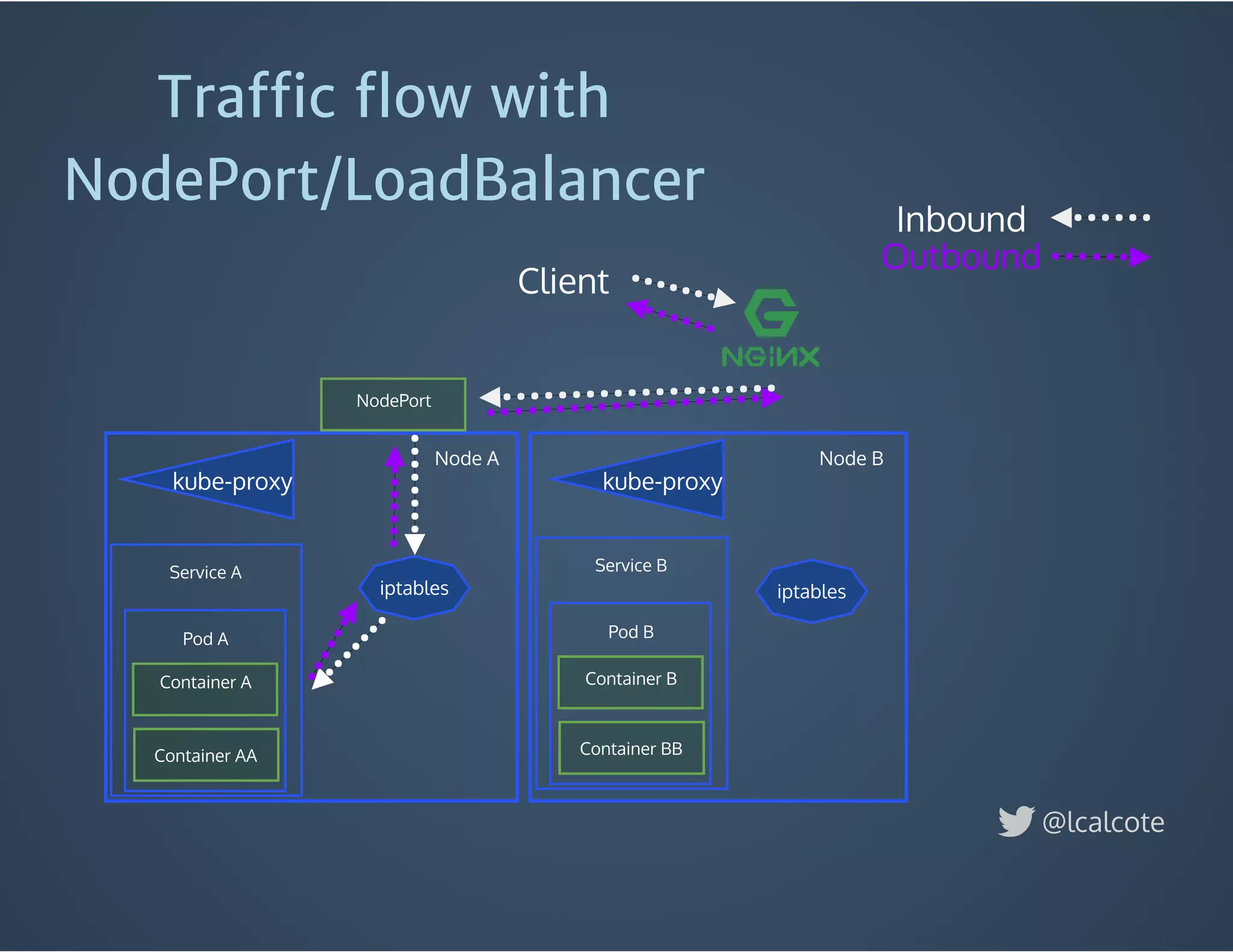
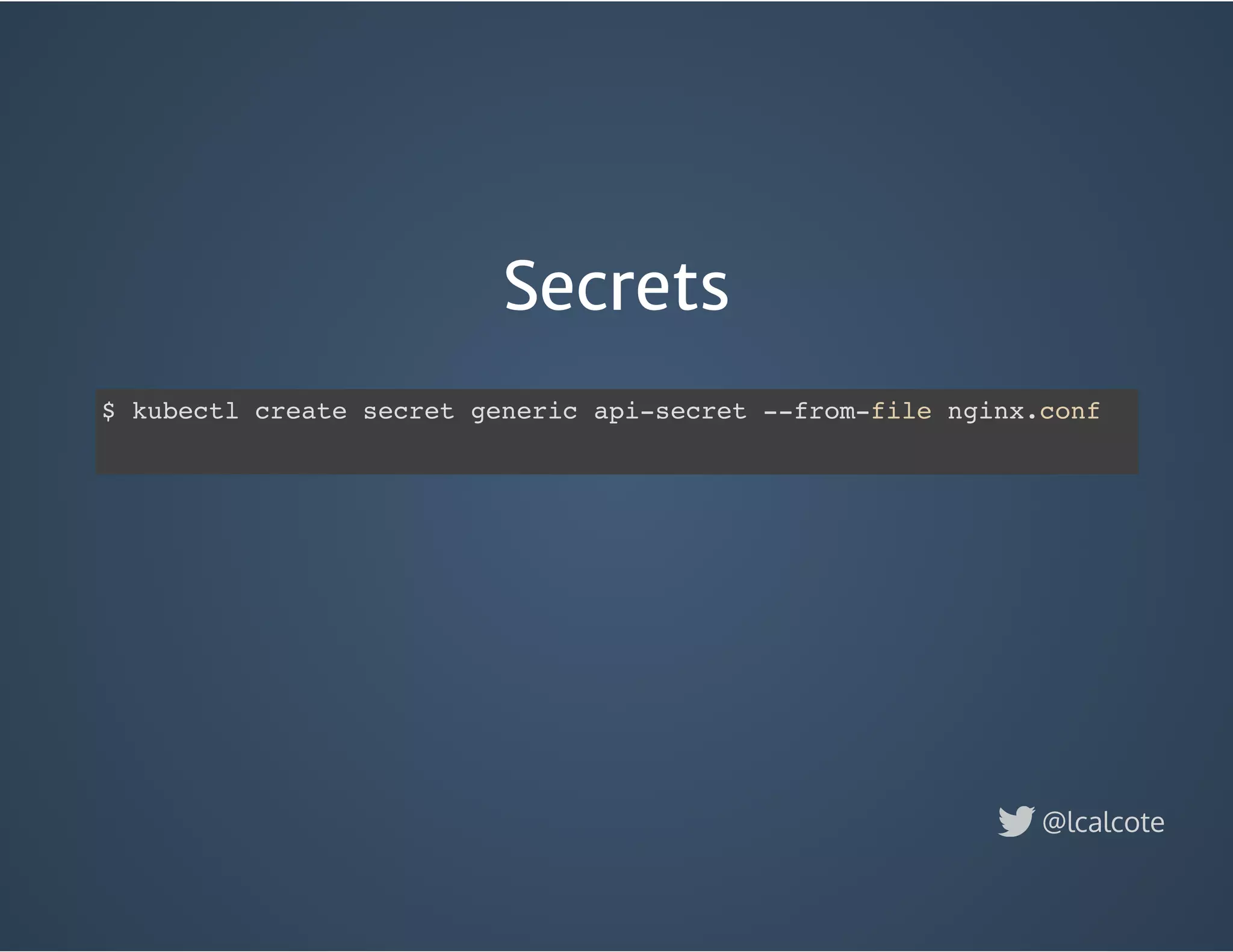
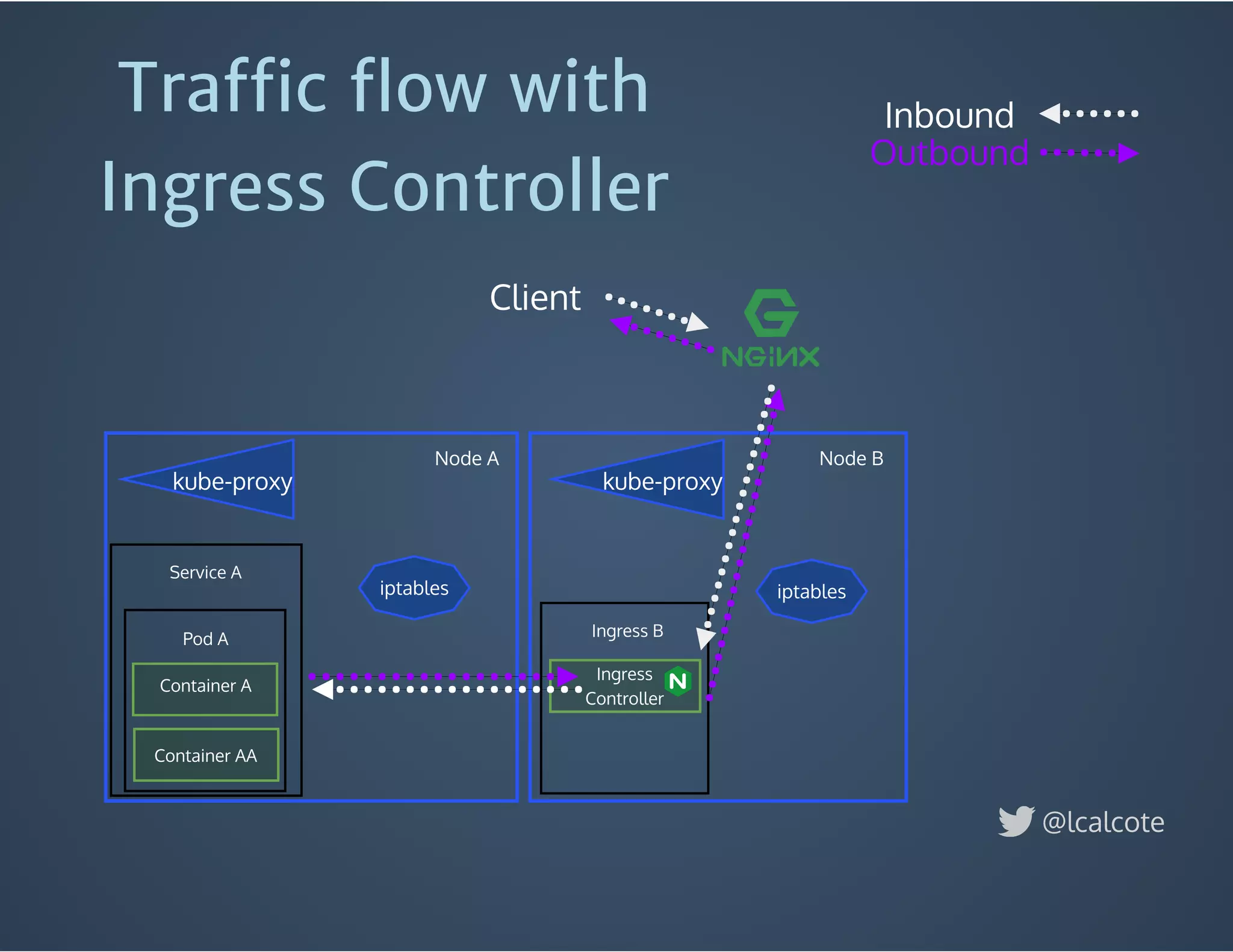
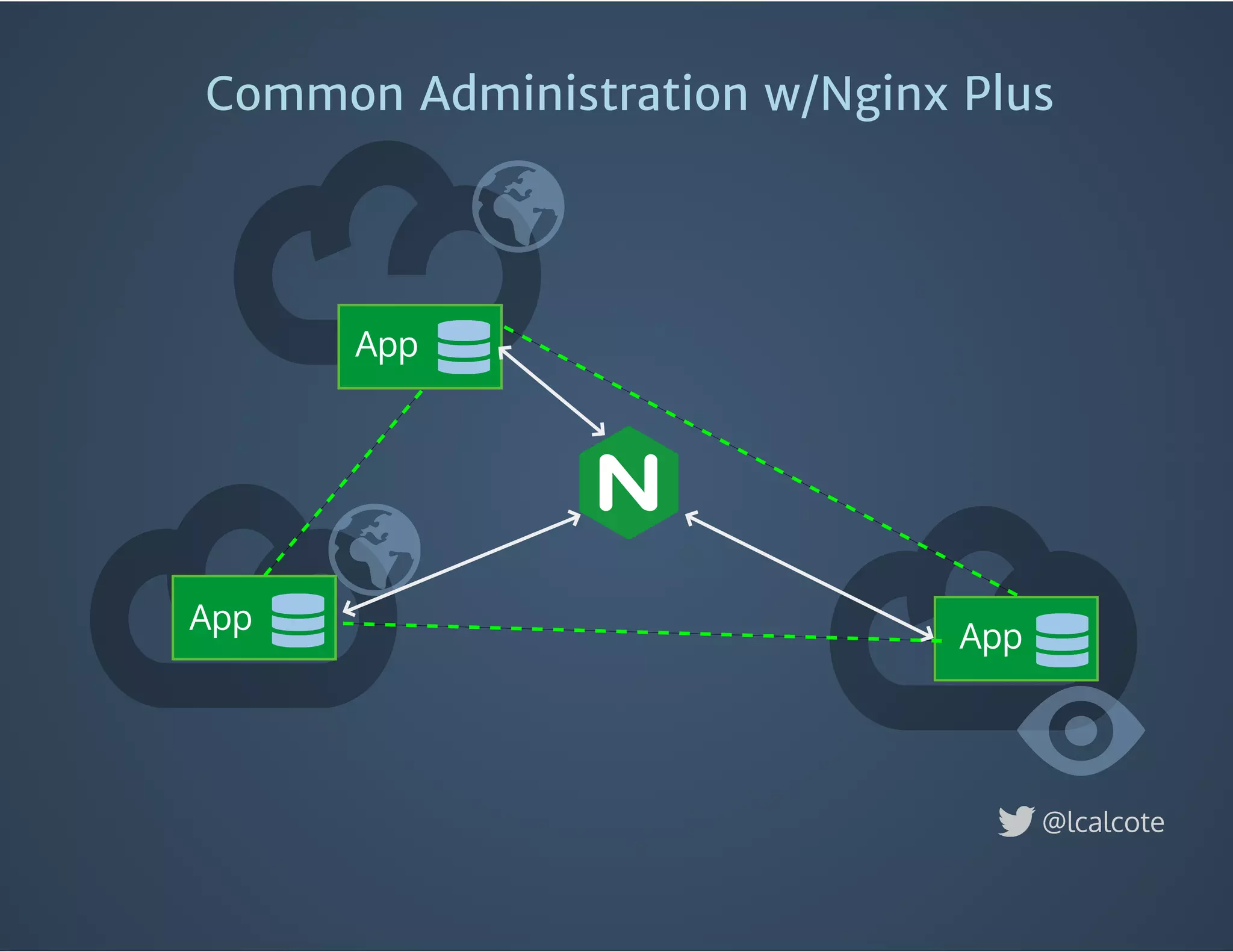
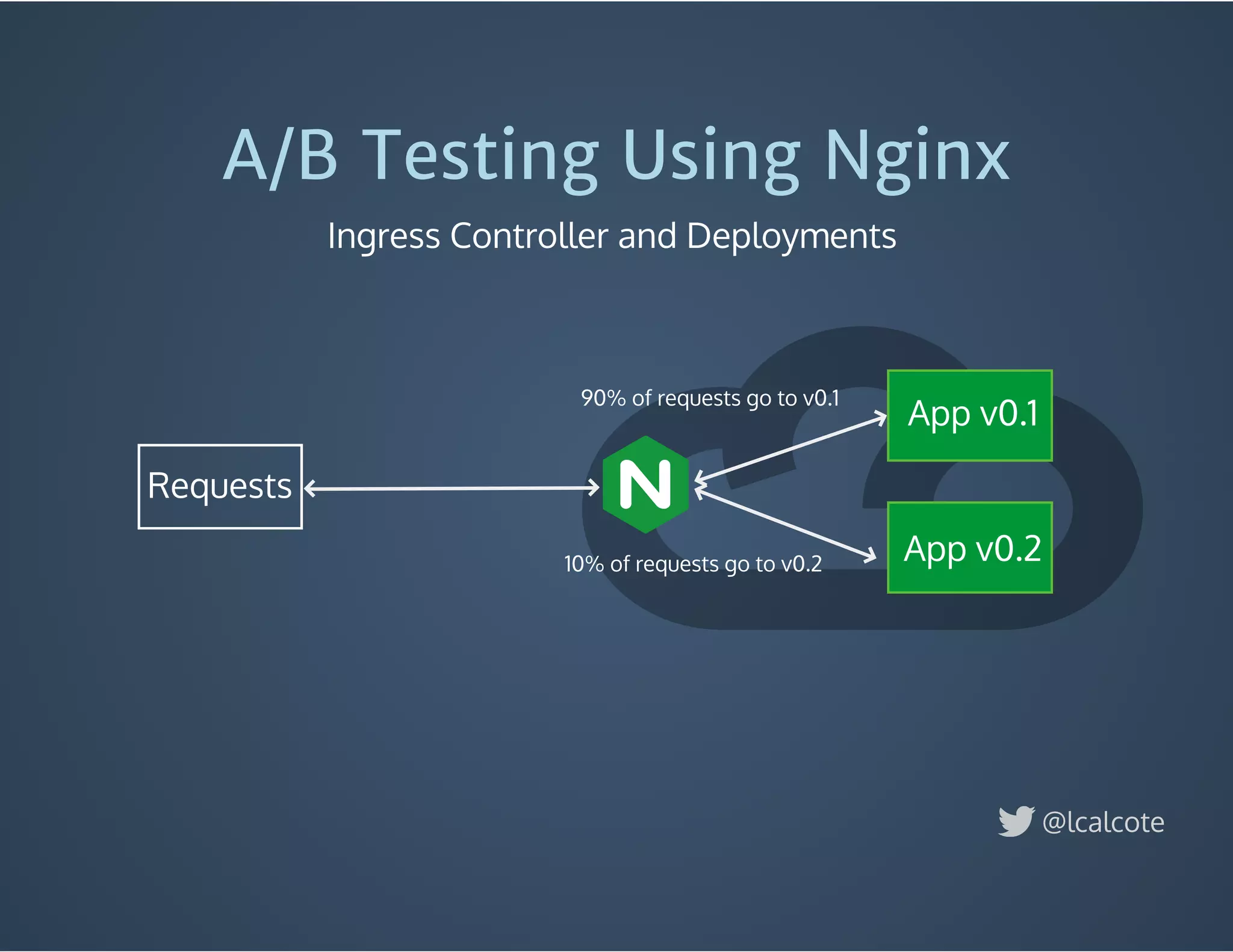
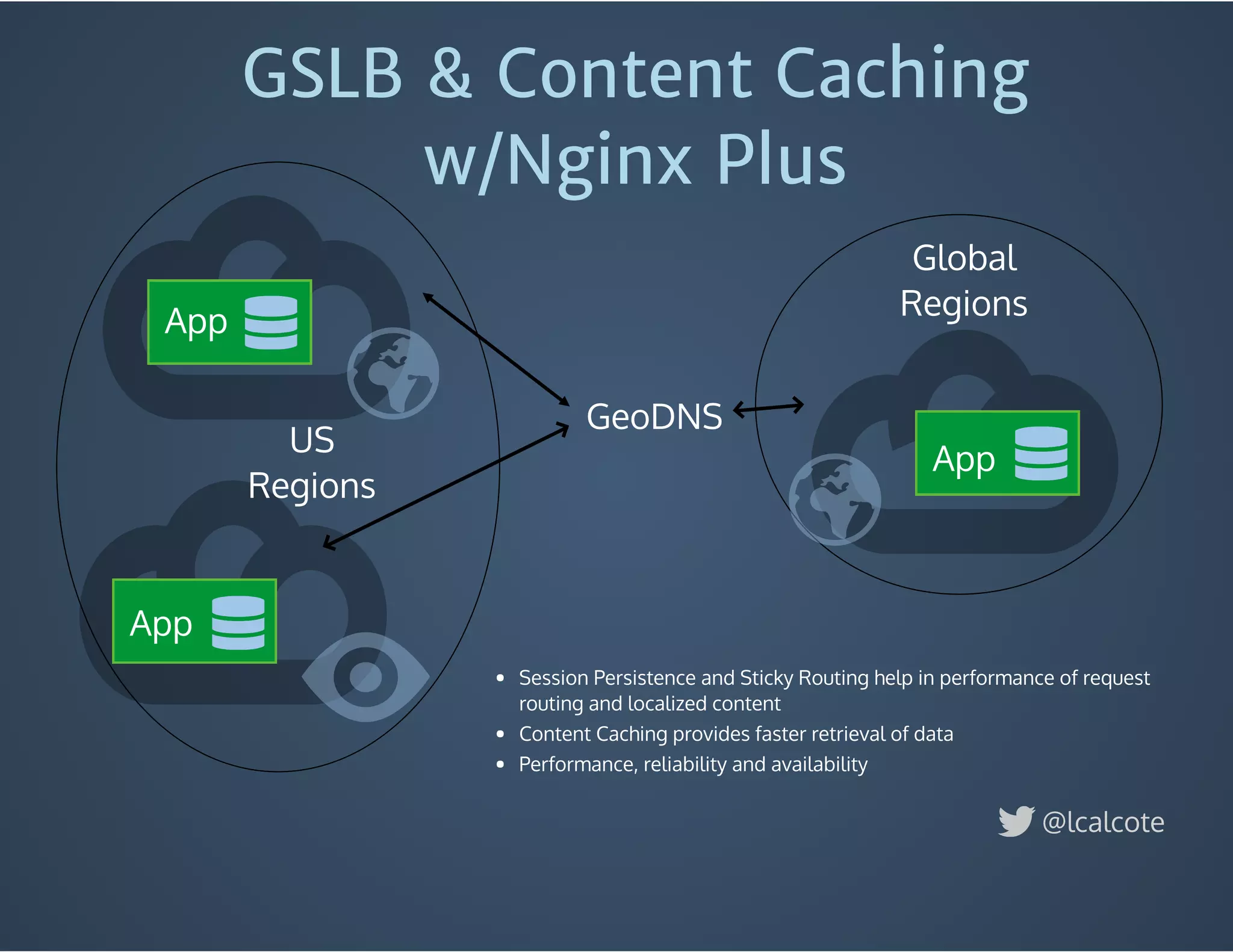
The document discusses load balancing in cloud computing, focusing on the evolution of application delivery controllers and the use of Kubernetes and NGINX for managing microservices architecture. It highlights the benefits of modular architecture, such as service isolation and resilience, and emphasizes the importance of intelligent rendering and low-latency services. Additionally, it covers various Kubernetes constructs and configurations for exposing services, as well as the integration of web socket support and traffic management through ingress controllers.